Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Pain
Uploaded by
Hu Dawi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesNCP for Acute Pain
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNCP for Acute Pain
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesAcute Pain
Uploaded by
Hu DawiNCP for Acute Pain
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
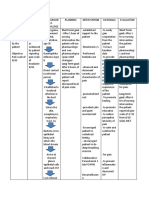
Nursing Diagnosis / Scientific Explanation Expected Outcomes/ Nursing Interventions Rationale of the Evaluation
Problems in Nursing Objectives Interventions
Collaboration
Acute pain related In performing By the end of my Assessment: Patient reported his
to cholecystectomy, surgical shift, the patient will 1-Assess vital signs 1-Rise of BP, HR, and pain has decreased
cholecystectomy incision is done. be able to: (BP, HR, RR, Temp). temperature may to minimal level
surgery evidenced First, tissue damage indicate acute pain. which the outcome
by patient releases chemical 1-report increased has completely met.
verbalizing pain mediators, such as comfort and 2-Assess for 2-Changes can
6/10, stabbing pain prostaglandins, bradykinin, describe satisfactory peripheral pulses and indicate ineffective 1-Vitale sign- stable.
on his abdominal serotonin, substance P, and pain control at a capillary refill. ventilation or
sites with no histamine. These level less than 3 on respiratory distress or 2-Pulses were
radiation, and substances then activate a scale pain of 1 to circulatory disturbance presented on his
provoked by nociceptors, resulting in 10. in extremities. upper/lower
movement. transduction, or the extremities.
generation of an action 2-show improved 3-Assess pain 3-To improve pain
potential (an electrical wellbeing such as characteristics of management 3-The patient felt no
impulse). In the second baseline levels for PQRSTU. strategies. stabbing/tangling
process -transmission- the vital signs (BP, HR, pain.
action potential moves from and RR) and 4-Assess for burning, 4-Effects and results
the site of injury along peripheral pulse. numbness and from hip replacement 4-The patient
afferent nerve fibers tangling in surgical to spinal nerve root verbalized more
nociceptors at the spinal 3-Notify the health sites. irritation. comfort after
cord. Release of substance care provider of pain administration of
P and other before the pain 5-Assess for 5-Indication for medications for pain
neurotransmitters carry the becomes ability/inability of complications of relief.
action potential across the unbearable. movement in bed. immobility.
cleft to the dorsal horn of the 5-The patient was
spinal cord, from where it 6-Monitor and record 6-May indicate for able to sleep and
ascends the spinothalamic neurological signs abnormality or spinal relax after the
tract to the thalamus and the every 4 hours. infection. medications.
midbrain. Finally, from the Interventions
thalamus, fibers send the 7-Administer 7-To reduce pain. 6-The patient
nociceptive message to the Paracetamol for pain reduced his stress by
somatosensory cortex, relief as ordered. integrating with his
parietal lobe, frontal lobe, wife and staff
and the limbic system, 8-Provide rest period 8-Fatigue may result nurse/student nurse.
where the third nociceptive to promote relief, in exaggerated pain.
process -perception- occurs. sleep and relaxation.
9-Use non- 9-To reduce the stress
pharmacological and tension which
techniques decreases the pain
(relaxation exercise according to gate
and listening to control therapy.
music…).
10- Provide non- 10-To provide comfort.
pharmacological
intervention such as
touch and frequent
changing of position.
Teaching:
11-Educate the 11-To improve the
patient relaxation patient’s coping to
technique and stress induced by pain
reduction of stressors which decreases the
and factors. pain as addition
stressors can intensify
pain.
12-Educate family 12-According to the
members to initiate gate control theory,
frequent visits to the identified cognitive
patient and behavioral
encourage the approaches to pain
patient to do management. A
something they like distraction and social
for example music. support help relieve
pain.
Updated by V.G Fall 2017 Page 16
You might also like
- Length Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesFrom EverandLength Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Pain - Post Partum MotherDocument2 pagesPain - Post Partum Motherulrikov91% (11)
- Evaluation and Management of Autonomic Disorders: A Case-Based Practical GuideFrom EverandEvaluation and Management of Autonomic Disorders: A Case-Based Practical GuideJuan IdiaquezNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Objective Data: - Well Appearing But Independent Nursing Interventions: - Review Intraoperative Desired Outcome. Goal Met. Patient Was Able ToDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Objective Data: - Well Appearing But Independent Nursing Interventions: - Review Intraoperative Desired Outcome. Goal Met. Patient Was Able ToMariel GamaloNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Perioperative Pain: Effective management has numerous benefitsFrom EverandFast Facts: Perioperative Pain: Effective management has numerous benefitsNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- NCP-PAIN-1Document6 pagesNCP-PAIN-1goodemonz15No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledJayelles Dixien JuguilonNo ratings yet
- NCP Pre OpDocument4 pagesNCP Pre OpKceey CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical Pain ManagementDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical Pain ManagementMacris BondocNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences Nursing Care Plan for Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument4 pagesCollege of Health Sciences Nursing Care Plan for Acute Myocardial InfarctionLouise GudmalinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Justine Jean GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background of Knowledge Nursing Objectives/Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background of Knowledge Nursing Objectives/Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationIvy Lapore100% (1)
- Short Term Goal: After 1 Hour of Short Term Goal: After 1Document2 pagesShort Term Goal: After 1 Hour of Short Term Goal: After 1Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan #1 - Acute Pain ManagementDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan #1 - Acute Pain Managementunnamed personNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation S: Short Term: Independent: Short TermDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation S: Short Term: Independent: Short TermTrixie Pablo AgustinNo ratings yet
- Sample Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageSample Nursing Care PlanQuiannë Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainGeorge FogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan-Herniated Nucleus PulposusDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan-Herniated Nucleus PulposusJasmin Jacob67% (3)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Ms II NCPDocument2 pagesMs II NCPABIL ABU BAKARNo ratings yet
- Septic Arthritis NCPDocument3 pagesSeptic Arthritis NCPMae Therese B. MAGNO0% (1)
- Andrian Dwi Herlambang (P17230181001) Acute PainDocument8 pagesAndrian Dwi Herlambang (P17230181001) Acute PainAndrian TakigawaNo ratings yet
- Not Transmitted From Person To Person.: Etilogic Agent Incubation Period Mode of Transmission Signs and SymptomsDocument3 pagesNot Transmitted From Person To Person.: Etilogic Agent Incubation Period Mode of Transmission Signs and SymptomskyawNo ratings yet
- Not Transmitted From Person To Person.: Etilogic Agent Incubation Period Mode of Transmission Signs and SymptomsDocument3 pagesNot Transmitted From Person To Person.: Etilogic Agent Incubation Period Mode of Transmission Signs and SymptomskyawNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument9 pagesAssessmentTawny Antonete LandinginNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain Related To Tissue Ischemia As Manifested by Changes in Level of Consciousness PDFDocument3 pagesNCP Acute Pain Related To Tissue Ischemia As Manifested by Changes in Level of Consciousness PDFOGNTVNo ratings yet
- PainDocument2 pagesPainpaulahhhNo ratings yet
- Promoting Comfort, Rest and SleepDocument59 pagesPromoting Comfort, Rest and Sleepkarendelarosa0627775% (4)
- NCP For HemorrhoidsDocument3 pagesNCP For HemorrhoidsTADURAN RENE MAE ANGELLI F.No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Isabella C. DomingoDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Isabella C. DomingojussNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture and Pain: A Review of The Literature: Ladan Eshkevari, CRNA, MS, Dipl. AcDocument10 pagesAcupuncture and Pain: A Review of The Literature: Ladan Eshkevari, CRNA, MS, Dipl. AcRatrika SariNo ratings yet
- Pain ManagementDocument2 pagesPain ManagementprokunoNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument3 pagesNCP FormatSuzete PagaduanNo ratings yet
- NCP For Postpartum DiscomfortsDocument3 pagesNCP For Postpartum DiscomfortsCamille Maluenda - Tan0% (1)
- The unexpected onset of acute pain reminds the patient to seek support, assistance, and reliefDocument1 pageThe unexpected onset of acute pain reminds the patient to seek support, assistance, and reliefJUN JUN PALISOCNo ratings yet
- Midterm MS3 (1 & 2)Document4 pagesMidterm MS3 (1 & 2)Rheeanne Mae AmilasanNo ratings yet
- Or NCPDocument5 pagesOr NCPjelopigar921No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation IndependentLau100% (1)
- Carry Out The Doctor's Order (E.g. Kardex, Meds Chart, Tickets)Document8 pagesCarry Out The Doctor's Order (E.g. Kardex, Meds Chart, Tickets)Yosef OxinioNo ratings yet
- Pain AssessmentDocument11 pagesPain AssessmentJenjen Cortey100% (1)
- 2010 Acute Pain - MurphyDocument10 pages2010 Acute Pain - MurphypNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument4 pagesNCP Formatsandie_bestNo ratings yet
- Source: Operating Room Technique by Nancymarie PhillipsDocument1 pageSource: Operating Room Technique by Nancymarie Phillipsnoreen ellieNo ratings yet
- Assessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Grand Case NP 2 Laparoscopic CholecystectomyDocument10 pagesGrand Case NP 2 Laparoscopic CholecystectomyFarida Paula R. SevillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Pathophysiology Obje Ctive Expected Outcome Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Pathophysiology Obje Ctive Expected Outcome Interventions Rationale EvaluationBuhkz Hermoso100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN ANALYSISDocument7 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN ANALYSISCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Kusain - NCP in NCM 112 RleDocument2 pagesKusain - NCP in NCM 112 Rlejay kusainNo ratings yet
- NCP For ChronicPain PDFDocument2 pagesNCP For ChronicPain PDFjay kusainNo ratings yet
- Name: Age: Gender: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: General: Independent: IndependentDocument2 pagesName: Age: Gender: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: General: Independent: IndependentRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Cambios Neuroplasticos en El Dolor Musculo Esqueletico Crónico Un Revision 2012Document18 pagesCambios Neuroplasticos en El Dolor Musculo Esqueletico Crónico Un Revision 2012Daniela Leyton PezoaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Postpartum Pain ManagementDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Postpartum Pain ManagementRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Tupas, Denzel C. Arrmc Duty-Ncp ActivityDocument13 pagesTupas, Denzel C. Arrmc Duty-Ncp ActivityDen TupasNo ratings yet
- Mcn-Rle-Ncp Postpartum Narce Bsn2aDocument3 pagesMcn-Rle-Ncp Postpartum Narce Bsn2aAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario NCPDocument2 pagesCase Scenario NCPDarwin QuirimitNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorDocument9 pagesBrain TumorKaren Viviene Cinco100% (4)
- The Anatomy and Physiology of Pain: Basic ScienceDocument5 pagesThe Anatomy and Physiology of Pain: Basic ScienceEncikKangRahmanNo ratings yet
- Pain Wida FridayDocument24 pagesPain Wida FridayWahida ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid NCPDocument2 pagesRheumatoid NCPMARK OLVIER E. MELCHORNo ratings yet
- ND - Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument2 pagesND - Disturbed Thought ProcessHu DawiNo ratings yet
- ND - Risk For SuicideDocument3 pagesND - Risk For SuicideHu Dawi100% (1)
- ND - Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesND - Impaired Skin IntegrityHu DawiNo ratings yet
- ND - Impaired Social InteractionDocument2 pagesND - Impaired Social InteractionHu Dawi67% (3)
- ND - Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument2 pagesND - Disturbed Thought ProcessHu DawiNo ratings yet
- Superb Estate: PricesDocument10 pagesSuperb Estate: PricesReal GandeaNo ratings yet
- Patrick Meyer Reliability Understanding Statistics 2010Document160 pagesPatrick Meyer Reliability Understanding Statistics 2010jcgueinj100% (1)
- Ground Penetrating Radar For Locating Buried Utilities: Operation ManualDocument75 pagesGround Penetrating Radar For Locating Buried Utilities: Operation ManualArmando BiringkanaeNo ratings yet
- The Principles Taj MahalDocument2 pagesThe Principles Taj MahalVishnuMohanNo ratings yet
- Final CBLMDocument66 pagesFinal CBLMRanilyn UrbiztundoNo ratings yet
- Hospital Food Service: October 2019Document28 pagesHospital Food Service: October 2019Shaikh Sobiya 57No ratings yet
- Electric Potential and CapacitanceDocument30 pagesElectric Potential and CapacitanceRachita PatangiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 G8Document11 pagesLesson 1 G8Malorie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- KORT RENZO C. BESARIO BS NURSING LESSON REVIEWDocument3 pagesKORT RENZO C. BESARIO BS NURSING LESSON REVIEWDummy AccountNo ratings yet
- Important Characteristics of an Ideal InductorDocument4 pagesImportant Characteristics of an Ideal Inductorsreekantha reddyNo ratings yet
- BS 0812-114 - 1989Document12 pagesBS 0812-114 - 1989عمر عمرNo ratings yet
- Customer Status Update Report 27th January 2015 ColourDocument20 pagesCustomer Status Update Report 27th January 2015 ColourmaryNo ratings yet
- Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 12Th Edition Shier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesHoles Human Anatomy and Physiology 12Th Edition Shier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFJakeOwensbnpm100% (9)
- NEM Report - IntroDocument11 pagesNEM Report - IntroRoshni PatelNo ratings yet
- Eriopon R LiqDocument4 pagesEriopon R LiqsaskoNo ratings yet
- Maximizing Emissions Control with Compact Fume ExtractionDocument9 pagesMaximizing Emissions Control with Compact Fume ExtractionS Ray Chaudhury100% (1)
- Parenteral Fluid Therapy: Types of Intravenous SolutionDocument18 pagesParenteral Fluid Therapy: Types of Intravenous SolutionKathleen Joy Costales Magtanong100% (1)
- Organic Compounds ExplainedDocument37 pagesOrganic Compounds ExplainedAlejandro VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Personal SWOT AnalysisDocument8 pagesPersonal SWOT AnalysisNamNo ratings yet
- EnrollNOLA Daily Seat Availability ReportDocument2 pagesEnrollNOLA Daily Seat Availability ReportAdvocateOnlineNo ratings yet
- Social Responsibility and Managerial Ethics (Principles of Management)Document35 pagesSocial Responsibility and Managerial Ethics (Principles of Management)Reader94% (16)
- Approximate Methods For The Estimation of Muskingum Flood Routing ParametersDocument12 pagesApproximate Methods For The Estimation of Muskingum Flood Routing Parameterssherif ashrafNo ratings yet
- COLORMATCHING GUIDELINES FOR DEMI-PERMANENT HAIR COLORDocument1 pageCOLORMATCHING GUIDELINES FOR DEMI-PERMANENT HAIR COLORss bbNo ratings yet
- Mystic Mystique Face Reading-IIDocument10 pagesMystic Mystique Face Reading-IIVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Paratech Brochures RSSDocument12 pagesParatech Brochures RSSTatiana Andrea Carvajal GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Manual vs Air Rotor Stripping SEM EvaluationDocument8 pagesManual vs Air Rotor Stripping SEM Evaluationlocos3dNo ratings yet
- Touch-Tone Recognition: EE301 Final Project April 26, 2010 MHP 101Document20 pagesTouch-Tone Recognition: EE301 Final Project April 26, 2010 MHP 101Sheelaj BabuNo ratings yet
- Downfall of Ayub Khan and Rise of Zulfikar Ali BhuttoDocument9 pagesDownfall of Ayub Khan and Rise of Zulfikar Ali Bhuttoabdullah sheikhNo ratings yet
- UX5HPDocument2 pagesUX5HPNazih ArifNo ratings yet
- Akali NihangsDocument19 pagesAkali NihangsAngad YuvrajNo ratings yet