Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cbse Question Paper CHEMISTRY (Theory) TT, "1 Pc. 1"1 ( Oiilki&i) Class-Xii
Uploaded by
ANUBHAB SWAINOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cbse Question Paper CHEMISTRY (Theory) TT, "1 Pc. 1"1 ( Oiilki&i) Class-Xii
Uploaded by
ANUBHAB SWAINCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE QUESTION PAPER
CHEMISTRY (Theory)
�tt,�"1 Pc.�1"1 (�oiilki&i)
CLASS-XII
1. Write a feature which will distinguish a metallic solid from an ionic solid. 1
2. Define ‘order of a reaction’. 1
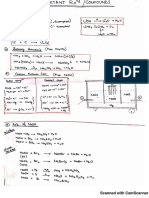
3. What is an emulsion? 1
4. Why does NO2 dimerise ? 1
5. Give an example of linkage isomerism. 1
6. A solution of KOH hydrolyses CH3CHClCH2CH3 and CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl.
Which one of these is more easily hydrolysed? 1
7. Draw the structural formula of I-phenylpropan-l-one molecule. 1
8. Give the IUPAC name of H2N – CH2 – CH2 - CH = CH2. 1
9. Non-ideal solutions exhibit either positive or negative deviations from Raoult’s law.
What are these deviations and why are they caused? Explain with one example for
each type. 2
10. A reaction is of first order in reactant A and of second order in reactant B. How is
the rate of this reaction affected when (i) the concentration of B alone is increased to
three times (ii) the concentrations of A as well as B are doubled? 2
11. The rate constant for a reaction of zero order in A is 0.0030 mol L –1 s –1. How long
will it take for the initial concentration of A to fall from 0.10 M to 0.075 M ? 2
12. Draw the structures of white phosphorus and red phosphorus. Which one of these
two types of phosphorus is more reactive and why? 2
13. Explain the following observations:
(i) Generally there is an increase in density of elements from titanium (Z = 22) to
copper (Z = 29) in the first series of transition elements.
(ii) Transition elements and their compounds are generally found to be good
catalysts in chemical reactions. 2
14. Name the following coordination compounds according to IUPAC system of nom-
enclature:
(i) [Co(NH3)4 (H2O)Cl]Cl2
(ii) [CrCl2(en)2]Cl, (en = ethane – 1, 2 – diamine) 2
15. Illustrate the following reactions giving a chemical equation for each:
(i) Kolbe’s reaction,
(ii) Williamson synthesis. 2
16. How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol,
(ii) Methyl magnesium bromide to 2-methylpropan-2-ol. 2
17. Explain the following terms. :
(i) Invert sugar
(ii) Polypeptides
OR
Name the products of hydrolysis of sucrose. Why is sucrose not a reducing sugar? 2
18. What are essential and non-essential amino acids in human food? Give one example
of each type. 2
19. The well known mineral fluorite is chemically calcium fluoride. It is known that in
–
one unit cell of this mineral there are 4 Ca2+ ions and 8 F ions and that Ca2+ ions are
–
arranged in a fcc lattice. The F ions fill all the tetrahedral holes in the face centred
–8
cubic lattice of Ca2+ ions. The edge of the unit cell is 5.46x10 cm in length. The
–3
density of the solid is 3.18 g cm . Use this information to calculate Avogadro’s
–1
number (Molar mass of CaF2 = 78.08 g mol ) 3
20. A solution prepared by dissolving 1.25 g of oil of winter green (methyl salicylate) in
99.0 g of benzene has a boiling point of 80.31 °C. Determine the molar mass of this
compound. (B.P. of pure benzene = 80.10 °C and Kb for benzene = 2.53 °C kg
mol –1) 3
21. What is the difference between multi molecular and macromolecular colloids? Give
one example of each type. How are associated colloids different from these two
types of col1oids ? 3
22. Describe how the following changes are brought about:
(i) Pig iron into steel.
(ii) Zinc oxide into metallic zinc.
(iii) Impure titanium into pure titanium. 3
OR
Describe the role of
(i) NaCN in the extraction of gold from gold are.
(ii) SiO2 in the extraction of copper from copper matte.
(iii) Iodine in the refining of zirconium.
Write chemical equations for the involved reactions.
23. How would you account for the following?
(i) The atomic radii of the metals of the third (5d) series of transition elements are
virtually the same as those of the corresponding members of the second (4d)
series.
o
(ii) The E value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that for
Cr3+/Cr2+ couple or Fe3+/Fe2+ couple.
(iii) The highest oxidation state of a metal is exhibited in its oxide or fluoride. 3
24. (i) State one use each of DDT and iodoform.
(ii) Which compound in the following couples will react faster in SN2 displacement
and why?
(a) 1-Bromopentane or 2-bromopentane
(b) 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane or 2-bromo-2-methylbutane. 3
25. In the following cases rearrange the compounds as directed:
(i) In an increasing order of basic strength:
C6H5NH2, C6H5N(CH3)2, (C2H5)6NH and CH3NH2
(ii) In a decreasing order of basic strength:
Aniline, p-nitroaniline and p-toluidine
(iii) In an increasing order of pKb values:
C2H5NH2, C6H5 NHCH3, (C2H5)2NH and C6H5NH2 3
26. Give one example each of
(i) addition polymers,
(ii) condensation polymers,
(iii) copolymers. 3
27. What are analgesic medicines? How are they c1assifiedand when are they
commonly recommended for use? 3
28. (a) State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions. Write an expression
for the molar conductivity of acetic acid at infinite dilution according to
Kohlrausch law.
o
(b) Calculate /\ m for acetic acid.
o
Given that /\ m (HCl) = 426 S cm2 mol –1
o
/\ m (NaCl) = 126 S cm2 mol –1
o
/\ m (CH3COONa) = 91 S cm2 mol –1 5
OR
(a) Write the anode and cathode reactions and the overall reaction occurring in a
lead storage battery.
(b) A copper-silver cell is set up. The copper ion concentration is 0.10 M. The
concentration of silver ion is not known. The cell potential when measured
was 0.422 V. Determine the concentration of silver ions in the cell. (Given
o o
E Ag+/Ag = + 0.80 V, E cu2+/cu = + 0.34 V) 5
29. (a) Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g)
(Hot and cone.)
(ii) XeF6(s) + H2O(l)
(b) How would you account for the following?
(i) The value of electron gain enthalpy with negative sign for sulphur is
higher than that for oxygen.
(ii) NF3 is an exothermic compound but NCl3 is endothermic compound.
(iii) ClF3 molecule has a T-shaped structure and not a trigonal planar one. 5
OR
(a) Complete the following chemical reaction equations:
(i) P4 + SO2Cl2
(ii) XeF4 + H2O
(b) Explain the following observations giving appropriate reasons:
(i) The stability of + 5 oxidation state decreases down the group in group
15 of the periodic table.
(ii) Solid phosphorus pentachloride behaves as an ionic compound.
(iii) Halogens are strong oxidizing agents. 5
30. (a) Explain the mechanism of a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl group of an
alciehyde or a ketone.
(b) An organic compound (A) (molecular formula C8H16O2) was hydrolysed with
dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). Oxidation
of (C) with chromic acid also produced (B). On dehydration (C) gives but-l-
ene. Write the equations for the reactions involved. 5
OR
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Ethanal and Propanal
(ii) Phenol and Benzoic acid
(b) How will you bring about the following conversions? 5
(i) Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
(ii) Ethanal to but-2-enal
(iii) Propanone to propene
Give complete reaction in each case.
You might also like
- CBSE 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2010 PDFDocument33 pagesCBSE 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2010 PDFsarvansirNo ratings yet
- Chem QP 9Document5 pagesChem QP 9jagpreetNo ratings yet
- ExaminationPaper PDFDocument331 pagesExaminationPaper PDFDebashisMishra100% (1)
- Sample Paper 4Document4 pagesSample Paper 4aryan_456_asNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument32 pagesChemistry190519123No ratings yet
- Sure-Shot Questions- Chemistry Class XII 1MARKDocument5 pagesSure-Shot Questions- Chemistry Class XII 1MARKudit pandyaNo ratings yet
- Examination Paper of CBSE CLass XIIDocument383 pagesExamination Paper of CBSE CLass XIIRON75% (4)
- Cbse SR Jee Apex & Neet Wisdom Chemistry Phase-1 QP (10.11.2023)Document6 pagesCbse SR Jee Apex & Neet Wisdom Chemistry Phase-1 QP (10.11.2023)SÁMÃÑ KANNANo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xam Idea PDFDocument285 pagesChemistry Xam Idea PDFArunabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Guntur Question Bank 2020-2021 Important Questions ChemistryDocument6 pagesGuntur Question Bank 2020-2021 Important Questions ChemistryKarra RavikiranNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 2011 Class - XII Subject - Chemistry: Which Is Better Reducing Agent CO or C at High Temperature? Q5Document0 pagesSample Paper - 2011 Class - XII Subject - Chemistry: Which Is Better Reducing Agent CO or C at High Temperature? Q5abhishekprasad677No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument23 pagesCHEMISTRYchoudharysaaabNo ratings yet
- Sure Shot 2Document23 pagesSure Shot 2abi100% (1)
- Chemistry Xii QP 3Document4 pagesChemistry Xii QP 3Sulekha Rani.R.No ratings yet
- Que Bank 12 ChemDocument8 pagesQue Bank 12 Chemtechblogger098No ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper For Class 12 Chemistry 2017 18Document5 pagesCBSE Sample Paper For Class 12 Chemistry 2017 18nileshmpharmNo ratings yet
- CBSE Chemistry Class 11 (Mid Term Exam Model Paper)Document3 pagesCBSE Chemistry Class 11 (Mid Term Exam Model Paper)RounakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Cbse Sample Paper For Class-12Document7 pagesChemistry: Cbse Sample Paper For Class-12Chunky ChipmunkNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry QP Final Exam 2024 _hssreporter•ComDocument5 pagesXII Chemistry QP Final Exam 2024 _hssreporter•Comsafwanenterprises.alpyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Model PaperDocument31 pagesChemistry Model PaperShimon JosephNo ratings yet
- Sulekha Chem Xii QP 1Document3 pagesSulekha Chem Xii QP 1Sulekha Rani.R.No ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set 4Document5 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set 4Sidharth SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Ruby Park: Class - XIIDocument5 pagesDelhi Public School, Ruby Park: Class - XIIAnnesha GoraNo ratings yet
- Question Paper For Class 12 ChemistryDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper For Class 12 ChemistryRitik Pandey0% (1)
- TITLE Chemistry Sample Paper Class XIIDocument5 pagesTITLE Chemistry Sample Paper Class XIIDominic AmbalatungalNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper +2 Chemistry 18.01.23Document3 pagesSample Paper +2 Chemistry 18.01.23Raj Online ServicesNo ratings yet
- Workshet For Pre Board 1 XII 17-18Document4 pagesWorkshet For Pre Board 1 XII 17-18Sunita NinganurNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA AFS BEGUMPET PERIODIC TEST - 1 CHEMISTRY CLASS 12Document2 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA AFS BEGUMPET PERIODIC TEST - 1 CHEMISTRY CLASS 12KhushiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SQP PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry SQP PDFÀĺťhàf AnsariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Theory) exam questionsDocument14 pagesChemistry (Theory) exam questionsAmit joshiNo ratings yet
- 11 Sample Papers ChemistryDocument6 pages11 Sample Papers ChemistryAnsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ts SR Chemistry Imp QuestionsDocument7 pagesTs SR Chemistry Imp QuestionsYuga Tejeshwar Reddy100% (2)
- Sr. Che. IMP. Q.Document10 pagesSr. Che. IMP. Q.amruthapingali86100% (1)
- Chemistry Sample Paper 2023-2024 XiDocument6 pagesChemistry Sample Paper 2023-2024 XiRandom UserNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Cbse Chemistry Sample Paper 2012-13Document14 pagesClass 12 Cbse Chemistry Sample Paper 2012-13Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set 8Document16 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set 8Sidharth SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Phy CheDocument11 pagesPhy CheVineeta MishraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Test 5Document7 pagesChemistry - Test 5Ahmed haatimNo ratings yet
- QUESTION BANK - CHEMISTRY XII - Checked 3Document5 pagesQUESTION BANK - CHEMISTRY XII - Checked 3JijendarNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Pre BoardDocument5 pagesCHEMISTRY Pre BoardRUDRANo ratings yet
- Previous Year Chemistry Question Paper For CBSE Class 12 - 2014Document11 pagesPrevious Year Chemistry Question Paper For CBSE Class 12 - 2014GouravNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sample Paper LS1Document3 pagesChemistry Sample Paper LS1surbhitaggarwalNo ratings yet
- c-1Document4 pagesc-1astlenathan15No ratings yet
- Question Paper 3 Kendriya Vidyalaya, Nal Campus, Bangalore: ChemistryDocument4 pagesQuestion Paper 3 Kendriya Vidyalaya, Nal Campus, Bangalore: ChemistryjagpreetNo ratings yet
- Xam Idea Chemistry XII QuestionsDocument478 pagesXam Idea Chemistry XII QuestionsADWAITH LALU100% (1)
- 2020 Solved Paper 1 PDFDocument8 pages2020 Solved Paper 1 PDFDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Ts JR Che Imp Questions 05-02-2024Document6 pagesTs JR Che Imp Questions 05-02-2024raniusha96905No ratings yet
- Karnataka PUC Board (KSEEB) Chemistry Class 12 Question Paper 2019Document12 pagesKarnataka PUC Board (KSEEB) Chemistry Class 12 Question Paper 2019sparkysanthosh69No ratings yet
- Senior Intermediate Chemistry Important Questions - 2022 Long Answer QuestionsDocument9 pagesSenior Intermediate Chemistry Important Questions - 2022 Long Answer QuestionsRam RmNo ratings yet
- Q. NO. Marks 1 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesQ. NO. Marks 1 Multiple Choice QuestionsSagar TiwariNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Paper - 2013 Class - XII Subject - Chemistry (Theory)Document5 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Paper - 2013 Class - XII Subject - Chemistry (Theory)Anil V SajithNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Cbse Sample Paper For Class-12Document14 pagesChemistry: Cbse Sample Paper For Class-12Chunky ChipmunkNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper-04 (For 2014)Document6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper-04 (For 2014)cbsestudymaterialsNo ratings yet
- Sr. Chemistry Important Questions - 2023Document4 pagesSr. Chemistry Important Questions - 2023lohithsoujan4569No ratings yet
- CBSE Chemistry Exam Papers 2008-2012Document285 pagesCBSE Chemistry Exam Papers 2008-2012manu5756No ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Principles of Heterocyclic ChemistryFrom EverandThe Principles of Heterocyclic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Cbse Question Paper Mathematics, (1) 1d C lass-XIIDocument12 pagesCbse Question Paper Mathematics, (1) 1d C lass-XIIANUBHAB SWAINNo ratings yet
- Physics v3Document16 pagesPhysics v3ridhushan yasodharanNo ratings yet
- CBSE QUESTION PAPER FOR CLASS XII MATHEMATICSDocument11 pagesCBSE QUESTION PAPER FOR CLASS XII MATHEMATICSANUBHAB SWAINNo ratings yet
- Cbse Question Paper CHEMISTRY (Theory) TT, "1 Pc. 1"1 ( Oiilki&i) Class-XiiDocument15 pagesCbse Question Paper CHEMISTRY (Theory) TT, "1 Pc. 1"1 ( Oiilki&i) Class-XiiANUBHAB SWAINNo ratings yet
- Cbse Question Paper CHEMISTRY (Theory) TT, "1 Pc. 1"1 ( Oiilki&i) Class-XiiDocument12 pagesCbse Question Paper CHEMISTRY (Theory) TT, "1 Pc. 1"1 ( Oiilki&i) Class-XiiANUBHAB SWAINNo ratings yet
- C Bse Question Paper CHEMISTRY (Theory) TT, "1 Pc. 1"1 ( Oiilki&i) C Lass-XiiDocument12 pagesC Bse Question Paper CHEMISTRY (Theory) TT, "1 Pc. 1"1 ( Oiilki&i) C Lass-XiiANUBHAB SWAINNo ratings yet
- Inorganic ReactionsDocument12 pagesInorganic ReactionsANUBHAB SWAINNo ratings yet
- Percent Composition and Chemical FormulasDocument14 pagesPercent Composition and Chemical FormulasElsaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Salt (Preparation of Insoluble SaltDocument10 pagesChemistry Salt (Preparation of Insoluble Saltcheers96No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 1Document110 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1Mahmoud RslanNo ratings yet
- 4.carbon and Its CompoundsDocument8 pages4.carbon and Its CompoundsBhai JaanNo ratings yet
- GlycosidesDocument9 pagesGlycosidesnilumpharmNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Chem CH29 Practice Question AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA A Level Chem CH29 Practice Question AnswersMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- 16 Petrucci10e CSM PDFDocument66 pages16 Petrucci10e CSM PDFRoxana VillalvaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report CompleteDocument20 pagesLab Report Completeiqhwan riatNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriaDocument2 pagesIonic EquilibriaAnonymous ZVYEN6rBNNo ratings yet
- SP Hybridization: Chapter 2: AlkanesDocument4 pagesSP Hybridization: Chapter 2: AlkanesTri FirdaNo ratings yet
- Polarity of Molecules: How Electronegativity Determines if a Molecule is Polar or Non-PolarDocument1 pagePolarity of Molecules: How Electronegativity Determines if a Molecule is Polar or Non-PolarMaria Di MakaototNo ratings yet
- Oleh: Prof. Dr. Hj. Maulidiyah, M.Si: Jurusan Kimia FMIPA UHO 2019Document21 pagesOleh: Prof. Dr. Hj. Maulidiyah, M.Si: Jurusan Kimia FMIPA UHO 2019ANDI ELSYA WIDIYA PRASTIKA WEMPI F1C117065No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument22 pagesCarbon and Its Compoundsapi-24735088294% (17)
- Chapter 7 - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Powerpoint Presentation.Document16 pagesChapter 7 - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Powerpoint Presentation.Nicholas KoerbitzNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Equilibrium Worksheet 1Document2 pagesAcid Base Equilibrium Worksheet 1Frank MassiahNo ratings yet
- Alkenes NotesDocument60 pagesAlkenes NotesLenz KnightNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11cgtDocument5 pagesWorksheet 11cgtJuliyaNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Chemistry and Metal CarbonylsDocument9 pagesOrganometallic Chemistry and Metal CarbonylsSandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- Cajepe, Cherry May F. Bses 1a ChemistryDocument4 pagesCajepe, Cherry May F. Bses 1a ChemistryNilda FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis ExerciseDocument4 pagesHydrolysis ExerciseetikaNo ratings yet
- Poc 2 MCQDocument20 pagesPoc 2 MCQj setty81% (26)
- Habib Public School Chemistry Class-X Unit: 10 Acids Bases and Salts Name of StudentDocument31 pagesHabib Public School Chemistry Class-X Unit: 10 Acids Bases and Salts Name of Studentmehwish razaNo ratings yet
- Solution Stoichiometry PDFDocument6 pagesSolution Stoichiometry PDFJulio100% (1)
- Molecular Geometry GuideDocument6 pagesMolecular Geometry GuideosvaldocossioNo ratings yet
- P Block2012 457Document143 pagesP Block2012 457Abhishek Bansal100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Allen QuestionsDocument20 pagesOrganic Chemistry Allen QuestionstiruvalarnayattyNo ratings yet
- Kimia Famili 100 Slide 33Document46 pagesKimia Famili 100 Slide 33Steven Gandadinata 王德良No ratings yet
- Practice Orgo ExamDocument7 pagesPractice Orgo ExamDoris GrimaldiNo ratings yet
- High Spin and Low Spin ComplexesDocument8 pagesHigh Spin and Low Spin ComplexesArnab ChakrabortyNo ratings yet