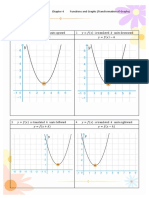
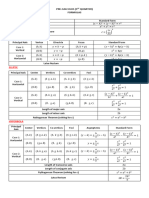
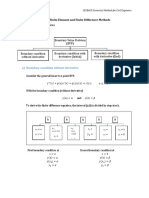
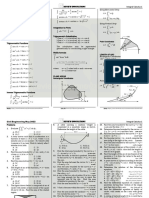
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analytic Geometry
Uploaded by
SamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analytic Geometry
Uploaded by
SamCopyright:
Available Formats
Civil Engineering May 2022 Review Innovations Analytic Geometry 1
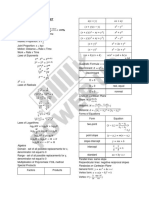
POINTS, LINES, AND CIRCLES Intercept form Distance from (𝑥1 , 𝑦1 ) to 𝐴𝑥 + 𝐵𝑦 + 𝐶 = 0
DISTANCE, SLOPE, AND MIDPOINT FORMULA 𝑥 𝑦 𝐴𝑥1 + 𝐵𝑦1 + 𝐶
+ =1 𝑑=| |
𝑎 𝑏 √𝐴2 + 𝐵2
Distance between parallel lines
ANGLE BETWEEN TWO LINES
𝐶2 − 𝐶1
𝑑=| |
√𝐴2 + 𝐵2
EQUATIONS OF CIRCLE
Distance Formula
𝑑 = √(𝑥2 − 𝑥1 )2 + (𝑦2 − 𝑦1 )2 𝑚2 − 𝑚1
θ = tan−1 ( )
Slope of a line 1 + 𝑚1 𝑚2
rise 𝑦2 − 𝑦1 or
𝑚= =
run 𝑥2 − 𝑥1 tan−1 (𝑚 − tan−1 (𝑚1 )
θ= 2)
Midpoint Formula Note: Center at 𝐶(ℎ, 𝑘)
𝑥1 + 𝑥2 1. Two lines are parallel if their slopes are equal.
𝑥̅ = (𝑥 − ℎ)2 + (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 𝑟 2
2 2. Two lines are perpendicular if the product of their
𝑦1 + 𝑦2 slopes is -1. Center at origin
𝑦̅ =
2 𝑥 2 + 𝑦2 = 𝑟 2
General equation of a line DISTANCE FROM A POINT TO A LINE
General form
𝐴𝑥 + 𝐵𝑦 + 𝐶 = 0
𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 + 𝐷𝑥 + 𝐸𝑦 + 𝐹 = 0
STANDARD EQUATIONS OF LINES
Point-slope form *Center(h,k): h = -D/2 k = -E/2
𝑦 − 𝑦1 = 𝑚(𝑥 − 𝑥1 ) A locus of a point which moves at a constant distance
Slope-intercept form from a fixed point called center and the constant distance
of any point from the center is called the radius.
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑏
Two-point form
𝑦2 − 𝑦1
𝑦 − 𝑦1 = (𝑥 − 𝑥1 )
𝑥2 − 𝑥1
Manila FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
(02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
Civil Engineering May 2022 Review Innovations Analytic Geometry 1
SAMPLE PROBLEMS Situation 2. For problems 11-15, refer here. A circle has 5. The two points on the line 2x + 3y + 4 = 0 which are at
1. The lines 2𝑥 + 𝑎𝑦 + 2𝑏 = 0 and 𝑎𝑥 − 𝑦 − 𝑏 = 1 the equation 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 − 4𝑥 + 6𝑦 − 12 = 0. Find the: distance 2 from the line 3x + 4y – 6 = 0
intersect at the point (-1,3). What is 2𝑎 + 𝑏? 11. center of the circle
a. -4 c. 6 a. (-2,3) c. (2,-3) 6. A line has an equation of x + 5y + 5 = 0. Find the
b. -6 d. 4 b. (-3,2) d. (3,-2) equation of the line through (3, 1) that makes an angle of
12. area of the circle 450 clockwise from the line that is perpendicular to the
Situation 1. For problems 2-10, refer here. Given the a. 78.5 sq. units c. 75.8 sq. units line x + 5y + 5 = 0 at that point.
triangle with vertices at A(1,4), B(9,6), and C(7,2). Find the: b. 87.5 sq. units d. 85.7 sq. units
2. equation of the line through side AB 7. Find the equation of the circle circumscribing the
13. farthest distance from the point (5,6) to the circle
triangle with vertices at A(-1, -4), B(3, -2) and C(5, 2).
a. 𝑥 + 4𝑦 + 15 = 0 c. 𝑥 + 4𝑦 − 15 = 0 a. 14.2 units c. 15.4 units
b. 𝑥 − 4𝑦 + 15 = 0 d. 𝑥 − 4𝑦 − 15 = 0 b. 14.5 units d. 15.2 units 8. Determine the length of the tangent to the circle x2 + y2
3. distance from C to side AB 14. nearest distance from the point (5,6) to the circle – 4x – 5 = 0 from (8, -2).
a. 3.4 c. 4.0 a. 5.4 units c. 4.2 units
b. 4.3 d. 3.7 b. 5.2 units d. 4.5 units 9. Find the equation of the circle a diameter of which is
4. equation of the line through (0,-3) and parallel to side the line segment connecting the centers of the following
15. tangent distance from the point (5,6) to the circle
AB circles:
a. 8.1 units c. 8.6 units
x2 + y2 + 2x + 2y – 7 = 0 and
a. 𝑥 + 4𝑦 + 12 = 0 c. 𝑥 + 4𝑦 − 12 = 0 b. 9.6 units d. 9.1 units x2 + y2 - 4x + 8y – 5 = 0
b. 𝑥 − 4𝑦 + 12 = 0 d. 𝑥 − 4𝑦 − 12 = 0
5. distance from 𝑥 − 4𝑦 − 12 = 0 to side AB 16. Find the equation of the circle having its center on the 10. What is the radius of a circle with the equation
a. 5.66 c. 6.55 line 4x – y = 7 and passing through the points (-2, 4)
b. 5.33 d. 6.88 2𝑥 2 + 2𝑦 2 − 3𝑥 + 4𝑦 − 1 = 0?
and (5, 5).
6. equation of the perpendicular bisector of side BC
a. 𝑥 − 𝑦 − 8 = 0 c. 𝑥 + 2𝑦 − 16 = 0 17. Find an equation(s) of the circle(s) tangent to both
b. 𝑥 − 2𝑦 + 8 = 0 d. 𝑥 + 𝑦 + 16 = 0 axes and containing the point (-8, -1).
7. angle C of the triangle
Answers:
a. 98.1° c. 81.9° Problems for Practice: 1. (7/8, 9/8)
b. 89.8° d. 91.1° 1. Find the coordinates of the point which is 3/8 of the 2. 9x + 20y + 42 = 0
8. terminal point if side AC is extended three times its way from the point A(-1, 3) to the point B(4, -2). 3. x + 2y = 6 and 8x + y = -12
own length from C 4. 23.16 units
2. Find the equation of the line passing through the point 5. (64, - 44) and (4, -4)
a. (24,-6) c. (24,-5)
A(2, -3) and perpendicular to the line having the 6. 2x – 3y = 3
b. (25,-4) d. (25,-3) parametric equations: 7. (x + 2)2 + (y – 3)2 = 50
9. area of the triangle 5x = 3t + 4 and 3y = 4t – 6 8. 5.57 units
a. 15 sq. units c. 13 sq. units 9. (x – 1/2)2 + (y + 5/2)2 = 9/2
b. 12 sq. units d. 14 sq. units 3. Determine the equations of the lines (two answers) 10. √33 / 4
10. point of intersection of the medians passing through (-2, 4) and forming with the axes a
a. (14/3, 3) c. (17/3, 4) triangle having an area of 9 square units.
b. (15/3, 4) d. (16/3, 3)
4. Find the farthest distance from the point (12, 2) to the
circle x2 + y2 + 6x – 16y + 24 = 0.
Manila FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
(02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
Civil Engineering May 2022 Review Innovations Analytic Geometry 2
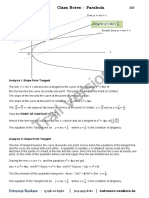
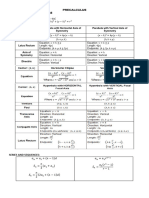
CONIC SECTIONS -locus of a point that moves such that it is always (𝑥 − ℎ)2 = 4𝑎(𝑦 − 𝑘) → 𝑢𝑝𝑤𝑎𝑟𝑑
equidistant from a fixed point called the center. The
General Definition of Conic Sections
constant distance is called the radius of the circle. (𝑥 − ℎ)2 = −4𝑎(𝑦 − 𝑘) → 𝑑𝑜𝑤𝑛𝑤𝑎𝑟𝑑
-locus (or path) of a point that moves such that the
ratio of its distance from a fixed point (focus) and a (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 4𝑎(𝑥 − ℎ) → 𝑡𝑜 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑟𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡
fixed line (directrix) is constant. This constant ratio is
(𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = −4𝑎(𝑥 − ℎ) → 𝑡𝑜 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑙𝑒𝑓𝑡
called the eccentricity of the conic.
Note: (ℎ, 𝑘) is the vertex of the parabola.
ELLIPSE
-locus of a point that moves such that the sum of its
distances from two fixed points called the foci is
constant
Standard Equation
(𝑥 − ℎ)2 + (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 𝑟 2
PARABOLA
-locus of a point that moves such that its distance from
a fixed point called the focus is always equal to its
distance from a fixed line called the directrix
Eccentricity of a conic
𝑓1 𝑓2 𝑓3
𝑒= = = Standard Equations
𝑑1 𝑑2 𝑑3
If 𝑒 = 0, it’s a circle. (𝑥 − ℎ)2 (𝑦 − 𝑘)2
If 𝑒 = 1, it’s a parabola. + =1 → ℎ𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑧𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙
𝑎2 𝑏2
If 𝑒 < 1, it’s an ellipse.
If 𝑒 > 1, it’s a hyperbola. (𝑥 − ℎ)2 (𝑦 − 𝑘)2
+ =1 → 𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑙
𝑏2 𝑎2
CIRCLE
Standard Equations
Note: (ℎ, 𝑘) is the center of the ellipse.
Manila: https://www.facebook.com/ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao: https://www.facebook.com/reviewinnovations.davaobranch
Civil Engineering May 2022 Review Innovations Analytic Geometry 2
Properties of Ellipse 7. A parabolic concrete arch spans a width of 40ft with a 16. The distance (center to center) of the moon from
20ft wide road passing under the bridge. The minimum the earth varies from a minimum of 221,463 miles to a
1. 𝑎2 = 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 vertical clearance over the roadway must be 10ft. What maximum of 252,710 miles. Find the eccentricity of the
𝑐
2. 𝑒= <1 is the height of the smallest such arch that can be used? moon’s orbit.
𝑎
𝑐
3. 𝑒′ =
𝑏 Situation 2. For problems 10-16, refer here. Given the Problem for Practice:
4. Area = π𝑎𝑏 1. Locate the vertex, focus and the coordinates of the
equation of a curve 9𝑥 2 + 25𝑦 2 + 54𝑥 − 100𝑦 − 44 = 0.
5. P = 2π√
𝑎 2 + 𝑏2
Find: length of the latus rectum of the parabola:
2
8. its center y2 + 4x - 4y + 16 = 0
𝑎
6. 𝑑= a. (-2,3) c. (2,-3)
𝑒
2𝑏2 2. Find the equation of the parabola whose vertex is
7. 𝑙𝑟 = b. (-3,2) d. (3,-2)
𝑎 the origin and whose directrix is the line x = 4.
9. its vertices
SAMPLE PROBLEMS a. (-6,2) & (0,2) c. (-8,2) & (2,2) 3. An arch in the shape of an arc of a parabola
Situation 1. For problems 1-5, refer here. Given a b. (-3,7) & (-3,-3) d. (-3,5) & (-3,-1) measures 6m across the base and its vertex is 2.50m
parabola whose equation is 𝑥 2 + 2𝑥 − 4𝑦 + 9 = 0, find 10. its foci above the base. Find the length of the beam parallel to
the following: a. (-6,2) & (0,2) c. (-8,2) & (2,2) the base and 2m above it.
1. vertex b. (-7,2) & (1,2) d. (-3,6) & (-3,-2)
a. (-1,2) c. (-2,1) 4. Find the equation of the ellipse whose vertices are
11. the equation of the directrices
b. (1,-2) d. (2,-1) the points (4, 6) and (4, -2) and whose eccentricity is
25 13 37 13
a. 𝑥= &𝑥 = c. 𝑥 = − &𝑥 = 3/4.
2. focus 4 4 4 4
37 25 37 13
a. (-2,2) c. (0,2) b. 𝑥=− &𝑥 = − d. 𝑥 = &𝑥 = −
4 4 4 4 5. A cross-section of a trough is a semi-ellipse with
b. (-1,1) d. (-1,3) 12. the length of latus rectum width at the top 18cm and depth 12cm. The trough is
3. equation of directrix a. 6.4 units c. 5.7 units filled with water to a depth of 8cm. Find the width at
a. 𝑥 = 1 c. 𝑦 = 1 b. 4.5 units d. 3.6 units the surface of the water.
b. 𝑦 = 3 d. 𝑥 = 3 13. its perimeter
a. 25.9 units c. 26.4 units 6. An earth satellite has an apogee of 2450 miles and a
4. length of latus rectum
perigee of 410 miles. Assuming that the earth’s radius
a. 1 unit c. 4 units b. 25.4 units d. 26.9 units
is 400 miles, what is the value of the eccentricity of
b. 8 units d. 2 units 14. its area ellipse, which form with the center of the earth at one
5. equation of the axis of symmetry a. 12π sq. units c. 18π sq. units focus and whose apogee ang perigee satisfy the
a. 𝑥 = 1 c. 𝑦 = 3 b. 15π sq. units d. 9π sq. units condition above.
b. 𝑥 =-1 d. 𝑦 = 2
15. Find the standard equation of the ellipse that has its Situation 1: A parabola has its axis parallel to the y-
center at (1, 1), a vertex at (3, 1), and that passes through axis, one end of its latus rectum is at (9, 6) and the
6. Find the equation of the locus of a point which moves
the origin. Also, determine the equation of the vertex is at (5, 4). Determine the following:
so that its distance from the line x + 4 = 0 is 5 more than
directrices. 7. length of latus rectum
its distance from the point (3, 1).
8. equation of the parabola
9. equation of the directrix of the parabola.
Manila: https://www.facebook.com/ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao: https://www.facebook.com/reviewinnovations.davaobranch
Civil Engineering May 2022 Review Innovations Analytic Geometry 2
Situation 2:
A point moves so that its distance from the line
x – 16 = 0 is always twice its distance from the point
(4, 0). Determine the following:
10. equation of the locus of the point
11. distance between the vertices of the curve
12. distance of the directrix from the center of the
curve.
Answers:
1. V(-3, 2); F(-4, 2); Ends of Latus Rectum (-4, 4) and
(-4, 0)
2. y2 = -16x
3. 2.68 m
(𝑥−4)2 (𝑦−2)2
4. + =1
7 16
5. 12√2 𝑐𝑚
6. 0.557
7. 8 units
8. x2 – 10x - 8y + 57 = 0
9. y – 2 = 0
10. 3x2 + 4y2 – 192 = 0
11. 16 units
12. 16 units
Manila: https://www.facebook.com/ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao: https://www.facebook.com/reviewinnovations.davaobranch
Civil Engineering May 2022 Review Innovations Analytic Geometry 3
HYPERBOLA GENERAL EQUATION OF CONIC SECTIONS To find the equation of a line tangent to a conic
section at a point P1 (x1, y1):
-locus of a point that moves such that the difference 𝟐 𝟐
𝑨𝒙 + 𝑩𝒙𝒚 + 𝑪𝒚 + 𝑫𝒙 + 𝑬𝒚 + 𝑭 = 𝟎
1. Replace x2 by xx1.
of its distance between two fixed points called the
To find what type of conic section is described by a 2. Replace y2 by yy1.
foci is constant
given equation, 3. Replace x by (x + x1)/2
Case 1: 𝑩=𝟎
4. Replace y by (y + y1)/2
• If A or C is zero, it is a parabola.
5. Replace xy by (xy1 + yx1)/2
• If A and C are not zero and:
where P1 (x1, y1) is the point of tangency.
→ having opposite signs, it is a hyperbola.
→ having same sign and:
SAMPLE PROBLEMS
→ A = C, it is a circle.
Situation 1. For problems 1-7, refer here. Sketch the
→ A ≠ C , it is an ellipse.
graph of the curve 16𝑥 2 − 9𝑦 2 − 64𝑥 − 72𝑦 − 224 =
Case 2: 𝑩≠𝟎
0 and find the following:
• Evaluate 𝐵2 − 4𝐴𝐶. If:
1. center
→ 𝐵2 − 4𝐴𝐶 = 0, it is a parabola.
a. (2,4) c. (-2,4)
→ 𝐵2 − 4𝐴𝐶 < 0, it is an ellipse.
→ 𝐵2 − 4𝐴𝐶 > 0, it is a hyperbola. b. (2,-4) d. (-2,-4)
2. transverse axis and conjugate axis,
POLAR COORDINATE SYSTEM respectively
a. 4 & 3 c. 3 & 4
In this system, the location of a point is expressed by
b. 8 & 6 d. 6 & 8
Standard Equations its distance 𝑟 from a fixed point called the pole and
its angle θ from a fixed line, usually the +𝑥-axis. 3. vertices
(𝑥 − ℎ)2 (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 a. (-1,-4) & (5,-4) c. (-1,-7) & (5,-1)
− =1 → ℎ𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑧𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙 b. (2,0) & (2,-8) d. (-3,-4) & (7,-4)
𝑎2 𝑏2
4. foci
(𝑦 − 𝑘)2 (𝑥 − ℎ)2 a. (-1,-4) & (5,-4) c. (-1,-7) & (5,-1)
− =1 → 𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑙
𝑎2 𝑏2 b. (2,0) & (2,-8) d. (-3,-4) & (7,-4)
5. length of latus rectum
Note: (ℎ, 𝑘) is the center of the hyperbola. a. 10.7 units c. 6.4 units
Properties of Hyperbola b. 16.7 units d. 4.5 units
Relationship between Polar and Cartesian
Coordinate Systems: 6. equation of the upward asymptote
1. 2
𝑐 =𝑎 +𝑏 2 2
a. 4𝑥 − 3𝑦 − 20 = 0 c. 4𝑥 − 3𝑦 − 4 = 0
2. 𝑒=
𝑐
>1 𝑟 2 = 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 or 𝑟 = √𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2
𝑎 b. 4𝑥 + 3𝑦 − 20 = 0 d. 4𝑥 + 3𝑦 + 4 = 0
3. 𝑑=
𝑎
𝑥 = 𝑟 cos θ 𝑦 = 𝑟 sin θ 7. equation of the downward asymptote
𝑒
𝑦 a. 4𝑥 − 3𝑦 − 20 = 0 c. 4𝑥 − 3𝑦 − 4 = 0
2𝑏 2 tan θ = =𝑚
4. 𝑙𝑟 = 𝑥 b. 4𝑥 + 3𝑦 − 20 = 0 d. 4𝑥 + 3𝑦 + 4 = 0
𝑎
Manila: https://www.facebook.com/ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao: https://www.facebook.com/reviewinnovations.davaobranch
Civil Engineering May 2022 Review Innovations Analytic Geometry 3
8. Find the equation of the curve whose center 14. Find the eccentricity of the curve represented by 9. The polar form of the equation 3𝑥 2 + 2𝑦 2 = 8 is:
is at (1,0) with one focus at (1,√13). The the parametric equations 𝑥 = 3 cos θ and 𝑦 = a. r 2 = 8 c. r = 8
8 8
eccentricity of the curve is √13/2. 4 sin θ. b. r= d. r2 =
cos2 θ + 2 cos2 θ + 2
a. 9𝑥 2 − 4𝑦 2 − 8𝑥 + 15 = 0 a. 1.34 c. 0.89
b. 4𝑥 2 − 9𝑦 2 + 8𝑥 + 24 = 0 b. 0.75 d. 0.66 Situation 1:
c. 4𝑦 2 − 9𝑥 2 + 8𝑦 − 23 = 0
The polar equation of the curve is equal to
d. 4𝑥 2 − 9𝑦 2 − 8𝑥 + 40 = 0 Problems for Practice:
1. Locate the center, vertices and foci of the r2 (4 sin2θ + 9 cos2θ) = 36
hyperbola:
9. Identify what conic section is described by 10. Compute the area bounded by the curve.
the following equations: 16y2 – 9x2 + 36x + 96y - 36 = 0 11. Compute the total length of curve.
a. 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 − 25𝑥 = 0 12. Determine the eccentricity of the given curve.
2. Find the equation of the hyperbola with center
b. 𝑦 2 + 8𝑥 − 3𝑦 + 27 = 0 (1, 3), vertex (4, 3) and end of conjugate axis (1, 1).
c. 9𝑥 2 + 4𝑦 2 + 54𝑥 − 25𝑦 − 8 = 0
d. 4𝑥 2 − 9𝑦 2 + 8𝑥 + 24 = 0 3. Compute the distance between the directrices of
e. 13𝑥 2 + 10𝑥𝑦 + 13𝑦 2 + 6𝑥 − 42𝑦 − 27 = 0 the curve 4x2 – 9y2 + 16x + 72y - 92 = 0
f. 4𝑥𝑦 + 3𝑦 2 − 8𝑥 + 16𝑦 + 19 = 0 Answers:
g. 4𝑥 2 + 8𝑥 + 4𝑦 2 − 16𝑦 − 20 = 0 4. The length of the latus rectum of a hyperbola is
equal to 18 and the distance between the foci is 12. 1. C(2, -3); V(2, 0) and V’(2, -6)
h. 4𝑥 2 + 4𝑥𝑦 + 𝑦 2 − 8𝑥 + 16𝑦 + 19 = 0
Find the equation of the curve (center at the origin) F(2, 2) and F’(2, -8)
if the conjugate axis is parallel to the y-axis. 2. 4x2 – 9y2 – 8x + 54y – 113 = 0
10. Find the equation of the line tangent to the 3. 2.22 units
curve x2 = 4y + 5 and passing through (3, 1). 4. x2/9 – y2/27 = 1
5. Find the equation of the line tangent to the conic
section 3x2 – 3xy + 4x + y – 3 = 0 at (-1, 1). 5. 5x – 4y + 9 = 0
11. Find the length of the sub-tangent and sub- 6. 12 units
normal of the curve y2 = 8x for the point (2, 4). 7. y = -2x2 (Parabola)
6. A curve has an equation of y = 2x2 + 1. Compute
the length of sub-normal at point (1,3). 8. 8.89 units
12. Find the length of the latus rectum of the curve 8
9. 𝑟 2 =
2 𝑐𝑜𝑠 2 𝜃 + 2
𝑟= . 7. Eliminate the parameter “t” from the parametric 10. 18.85 sq.units
1+ cos θ
a. 8 units c. 12 units equations: 11. 16.02 units
4 units d. 16 units 12. 0.745
b. x = sin t and y = cos 2t – 1
What is the equivalent conic section?
13. Find the length of the curve 𝑟 = 4 sin θ.
a. 10.23 units c. 9.42 units
b. 11.68 units d. 12.57 units 8. Find the length of the curve r = 2 sin θ + 2 cos θ.
Manila: https://www.facebook.com/ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao: https://www.facebook.com/reviewinnovations.davaobranch
You might also like
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Analytic Geometry 1Document2 pagesAnalytic Geometry 1ggomo15100% (1)
- Analytic GeometryDocument3 pagesAnalytic GeometryJennifer JumaquioNo ratings yet
- Pure Matheatics 1: Straight LineDocument22 pagesPure Matheatics 1: Straight LineLaughing HyenaNo ratings yet
- P Topic 6 Tangents ParabolaDocument3 pagesP Topic 6 Tangents ParabolaDuper JlNo ratings yet
- Answers - Online Daily Test 2 - Trockers-1Document5 pagesAnswers - Online Daily Test 2 - Trockers-1Michael MyamboNo ratings yet
- 1600.io Essential SAT Math Study Notes - V1.3Document46 pages1600.io Essential SAT Math Study Notes - V1.3enonumousthekillerNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry CAPE Integrated Mathematics-1 PDFDocument18 pagesCoordinate Geometry CAPE Integrated Mathematics-1 PDFDequanNo ratings yet
- POWER UP 2020 Mathematics EquationsDocument3 pagesPOWER UP 2020 Mathematics EquationsLorniel GraxielNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Separation of Variables: Differential EquationsDocument6 pagesTopic 4 Separation of Variables: Differential Equationsjohn dave rivasNo ratings yet
- Lines and CirclesDocument3 pagesLines and CirclesIlliad De ChavezNo ratings yet
- Functions Last PushDocument56 pagesFunctions Last Pushvanessamahlatse81No ratings yet
- Precalculus q1 FormulasDocument1 pagePrecalculus q1 FormulasGeronimo LucesNo ratings yet
- The Circle LCHL Reference SheetDocument5 pagesThe Circle LCHL Reference Sheetmarco.chiappero.ieNo ratings yet
- SAT Formula Sheet: Linear FunctionsDocument8 pagesSAT Formula Sheet: Linear FunctionsShreyaNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Analysis of Curves and Parametric EquationsDocument21 pagesWeek 11 Analysis of Curves and Parametric EquationsCharlize Kristel Diana DelabahanNo ratings yet
- Calculus Reference SheetDocument6 pagesCalculus Reference SheetKevinNo ratings yet
- The Straight LineDocument1 pageThe Straight LineFATIN NOORNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Formula SheetDocument1 pageMath 10 Formula SheetAdrienNo ratings yet
- Higher Mathematics Checklist ZETA MATHSDocument22 pagesHigher Mathematics Checklist ZETA MATHSbrunaalvesbento.1997No ratings yet
- Vector Calculus: Line IntegralDocument26 pagesVector Calculus: Line IntegralSiti HajarNo ratings yet
- C1 Essentials: Summary of AQA Core 1 Content Not Provided in The Formula BookDocument1 pageC1 Essentials: Summary of AQA Core 1 Content Not Provided in The Formula BookHadirah DunglahNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Document1 pageFormula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Roberto DiscutidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DifferentiationDocument19 pagesChapter 2 DifferentiationMNo ratings yet
- Harold's Precalculus Rectangular - Polar - Parametric "Cheat Sheet"Document7 pagesHarold's Precalculus Rectangular - Polar - Parametric "Cheat Sheet"HarshNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 1Document2 pagesAnalytic Geometry 1Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Pure 1 PDFDocument8 pagesPure 1 PDFSteveNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 1Document2 pagesAnalytic Geometry 1Wayne VillarozaNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus Notes 3Document3 pagesPre Calculus Notes 3Lex LabadoNo ratings yet
- The Straight Line: Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation Engineering Analytic GeometryDocument6 pagesThe Straight Line: Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation Engineering Analytic GeometryJames Darwin SorianoNo ratings yet
- NCS21 - 02 - Phase Plane Analysis of Nonlinear Systems - 03Document7 pagesNCS21 - 02 - Phase Plane Analysis of Nonlinear Systems - 03zain khuramNo ratings yet
- AQA C1 EssentialsDocument2 pagesAQA C1 Essentials965161191No ratings yet
- MAKALAH Matematika Ekonomi Materi Fungsi Permintaan Dan Fungsi PenawaranDocument28 pagesMAKALAH Matematika Ekonomi Materi Fungsi Permintaan Dan Fungsi PenawaranshintaNo ratings yet
- Section 2.4 - Transformations of GraphsDocument23 pagesSection 2.4 - Transformations of GraphsmohamedNo ratings yet
- Shapes of GraphsDocument1 pageShapes of GraphsLiviNo ratings yet
- AS A LEVEL Pure Maths 1 NotesDocument5 pagesAS A LEVEL Pure Maths 1 Noteshillkwok99No ratings yet
- Lesson 1.i - 1.j - Integration Concepts & FormulasDocument5 pagesLesson 1.i - 1.j - Integration Concepts & FormulasLester GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tangent Line and The DerivativesDocument10 pagesTangent Line and The DerivativesandreaNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFormula SheetSyasya AziziNo ratings yet
- Mathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesDocument10 pagesMathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesNUR RAIHAN BINTI ABDUL RAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesDocument10 pagesMathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesNUR RAIHAN BINTI ABDUL RAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Questão 01 NOTAÇÃO INDICIALDocument5 pagesQuestão 01 NOTAÇÃO INDICIALAnderson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Suspension Bridge Chapter 0 Parabola CableDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Suspension Bridge Chapter 0 Parabola CableSeungWoo LEENo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS - Analytic Geometry 1Document2 pagesMATHEMATICS - Analytic Geometry 1ARNOLD MORAN100% (1)
- Ch04 SummaryDocument4 pagesCh04 SummaryL TangNo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument21 pagesPre CalculusSUSANA, NIÑA FELIZ C.No ratings yet
- TypingDocument6 pagesTypingAleem AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Functions and Models IIDocument57 pagesChapter 2 Functions and Models IITOS CCLNo ratings yet
- 3-Lecture-Special Functions MAT - M Sc-IVDocument7 pages3-Lecture-Special Functions MAT - M Sc-IVMadina GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry (11-21)Document4 pagesAnalytic Geometry (11-21)blueberrytimeNo ratings yet
- A Math Summary BookletDocument113 pagesA Math Summary BookletbusinessNo ratings yet
- Pre-Cal FormulasDocument1 pagePre-Cal FormulasshannenkrishagwapaNo ratings yet
- 1714methods Unit 1 Exam NotesDocument2 pages1714methods Unit 1 Exam NotesIsaiah KimNo ratings yet
- Some Pages From Parametric Representations Samples 2Document7 pagesSome Pages From Parametric Representations Samples 2TiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesEngineering Mathematics Cheat Sheettevin sessa67% (3)
- Finding The Equation of A Line From Two PointsDocument9 pagesFinding The Equation of A Line From Two PointsParikNo ratings yet
- Boundary Value Problem PDFDocument30 pagesBoundary Value Problem PDFrazNo ratings yet
- DE Sample ProblemDocument5 pagesDE Sample ProblemMiggy CidNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- 8b - Circular FunctionsDocument39 pages8b - Circular FunctionsSamNo ratings yet
- 11a - Oblique TrianglesDocument28 pages11a - Oblique TrianglesSamNo ratings yet
- 11b - Spherical TrigonometryDocument19 pages11b - Spherical TrigonometrySamNo ratings yet
- 8a - Right TrianglesDocument25 pages8a - Right TrianglesSamNo ratings yet
- 9a - Trigonometric Formulas and IdentitiesDocument6 pages9a - Trigonometric Formulas and IdentitiesSamNo ratings yet
- 10 - Trigonometric EquationsDocument13 pages10 - Trigonometric EquationsSamNo ratings yet
- L4 - InequalitiesDocument35 pagesL4 - InequalitiesSamNo ratings yet
- Timber DesignDocument7 pagesTimber DesignSamNo ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument4 pagesIntegral CalculusSamNo ratings yet
- L5b - Decomposition of Fractions To Partial FractionsDocument41 pagesL5b - Decomposition of Fractions To Partial FractionsSamNo ratings yet
- Gillesania Shear and MomentDocument10 pagesGillesania Shear and MomentSamNo ratings yet
- 9b - Proving Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument7 pages9b - Proving Trigonometric IdentitiesSamNo ratings yet
- 7b - Combinatorial MathematicsDocument48 pages7b - Combinatorial MathematicsSamNo ratings yet
- Psad - 14Document2 pagesPsad - 14SamNo ratings yet
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument5 pagesPrestressed ConcreteSamNo ratings yet
- Xpertz Terms-4Document2 pagesXpertz Terms-4SamNo ratings yet
- Hyd - 4Document2 pagesHyd - 4SamNo ratings yet
- SURVEYINGDocument9 pagesSURVEYINGSamNo ratings yet
- Bridge Construction Methodology DPWH TARLAC 1ST DEODocument19 pagesBridge Construction Methodology DPWH TARLAC 1ST DEOSam100% (1)
- Gillesania Shear StrengthDocument6 pagesGillesania Shear StrengthSamNo ratings yet
- Gillesania TrigonometryDocument43 pagesGillesania TrigonometrySamNo ratings yet
- Geo - 4Document2 pagesGeo - 4SamNo ratings yet
- Sup 1aDocument6 pagesSup 1aSamNo ratings yet
- Gillesania Plane GeometryDocument71 pagesGillesania Plane GeometrySamNo ratings yet
- Gillesania DynamicsDocument40 pagesGillesania DynamicsSam100% (1)
- Gillesania Solid GeometryDocument50 pagesGillesania Solid GeometrySamNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry HandoutsDocument15 pagesAnalytic Geometry Handoutskreuxtempest50% (2)
- Generalized Class of Sakaguchi Functions in Conic Region: Saritha. G. P, Fuad. S. Al Sarari, S. LathaDocument5 pagesGeneralized Class of Sakaguchi Functions in Conic Region: Saritha. G. P, Fuad. S. Al Sarari, S. LathaerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Conic Word ProblemsDocument4 pagesConic Word ProblemsAubrey Love LabardaNo ratings yet
- Blobby ObjectsDocument15 pagesBlobby Objectslarenjose2007No ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument26 pagesAnalytic GeometryJohn Rey Blasco33% (3)
- Mathematics T STPM 2014 Sem 1 Trial Paper SIGSDocument4 pagesMathematics T STPM 2014 Sem 1 Trial Paper SIGSKenneth Chan100% (2)
- Catia NotesDocument102 pagesCatia NotesSunny100% (1)
- Optimising The Design of Textured Surfaces For Reducing Lubricated Friction Coef FicientDocument17 pagesOptimising The Design of Textured Surfaces For Reducing Lubricated Friction Coef FicientOmar KeshkNo ratings yet
- Math Boards ProblemDocument16 pagesMath Boards ProblemJerdNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Ellipse ProblemsDocument12 pagesAnalytic Geometry Ellipse ProblemsOjit QuizonNo ratings yet
- Graphics Notes 3Document200 pagesGraphics Notes 3m.No ratings yet
- DG2 Lecture Notes 11 SpringDocument82 pagesDG2 Lecture Notes 11 Springbolekaca1No ratings yet
- Gravitational WavesDocument18 pagesGravitational Wavesmarc millisNo ratings yet
- Photoshop Clone Part-1Document50 pagesPhotoshop Clone Part-1Kedia RahulNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Quiz S2023Document17 pagesAnalytic Geometry Quiz S2023madelene gatuteoNo ratings yet
- 3D STRINGCRAFT IJCMLStringDocument12 pages3D STRINGCRAFT IJCMLStringAaisha JagotNo ratings yet
- A. D.D.S., MS.": An Evaluation of Basic Articulators and Their Concepts Part I. Basic ConceptsDocument23 pagesA. D.D.S., MS.": An Evaluation of Basic Articulators and Their Concepts Part I. Basic Conceptsjinny1_0No ratings yet
- Olympiad Paper 1 October 2010 SolutionsDocument5 pagesOlympiad Paper 1 October 2010 SolutionsKarn KumarNo ratings yet
- Buckling of Imperfect Elliptical Cylindrical Shells UnderDocument6 pagesBuckling of Imperfect Elliptical Cylindrical Shells UnderAdel MuslehNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics (EG)Document8 pagesEngineering Graphics (EG)Sudalai MadanNo ratings yet
- Mackay Early History of The Symmedian PointDocument12 pagesMackay Early History of The Symmedian PointgrigoriytamasjanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Section 1 Mat061 PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 2 Section 1 Mat061 PDFBenhar Masahod BLM-VLOGNo ratings yet
- Unit 1E Equation of LocusDocument16 pagesUnit 1E Equation of LocusAnn Pamila SantosNo ratings yet
- Screw Conveyor Vane DesignDocument4 pagesScrew Conveyor Vane DesignVishal V Bhagwat100% (1)
- MATHS Class XI - Revision Assignment (2022 - 23)Document10 pagesMATHS Class XI - Revision Assignment (2022 - 23)spy arrowNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections: Parts of ConicsDocument16 pagesConic Sections: Parts of ConicsSophia AbendanNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus First Quarter WorksheetsDocument28 pagesPre-Calculus First Quarter Worksheetsjoshua tanNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 AS Sir Lecture DetailsDocument21 pagesGrade 12 AS Sir Lecture DetailsManthan HaritashNo ratings yet
- Applications: Otation of XESDocument1 pageApplications: Otation of XESthank highNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Khan Academy Activity - Pre-Calculus B 2223Document3 pagesUnit 1 Khan Academy Activity - Pre-Calculus B 2223yazminNo ratings yet