Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochem
Uploaded by
Kyla Barrera Tabungar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pagebiochem
Original Title
biochem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbiochem
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageBiochem
Uploaded by
Kyla Barrera Tabungarbiochem
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
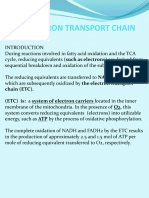
C.
Respiration - The + ▵ E indicates that O2 can serve as
- also known as cellular respiration a strong electron acceptor (hence its
- in biological systems, this is the process placement in the ETC)
by which cells derive energy in the form
of ATP from the controlled reaction of
hydrogen with oxygen to form water
- enzymes involved in this process are
called enzymes of biological oxidation
Figure (). Cellular respiration is a controlled formation of water
using heat generated midway to form ATP.
Figure (). Redox potentials. **The relative positions
D. Redox Potential of redox systems (decreasing negativity until it
- the tendency of reactants in redox becomes positive; increasing E’0) as shown in the
table allows prediction of the direction.
reaction to donate or accept electrons
- Proportionate to the Gibbs free energy in
the 1st law of thermodynamics References
→ Where Gibbs free energy is the Doc Menorca’ss PPT
standard free energy change Previous Transes (2022 1A, 1B)
→ E’ is the standard redox potential
- At standard conditions (biochem’s
POV): E’ is normally expressed at pH 7.0
where the electrode potential of
hydrogen electrode is- 0.42V. This heat
energy (kJ) is transformed into electrical
energy (V), consistent with the 1st law of
thermodynamics
- The equation relates the redox potential
to the free energy. This could be used to
determine if the reaction is spontaneous
or not based on the redox potential (▵ E)
- Moreover, the more negative ▵ E
means that it can donate electron and
tend to be a reducing agent
- The more positive ▵ E means that it can
accept electron and tend to be an
oxidizing agent
You might also like
- Electronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestFrom EverandElectronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestNo ratings yet
- Biophysics 6Document25 pagesBiophysics 6ADITYAROOP PATHAKNo ratings yet
- Potential: Reference ElectrodeDocument2 pagesPotential: Reference ElectrodeGIRMA SELALE GELETANo ratings yet
- QED Coherence and Electrolyte SolutionsDocument7 pagesQED Coherence and Electrolyte SolutionsScribd PipottNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Alkaline Water ElectrolysisDocument6 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Alkaline Water Electrolysisjorge bustosNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PRT2Document8 pagesReviewer PRT2John SecretNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DefinitionsDocument3 pagesChemistry DefinitionscesgemsNo ratings yet
- 5 - Electron Donors and Electron Acceptors - HandoutDocument20 pages5 - Electron Donors and Electron Acceptors - Handouttoo876555No ratings yet
- Unifying Solution and Surface Electrochemistry: Limitations and Opportunities in Surface ElectrocatalysisDocument7 pagesUnifying Solution and Surface Electrochemistry: Limitations and Opportunities in Surface ElectrocatalysisMiguel Angel SandovalNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Redox Reactions: Discover How Batteries WorkDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Redox Reactions: Discover How Batteries WorkFrank Ian EscorsaNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity Seen As The Ground State Average Valence Electron Binding EnergyDocument12 pagesElectronegativity Seen As The Ground State Average Valence Electron Binding EnergyAdani GhinaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction (Redox) Reactions: Electron DonorsDocument11 pagesOxidation and Reduction (Redox) Reactions: Electron DonorsMilica RančićNo ratings yet
- Transduction Elements: Dr. Ashish A Prabhu Assistant Professor Department of Biotechnology NIT WarangalDocument27 pagesTransduction Elements: Dr. Ashish A Prabhu Assistant Professor Department of Biotechnology NIT WarangalAMRUTHA VARSHININo ratings yet
- 10 - Corrosion Thermodynamics-2Document46 pages10 - Corrosion Thermodynamics-2Ridzaldi AldiNo ratings yet
- BFC Review FCell2009ian PDFDocument18 pagesBFC Review FCell2009ian PDFTeodor CostacheNo ratings yet
- Trans Notes For ElectrochemDocument2 pagesTrans Notes For ElectrochemDarwin ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chem Midterm ReviewerDocument12 pagesChem Midterm ReviewerKyle Andre MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Stoic TheoryDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Stoic TheoryKent Harry CumpioNo ratings yet
- Biological Science 6th Edition Freeman Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesBiological Science 6th Edition Freeman Solutions Manualdonaldthachdeslq100% (26)
- Redox SystemDocument22 pagesRedox SystemAnurag SharmaNo ratings yet
- 6 CLASS Electrochem Part III Prof. CortonDocument21 pages6 CLASS Electrochem Part III Prof. CortonSneha SinghNo ratings yet
- 22CHE22Document52 pages22CHE22GAT LIBRARYNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesElectrochemistrydanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument18 pagesElectrochemistryPRAISENo ratings yet
- Fundametals of Electrchemistry-Class2Document19 pagesFundametals of Electrchemistry-Class2PARVATHY ANILNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain: Chain (ETC) - (ETC) Is: A System of Electron Carriers Located in The InnerDocument8 pagesElectron Transport Chain: Chain (ETC) - (ETC) Is: A System of Electron Carriers Located in The InnerSameer FataniNo ratings yet
- 429 Chapter 1-3 2009Document22 pages429 Chapter 1-3 2009Amit BidlanNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction (Redox) ReactionsDocument11 pagesOxidation and Reduction (Redox) ReactionsAbie BadhurahmanNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen ProductionDocument6 pagesHydrogen Productionsekhar_jvjNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Electrochemistry of Fuel CellDocument4 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Electrochemistry of Fuel CellAshish kumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 44 Slides No AnimationsDocument38 pagesLecture 44 Slides No AnimationsArshia HematpoorNo ratings yet
- Surigao State College of Technology: Learning ModuleDocument34 pagesSurigao State College of Technology: Learning ModuleJenemarNo ratings yet
- Reduction Potential - WikipediaDocument28 pagesReduction Potential - WikipediaBabar AliNo ratings yet
- Ionization in Gases PDFDocument24 pagesIonization in Gases PDFShivam ThakurNo ratings yet
- Catabolic PathwaysDocument13 pagesCatabolic PathwaysStudy SmarterNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Water - WikipediaDocument20 pagesElectrolysis of Water - Wikipediapowew28978No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry IntroductionDocument9 pagesElectrochemistry IntroductionJericho Iza VibarNo ratings yet
- 11 Electrode Potentials 1Document18 pages11 Electrode Potentials 1Behruz ArghavaniNo ratings yet
- IOQC2021 PartII Questions enDocument13 pagesIOQC2021 PartII Questions enDhamodharan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Thermo&Molecular Forces 22 PostDocument52 pagesThermo&Molecular Forces 22 PostPedro RamosNo ratings yet
- Reduction Potential - wikipediaPDFDocument7 pagesReduction Potential - wikipediaPDFGeetha ThiruvengadamNo ratings yet
- Reusing A Hard Drive Platter To Demonstrate Electrocatalysts For Hydrogen and Oxygen Evolution ReactionsDocument5 pagesReusing A Hard Drive Platter To Demonstrate Electrocatalysts For Hydrogen and Oxygen Evolution ReactionsJuan Diego CarrilloNo ratings yet
- E10 Electrochemistry and Thermodynamics: Cathode Anode Salt BridgeDocument12 pagesE10 Electrochemistry and Thermodynamics: Cathode Anode Salt BridgeNorazwan NorNo ratings yet
- Step 3: If Sufficient Energy IsDocument8 pagesStep 3: If Sufficient Energy IsClarette GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ManahanDocument72 pagesChapter 4 ManahanSunita ChayalNo ratings yet
- Appendix. A Primer On Biologically Mediated Redox Reactions in EcosystemsDocument5 pagesAppendix. A Primer On Biologically Mediated Redox Reactions in EcosystemsCélula Juan Pablo JiménezNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 01 Answer 8b9m PDFDocument2 pages12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 01 Answer 8b9m PDFMohit SahuNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 01 Answer 8b9mDocument2 pages12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 01 Answer 8b9mMohit SahuNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument67 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYGOVIND RANJANNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument25 pagesElectrochemistryNani NaniNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Energy Conversions in Living SystemsDocument48 pagesThermodynamics of Energy Conversions in Living SystemsraassfasfsaNo ratings yet
- Damaskin 1969Document10 pagesDamaskin 1969pescaofritoNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Thermodynamics: Information Modules Click Here To EnterDocument39 pagesCorrosion Thermodynamics: Information Modules Click Here To EnterAndrianPratamaNo ratings yet
- Electrochem Rep PDFDocument29 pagesElectrochem Rep PDFRevlemmor SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Cyclic Voltammetry - A Versatile ElectrochemicalDocument5 pagesCyclic Voltammetry - A Versatile ElectrochemicalEric FernandoNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and Energy Storage Systems Module 1 Notes 2018Document24 pagesElectrochemistry and Energy Storage Systems Module 1 Notes 2018Mohith BC100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Lecture Notes: Metabolism - Energy and EnzymesDocument4 pagesChapter 8 Lecture Notes: Metabolism - Energy and Enzymesasraghu100% (1)
- Week 5. ElectrochemistryDocument55 pagesWeek 5. ElectrochemistrynorsiahNo ratings yet
- Ch2-Thermodynamics and Electrode PotentialDocument53 pagesCh2-Thermodynamics and Electrode PotentialFAHED AYYADNo ratings yet
- 5 Electrochemistry NotesDocument55 pages5 Electrochemistry NotesZubaer RahmanNo ratings yet
- Airways Resistance - Lab ReportDocument10 pagesAirways Resistance - Lab ReportKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Urinary Tract Infection Case StudyDocument17 pagesPediatric Urinary Tract Infection Case StudyKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- DOCOS - SA BiblioDocument5 pagesDOCOS - SA BiblioKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Female Genital TractDocument7 pagesFemale Genital TractKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Health Sector MainDocument18 pagesHealth Sector MainKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Paralytic Shallfish PoisoningDocument33 pagesParalytic Shallfish PoisoningKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Practice Guidelines For Informed Consent Dec 2011Document8 pagesPractice Guidelines For Informed Consent Dec 2011Kyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Ethics Assignment - Karen-2Document1 pageEthics Assignment - Karen-2Kyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Bond University Research RepositoryDocument36 pagesBond University Research RepositoryKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Title of Lecture: Name of Lecturer/Presenters 01 Jan 2020 - S01.T01Document3 pagesTitle of Lecture: Name of Lecturer/Presenters 01 Jan 2020 - S01.T01Kyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- A Review of Hereditary Fructose Intolerance: Tiberius Mogoș, Andra Evelin IacobiniDocument5 pagesA Review of Hereditary Fructose Intolerance: Tiberius Mogoș, Andra Evelin IacobiniKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Mon IdbDocument8 pagesMon IdbKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- (14796805 - Journal of Endocrinology) Hyperprolactinemia Induced by HCG Leads To Metabolic Disturbances in Female MiceDocument13 pages(14796805 - Journal of Endocrinology) Hyperprolactinemia Induced by HCG Leads To Metabolic Disturbances in Female MiceasfsdfsdfNo ratings yet
- Renal ExptDocument1 pageRenal ExptKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Subtitle: EducatorDocument3 pagesSubtitle: EducatorKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- C. Tight Junctions: References Batch 2022-B TranscriptionDocument2 pagesC. Tight Junctions: References Batch 2022-B TranscriptionKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Document11 pagesExperiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Kyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Document11 pagesExperiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Kyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Patho PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPatho Pneumoniaailyne_galicia100% (2)
- Relationships Patch AdamsDocument1 pageRelationships Patch AdamsKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Marine Drugs: Neurotoxins From Marine Dinoflagellates: A Brief ReviewDocument23 pagesMarine Drugs: Neurotoxins From Marine Dinoflagellates: A Brief ReviewKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Enzyme Activity A. Pathway ControlDocument4 pagesRegulation of Enzyme Activity A. Pathway ControlKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Lisondra DrugsDocument6 pagesLisondra DrugsKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Document11 pagesExperiment 6 Electromyography (EMG)Kyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Malignant Hyperthermia PDFDocument5 pagesMalignant Hyperthermia PDFKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TemplateDocument5 pagesDrug Study TemplateKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TemplateDocument5 pagesDrug Study TemplateKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol : Indication: ClassificationDocument1 pageParacetamol : Indication: ClassificationKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TemplateDocument5 pagesDrug Study TemplateKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet