Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Huntington'S Chorea I.Overview
Uploaded by
Adriane TomakinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Huntington'S Chorea I.Overview
Uploaded by
Adriane TomakinCopyright:
Available Formats
HUNTINGTON’S CHOREA
I.Overview
Huntington's disease is an inherited disease that causes the progressive
breakdown (degeneration) of nerve cells in the brain. Huntington's disease has a broad
impact on a person's functional abilities and usually results in movement, thinking
(cognitive) and psychiatric disorders.
Medications are available to help manage the symptoms of Huntington's disease, but
treatments can't prevent the physical, mental and behavioral decline associated with the
condition.
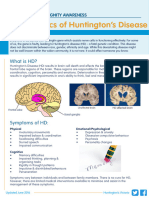
II. Symptoms
Symptoms can vary greatly from person to person. And stress or excitement can
worsen symptoms. Some symptoms are easier to spot than others. Abnormal
movements may be the first thing you notice. Weight loss can be a concern at all
stages. In the later stage of the disease people with it tend to depend on other people
for their everyday needs. Walking and speaking are no longer possible.
III. Causes
Huntington’s is a hereditary disease you can’t “catch it” from someone else. It is
caused by a defect in a single gene. Huntington's disease is an autosomal dominant
disorder, which means that a person needs only one copy of the defective gene to
develop the disorder.
IV. Risk Factors
Having a parent with Huntington’s is the risk factor. An offspring of the parent
having Huntington’s has a 50% chance of inheriting the disease.
V. Treatment
No treatment can alter the course of Huntington’s disease. But medication can
lessen some symptoms of movement and psychiatric disorders. And multiple
interventions can help a person adapt to changes to his or her abilities for a certain
amount of time.
You might also like
- Huntington's DiseaseDocument8 pagesHuntington's Diseasemoumin800No ratings yet
- Title: Name: Date: Course: Section: InstructorDocument7 pagesTitle: Name: Date: Course: Section: InstructorAbir M. BaydounNo ratings yet
- Huntington DiseaseDocument10 pagesHuntington Diseaseapi-498055661No ratings yet
- Huntington's Disease - BiopsychDocument8 pagesHuntington's Disease - BiopsychRia り あ HitsugayaNo ratings yet
- Huntington's DiseaseDocument13 pagesHuntington's DiseaseGEETA MOHAN100% (1)
- Huntington's Disease: Movement DisordersDocument18 pagesHuntington's Disease: Movement DisordersaureliasartikaNo ratings yet
- Huntington'S Disease: By: Logan SnowDocument9 pagesHuntington'S Disease: By: Logan Snowapi-390350832No ratings yet
- What Is HDDocument8 pagesWhat Is HDMichael Andrew OlsenNo ratings yet
- Makayla Walley - Genetic Disorder Research ProjectDocument2 pagesMakayla Walley - Genetic Disorder Research ProjectmakaylaNo ratings yet
- Huntington’s Disease What It Is, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument1 pageHuntington’s Disease What It Is, Symptoms & Treatmentariel.gidalevitzNo ratings yet
- Speech Outline - Mental IllnessDocument5 pagesSpeech Outline - Mental Illnessnaurahiman100% (1)
- Mental Health Guide: For students, teachers, school psychologists, nurses, social workers, counselors and parents.From EverandMental Health Guide: For students, teachers, school psychologists, nurses, social workers, counselors and parents.No ratings yet
- Speech Outline Mental IllnessDocument5 pagesSpeech Outline Mental IllnessMiss D79% (19)
- Understanding Huntington's Disease Causes, Symptoms and DiagnosesDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Huntington's Disease Causes, Symptoms and Diagnosessmithetvin625No ratings yet
- Huntington's Disease BrochureDocument2 pagesHuntington's Disease Brochureapi-265734414No ratings yet
- Decoding the Brain: A Comprehensive Introduction to Neurocognitive DisordersFrom EverandDecoding the Brain: A Comprehensive Introduction to Neurocognitive DisordersNo ratings yet
- Insertion 20240315 134804 0000Document32 pagesInsertion 20240315 134804 0000sajikurkogaNo ratings yet
- Huntington's Chorea Disease IDocument4 pagesHuntington's Chorea Disease ILukes GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Huntington's Disease Symptoms and CausesDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Huntington's Disease Symptoms and CausesNurul Fathia Shafira AmiantiNo ratings yet
- Pandemic Mental - Learn the Secrets to Stay Positive and Improve your Mental Health During this PandemicFrom EverandPandemic Mental - Learn the Secrets to Stay Positive and Improve your Mental Health During this PandemicNo ratings yet
- Huntingtons Disease ResearchDocument6 pagesHuntingtons Disease Researchapi-286758680No ratings yet
- Huntingtons Disease ProjectDocument9 pagesHuntingtons Disease Projectapi-306544419No ratings yet
- Term Paper - Group 12Document7 pagesTerm Paper - Group 12Aarzoo AarzooNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Brain; A Reference Guide to Mental Health and IllnessFrom EverandDisorders of The Brain; A Reference Guide to Mental Health and IllnessNo ratings yet
- What is mental illness? Understanding causes and mythsDocument6 pagesWhat is mental illness? Understanding causes and mythsBrenda AbelgosNo ratings yet
- HuntingtonDocument2 pagesHuntingtonapi-252217084No ratings yet
- 1 Basics of HDDocument2 pages1 Basics of HDRachael BrookingNo ratings yet
- HIV and Delirium: Hiv Mental Health Treatment IssuesDocument2 pagesHIV and Delirium: Hiv Mental Health Treatment IssuesbraulioNo ratings yet
- Huntington’s Chorea, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHuntington’s Chorea, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Mental Disorders WHO 2020Document6 pagesMental Disorders WHO 2020BeatrizNo ratings yet
- Huntington 5Document2 pagesHuntington 5api-240255006No ratings yet
- AIDS DementiaDocument7 pagesAIDS DementiaRevatiNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Understanding the Signs and Symptoms of a Schizophrenic BrainFrom EverandSchizophrenia: Understanding the Signs and Symptoms of a Schizophrenic BrainNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Grasping the Infernal Frustrations of a Mind Filled with Hallucinations and DelusionsFrom EverandSchizophrenia: Grasping the Infernal Frustrations of a Mind Filled with Hallucinations and DelusionsNo ratings yet
- Huntingtons 1Document9 pagesHuntingtons 1api-319386998No ratings yet
- Chan ReferencesDocument93 pagesChan ReferencesAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: The Ultimate Guide to Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of SchizophrenicsFrom EverandSchizophrenia: The Ultimate Guide to Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of SchizophrenicsNo ratings yet
- 1.0 The TruthDocument22 pages1.0 The Truthv@r0_5No ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder: Understanding and managing bipolar disorder, bipolar disorder remedies, treatments, and much more!From EverandBipolar Disorder: Understanding and managing bipolar disorder, bipolar disorder remedies, treatments, and much more!No ratings yet
- Myths and Facts of Mental IllnessDocument18 pagesMyths and Facts of Mental Illnessshamala anjanappaNo ratings yet
- Understanding DementiaDocument2 pagesUnderstanding DementiaSheenaGuinoCullaNo ratings yet
- HD Chad IkerdDocument9 pagesHD Chad Ikerdapi-361190826No ratings yet
- Huntingtons DiseaseDocument4 pagesHuntingtons Diseaseapi-390350832No ratings yet
- 02 - Community Mental HealthDocument41 pages02 - Community Mental HealthNinad KupwadeNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Recovery: Can Prayer Cure Mental Illness? Can people fully recover from mental illness ?From EverandMental Health Recovery: Can Prayer Cure Mental Illness? Can people fully recover from mental illness ?Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bipolar Disorder: Understanding Bipolar Disorder, and how it can be managed, treated, and improvedFrom EverandBipolar Disorder: Understanding Bipolar Disorder, and how it can be managed, treated, and improvedNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Causes, Consequences, and Treatment of PsychosisFrom EverandSchizophrenia: Causes, Consequences, and Treatment of PsychosisNo ratings yet
- Huntington Chorea: April 21, 2006 Articles Images CME Advanced Search Consumer Health Link To This SiteDocument8 pagesHuntington Chorea: April 21, 2006 Articles Images CME Advanced Search Consumer Health Link To This SiteNicolas SaputraNo ratings yet
- Huntingtons Disease BrochureDocument2 pagesHuntingtons Disease Brochureapi-455212625No ratings yet
- HIV and AIDS - PsychiatryDocument3 pagesHIV and AIDS - PsychiatryHaziq ZaidelNo ratings yet
- Without Stigma: About the Stigma of the Mental IllnessFrom EverandWithout Stigma: About the Stigma of the Mental IllnessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dementia by IBSHAM HUSSAIN SHAHDocument14 pagesDementia by IBSHAM HUSSAIN SHAHibbihussain12No ratings yet
- Blue Textured Scrapbook Collage Literature Elements of Historical Fiction InfographicDocument1 pageBlue Textured Scrapbook Collage Literature Elements of Historical Fiction Infographic27mandellsNo ratings yet
- 8a PDFDocument2 pages8a PDFAnonymous OZByhom2wNo ratings yet
- Causes and Treatment of AddictionDocument21 pagesCauses and Treatment of AddictionNizam100% (1)