Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supplementary Discussion 2 TY Questionnaire
Uploaded by
Kayle Fajutagana FormillezaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supplementary Discussion 2 TY Questionnaire
Uploaded by
Kayle Fajutagana FormillezaCopyright:
Available Formats
SET A QUIZ (TERMINAL YEAR)
FAR EASTERN UNIVERSITY
14. Find the specific weight of benzene.
Situation 1: 3 3
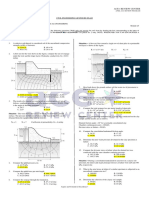
a. 8.34 kN/m c. 11.32 kN/m
A layered soil is shown with the corresponding values of K1, K2, b. 8.50 kN/m
3
d. 11.10 kN/m
3
and K3.
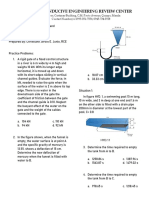
15. Calculate the specific volume of benzene.
3 3
1. Compute the equivalent horizontal coefficient of permeability. a. 0.0012 m /kg c. 0.0009 m /kg
3 3
a.
-4
108.9 x 10 cm/s c.
-4
107.5 x 10 cm/s b. 0.0021 m /kg d. 0.0015 m /kg
-4 -4
b. 109.8 x 10 cm/s d. 105.7 x 10 cm/s
Situation 6: A plate with a regular pentagon cross-section of side
2. Compute the equivalent vertical coefficient of permeability. 5cm is submerged in water where one of its edges is
a.
-4
4.93 x 10 cm/s c.
-4
4.39 x 10 cm/s at the liquid surface.
-4 -4
b. 3.94 x 10 cm/s d. 9.43 x 10 cm/s
16. Determine the location of the center of gravity from the water
3. Compute the ratio of the equivalent horizontal coefficient of surface.
permeability to the equivalent vertical coefficient of permeability. a. 3.17 cm c. 3.44 cm
b. 3.61 cm d. 3.71 cm
a. 24.18 c. 28.14
b. 28.41 d. 24.81
17. Determine the location of the center of pressure from the center
of gravity.
Situation 2: CE Board November 2005
a. 1.012 cm c. 0.121 cm
The laboratory apparatus shown in the figure maintains a constant b. 0.211 cm d. 1.210 cm
head in both the upper and lower reservoirs. The soil sample is a
-3
silty sand with a hydraulic conductivity K = 5 x 10 cm/sec and a 18. Determine the total hydrostatic force acting on the plate.
moisture content of 18.5%. Specific gravity of soil sample is 2.70. a. 1.34 N c. 1.45 N
b. 1.52 N d. 1.57 N
4. Compute the seepage velocity in cm/sec.
Situation 7: A trapezoidal canal with sides slope of 1H:2V
a. 0.011 cm/s c. 0.033 cm/s 3
discharges 20m /sec. The velocity of flow is 2m/sec.
b. 0.022 cm/s d. 0.044 cm/s Consider the bottom width is twice its depth. (Use
n=0.0142).
5. Determine the time required for the plug of colored water to pass
through the soil, assume there is no diffusion, that is the colored 19. Determine the hydraulics radius
water plug has the same volume when it exits as when it entered a. 1.18 m c. 6.47 m
the soil and assume also that the colored water has the same unit b. 7.49 m d. 10.23 m
weight and viscosity as plain water.
20. Determine the slope of the channel
a. 23.33min c. 26.67 min
a. 0.00647 c. 0.0647
b. 33.33min d. 36.67 min b. 0.0000647 d. 0.000647
6. Compute the discharge of water. 21. Determine the average shearing stress on the boundary surface.
3 3
a. 0.287 m /s c. 0.487 m /s a. 1.18 Pa c. 6.47 Pa
3 3
b. 0.387 m /s d. 0.587 m /s b. 7.49 Pa d. 10.23 Pa
Situation 3: CE Board May 2006 SITUATION 8: For the object below:
A thick layer of clay underlies a sand formation having a thickness 22. What fraction of the volume of solid object of specific gravity 7.3
of 5m. The groundwater is located 2m below the ground surface. Specific floats above the surface of a container of mercury?
gravity of sand and clay is 2.65 with sand having an average void ratio of 0.52. a. 0.646
The clay has a water content of 42%. b. 0.564
c. 0.464
7. Compute the saturated unit weight of clay.
d. 0.362
a. 17.47 kN/cu.m c. 19.47 kN/cu.m 23. If the volume of the object below the liquid surface is 0.014 cu.m,
b. 18.47 kn/cu.m d. 20.47 kN/cu.m what is the weight of the object?
a. 3.19 kN
8. Compute the total stress at a depth of 10m below the ground b. 2.56 kN
surface. c. 1.86 kN
a. 182.93 kPa c. 183.29 kPa d. 1.61 kN
b. 192.38 kPa d. 198.32 kPa 24. What load applied vertically that would cause the object to be fully
submerged?
9. Compute the effective stress at a depth of 10m below the ground a. 3.19 kN
surface. b. 2.56 kN
a. 153.5 kPa c. 145.4 kPa c. 1.86 kN
b. 155.3 kPa d. 144.5 KPa d. 1.61 kN
SITUATION 9: An open cylindrical tank 3m high and 1m in diameter contains
2m of water. If the cylinder rotates about its geometrical axis:
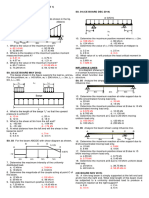
SITUATION 4: Three pipes A, B and C are connected in parallel. If the
3 25. What is the constant angular velocity that can be attained without
combined discharge of the pipes is 0.61 m /sec and assuming they have an
equal value of friction factor f = 0.020, using the tabulated data below: spilling the water?
PIPELINE LENGTH (m) DIAMETER (mm) a. 12.53 rad/sec
A 600 150 b. 14.01 rad/sec
B 480 200 c. 15.45 rad/sec
C 750 100 d. 16.22 rad/sec
10. What is the flow rate in pipeline A in L/sec? 26. What is the constant angular velocity that can be attained if the
a. 170 depth of the water at the center is 0.50 m?
b. 140 a. 12.53 rad/sec
c. 390 b. 14.01 rad/sec
d. 50 c. 15.45 rad/sec
11. What is the flow rate in pipeline B in L/sec? d. 16.22 rad/sec
a. 170 27. What is the constant angular velocity that can be attained if the
3
b. 140 volume of the water spilled out is 0.196 m ?
c. 390 a. 12.53 rad/sec
d. 50 b. 14.01 rad/sec
12. What is the flow rate in pipeline C in L/sec? c. 15.45 rad/sec
a. 170 d. 16.22 rad/sec
b. 140
c. 390
SITUATION 10: CE Board November 2004
d. 55
A consolidated drained tri-axial test was conducted on a normally
consolidated clay. The results were as follows:
Chamber confining pressure = 138 kPa
Deviator stress = 258 kPa
28. Compute the friction angle of the soil.
Situation 5: A 300 L of benzene weighs 260 kg.
a. 28.89 degrees
b. 29.98 degrees
13. Determine the density of benzene.
a. 866.67 kg/m
3
c. 1, 153.85 kg/m
3 c. 27.76 degrees
b. 850.20 kg/m
3
d. 1, 131.92 kg/m
3 d. 26.67 degrees
Engr. Louie A. Alcantara, CE,
MP
SET A QUIZ (TERMINAL YEAR)
FAR EASTERN UNIVERSITY
29. Compute the shear stress at failure.
a. 206.48 kPa
b. 204.68 kPa
c. 208.46 kPa
d. 211.34 kPa
30. Compute the shear stress at failure.
a. 113.95 kPa
b. 112.95 kPa
c. 114.95 kPa
d. 115.95 kPa
Situation 11: CE Board May 2005
A retaining wall 6m high is supporting a horizontal backfill having a dry unit
weight of 1600 kg/cu.m. The cohesionless soil has an angle of friction of 32
degrees and a void ratio of 0.68.
31. Compute the rankine active force on the wall.
a. 87.66 kN c. 86.76 kN
b. 76.68 kN d. 78.66 kN
32. Compute the rankine active force on the wall if water logging
occurs at a depth of 3.5m from the ground surface.
a. 111.90 kN c. 113.70 kN
b. 112.90 kN d. 114.60 kN
33. Compute the location of the resultant active force from the
bottom.
a. 1.54 m c. 1.74 m
b. 1.64 m d. 1.84 m
Situation 12: CE Board Nov 2007
A soil sample has a mass of 1830 g taken from the field having a volume of
-3
1x10 cu.m. It has a specific gravity of 2.60 and a water content of 10%.
Values of emax = 0.63 and emin = 0.44.
34. Compute the void ratio.
a. 0.36 c. 0.56
b. 0.46 d. 0.66
35 . Compute the relative density.
a. 36.8% c. 43.5%
b. 38.6% d. 45.3%
Engr. Louie A. Alcantara, CE,
MP
You might also like
- Quiz 4 Experts - Soil Mech PartDocument4 pagesQuiz 4 Experts - Soil Mech PartBenjamin Benicarlo Juanillo IIINo ratings yet
- Math 1Document1 pageMath 1adonis bibatNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation, Slope Stability & Braced CutsDocument25 pagesPile Foundation, Slope Stability & Braced CutsJommarVocalTagalogNo ratings yet
- .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Mm/s .106 Cm/s 0.750 Cm/s .106 Mm/s 0.750 Mm/s .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Cm/sDocument2 pages.0106 Mm/s 0.075 Mm/s .106 Cm/s 0.750 Cm/s .106 Mm/s 0.750 Mm/s .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Cm/sReech Aerol AlmendralNo ratings yet
- X. FLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOIL IIDocument2 pagesX. FLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOIL IIodilonrempillo.26No ratings yet
- Situation 2. A 800 MM Ø Main Carrying 2.4 M 3/sDocument1 pageSituation 2. A 800 MM Ø Main Carrying 2.4 M 3/sFrancis VillacortaNo ratings yet
- Geo - 3Document2 pagesGeo - 3SamNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ii Geotech HydraulicsDocument2 pagesAssignment-Ii Geotech Hydraulicspat cruzNo ratings yet
- Q4Document6 pagesQ4Ritsu TainakaNo ratings yet
- Hydau GeoDocument9 pagesHydau GeoAngelica TecsonNo ratings yet
- SurveyingDocument1 pageSurveyingrommel baldagoNo ratings yet
- Gs 1 HDocument7 pagesGs 1 HRommel Dave Tejano100% (1)
- CE Module 25 - Soil Testing (Answer Key)Document3 pagesCE Module 25 - Soil Testing (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Assessment B2 (HG) - November 2022Document3 pagesDiagnostic Assessment B2 (HG) - November 2022Yoshjordan LambNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 GeoDocument4 pagesPreboard 2 GeoLienardNo ratings yet
- REFRESHER - GEO 7 April 2024Document2 pagesREFRESHER - GEO 7 April 2024rando12345No ratings yet
- TOS LectureDocument6 pagesTOS LectureAngelo Brian IlaganNo ratings yet
- A Soil Has A BulkDocument12 pagesA Soil Has A BulkMaverick Timbol100% (1)
- Refresher GEO Part2Document2 pagesRefresher GEO Part2Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- Refresher - Geo - 5 - Nov - 2022-Policarpio 2Document2 pagesRefresher - Geo - 5 - Nov - 2022-Policarpio 2Jocelyn CabarlesNo ratings yet
- PREBOARD GEO HYDRA WITH ANSWERS NOV 2017 - Set ADocument2 pagesPREBOARD GEO HYDRA WITH ANSWERS NOV 2017 - Set AEngr. HLDCNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture 101820Document1 pageFluid Mechanics Lecture 101820John Dalton ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Module 15 Module ExamDocument1 pageModule 15 Module ExamMark NatividadNo ratings yet
- Problem Set GeotechDocument1 pageProblem Set Geotechluther joyda alafrizNo ratings yet
- Hydro Geo Online Preboard Questionnaire PDFDocument6 pagesHydro Geo Online Preboard Questionnaire PDFCarl Justin AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Chnical Engineering Refresher PDF Version 1Document4 pagesChnical Engineering Refresher PDF Version 1ELMERNo ratings yet
- FCE - 15: Geotechnical Engineering Semi-Final/Final ExaminationDocument4 pagesFCE - 15: Geotechnical Engineering Semi-Final/Final ExaminationcimpstazNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam StructDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Exam StructJejomar MotolNo ratings yet
- CECA 2 - Problem Set No. 06Document3 pagesCECA 2 - Problem Set No. 06carldomingoNo ratings yet
- Eview Nnovations: First Evaluation Examination Review For Nov 2022 Ce Board ExamDocument2 pagesEview Nnovations: First Evaluation Examination Review For Nov 2022 Ce Board Examaja øNo ratings yet
- Eval 1 - AnsDocument4 pagesEval 1 - AnsGreg Rasco, REE, RMPNo ratings yet
- Quizbowl - ElimDocument4 pagesQuizbowl - ElimChrysler DuasoNo ratings yet
- CE Refresher Apr 2024 - GEO 2Document3 pagesCE Refresher Apr 2024 - GEO 2rando12345No ratings yet
- November 2021 Ce Board Exam Tuzon 1: Eview NnovationsDocument2 pagesNovember 2021 Ce Board Exam Tuzon 1: Eview NnovationsFleight VandollinNo ratings yet
- November 2021 Ce Board Exam Tuzon 6: Eview NnovationsDocument3 pagesNovember 2021 Ce Board Exam Tuzon 6: Eview NnovationsamberNo ratings yet
- Hge Mid PreboardDocument7 pagesHge Mid PreboardChrisneil Delosreyes0% (1)
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyDocument2 pagesHydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyAngelica RomeroNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Examination - Geotech and HydraulicsDocument4 pagesPre Board Examination - Geotech and HydraulicsjefreyNo ratings yet
- 2021 Nov HG 1st PBDocument10 pages2021 Nov HG 1st PBGlaiza MarieNo ratings yet
- GS1 AnsDocument3 pagesGS1 AnsGiemhel GeleraNo ratings yet
- Geo 5Document2 pagesGeo 5Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics10 Neric10Document12 pagesHydraulics10 Neric10jrmmansayonNo ratings yet
- Policarpio 3 - Refresher GEODocument2 pagesPolicarpio 3 - Refresher GEOJohn RoaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Samiksha's MBBS Entrance SOLVED QUESTIONS - 1Document8 pagesPhysics: Samiksha's MBBS Entrance SOLVED QUESTIONS - 1Inesh0% (1)
- Sw3 Answer KeyDocument1 pageSw3 Answer KeyPati DukaNo ratings yet
- Geo - 4Document2 pagesGeo - 4SamNo ratings yet
- 2 Printed MIT CORREL HYDRAULICS GEOTECH 1ST TERM SY 2014 2015 DRAFT PDFDocument13 pages2 Printed MIT CORREL HYDRAULICS GEOTECH 1ST TERM SY 2014 2015 DRAFT PDFMarie kayNo ratings yet
- Eval 3 AnsDocument3 pagesEval 3 AnsGreg Rasco, REE, RMPNo ratings yet
- FOUNDATIONDocument5 pagesFOUNDATIONLYNSER CORONEL ABANZADONo ratings yet
- Eval 2 FinalDocument4 pagesEval 2 FinalGreg Rasco, REE, RMPNo ratings yet
- 115Document10 pages115Memo LyNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Refresher Module PDFDocument5 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Refresher Module PDFjonilyn florentinoNo ratings yet
- Preboard Geo May 2015Document10 pagesPreboard Geo May 2015Nicole RodilNo ratings yet
- Hyd - 6Document2 pagesHyd - 6SamNo ratings yet
- 2000 May ProblemDocument2 pages2000 May ProblemreynaldmiasisNo ratings yet
- Hyd Ref 2Document2 pagesHyd Ref 2rando12345No ratings yet
- Geomorphological Processes: Studies in Physical GeographyFrom EverandGeomorphological Processes: Studies in Physical GeographyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Steering SystemDocument54 pagesSteering SystemPraveen RathodNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 1 SECTION B: Question Book B: This Paper Must Be Answered in EnglishDocument6 pagesPhysics Paper 1 SECTION B: Question Book B: This Paper Must Be Answered in EnglishporterNo ratings yet
- XII - Physics - Frequently Asked Question BankDocument200 pagesXII - Physics - Frequently Asked Question BankPiyush SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- MD Module 1 StressDocument5 pagesMD Module 1 StressCllyan Reyes100% (1)
- Shear Comparison ACI & EURODocument24 pagesShear Comparison ACI & EUROSangamesh BachaneNo ratings yet
- Training CourseDocument44 pagesTraining CourseTugay ArıçNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Temperature Conversions: Chapter 2 Energy and MatterDocument18 pages2.3 Temperature Conversions: Chapter 2 Energy and MatterBeverly PamanNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Textbook PDFDocument28 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Textbook PDFRamprasadNo ratings yet
- Change of Standard Gibbs Free Energy For The Decomposition of Sodium Hydrogen CarbonaDocument13 pagesChange of Standard Gibbs Free Energy For The Decomposition of Sodium Hydrogen CarbonaEuphoria V KhosaNo ratings yet
- Door and Window Seal Impact On Acoustic and Vi-Brational Behavior of Aerodynamic NoiseDocument8 pagesDoor and Window Seal Impact On Acoustic and Vi-Brational Behavior of Aerodynamic NoiseNivedita SahooNo ratings yet
- Sylhet Gas Field QS 2017Document2 pagesSylhet Gas Field QS 2017Sajedur Rahman MishukNo ratings yet
- Experiment EME4016 - 2015 - 2016 Sem 1Document9 pagesExperiment EME4016 - 2015 - 2016 Sem 1Joshua ChongNo ratings yet
- Vibration and Rotation SpectrosDocument6 pagesVibration and Rotation SpectrosWendyLimNo ratings yet
- Straw Rocket LabDocument4 pagesStraw Rocket Labaaguiar1No ratings yet
- Gas/Liquids Separators - Part 3: Quantifying Separation PerformanceDocument14 pagesGas/Liquids Separators - Part 3: Quantifying Separation PerformanceWendellReeceFrankNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Triple Friction Pendulum Bearing in Sap2000 PDFDocument8 pagesModelling of Triple Friction Pendulum Bearing in Sap2000 PDFJ Guerhard GuerhardNo ratings yet
- Cvle472 Lecture 4 Tension MembersDocument82 pagesCvle472 Lecture 4 Tension MembersMohammad Reza Bagerzadeh KarimiNo ratings yet
- Modal AnalysisDocument43 pagesModal AnalysisAhmed Ibrahim100% (1)
- P11 Practice 7 SolnsDocument7 pagesP11 Practice 7 SolnsajjagottuNo ratings yet
- 3 Mass Balance Agro1 PDFDocument28 pages3 Mass Balance Agro1 PDFLiam LagartoNo ratings yet
- Nueva Vizcaya State University College of Engineering: Transport Mechanism For Variable LoadsDocument59 pagesNueva Vizcaya State University College of Engineering: Transport Mechanism For Variable LoadsIvy Joy UbinaNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of High-Performance Surfaces Used For Transversal Stability of Ships (Bilge Keels)Document6 pagesFailure Analysis of High-Performance Surfaces Used For Transversal Stability of Ships (Bilge Keels)Brizamar AguiarNo ratings yet
- Double Helical - Herring BoneDocument6 pagesDouble Helical - Herring BoneMohamed Abd El RahmanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Absolute Permeability of Core Sample by Using Liquid Phase FluidDocument14 pagesDetermination of Absolute Permeability of Core Sample by Using Liquid Phase FluidNurrahmisrNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Engineering Properties of Soils From Field SPT Using Random Number Generation (Kumar Et Al. 2016)Document8 pagesEstimation of Engineering Properties of Soils From Field SPT Using Random Number Generation (Kumar Et Al. 2016)David BendezúNo ratings yet
- Laser Plasma Accelerators For Charged Particles PDFDocument105 pagesLaser Plasma Accelerators For Charged Particles PDFAjit UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Biomechanical Analysis of The ShotDocument20 pagesBiomechanical Analysis of The Shotapi-286492938No ratings yet
- 06 Chapter 12 (Compiled) PDFDocument80 pages06 Chapter 12 (Compiled) PDFHaziq KhairiNo ratings yet
- Eng Mat Design02 PDFDocument57 pagesEng Mat Design02 PDFChandan Varma MamallaNo ratings yet