0% found this document useful (0 votes)
643 views2 pagesCE Board Exam Geo Refresher 2023
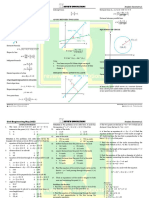
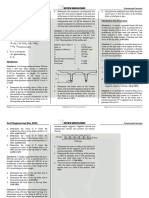
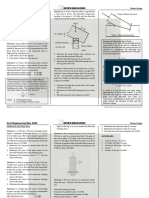
The document is a review for the November 2023 CE Board Exam that covers topics in geotechnical engineering. It contains 26 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of topics like footing design, confined aquifer flow, soil classification, consolidation, and allowable bearing capacity. The questions cover calculations and identifying properties, behaviors, and relationships between different geotechnical engineering concepts.
Uploaded by
mammasddCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
643 views2 pagesCE Board Exam Geo Refresher 2023
The document is a review for the November 2023 CE Board Exam that covers topics in geotechnical engineering. It contains 26 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of topics like footing design, confined aquifer flow, soil classification, consolidation, and allowable bearing capacity. The questions cover calculations and identifying properties, behaviors, and relationships between different geotechnical engineering concepts.
Uploaded by
mammasddCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- CE Board Exam Refresher Questions
- Continuation of Exam Questions