Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classical Conditioning: Theories Example
Uploaded by
Divine Bob0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageThe document outlines several theories of learning including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, social learning theory, cognitive development theory, constructivism, sociocultural theory, schema theory, attribution theory, and moral development theory. Each theory is explained with a brief example of how it applies to learning.
Original Description:
Original Title
THEORIES-OF-LEARNING.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines several theories of learning including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, social learning theory, cognitive development theory, constructivism, sociocultural theory, schema theory, attribution theory, and moral development theory. Each theory is explained with a brief example of how it applies to learning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageClassical Conditioning: Theories Example
Uploaded by
Divine BobThe document outlines several theories of learning including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, social learning theory, cognitive development theory, constructivism, sociocultural theory, schema theory, attribution theory, and moral development theory. Each theory is explained with a brief example of how it applies to learning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
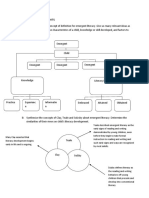
THEORIES OF LEARNING
Theories Example
Classical conditioning A familiar example is conditioned nausea, in
which the sight or smell of a particular food
causes nausea because it caused stomach
upset in the past.
Operant conditioning A student will continue to do his/her
homework because he/she knows that
he/she will be rewarded with a candy
(action) or is praised (behavior) by his/her
parents or teachers if he/she completes it.
Social learning theory For example, a teenager might learn slang by
observing peers.
Cognitive development theory Another example of cognitive development is
the neurological development which occurs
in the brain.
Constructivism Furthermore, in the constructivist classroom,
students work primarily in groups and
learning and knowledge are interactive and
dynamic.
Sociocultural theory Similarly, people also develop their own
cognition by reading, interacting, using
various tools, etc. So, a person's cognitive
level and another person's can be different.
One child can be curious, exploring, eager to
learn and hardworking, while another child
might not be.
Schema theory Examples of schemata include academic
rubrics, social schemas, stereotypes, social
roles, scripts, worldviews, and archetypes.
Attribution theory Maria's car breaks down on the freeway. If
she believes the breakdown happened
because of her ignorance about cars, she is
making an internal attribution.
Moral development theory A child may think, 'I don't want to be spanked
so I'm not going to hit my brother!' Stage 2 is
about self-reward.
You might also like
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Improves Erectile Dysfunction and Premature EjaculationDocument9 pagesPelvic Floor Muscle Training Improves Erectile Dysfunction and Premature EjaculationGe NomNo ratings yet
- Language and The Pursuit of Hap - Chalmers BrothersDocument1,184 pagesLanguage and The Pursuit of Hap - Chalmers BrothersGeorge Adrian Oprea100% (2)
- Teach Yourself Complete Vietnamese (PDFDrive)Document383 pagesTeach Yourself Complete Vietnamese (PDFDrive)Djfrost 888No ratings yet
- Organizational Changes and Stress Management - OBDocument52 pagesOrganizational Changes and Stress Management - OBBenny WeeNo ratings yet
- Social Learning TheoryDocument12 pagesSocial Learning TheoryJun Junoesque Okubo100% (2)
- Electrical Engineering Portal Com Electrical Thumb Rules You Must Follow Part 1Document10 pagesElectrical Engineering Portal Com Electrical Thumb Rules You Must Follow Part 1m khNo ratings yet
- Figure Out Your ThoughtsDocument50 pagesFigure Out Your ThoughtsMaria Victoria Padro100% (3)
- Gravitation PDFDocument42 pagesGravitation PDFcaiogabrielNo ratings yet
- The Brain's Sense of Movement - Alan BerthozDocument352 pagesThe Brain's Sense of Movement - Alan BerthozKaroline MarxNo ratings yet
- Iso 3675 en PDFDocument6 pagesIso 3675 en PDFGery Arturo Perez AltamarNo ratings yet
- What Did You Ask At School Today: A Handbook Of Child Learning Book 1From EverandWhat Did You Ask At School Today: A Handbook Of Child Learning Book 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Matrix On Philosophies of EducationDocument8 pagesMatrix On Philosophies of EducationANELEE GARCIA100% (5)
- Bell Hooks - Teaching - Critical - Thinking - Chapt - 1Document5 pagesBell Hooks - Teaching - Critical - Thinking - Chapt - 1Francesca MeloniNo ratings yet
- Cheng IEP PlanDocument2 pagesCheng IEP PlanMary Kate ArtecheNo ratings yet
- Labeling Theory Was Developed by Howard BeckerDocument2 pagesLabeling Theory Was Developed by Howard BeckerRoeina Abdul100% (1)
- Go To Page Word 2022 DowningDocument17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022 Downingapi-672027388No ratings yet
- Standard 1Document6 pagesStandard 1api-525123857No ratings yet
- Educational Psychology-Basic ConceptsDocument25 pagesEducational Psychology-Basic ConceptsLiza KrizelNo ratings yet
- Part 3: On The CurriculumDocument2 pagesPart 3: On The Curriculumflory mae gudiaNo ratings yet
- Psycologi CompressedDocument27 pagesPsycologi CompressedPipit MarshandaNo ratings yet
- Albert Pandura's TheoryDocument10 pagesAlbert Pandura's TheoryJelly Mae Malig-onNo ratings yet
- Comparative AnalysisDocument13 pagesComparative AnalysisGladys Galorport AstronomoNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022api-714163201No ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document56 pagesLesson 2Annie WallaceNo ratings yet
- Past Paper QuestionsDocument16 pagesPast Paper QuestionshNo ratings yet
- TAMS MatrixDocument6 pagesTAMS MatrixAisiah IshiNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022-1Document19 pagesGo To Page Word 2022-1api-662474937No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022-1Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022-1api-730339009No ratings yet
- Discuss Briefly Your Own Understanding of Philosophy and Its Importance in Teaching. Give Examples or Real Life ExperiencesDocument8 pagesDiscuss Briefly Your Own Understanding of Philosophy and Its Importance in Teaching. Give Examples or Real Life Experiencesjhun ecleoNo ratings yet
- Learning TheoriesDocument27 pagesLearning TheoriesRiza Ann FloresNo ratings yet
- Social CognitiveDocument26 pagesSocial Cognitiveapi-558491172No ratings yet
- What We Mean by LearningDocument7 pagesWhat We Mean by Learninggaurav khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Personality and Social Characteristics - Sept19Document23 pagesTopic 6 Personality and Social Characteristics - Sept19ainabalqis roslyNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022api-622900349No ratings yet
- Module 10 - Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingDocument3 pagesModule 10 - Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingSheila Mae Paltep100% (2)
- Bardajevinarosebeed1b 085211Document6 pagesBardajevinarosebeed1b 085211mabulaymaryannmaeNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning: Professional EducationDocument8 pagesFacilitating Learning: Professional EducationNiño Embile DellomasNo ratings yet
- Albert Bandura's Social Learning Theory in PsychologyDocument28 pagesAlbert Bandura's Social Learning Theory in PsychologyMonu MohanNo ratings yet
- Session 2 AssignmentActivityDocument5 pagesSession 2 AssignmentActivityKarieDetoreTolonesNo ratings yet
- Contri Butions of The Psychosoc I A L SC Iences: 2.1 Jean Piaget and Cognitive DevelopmentDocument38 pagesContri Butions of The Psychosoc I A L SC Iences: 2.1 Jean Piaget and Cognitive Developmentdaily of sinta fuNo ratings yet
- ED101 Final-Dela CruzDocument1 pageED101 Final-Dela CruzCheloumae Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Philosophers of Education (Maymay)Document3 pagesPhilosophers of Education (Maymay)Rona Mae Talamera0% (1)
- ED2Document1 pageED2jeffrey QuezoraNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Porro Folder of WisdomDocument4 pagesJonathan Porro Folder of Wisdomapi-437415281100% (1)
- Social Learning TheoryDocument3 pagesSocial Learning TheorysummersibalamontesinoNo ratings yet
- PED 109 Activities For Unit 2Document8 pagesPED 109 Activities For Unit 2Kyla JadjurieNo ratings yet
- Five Educational Learning TheoriesDocument7 pagesFive Educational Learning TheoriesNicole DuranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Traditional and Contemporary Educational PhilosophiesDocument26 pagesLesson 2 - Traditional and Contemporary Educational PhilosophiesGerhardNo ratings yet
- Shared Study #1-Ramos, Matilde T.Document7 pagesShared Study #1-Ramos, Matilde T.Matie RamosNo ratings yet
- Bully ResearchDocument1 pageBully ResearchLucasNo ratings yet
- Developmental Reading 2Document51 pagesDevelopmental Reading 2Arissa Jane LacbayNo ratings yet
- Educ 7010 Finals ReviewerDocument18 pagesEduc 7010 Finals ReviewerMARK FLORESNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022 FinalDocument17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022 Finalapi-654127046No ratings yet
- PhilosophiesDocument3 pagesPhilosophiesAllondra RosalesNo ratings yet
- Final EdittedDocument6 pagesFinal Edittedapi-302569415No ratings yet
- Tarea 1 Psic Educat YokastaDocument5 pagesTarea 1 Psic Educat YokastaMiguel LopezNo ratings yet
- Motivating Young Learners: Barbara Hoskins SakamotoDocument36 pagesMotivating Young Learners: Barbara Hoskins SakamotoGABRIELANo ratings yet
- Review Lectures On Ecadev and FlearnDocument49 pagesReview Lectures On Ecadev and FlearnMichaela LugtuNo ratings yet
- Englishlp Biasandprejudicegrade9 220504115813Document4 pagesEnglishlp Biasandprejudicegrade9 220504115813Gilda TangposNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022 1Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022 1api-726473944No ratings yet
- CHILD - AND - ADOLESCENT - DEVELOPMENT - Docx Filename - UTF-8''CHILD AND ADOLESCENT DEVELOPMENTDocument5 pagesCHILD - AND - ADOLESCENT - DEVELOPMENT - Docx Filename - UTF-8''CHILD AND ADOLESCENT DEVELOPMENTEd Doloriel MoralesNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module PDFDocument17 pagesThe Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module PDFAnnie JoeNo ratings yet
- PSY406-MidTerm SolvedbymeDocument6 pagesPSY406-MidTerm SolvedbymeAhmed RajpootNo ratings yet
- Reflection Journal # 3 Name of Student Angelyn O. Lipardo Subject Code SC TLE-301 Date Submitted 2/11/22 Topic Learning TheoriesDocument3 pagesReflection Journal # 3 Name of Student Angelyn O. Lipardo Subject Code SC TLE-301 Date Submitted 2/11/22 Topic Learning TheoriesMaya BabaoNo ratings yet
- Level 5 Assignment 1 CompleteDocument8 pagesLevel 5 Assignment 1 CompletejovibonNo ratings yet
- Module 2. Sociological and Anthropological PerspectiveDocument6 pagesModule 2. Sociological and Anthropological PerspectiveMaka-KALOGS VLOGNo ratings yet
- Turaray Jonelyn ED 7 Activity 3Document7 pagesTuraray Jonelyn ED 7 Activity 3KyleNo ratings yet
- EducativaDocument1 pageEducativaKata'ou ColombiaNo ratings yet
- Mud Motor DV826Document1 pageMud Motor DV826CAMILO ALFONSO VIVEROS BRICEÑONo ratings yet
- Format of Actual BatchDocument16 pagesFormat of Actual Batchaljhon dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Hi ThereDocument4 pagesHi TherePipun MaliNo ratings yet
- Pemco OperationsDocument76 pagesPemco OperationsRodrigo PereiraNo ratings yet
- Pugh ChartDocument1 pagePugh Chartapi-92134725No ratings yet
- Ductile-Iron Pressure Pipe: Standard Index of Specifications ForDocument2 pagesDuctile-Iron Pressure Pipe: Standard Index of Specifications ForTamil funNo ratings yet
- Borland C++Document3 pagesBorland C++Sanjay SethNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec 1Document2 pagesAnaphy Lec 1Kiana SanchezNo ratings yet
- Analisis Perencanaan Strategis Sebagai Determinan Kinerja Perusahaan Daerah Air Minum PDAM Kota Gorontalo PDFDocument19 pagesAnalisis Perencanaan Strategis Sebagai Determinan Kinerja Perusahaan Daerah Air Minum PDAM Kota Gorontalo PDFMuhammat Nur SalamNo ratings yet
- 312 Full-3Document8 pages312 Full-3Le TrungNo ratings yet
- Syncronex Single Copy 3.1 Users GuideDocument208 pagesSyncronex Single Copy 3.1 Users GuideTony BoscoNo ratings yet
- ECE - 1551 Digital Logic Lecture 15: Combinational Circuits: Assistant Prof. Fareena SaqibDocument19 pagesECE - 1551 Digital Logic Lecture 15: Combinational Circuits: Assistant Prof. Fareena SaqibAll aboutNo ratings yet
- IMPRSDocument11 pagesIMPRSridho kusumaNo ratings yet
- Chart-5050 by Songram BMA 54thDocument4 pagesChart-5050 by Songram BMA 54thMd. Noor HasanNo ratings yet
- Sikatard 930: Cement Hydration StabiliserDocument2 pagesSikatard 930: Cement Hydration StabiliserBudhi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Control 4Document17 pagesControl 4muhamed mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual Organizational, Direct Support, and General Support Maintenance Repair Parts and Special Tools Lists (Including Depot Maintenance Repair Parts and Special Tools)Document30 pagesTechnical Manual Organizational, Direct Support, and General Support Maintenance Repair Parts and Special Tools Lists (Including Depot Maintenance Repair Parts and Special Tools)Henry PalNo ratings yet
- Lucas - Econometric Policy Evaluation, A CritiqueDocument28 pagesLucas - Econometric Policy Evaluation, A CritiqueFederico Perez CusseNo ratings yet
- Franchise Model For Coaching ClassesDocument7 pagesFranchise Model For Coaching ClassesvastuperceptNo ratings yet
- Csir Net Unit 13 Min Maps BiotecnikDocument12 pagesCsir Net Unit 13 Min Maps BiotecniksantsarnsinghNo ratings yet
- The Differences Between OHS Management System StandardsDocument27 pagesThe Differences Between OHS Management System StandardsRommel100% (2)
- Transitive & Intransitive Verbs: Grammar PracticeDocument5 pagesTransitive & Intransitive Verbs: Grammar PracticeSzeman YipNo ratings yet