Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hirschsprung's Disease Concept Map
Uploaded by
kaycee gwapa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
375 views3 pagesconcept map for hirschsprung disease. a comprehensive concept map. you can use this for your case presentations eseciall in pediatric diseases or conditions. not a complex concept map to follow.
Original Title
CONCEPT MAP Hirschsprungs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentconcept map for hirschsprung disease. a comprehensive concept map. you can use this for your case presentations eseciall in pediatric diseases or conditions. not a complex concept map to follow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
375 views3 pagesHirschsprung's Disease Concept Map
Uploaded by
kaycee gwapaconcept map for hirschsprung disease. a comprehensive concept map. you can use this for your case presentations eseciall in pediatric diseases or conditions. not a complex concept map to follow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
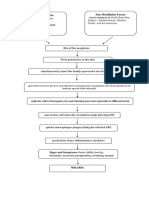
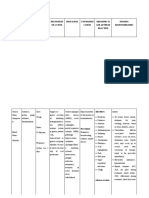
CONCEPT MAP- HIRSCHPRUNG’S DISEASE
MODIFIABLE FACTORS NON-MODIFIABLE FACTORS
●Exposure to cigarette smoking ●Gender: Male
●Genetic
●Having other inherited conditions
Absence of ganglion cells
(-) ganglionic innervation= (-) nerve cell
(-) peristalsis
Chronic constipation Red, Bark Blood Stool
Intestinal obstruction/discomfort Impaction Anemia
Abdominal pain SHOCK
Abdominal fullness/distention
DEATH
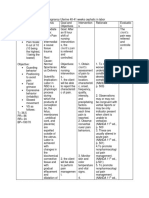
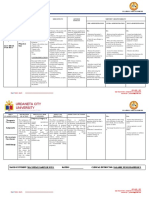
INTEGUMENTARY GASTROINTESTINAL HEENT
SYSTEM SYSTEM
●Sclerema ●Abdominal distention ●Eyes- Anicteric Sclera
●Constipation ●Mouth- Dry Lips
Fluid volume ●Change in Bowel movement
excess Impaired oral and nasal
●Soft to touch
mucous membrane
●Hypoactive Bowel Sound
a. Careful monitoring, correction of
electrolyte, respiratory support, correction
a. Assess oral cavity of the least once
of hypovolemia and control of hypothermia Acute Pain
daily and note any discoloration, lesion,
are important in infants with sclerema.
Constipation edema, bleeding, exudate or dryness.
Refer to a physician or specialists as
Altered Bowel appropriate.
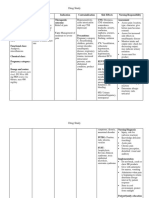
MEDICATIONS: Elimination
b. Inspect for any indication of infection,
and culture lesions as needed. Refer to a
●Metronidazole 6mg IV Imbalanced nutrition: less
physician, nurse or specialist as
than body requirements
●Paracetamol 65mg slow IVTT appropriate.
●Ranitidine 6mg slow IVTT
a. Assess pain using facial expression
●Calcium Gluconate 5cc scale that is appropriate to the age. DIAGNOSTIC TESTS:
●Amikacin 90mg IV b. Observed non-verbal cues of pain and ●Hemoglucotest
other characteristics.
●Digoxin 0.02mg ●Serum Calcium
c. Provide comfort measures like calming
●Piperacillin and Tazobactam 600mg the infant after a stress procedure, gently ●Serum Potassium and Sodium
slow IV pat or massage the infant, talking in a
●ABG
●Dopamine soothing voice, hold your infant with as
much skin to skin as possible. ●CBC and Platelet Count
●Salbutamol (Asmacare) ½ neb.
●Abdominal X-ray
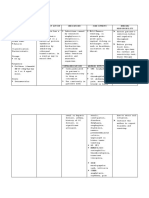
a. Before surgery, the child may be
prescribed daily enemas to observe
bowel movements.
b. Remind parents that the fluid used for
enemas must be normal saline (0.9%
NaCL) and not tap water.
a. Determine stool color, consistency,
frequency and amount.
b. Auscultate bowel sounds.
c. Monitor intake output with specific
attention to food of fluid intake.
d. Assess perianal skin condition
frequently, noting changes or beginning
breakdown. Encourage or assist with
perineal care after each bowel
movement.
LEGENDS:
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
a. Placed on a minimal residue diet. Stool
MEDICATIONS
softeners, vitamin supplements and perhaps
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS daily enemas until their condition improves.
NURSING DIAGNOSTIC b. TPN can offer another source of nutrition.
NURSING INTERVENTION c. If a child is to be cared for at home, help
the parents learn about minimal- residue diet
MANIFESTATION or are that is slow in indigestible fiber and
BODY SYSTEM AFFECTED residue.
d. Observe for abdominal distention.
You might also like
- Nursing Diagnosis: Aurelio, Lyca Mae M. BSN II-DDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Aurelio, Lyca Mae M. BSN II-DLyca Mae AurelioNo ratings yet
- TahbsoDocument77 pagesTahbsoCzarina Charmaine DiwaNo ratings yet
- Case Study TabhsoDocument7 pagesCase Study TabhsoGina Barredo Bustamante100% (1)
- Nursing Care for Couples Struggling with InfertilityDocument25 pagesNursing Care for Couples Struggling with InfertilityTiffany Joy QuiliopeNo ratings yet
- Ov Ov OvDocument15 pagesOv Ov OvHayyana Mae Taguba LadiaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Nursing Outcome: (Goal Attainable Within The Shift) (With Rationale & Source)Document2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Nursing Outcome: (Goal Attainable Within The Shift) (With Rationale & Source)merryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for a Child with IntussusceptionDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for a Child with IntussusceptionCharina Aubrey100% (1)
- NCP - Gestational HypertensionDocument3 pagesNCP - Gestational HypertensionCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NCP NephrolithiasisDocument1 pageNCP NephrolithiasisDonna Cabal AmogNo ratings yet
- CHOLElithiasisDocument93 pagesCHOLElithiasisfranciscomaricris13No ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis With Severe DehydrationDocument22 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis With Severe DehydrationCess Dunwan100% (1)
- Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Hydatidiform MoleDocument15 pagesCauses, Symptoms and Treatment of Hydatidiform MoleRegine Mae Morales EncinadaNo ratings yet
- Cord Prolapse March 23Document2 pagesCord Prolapse March 23Kathleen Vargas100% (1)
- IDBDocument2 pagesIDBPaulo PolinagNo ratings yet
- In (Ampinex, Clovilin, Vatacil)Document2 pagesIn (Ampinex, Clovilin, Vatacil)karenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY PheumoniaDocument5 pagesCASE STUDY PheumoniaEdelweiss Marie CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Long Term: PT Will Demonstrate Increased Tolerance To Activity by DischargeDocument18 pagesLong Term: PT Will Demonstrate Increased Tolerance To Activity by DischargeMary Ann Ebol0% (1)
- NCP For UTIDocument3 pagesNCP For UTIlachrymoseai100% (4)
- N. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Document32 pagesN. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Joule PeirreNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJP2001100% (1)
- Family Nursing Care Plan for ConstipationDocument4 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan for ConstipationErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki DiseaseDocument22 pagesKawasaki DiseaseMax LocoNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Hemophilia: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Hemophilia: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocument2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitNo ratings yet
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyBarda GulanNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis & NPI - Edmalyn GozarDocument78 pagesAcute Appendicitis & NPI - Edmalyn GozarKM100% (1)
- Personal-Soc Interpretation: Tower of 4 CubesDocument15 pagesPersonal-Soc Interpretation: Tower of 4 CubesteuuuuNo ratings yet
- Hernandez NCP Drug StudyDocument7 pagesHernandez NCP Drug StudyEliza Joyce HernandezNo ratings yet
- Soapie, Assessment and NCP On PAINDocument7 pagesSoapie, Assessment and NCP On PAINAna100% (2)
- NCP CSDocument7 pagesNCP CSTwobee Kriz LeghidNo ratings yet
- Learning Derived (Lysha)Document1 pageLearning Derived (Lysha)Choy DavidNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- Pcap Case StudyDocument7 pagesPcap Case StudyArlly Faena AbadNo ratings yet
- Bea-Case StudyDocument21 pagesBea-Case Studybea pegadNo ratings yet
- Pre Term LaborDocument3 pagesPre Term LaborHazel Marie Echavez100% (1)
- Deficient KnowledgeDocument3 pagesDeficient KnowledgeCamilleAnneRoseRabinoNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart Disease - Patho - DiagramDocument10 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease - Patho - DiagramJoann100% (12)
- Appendicitis NCSDocument25 pagesAppendicitis NCSZyrah Ziska ZafraNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain OB Ward PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Acute Pain OB Ward PDFambiit25No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing RotationDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan: Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing RotationMary Justine Nuyad-AfricaNo ratings yet
- COPARDocument12 pagesCOPARGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- 317 Care PlanDocument4 pages317 Care PlanSandra HaggertyNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolDocument3 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Post-Cesarean and Bilateral Tubal Ligation Nursing CareDocument18 pagesPost-Cesarean and Bilateral Tubal Ligation Nursing CaregenzpogiiNo ratings yet
- Individual Activity 3 PDFDocument11 pagesIndividual Activity 3 PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- Patho NCP DrugsDocument8 pagesPatho NCP DrugsMyco Reyes GarcesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument1 pageNursing Care Plansapplensweety100% (2)
- College of Nursing: Rupture of Membrames On Full Term PrimigravidaDocument7 pagesCollege of Nursing: Rupture of Membrames On Full Term PrimigravidaJulia BanagodosNo ratings yet
- Service Quality of Hospital Outpatient Departments: Patients' PerspectiveDocument2 pagesService Quality of Hospital Outpatient Departments: Patients' Perspectivelouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- Case NCPDocument25 pagesCase NCPJoher Bolante Mendez100% (1)
- Drugstudy CalciumcarbonateDocument3 pagesDrugstudy Calciumcarbonateduane27fronterasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- GI OutlineDocument11 pagesGI OutlineLiz TollefsonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Omeprazole and ParacetamolDocument11 pagesDrug Study - Omeprazole and ParacetamolMarceline VueenNo ratings yet
- Dwug StudyDocument7 pagesDwug StudyCherubNo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized Title for Drug DocumentDocument2 pagesSEO-Optimized Title for Drug DocumentHeavenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyMonique VillartaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Template 1Document2 pagesDrug Study Template 1Karylle Joy WacguisanNo ratings yet
- Drug-study-OmeprazoleDocument2 pagesDrug-study-OmeprazolemaxynezolayvarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CISPLATINDocument2 pagesDrug Study CISPLATINCorrine IvyNo ratings yet
- NOTESDocument13 pagesNOTESkaycee gwapaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer WorksheetDocument3 pagesCervical Cancer Worksheetkaycee gwapaNo ratings yet
- Phase Phase1Document2 pagesPhase Phase1kaycee gwapaNo ratings yet
- Phase Phase1Document2 pagesPhase Phase1kaycee gwapaNo ratings yet
- 1700 Ebook DiseasesDocument250 pages1700 Ebook DiseasesAhmad Arif100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Nursing: Infection, Asepsis, Basic Concept of Stress and Illness Fundamentals of Nursing Test IiDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Nursing: Infection, Asepsis, Basic Concept of Stress and Illness Fundamentals of Nursing Test IiElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNo ratings yet
- Healing Colon Liver & PancreasDocument13 pagesHealing Colon Liver & PancreasDarryl I. Jones100% (3)
- Lee Holmes: A Step by Step Protocol To Restore Inner HealthDocument120 pagesLee Holmes: A Step by Step Protocol To Restore Inner HealthJessica Manning100% (6)
- Velammal VidyalayaDocument19 pagesVelammal VidyalayaRammesh Kumar RNo ratings yet
- PBL Report ThalassemiaDocument10 pagesPBL Report Thalassemiasarah_amigurlz88100% (2)
- Assignment No. 1Document7 pagesAssignment No. 1heidisjdhdhdhNo ratings yet
- Prescott's Microbiology: A Concise GuideDocument9 pagesPrescott's Microbiology: A Concise Guideethan jasonNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesEnzyme Lecture NotesryanNo ratings yet
- Barr Body Detection in Buccal SmearsDocument8 pagesBarr Body Detection in Buccal Smearsashok k pNo ratings yet
- SGD Renal 2Document3 pagesSGD Renal 2Alexandra Duque-DavidNo ratings yet
- 438tr FDA & 23andmeDocument438 pages438tr FDA & 23andmeNguyễn Tiến HồngNo ratings yet
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument33 pagesFetal DevelopmentAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Fisiop de Enfermedades DesmielinizantesDocument75 pagesFisiop de Enfermedades DesmielinizantesPía CasasNo ratings yet
- FullDocument745 pagesFullVanessa AlbaciteNo ratings yet
- 11 Flora Normal KulitDocument58 pages11 Flora Normal KulitmasithaNo ratings yet
- Molecular VirologyDocument11 pagesMolecular VirologySUTHANNo ratings yet
- Applications of Biotechnology in HealthDocument21 pagesApplications of Biotechnology in Healtherinliannamanalad4210No ratings yet
- Gold Standard GuidelinesDocument16 pagesGold Standard GuidelinesCaio LeônidasNo ratings yet
- Als Et Al - 2023 - Depression Pathophysiology, Risk Prediction of Recurrence and ComorbidDocument39 pagesAls Et Al - 2023 - Depression Pathophysiology, Risk Prediction of Recurrence and Comorbidkeon.arbabi.altNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Month QuestionsDocument5 pagesNutrition Month QuestionsRosa Lynn YaunNo ratings yet
- Psychology For PhysiotherapistsDocument211 pagesPsychology For PhysiotherapistsAkshaya Mistry89% (18)
- Research Papers Fangruida Discovery and PapersDocument113 pagesResearch Papers Fangruida Discovery and PapersRs BriceNo ratings yet
- Questions 1 Through 10 Are Based On The Following PassageDocument5 pagesQuestions 1 Through 10 Are Based On The Following PassageSarjitoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Solid TumorsDocument43 pagesPediatric Solid Tumorsririliberti100% (1)
- Biology NotesDocument102 pagesBiology Notesajabgul123493No ratings yet
- AmniocentesisDocument15 pagesAmniocentesisGYPSY CAT100% (1)
- Madras Christian College, Dept. of Zoology: B. Sc. (Vi) Zoology Curriculum For Students Admitted From 2008-09Document3 pagesMadras Christian College, Dept. of Zoology: B. Sc. (Vi) Zoology Curriculum For Students Admitted From 2008-09shilueeeNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Retinoblastoma Management and GeneticsDocument12 pagesRecent Advances in Retinoblastoma Management and GeneticsDr Pranesh BalasubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Paramolar - A Supernumerary Molar A Case Report and An OverviewDocument7 pagesParamolar - A Supernumerary Molar A Case Report and An OverviewGurudutt NayakNo ratings yet