Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cisco™ CCNA: IOS
Uploaded by
Nheb Naares Nheb NaareesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cisco™ CCNA: IOS
Uploaded by
Nheb Naares Nheb NaareesCopyright:
Available Formats
Cisco™ CCNA : IOS
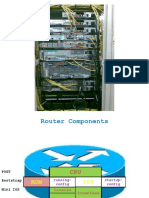
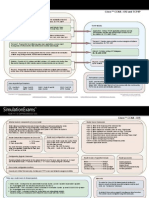
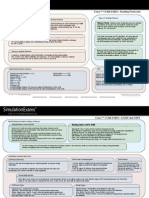
Internal memory components of a cisco router Router Cursor Commands
ROM : Memory containing micro-code for basic functions to start and maintain the router. <ctrl> A: Move to the beginning of the command line
RAM/DRAM : Stores the running configuration, routing tables, and packet buffers. <ctrl> E: Move to the end of the command line
NVRAM : Memory that does not lose information when power is lost. Stores the system’s <ctrl> F: Move forward one character, same as using “Right Arrow”
configuration file and the configuration register. <ctrl> B: Move backward one character, same as using “Left Arrow".
Flash Memory : Stores the compressed IOS image. <ctrl> P: Repeat Previous command, same as using “Up Arrow”
CertExams.com
<ctrl> N: Repeat Next (more recent) command, same as using "Down Arrow"
Router Default Boot Sequence for Cisco IOS Router boot configuration commands <esc> B: Moves to beginning of previous word.
<esc> F: Moves to beginning of next word.
1. NVRAM 3. TFTP server boot system ROM : boots from system ROM <ctrl>R: Creates new command prompt, followed by all the
2. Flash (sequential) 4. ROM boot system flash <IOS file name> : boots characters typed at the last one.
IOS from flash memory
boot system tftp <IOS file name>
The router first looks at Startup Config file in NV
RAM, if not available, it falls back to Flash, then <tftp_addr> : boots IOS from a tftp server
to TFTP and then to ROM.
Configuration Register Command
Router modes of operation include Router passwords
Router(config)# config-register 0x10x (where that last x is 0-F in hex), when the last x is: 0 = boot
into ROM Monitor mode; 1 = boot the ROM IOS; 2 - 15 = look in startup-config file in NVRAM. Mode---------------------------> Prompt Enable password
user exec---------------------> Router> Console password
Privileged----------------------> Router # Enable Secret
Cisco router configurable locations global config------------------> Router(config)# Virtual terminal password (vty)
Interface config--------------> Router(config-if)# Auxiliary password
Console port, Virtual Terminals (vty), Auxiliary port, TFTP server and Network management station
Three ways router learns to forward packets More info
To enable the Cisco IOS to forward packets destined for
1. Static routes : Configured by the administrator manually. Syntax : ip route <ip-addr><mask-addr><ip-addr> obscure subnets of directly connected networks onto the best
Ex: R1(config)#ip route 192.168.200.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.2 route, use "ip classless" command.
2. Default routes : This is used when a route is not known or is infeasible. Syntax : ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 <ip-addr>
Ex: R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.2
3. Dynamic routes : In dynamic routing, the routing tables are automatically updated. By default, Cisco routers support 5 simultaneous telnet sessions.
Dynamic routing uses broadcasts and multicasts to communicate with other routers. This number can be configured using IOS commands.
Copyright © 2018 CertExams.com Version 2.0
CCNA Network Simulator CCNA Exam Simulator CCENT Network Simulator CCENT Exam Simulator Juniper Simulator
Disclaimer: CertExams.com is NOT associated or affiliated with Cisco Systems ®. All CertExams practice tests, exam cram notes and/or material are neither sponsored by, nor endorsed by Cisco ®
Systems. CCNA®, CCENT®, ICND2® are registered trade marks of Cisco® Systems and duly acknowledged.
You might also like
- Config RouterDocument33 pagesConfig RouterJack CordNo ratings yet
- 5 - Basic ConfigDocument40 pages5 - Basic Configemanaboura0No ratings yet
- RAM. Most of The Configuration Commands Deal With Moving Information Into and Out From RAMDocument53 pagesRAM. Most of The Configuration Commands Deal With Moving Information Into and Out From RAMEdara PrasaadNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router FundamentalsDocument127 pagesCisco Router FundamentalsVVNAGESWARNo ratings yet
- Configuring Cisco Switch and RouterDocument23 pagesConfiguring Cisco Switch and Router23wingsNo ratings yet
- Managing A Cisco Internetwork: Sonia Hanif Roll NoDocument32 pagesManaging A Cisco Internetwork: Sonia Hanif Roll NoHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Configuring Cisco Switch and RouterDocument23 pagesConfiguring Cisco Switch and RouterAmourtaha UsiNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS CommandsDocument9 pagesCisco IOS CommandsBogart RorasNo ratings yet
- Ccna2 4p1Document35 pagesCcna2 4p1Alok SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS (Internetworking Operating System)Document8 pagesCisco IOS (Internetworking Operating System)Eincop Netwax LabNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cisco RoutersDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Cisco RouterssutharshanlkNo ratings yet
- Buku Ccna 200-120, 1.6 3-Juni-2015Document345 pagesBuku Ccna 200-120, 1.6 3-Juni-2015kaesihNo ratings yet
- Brocade CLIDocument21 pagesBrocade CLIdpsguard-buy8922No ratings yet
- Assignment: Submitted By: Pankaj YadavDocument128 pagesAssignment: Submitted By: Pankaj YadavRandy DookheranNo ratings yet
- Basic Cisco Router ConfigurationDocument6 pagesBasic Cisco Router ConfigurationKhan JamalNo ratings yet
- Ccna NotesDocument127 pagesCcna NotesRajumallepoola93% (14)
- Ccna Lab UpdatedDocument144 pagesCcna Lab UpdatedSatya VasuNo ratings yet
- Basic Cisco Packet Tracer Network Configuration ExperimentDocument6 pagesBasic Cisco Packet Tracer Network Configuration ExperimenttowhidulNo ratings yet
- CCNA Descovery 2 Lacture 1&2Document5 pagesCCNA Descovery 2 Lacture 1&2MAQSOOD_ITNo ratings yet
- Ccna Lab UpdatedDocument63 pagesCcna Lab UpdatedNETRICH IT SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Router Components: Cisco Router Configuration Afnog 2003 / Track 2 # 1Document69 pagesRouter Components: Cisco Router Configuration Afnog 2003 / Track 2 # 1Sunil KarningNo ratings yet
- Shajar DocumentsDocument13 pagesShajar DocumentsKaushal JangraNo ratings yet
- CCNA1 - H2/H6: Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesCCNA1 - H2/H6: Cheat SheetBart De ZaeytydtNo ratings yet
- CCNA Basic Cofiguration CommandsDocument3 pagesCCNA Basic Cofiguration CommandsValeri ProninNo ratings yet
- Day3 Ch2 Manag IOSDocument27 pagesDay3 Ch2 Manag IOSManoj BorahNo ratings yet
- Guide to rommon recovery, IOS upgrades and file downloadsDocument16 pagesGuide to rommon recovery, IOS upgrades and file downloadsChanchal Kumar BiswasNo ratings yet
- CCNA CheatSheet PDFDocument19 pagesCCNA CheatSheet PDFpranali50% (2)
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- CCNA Study SummaryDocument15 pagesCCNA Study SummaryJaimal Singh JaimalNo ratings yet
- CCENT Cheat SheetDocument18 pagesCCENT Cheat SheetJim D'FotoNo ratings yet
- Comandos Configurar Switch CiscoDocument12 pagesComandos Configurar Switch CiscoAndres GomezNo ratings yet
- Configure Network Devices for SMBs & ISPsDocument52 pagesConfigure Network Devices for SMBs & ISPsMĄd Loubna TebibNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS Switch Basic ConfigurationDocument23 pagesCisco IOS Switch Basic ConfigurationSivaraman AlagappanNo ratings yet
- PT Commands ROUTERDocument7 pagesPT Commands ROUTERconstantrazNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router Configuration CommandsDocument4 pagesCisco Router Configuration CommandsTeny VargheseNo ratings yet
- Quick CommandsDocument9 pagesQuick CommandsMark WoffardNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Basic Config RouterDocument29 pages3.1. Basic Config RouterQuân Lâm MinhNo ratings yet
- Basic Config Router-CDP-LLDPDocument37 pagesBasic Config Router-CDP-LLDPĐinh TúNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router Configuration NTW2000 / Track 2 # 1Document23 pagesCisco Router Configuration NTW2000 / Track 2 # 1srikantNo ratings yet
- Casa To Cisco Command Reference: For Commands Contained in The C100G LabDocument26 pagesCasa To Cisco Command Reference: For Commands Contained in The C100G LabjcheNo ratings yet
- Advanced IOS Functions - : The Configuration RegisterDocument5 pagesAdvanced IOS Functions - : The Configuration RegisterMkNo ratings yet
- Lab 1.5.2 - Basic Router ConfigurationDocument4 pagesLab 1.5.2 - Basic Router Configurationvictor teopezNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router rommonDocument10 pagesCisco Router rommonSamy MohammedNo ratings yet
- 10.1.4-Packet-Tracer - Configure-Initial-Router-SettingsDocument5 pages10.1.4-Packet-Tracer - Configure-Initial-Router-SettingsPetru SpînuNo ratings yet
- Cisco Command Summary: Cisco Router Configuration CommandsDocument13 pagesCisco Command Summary: Cisco Router Configuration CommandsGUnndiNo ratings yet
- Sybex CCNA 640-802: Chapter 7: Managing A Cisco InternetworkDocument33 pagesSybex CCNA 640-802: Chapter 7: Managing A Cisco InternetworkxkerberosxNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS Administrative WorkBookDocument19 pagesCisco IOS Administrative WorkBookDrew DwyerNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityFrom EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityNo ratings yet
- Configuration of a Simple Samba File Server, Quota and Schedule BackupFrom EverandConfiguration of a Simple Samba File Server, Quota and Schedule BackupNo ratings yet
- Using C-Kermit: Communication Software for OS/2, Atari ST, UNIX, OS-9, VMS, AOS/VS, AMIGAFrom EverandUsing C-Kermit: Communication Software for OS/2, Atari ST, UNIX, OS-9, VMS, AOS/VS, AMIGANo ratings yet
- Configuration of a Simple Samba File Server, Quota and Schedule BackupFrom EverandConfiguration of a Simple Samba File Server, Quota and Schedule BackupNo ratings yet
- Next-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsFrom EverandNext-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsNo ratings yet
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- Access List CheatsheetDocument1 pageAccess List CheatsheetNheb Naares Nheb NaareesNo ratings yet
- CCNA ICND2 CheatsheetDocument10 pagesCCNA ICND2 CheatsheetLulzim BruçajNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCheat SheetNheb Naares Nheb NaareesNo ratings yet
- CCNA CheatSheetDocument25 pagesCCNA CheatSheetimranpathan22No ratings yet
- 7.2.4.9 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv6 Addressing - ILM PDFDocument3 pages7.2.4.9 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv6 Addressing - ILM PDFkds20850No ratings yet
- CSharp For Java Developers - Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCSharp For Java Developers - Cheat SheetArianit HoxhaNo ratings yet
- VisualStudio2017 ProductLaunchPosterDocument1 pageVisualStudio2017 ProductLaunchPostervoodoo234No ratings yet
- SeleniumDocument284 pagesSeleniumNheb Naares Nheb NaareesNo ratings yet
- C# Cheat Sheet: Comments, Scopes, Functions, Data Types, Operators, Classes & MoreDocument15 pagesC# Cheat Sheet: Comments, Scopes, Functions, Data Types, Operators, Classes & MoreNheb Naares Nheb NaareesNo ratings yet
- Kwilt For Mobile User GuideDocument72 pagesKwilt For Mobile User GuideNheb Naares Nheb NaareesNo ratings yet
- C# Cheat Sheet: Comments, Scopes, Functions, Data Types, Operators, Classes & MoreDocument15 pagesC# Cheat Sheet: Comments, Scopes, Functions, Data Types, Operators, Classes & MoreNheb Naares Nheb NaareesNo ratings yet
- Smoothwall 2.0-Advproxy-V1.0.1Document40 pagesSmoothwall 2.0-Advproxy-V1.0.1foubianNo ratings yet
- Careers at FEWA-DubaiDocument8 pagesCareers at FEWA-DubaiJnanamNo ratings yet
- Power Grid FailureDocument18 pagesPower Grid Failurechandra 798No ratings yet
- Employee Leave Management System: FUDMA Journal of Sciences July 2020Document7 pagesEmployee Leave Management System: FUDMA Journal of Sciences July 2020MOHAMMED ASHICKNo ratings yet
- Legalism QuotesDocument14 pagesLegalism QuotesfruittinglesNo ratings yet
- Journal of Materials Processing Technology: Jun Cao, Michael A. Gharghouri, Philip NashDocument11 pagesJournal of Materials Processing Technology: Jun Cao, Michael A. Gharghouri, Philip NashJesus Ismael Jimenez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Legal Documents Evidence in Safety Related Proceedings 1663086621Document9 pagesLegal Documents Evidence in Safety Related Proceedings 1663086621richardNo ratings yet
- English Team Agenda 2023-2024Document4 pagesEnglish Team Agenda 2023-2024api-604869051No ratings yet
- Basic Life Support Checklist CSLLFIDocument1 pageBasic Life Support Checklist CSLLFIShane Frances SaborridoNo ratings yet
- Company Introduction PT GEADocument8 pagesCompany Introduction PT GEABegawan Half DoneNo ratings yet
- ESBG Financial Systems Difference EU-US PDFDocument12 pagesESBG Financial Systems Difference EU-US PDFDominiqueCarriouNo ratings yet
- Standardized Trade Types Fact SheetDocument2 pagesStandardized Trade Types Fact SheetRik100% (1)
- Excerpts From The Way of The Samurai (Shīdo) : Primary Source Document With Questions (DBQS)Document2 pagesExcerpts From The Way of The Samurai (Shīdo) : Primary Source Document With Questions (DBQS)Valeria MontalvaNo ratings yet
- DNA Discoveries Reveal Human DNA as a Biological InternetDocument7 pagesDNA Discoveries Reveal Human DNA as a Biological InternetUmbrielNo ratings yet
- Faktor OrganisasiDocument9 pagesFaktor OrganisasiNur Fatin NabilahNo ratings yet
- Senior Power Apps Engineer JobDocument3 pagesSenior Power Apps Engineer JobMichałNo ratings yet
- ST Patrick Lodge 199 BibleDocument5 pagesST Patrick Lodge 199 Bibletofique_fatehiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 15 Signal TransductionDocument4 pagesExercise 15 Signal TransductionTrina Rose AutidaNo ratings yet
- Biotensegrity and Myofascial Chains A Global Approach To An Integrated Kinetic ChainDocument8 pagesBiotensegrity and Myofascial Chains A Global Approach To An Integrated Kinetic ChainMohamed ElMeligieNo ratings yet
- An Engineer's Guide To Designing With Precision Amplifiers: E-BookDocument60 pagesAn Engineer's Guide To Designing With Precision Amplifiers: E-BookIan ChegeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guidelines On Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: An Executive Summary and Recommendations - Update 2019-2020Document17 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines On Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: An Executive Summary and Recommendations - Update 2019-2020Marwa YassinNo ratings yet
- Materials that absorb and decayDocument2 pagesMaterials that absorb and decayDominic NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Kwame Ture InterviewDocument8 pagesKwame Ture InterviewSumayya K AliNo ratings yet
- تركيب وتشغيل وحدات تكييف الهواءDocument49 pagesتركيب وتشغيل وحدات تكييف الهواءOmar NabilNo ratings yet
- Timbering Week 5Document22 pagesTimbering Week 5FikaduKitessa0% (1)
- Kinetic Study of The Catalytic Reforming of Methane With Carbon Dioxide To Synthesis Gas Over Ni - La2O3 Catalyst PDFDocument8 pagesKinetic Study of The Catalytic Reforming of Methane With Carbon Dioxide To Synthesis Gas Over Ni - La2O3 Catalyst PDFMarcus NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Resilience WorkbookDocument54 pagesResilience WorkbookLeo Siu100% (1)
- Astm A710Document3 pagesAstm A710Cristian Otivo100% (1)
- Technical Information No. 12 Vermicular Graphite Cast Iron: MicrostructureDocument1 pageTechnical Information No. 12 Vermicular Graphite Cast Iron: MicrostructureVelina MilevaNo ratings yet
- 21eb7 0 PDFDocument1 page21eb7 0 PDFdediranduNo ratings yet
- Practical File ON Programming For Problem Solving Lab (: 21BTCS181)Document15 pagesPractical File ON Programming For Problem Solving Lab (: 21BTCS181)Vaibhavi SinghNo ratings yet