Professional Documents
Culture Documents
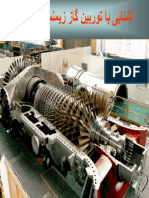
Gas Turbine Engines Characteristics and Performance Combustion Chamber
Uploaded by
Nicolas Guatibonza LOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gas Turbine Engines Characteristics and Performance Combustion Chamber
Uploaded by
Nicolas Guatibonza LCopyright:
Available Formats
Gas Turbine Engines
Characteristics and Performance Combustion
Chamber
Camilo Andres Daza Hurtado Nicolas Guatibonza Loza
Universidad de San Universidad de San
Buenaventura Buenaventura
Facultad de ingeniería Facultad de Ingeniería
Ingenieria Aeronautica Ingenieria Aeronautica
Bogota D.C. Bogota D.C.
cdaza@academia.usbbog.edu.co nguatibonza@academia.usbbog.e
du.co.
Abstract—the main characteristics and zones of a combustion II. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE COMBUSTION
chamber are known, followed by combustion efficiency, total CHAMBER
combustion losses, temperature profile of the combustion chamber
outlet, and finally the durability of the materials of the combustion
chamber. combustion combustion chamber.
III. COMBUSTION PERFORMANCE
Keywords—combustion chamber, durability, performance, pattern
factor, recirculation zona, burning zona, dilution zona. The fuel consumption is given by the thrust generated by the
propulsion system, has a direct effect on the aircraft systems,
I. INTRODUCTION the useful face and the cost of operation is related to the
The combustion chamber has three main areas or characteristics efficiency of combustion. The theoretical efficiency of the
that are found in almost all combustion chambers; whether design is 100 percent or the closest possible by the
multiple or can type, annular type and can-annular type. It only manufacturer, the efficiency of combustion may change due to
varies in its geometry but has the same combustion process. the high power of the payload of the aircraft or the increase in
Next of these we will obtain the fuel injection and mix with the fuel consumption of take-off and cruise is close to 100 percent
air that enters through the compressor, we can obtain a and less respectively.
combustion efficiency theoretically 100% in standard
atmospheric conditions, this efficiency can vary if the
pulverized fuel is dirty or the components of the fuel injection
are in poor condition; It also varies if the engine operates in
other conditions where density, temperature and pressure vary,
this means that the efficiency is not 100%. Combustion pressure
losses are obtained from the summation of the losses of the
compressor, combustion chamber, material coating and
acceleration of the flow. followed by these at the end of the
combustion chamber we have the outlet temperature profile of
the combustion chamber where the outlet temperature must be
known if it is very high it may melt the turbine blades. while
the durability of the material is linked by the motor cycle or in
the conditions where it can operate.
Fig.# combustion efficiency and Air/fuel ratio
As can be seen in the figure combustion efficiency and Air /
fuel ratio that a function of the increase in fuel consumption
decreases the combustion efficiency, these can also vary since
the standard atmospheric conditions change. [1] 1.SARAVANAMUTTOO, H.I.H. Gas Turbine Theory,
Edición 5, 2001
The combustion efficiency can really be at 90%, due to the
[2] 2.MATTINGLY, Jack. Elements of Gas Turbine Propulsion,
controls and limitations of pollutant emissions, this paramatro
is of great importance since it limits us some conditions of the 1996
engine performance. [3] 3.Rolls-Royce Aviation. The Jet Engine.
Combustion efficiency is a measure of combustion integrity. [4] 4.Advanced industrial gas turbines for power generation,
The integrity of combustion directly affects fuel consumption, M.P. Boyce, in Combined Cycle Systems for Near-Zero Emission
since the specific heat of any unburned fuel is not used to Power Generation, 2012
increase the turbine inlet temperature. The combustion [5] 5.An Overview of Gas Turbines, Meherwan P. Boyce, in Gas
efficiency is calculated as the ratio between the actual heat Turbine Engineering Handbook (Fourth Edition), 2012
increase of the gas and the theoretical heat input of the fuel. [6] 6.https://www.faa.gov/regulations_policies/handbooks_ma
𝛥ℎ nuals/aircraft/media/FAA-H-8083-32-AMT-Powerplant-Vol-1.pdf
𝜂𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑏𝑢𝑠 = [7]
𝛥ℎ 7.Reference Area Investigation in a Gas Turbine
Some factors that may affect combustion efficiency may be; If Combustion Chamber Using CFD Fagner Luis Goular Dias
the fuel that is injected has impurities, this can affect the
efficiency since impurities do not burn and lowers the
performance, another problem that can be found is that the
ducts where the fuel is injected are dirty or the nozzles
themselves are defective.
IV. TOTAL PRESSURE LOSS
THE TOTAL LOSS OF TOTAL PRESSURE OF THE MAIN BURNER IS
THE SUM OF THE LOSS OF THE INLET DIFFUSER, THE LOSS OF
THE BURNER DOME AND THE LOSS OF THE LINING, AND THE
LOSS OF IMPULSE RESULTING FROM THE ACCELERATION OF THE
FLOW OF THE MAIN BURNER WITH INCREASING TOTAL GAS
TEMPERATURE. IT IS USUALLY EXPRESSED AS A PERCENTAGE
OF THE COMPRESSOR DISCHARGE PRESSURE. TOTAL PRESSURE
LOSSES OF 2 TO 5% ARE USUALLY FOCUSED ON CURRENT
SYSTEMS.
THE PRESSURE LOSS OF THE MAIN BURNER SYSTEM IS
RECOGNIZED AS NECESSARY TO ACHIEVE CERTAIN DESIGN
OBJECTIVES (PATTERN FACTOR, EFFECTIVE COOLING, ETC.) AND
CAN ALSO PROVIDE A STABILIZING EFFECT OF THE MAIN
BURNER AERODYNAMICS. HOWEVER, TOTAL PRESSURE LOSS
ALSO AFFECTS ENGINE THRUST AND SPECIFIC FUEL
CONSUMPTION.
CONSEQUENTLY, THE DESIGN OBJECTIVES FOR THE TOTAL
PRESSURE LOSS OF THE MAIN BURNER REPRESENT A
COMPROMISE BETWEEN THE ABOVE FACTORS.
V.
VI. THERMAL PROFILE AT THE OUTSIDE PART OF THE
COMBUSTION CHAMBER
VII.
VIII. DURABILITY
REFERENCES
You might also like
- Maintenance Manual For GPB30Document65 pagesMaintenance Manual For GPB30Aceel FitchNo ratings yet
- Simjet Miniature Turbojet Engine: Owner'S ManualDocument20 pagesSimjet Miniature Turbojet Engine: Owner'S Manualamir hosseinNo ratings yet
- Flame Detector System: PurchaserDocument2 pagesFlame Detector System: PurchaserDenis JimenezNo ratings yet
- Solar 5.2MVADocument15 pagesSolar 5.2MVAsohaila7No ratings yet
- Tr-1 Mar2014, Mapna TurbineDocument36 pagesTr-1 Mar2014, Mapna TurbineMehmet ErenNo ratings yet
- 07 Gas Turbine Valves - 0Document14 pages07 Gas Turbine Valves - 0VILAS VIJAYANNo ratings yet
- Siemens 1 GTX 100 TurbineDocument16 pagesSiemens 1 GTX 100 TurbinejparmarNo ratings yet
- Ansaldo Thomassen - CMU (2014)Document4 pagesAnsaldo Thomassen - CMU (2014)guerrezNo ratings yet
- Thermal Peaking PDFDocument26 pagesThermal Peaking PDFkhozaqiNo ratings yet
- EEI 7FA Supplement r1 2octDocument42 pagesEEI 7FA Supplement r1 2octkshalawi0% (1)
- Fast, Efficient and Flexible Smart Maintenance Approach: The Compact ValueDocument2 pagesFast, Efficient and Flexible Smart Maintenance Approach: The Compact ValueIvana SpanovicNo ratings yet
- Harbin Electric InternationalDocument14 pagesHarbin Electric Internationalawais khanNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Performance: by Rainer KurzDocument16 pagesGas Turbine Performance: by Rainer Kurzthryee100% (1)
- An Investigation of Air-Swirl Design Criteria For Gas Turbine Combustors Through A Multi-Objective CFD OptimizationDocument16 pagesAn Investigation of Air-Swirl Design Criteria For Gas Turbine Combustors Through A Multi-Objective CFD Optimizationperules100% (1)
- 11-Presentation MitchCohen PDFDocument32 pages11-Presentation MitchCohen PDFbigsteve9088No ratings yet
- GE MS6001B - EmissionDocument33 pagesGE MS6001B - EmissionMohamad AfifNo ratings yet
- GFA - GT Exhaust Spread ProblemDocument5 pagesGFA - GT Exhaust Spread Problemأمير معروف100% (1)
- EEI 7FA Supplement r1 2octDocument42 pagesEEI 7FA Supplement r1 2octAnonymous ieWpd823LgNo ratings yet
- Inspections, As A Part of A Maintenance Program That Must Be Put in Place With TheDocument29 pagesInspections, As A Part of A Maintenance Program That Must Be Put in Place With TheFrankNo ratings yet
- 7FA Upgrade Combustion HardwareDocument2 pages7FA Upgrade Combustion Hardwaresauerbach1No ratings yet
- 2.4 MBM Combustor Dilution Air SystemDocument6 pages2.4 MBM Combustor Dilution Air SystemmiladNo ratings yet
- 9FA Enhancement Brochure - GEA17570Document8 pages9FA Enhancement Brochure - GEA17570Peter_Phee_341No ratings yet
- GT Gas Fuel and Air FlowDocument38 pagesGT Gas Fuel and Air FlowhinaNo ratings yet
- List of Illustrations: Lm6000 PD Gek 105061 Ge Industrial Aeroderivative Gas TurbinesDocument4 pagesList of Illustrations: Lm6000 PD Gek 105061 Ge Industrial Aeroderivative Gas TurbinesJHONNATTAN RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Technical Paper - SGT400 ASME 2002Document9 pagesTechnical Paper - SGT400 ASME 2002usaid saifullahNo ratings yet
- DLN1+ Combustion Upgrade Solution: Fact SheetDocument1 pageDLN1+ Combustion Upgrade Solution: Fact SheetAhmad Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Marine Gas Turbine: Performance LM6000PC LM6000PG OutputDocument2 pagesMarine Gas Turbine: Performance LM6000PC LM6000PG Outputgasturbina4983No ratings yet
- CCGT Cycle Selection CriteriaDocument29 pagesCCGT Cycle Selection CriteriapsmajuNo ratings yet
- Lokasi Sensor Terkait MBA MBR PlaneDocument1 pageLokasi Sensor Terkait MBA MBR PlanedananNo ratings yet
- DLN 2.0+ Fuel NozzleDocument1 pageDLN 2.0+ Fuel NozzleWedneslao LopezNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Lm5000 Operations ManualDocument4 pagesGas Turbine Lm5000 Operations ManualMuhammad Ilham RiyadiNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine ResearchDocument13 pagesGas Turbine ResearchKrishna MyakalaNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Range OverviewDocument2 pagesGas Turbine Range Overviewyourikats6161No ratings yet
- Answer: Solution:: Gas TurbineDocument16 pagesAnswer: Solution:: Gas TurbineAman SheikhNo ratings yet
- Power PlantDocument62 pagesPower PlantIkhlas KittaNo ratings yet
- Gea32081a LM6000 - Pa - Us - R1 - LRDocument1 pageGea32081a LM6000 - Pa - Us - R1 - LRErik Van GroningenNo ratings yet
- V005t15a001 88 GT 150Document13 pagesV005t15a001 88 GT 150Antonio CilindroNo ratings yet
- Amozesh Gas TurbineDocument114 pagesAmozesh Gas Turbinearmin heidari100% (1)
- Combustion InspectionsDocument81 pagesCombustion InspectionsPhong leNo ratings yet
- GearboxDocument16 pagesGearboxMehul zareNo ratings yet
- GE Frame 6 - Change The Start EngineDocument9 pagesGE Frame 6 - Change The Start EngineShahzad JamesNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine SlideDocument212 pagesGas Turbine SlideMuhd RizzuwanNo ratings yet
- Scope of Supply Titan130Document32 pagesScope of Supply Titan130danferreiro8318No ratings yet
- 6FA DLN 2.6 Extended Interval Combustion System - GEA17898 PDFDocument1 page6FA DLN 2.6 Extended Interval Combustion System - GEA17898 PDFLenin RamonNo ratings yet
- Nigeria Gas Specification - GACNDocument1 pageNigeria Gas Specification - GACNOlusegun OyebanjiNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Performance Based On Inlet ADocument82 pagesGas Turbine Performance Based On Inlet Afateh1982No ratings yet
- SBLM2500 Ind 217Document5 pagesSBLM2500 Ind 217Daniil SerovNo ratings yet
- Lefebvre 1995Document38 pagesLefebvre 1995stepanovatvNo ratings yet
- General Electric Power Business Unit: Strategic Analysis Tools and Techniques - Coursework 2Document13 pagesGeneral Electric Power Business Unit: Strategic Analysis Tools and Techniques - Coursework 2Ibilola IbisankaleNo ratings yet
- GT Hot Gas Path Inspection PDFDocument1 pageGT Hot Gas Path Inspection PDFNagarajakumar DNo ratings yet
- 10.1115 1.3240303Document6 pages10.1115 1.3240303ali a100% (1)
- GT13E2 Infographic - Final - PDFDocument1 pageGT13E2 Infographic - Final - PDFGregory StockNo ratings yet
- LM2500 50Hz Fact Sheet 2016Document2 pagesLM2500 50Hz Fact Sheet 2016joseomarlmNo ratings yet
- 1989 Aker Predicting Gas Turbine Performance Degradation Due To Compressor Fouling Using Computer Simulation TechniquesDocument8 pages1989 Aker Predicting Gas Turbine Performance Degradation Due To Compressor Fouling Using Computer Simulation TechniquesArgenomSaubiNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine and Electrical Power Generation PDFDocument141 pagesGas Turbine and Electrical Power Generation PDFRafael100% (1)
- Mets 2 Tutorial 5Document43 pagesMets 2 Tutorial 5Saurav AryanNo ratings yet
- Development of Aero Gas Turbine Annular CombustorDocument14 pagesDevelopment of Aero Gas Turbine Annular CombustorSurya NarayananNo ratings yet
- Design Manufacturing and Rig Test of A SDocument4 pagesDesign Manufacturing and Rig Test of A SdikoginNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Combustion ChambersDocument31 pagesChapter 6 Combustion Chambersmustafaxdar4No ratings yet
- 2019 - An Overview On Dry Low NOx Micromix Combustor Development For Hydrogen-Rich Gas Turbine ApplicationsDocument13 pages2019 - An Overview On Dry Low NOx Micromix Combustor Development For Hydrogen-Rich Gas Turbine ApplicationsАлександр ТумановNo ratings yet
- LGDocument10 pagesLGAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Chery A1 PartesDocument54 pagesChery A1 PartesAlexferminNo ratings yet
- 036 Siga-UmDocument6 pages036 Siga-UmzezohomeNo ratings yet
- Topic 1:: Preliminary EstimatesDocument22 pagesTopic 1:: Preliminary EstimatesRajan RanjanNo ratings yet
- AAFDS Service SpecificationDocument20 pagesAAFDS Service SpecificationLUIS GIRALDONo ratings yet
- 2N Lift1: Brief ManualDocument12 pages2N Lift1: Brief ManualMartijnMartensNo ratings yet
- Rendering An Exterior Scene - V-Ray 2.0 For SketchUp - Chaos Group HelpDocument9 pagesRendering An Exterior Scene - V-Ray 2.0 For SketchUp - Chaos Group HelpRapha RachoNo ratings yet
- SAE-J1926 Port Reference DimensionsDocument1 pageSAE-J1926 Port Reference DimensionsSamuel RochetteNo ratings yet
- The CPL Exams: CHUF - CPL Human Factors ExaminationDocument5 pagesThe CPL Exams: CHUF - CPL Human Factors Examinationgreg mNo ratings yet
- Seat Plan ChartsDocument10 pagesSeat Plan ChartsJayvee Montoya-PujanteNo ratings yet
- Architecture Ebook Outstanding Wood Buildings - CWCDocument28 pagesArchitecture Ebook Outstanding Wood Buildings - CWCAc Arquitetos Associados50% (2)
- On Windows Syscall Mechanism and Syscall Numbers Extraction MethodsDocument26 pagesOn Windows Syscall Mechanism and Syscall Numbers Extraction MethodsqdwqdNo ratings yet
- How To Adjust The Idle Mixture On Holley CarbsDocument4 pagesHow To Adjust The Idle Mixture On Holley CarbsIsaias PrestesNo ratings yet
- DIN - EN-571-1 Penetrent-TestingDocument18 pagesDIN - EN-571-1 Penetrent-TestingraldelgadomaNo ratings yet
- Goals of True Broad Band's Wireless Next Wave (4G-5G)Document5 pagesGoals of True Broad Band's Wireless Next Wave (4G-5G)alokcena007No ratings yet
- Mujahadeen AR-15Document13 pagesMujahadeen AR-15Chris Leahy100% (2)
- HVAC Dampers Installation Method StatementDocument3 pagesHVAC Dampers Installation Method StatementDong VanraNo ratings yet
- 4 - Ce133 - Strength Analysis of Beams According To Aci or NSCP Codes PDFDocument22 pages4 - Ce133 - Strength Analysis of Beams According To Aci or NSCP Codes PDFRalph PacilNo ratings yet
- 2 - WCDMA Power ControlDocument50 pages2 - WCDMA Power ControlSabrine Chahbi100% (1)
- PERFORMANCEDocument4 pagesPERFORMANCEKorong KapampanganNo ratings yet
- Steel Structures - GeneralDocument16 pagesSteel Structures - Generalonur gunesNo ratings yet
- Simoco TSF2000Document2 pagesSimoco TSF2000Paolo UssiNo ratings yet
- Wtm-058 Ut Procedure Aws d1.5 (2010)Document9 pagesWtm-058 Ut Procedure Aws d1.5 (2010)Wisüttisäk Peäröön0% (1)
- AENG 24a - Environmental Engineering EEDocument6 pagesAENG 24a - Environmental Engineering EEMichael Pantonilla100% (1)
- Harman-Kardon Hk-3490 SM 1Document70 pagesHarman-Kardon Hk-3490 SM 1ymitevNo ratings yet
- Infineon Bar64series Ds v01 01 enDocument15 pagesInfineon Bar64series Ds v01 01 enAbohicham AbhNo ratings yet
- GA-I (H) D 1000 Series ROBOTDocument1 pageGA-I (H) D 1000 Series ROBOTmfarrukhkNo ratings yet
- 555 - 00028 Material Review Board Process Flow and Visual Managment1Document14 pages555 - 00028 Material Review Board Process Flow and Visual Managment1Samsung Joseph0% (1)
- D4ga - Euro4 Engine - EGRDocument59 pagesD4ga - Euro4 Engine - EGRBigfair HD78100% (15)
- DM Automatic Irrigation System SpecsDocument56 pagesDM Automatic Irrigation System SpecsSarfraz AhmadNo ratings yet