Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Educativa
Uploaded by
Kata'ou ColombiaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Educativa
Uploaded by
Kata'ou ColombiaCopyright:
Available Formats
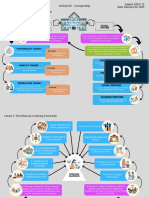
Learning as a social act
Socio-cultural
Socio-cognitive Differences
1. Learning in an academic Triadic reciprocity model The socio-cultural approach of learning is based on
Socio-cognitive the mastery and internalization of social
environment is done through the
perspective: 1. States Socio-cultural perspective: interactions within one?s cultural environment to
observation and interaction with others.
that the 1. Afirms that the improve mental functioning
Enviroment: Is based on the acknowledgement of ackknowledgement of
2. Moreover, this model focuses on the physical setting and the people is individual or individuals are common
interaction between the environment, elements within the setting personal (non-shared). 2. and shared. 2. Is based on
personal characteristics and behavior. with which the individual Is based on the the interaction
observes and interacts abstraction of knowledge (interpersonal approach) 3.
(Intrapersonal approach). The teacher or expert is Evolutionary
3. It is fundamented in the Vygotsky and Zone of psychology and
Personal Characteristics: 3. The teacher or expert active. Proximal Development
observational model that is based on anthropology view
Students attend to a coping is passive.
attetion, retention, reproduction, and
model because they share
motivation. These processes are
similar characteristics, they
required for effective and correct might include academic
learning. ability, age, major, or gender. He defined as the difference between the
References: Black, S., & Allen, J. (2017). Part 5: Learning is a Social Act. The cognitive level of what one currently Proposes that collaborate learning leads to
understands and can do independently and the individual intellectual development and learning Appropriation: students learn
Behavior: open demeanor Reference Librarian, 59(2), 76?91. doi:10.1080/02763877.2017.1400932
potential cognitive level of what one can in three ways: appropriation, co-construction, strategies by observing others during
or positive attitude to learn. understand with support and guidance. and transformation of the apprehended joint activities
knowledge .
Scaffolding: how tutors support
Co-construction: different perspectives and
Types of model lerner?s ability to complete a task
A good guide needs: collaborating on a solution gives greater personal
and keep the learning.
meaning to what is being learned
(1) Recruit interest in and
adherence to requirements Transformation: the
of the task. transformation of a learner's
reasoning from collaborative
Coping model (2) Simplify the task by
Mastery model learning
reducing the number of
actions.
(3) To motive the learner
Is a way by which individuals to stay on task
through expertise and skill Is another way by which
have obtained a deep students learn through the
understanding and mastery of observation of their peers or (4) Mark critical features
colleagues activities. by accentuating the most
a subjetc (Ex. College
important points.
professors, content
specialists, among other.) (5) Control learner's
frustration.
(6) Demonstrate solutions
You might also like
- BSBINS603 - Assessment Task 2Document18 pagesBSBINS603 - Assessment Task 2Skylar Stella83% (6)
- Cot in Science 6Document38 pagesCot in Science 6toffy luck100% (4)
- Three IdeologiesDocument5 pagesThree Ideologiesbing amihan100% (1)
- Summarize The TWO (2) Learning Theories and Their Impacts To EPP Teaching Using The Below: Behaviorism Social LearningDocument2 pagesSummarize The TWO (2) Learning Theories and Their Impacts To EPP Teaching Using The Below: Behaviorism Social LearningBONILITA CORDITANo ratings yet
- Learning TheoryDocument15 pagesLearning Theoryapi-457487068No ratings yet
- Santos Judy Ann A. Activity 1 Beed2a.....Document3 pagesSantos Judy Ann A. Activity 1 Beed2a.....Rosanna TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning HandoutsDocument12 pagesFacilitating Learning HandoutsangeloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Philosophies of EducationImplication To Teachinglearning Process Short NewDocument8 pagesLesson 3 Philosophies of EducationImplication To Teachinglearning Process Short NewMae Therese TaguriganNo ratings yet
- EDUC 101 MODULE 5 - Basilio, Francia Neil T.Document13 pagesEDUC 101 MODULE 5 - Basilio, Francia Neil T.Francia Neil BasilioNo ratings yet
- Western Colleges: Theory-Proponent Basic Principles Strengths/ Applications Personal Criticism/SDocument3 pagesWestern Colleges: Theory-Proponent Basic Principles Strengths/ Applications Personal Criticism/SShane Catherine FabiocNo ratings yet
- CAL - ReportDocument4 pagesCAL - ReportGrace DegzNo ratings yet
- Constructivism Approach Business 304Document4 pagesConstructivism Approach Business 304syrexdestroyerNo ratings yet
- Act FaciDocument28 pagesAct Faciricapearl.zorillaNo ratings yet
- Module BSED BTLED PROFED3-Module3-1-1Document12 pagesModule BSED BTLED PROFED3-Module3-1-1jasminebueno delfinNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Postlecture Assignment 1Document8 pagesSocial Psychology Postlecture Assignment 1Bea BalaoroNo ratings yet
- Health Education (Midterm) : PPT Based NotesDocument7 pagesHealth Education (Midterm) : PPT Based NotesKysha HuangNo ratings yet
- Ailawilliams - Ib Psychology Revision SheetDocument3 pagesAilawilliams - Ib Psychology Revision SheetHanie OriginalNo ratings yet
- Implikasi Teori Belajar Sosial Social Learning TheDocument8 pagesImplikasi Teori Belajar Sosial Social Learning TheZafarani HamkaNo ratings yet
- Jebona Activity 3Document1 pageJebona Activity 3Reyvie Cañete GalanzaNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Riley Skains FinalDocument17 pagesGo To Page Riley Skains Finalapi-734710904No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 0617022Document18 pagesGo To Page Word 0617022api-618483692No ratings yet
- Developmental and Soci Cultural Dimensions of LearningDocument23 pagesDevelopmental and Soci Cultural Dimensions of LearningLea Lian Aquino AbejeroNo ratings yet
- Theories of Learning EDS-103: Social Cognitive TheoryDocument15 pagesTheories of Learning EDS-103: Social Cognitive TheoryLyza LancianNo ratings yet
- Meeting The Educational Philosophers: - He Was AnDocument3 pagesMeeting The Educational Philosophers: - He Was AnAlexa GandioncoNo ratings yet
- Constructivism and ReflectiveDocument4 pagesConstructivism and ReflectiveMa. Cherry May F. VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Government Elementary College of Education (Qasimabad) : Name: Sitara RiazDocument8 pagesGovernment Elementary College of Education (Qasimabad) : Name: Sitara RiazSitara RiazNo ratings yet
- EDUC5410 Unit 2 WrittenDocument9 pagesEDUC5410 Unit 2 Writtenus nNo ratings yet
- EDUC5410 Unit 2 Written 1Document9 pagesEDUC5410 Unit 2 Written 1us nNo ratings yet
- Abueva - Lesson 1-2 Concept MapsDocument2 pagesAbueva - Lesson 1-2 Concept MapsJaye LenizoNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022api-714163201No ratings yet
- Bba Sem 2 Ob 2022Document30 pagesBba Sem 2 Ob 2022Anmol GedaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1-Villanueva, January Isaac M.-BPED I-2Document1 pageActivity 1-Villanueva, January Isaac M.-BPED I-2therealisaac.No ratings yet
- Biography of Albert Bandura: LearningDocument6 pagesBiography of Albert Bandura: LearningRustumme Mirelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module PDFDocument17 pagesThe Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module PDFAnnie JoeNo ratings yet
- MATRIX - Learning Theories FinalDocument11 pagesMATRIX - Learning Theories FinalNicole BurdeosNo ratings yet
- Insights For Educational PsychologyDocument17 pagesInsights For Educational PsychologyDanna GilNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ibu Lita LCDDocument2 pagesTugas Ibu Lita LCDLordChrisna AnimeMVGamingNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 1 GEC 3Document4 pagesModule 2 Lesson 1 GEC 3Rizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- Theories of LearningDocument5 pagesTheories of LearningAsmaa MoutaouakilNo ratings yet
- eDUCATIONAL LEARNING THEORYDocument8 pageseDUCATIONAL LEARNING THEORYINGELPOWER ECNo ratings yet
- Varey 2015Document4 pagesVarey 2015anitamunoz11No ratings yet
- Learning Science: Unit 4 BY Atika AbidDocument22 pagesLearning Science: Unit 4 BY Atika AbidAamir HabibNo ratings yet
- Teaching Approaches in Secondary in Social Studies - Proper LectureDocument8 pagesTeaching Approaches in Secondary in Social Studies - Proper LectureAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- CM 8.2 EspDocument3 pagesCM 8.2 Espagathaolanday.umsNo ratings yet
- Matrix of Human Dev.Document2 pagesMatrix of Human Dev.Maria Cristina Santos BartolomeNo ratings yet
- UTS ReviewerDocument4 pagesUTS Reviewerjaninasachadelacruz0119No ratings yet
- Albert Bandura's Social Learning Theory in PsychologyDocument28 pagesAlbert Bandura's Social Learning Theory in PsychologyMonu MohanNo ratings yet
- FLCT Module 5Document6 pagesFLCT Module 5Jerico VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Ed 203 Module 1Document26 pagesEd 203 Module 1Aberia Juwimae Kristel AberiaNo ratings yet
- College of Subic Montessori Subic Bay, Inc: "Seipsum Facit Persona - Man Makes Himself"Document7 pagesCollege of Subic Montessori Subic Bay, Inc: "Seipsum Facit Persona - Man Makes Himself"Aira Jane FerdivilaNo ratings yet
- Principles Based On Social Cues in Multimedia Learning: Personalization, Voice, Image, and Embodiment PrinciplesDocument9 pagesPrinciples Based On Social Cues in Multimedia Learning: Personalization, Voice, Image, and Embodiment Principlesmadeline bebarNo ratings yet
- Discuss Briefly Your Own Understanding of Philosophy and Its Importance in Teaching. Give Examples or Real Life ExperiencesDocument8 pagesDiscuss Briefly Your Own Understanding of Philosophy and Its Importance in Teaching. Give Examples or Real Life Experiencesjhun ecleoNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories FLFDocument25 pagesLearning Theories FLFRenell FriasNo ratings yet
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocument7 pagesCurriculum DevelopmentStephanie Joy Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Gen 002 Day 4 - Lesson 2Document6 pagesGen 002 Day 4 - Lesson 2Zschaila QuiñoNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument3 pagesThesisJolina Mae NatuelNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Social Learning TheoryDocument44 pagesGroup 5 Social Learning TheoryShiela Yam-idNo ratings yet
- Global Trends MayaDocument10 pagesGlobal Trends MayaMay RamonesNo ratings yet
- Ucsp WK3 IplanDocument3 pagesUcsp WK3 IplanJosephine May PitosNo ratings yet
- Social Learning Sudipta SamantaDocument3 pagesSocial Learning Sudipta SamantaSudipta SamantaNo ratings yet
- Appendix A - Project Planning Grid - Your Story My StoryDocument9 pagesAppendix A - Project Planning Grid - Your Story My Storyapi-209731670No ratings yet
- The ABCs of Human Behavior Behavioral Principles For The Practicing Clinician (PDFDrive)Document236 pagesThe ABCs of Human Behavior Behavioral Principles For The Practicing Clinician (PDFDrive)Florin Ujog100% (1)
- The Role and Importance of Media and Information Literacy2Document12 pagesThe Role and Importance of Media and Information Literacy2Elisa Medina AlbinoNo ratings yet
- Short Story Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesShort Story Lesson Planapi-302202015No ratings yet
- MGMT5050 SI wk1 T2 2023Document32 pagesMGMT5050 SI wk1 T2 2023123No ratings yet
- Can We Use The Same Real Text For Students of Different Proficiency Levels Without Adaptation?Document2 pagesCan We Use The Same Real Text For Students of Different Proficiency Levels Without Adaptation?Hải Trà NguyễnNo ratings yet
- COLLABORATION RUBRIC For PBL: Individual Performance (For Grades 3-5 CCSS ELA Aligned)Document2 pagesCOLLABORATION RUBRIC For PBL: Individual Performance (For Grades 3-5 CCSS ELA Aligned)Mariana RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Teaching English Through Songs and GamesDocument19 pagesTeaching English Through Songs and GamesTri Sutyoso HarumningsihNo ratings yet
- Ps B 0563 Web SlidesDocument58 pagesPs B 0563 Web SlidesCristian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Spring 2010Document148 pagesSpring 2010jtpatelNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal For Students GAD TrainingDocument5 pagesProject Proposal For Students GAD TrainingAnatasukiNo ratings yet
- Coding Lesson Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesCoding Lesson Plan Templateapi-444425700No ratings yet
- Tle Action ResearchDocument8 pagesTle Action ResearchJoyfen Cabingas BacalaNo ratings yet
- Theory Unit 32 - 1993 Listing - Updated 2017Document12 pagesTheory Unit 32 - 1993 Listing - Updated 2017LGFNo ratings yet
- PSFO Guide 2Document18 pagesPSFO Guide 2richagoel.272513No ratings yet
- EDUC6 - Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument10 pagesEDUC6 - Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationMarvin Pame100% (1)
- Leanza Lesson Plan 1Document3 pagesLeanza Lesson Plan 1api-519086780No ratings yet
- Flipped Classroom Presentation Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesFlipped Classroom Presentation Lesson PlanMolly Cragun KendallNo ratings yet
- Insights The First Day Seminar Was Considered A Fruitful One. The Facilitators Discussed Their Assigned TopicDocument3 pagesInsights The First Day Seminar Was Considered A Fruitful One. The Facilitators Discussed Their Assigned TopicMicahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge CELTA Lesson Plan: Background InformationDocument7 pagesCambridge CELTA Lesson Plan: Background InformationPin juNo ratings yet
- A: Show Cooperation in Group Activities Maintain Order in Performing An ActivityDocument4 pagesA: Show Cooperation in Group Activities Maintain Order in Performing An ActivityRiola Lao Waz100% (2)
- University of Hull Learning Outcomes ToolDocument25 pagesUniversity of Hull Learning Outcomes ToolMwaisa BangaNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University: College of Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument3 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University: College of Medical Laboratory ScienceRoelineRosalSerenoNo ratings yet
- Mme Reflection PaperDocument10 pagesMme Reflection Paperapi-622190193No ratings yet
- CS 370 - Artificial IntelligenceDocument26 pagesCS 370 - Artificial IntelligenceANo ratings yet
- Theory PaperDocument3 pagesTheory Paperapi-314958325No ratings yet
- EMA1501 Assignment 4 Amalia Engelbrecht 31697917Document19 pagesEMA1501 Assignment 4 Amalia Engelbrecht 31697917Amalia EngelbrechtNo ratings yet
- High Performance TeamsDocument9 pagesHigh Performance TeamsAsif HamidNo ratings yet