Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analytic Geometry 1
Uploaded by
Lemuel TeopeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analytic Geometry 1
Uploaded by
Lemuel TeopeCopyright:
Available Formats
Civil Engineering November 2021 Review Innovations Analytic Geometry 1
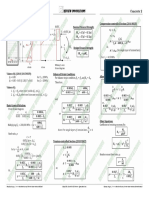
Distance Between Two Points: 𝑦2 − 𝑦1 Distance between Parallel Lines:
𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒: 𝑚 =
𝑥2 − 𝑥1
Given: P1(x1,y1) & P2(x2,y2) 𝐶1 − 𝐶2
𝑑=| |
D. Two-Intercept Form: ±√𝐴2 + 𝐵2
Then, 𝑃1 𝑃2 = √(𝑥2 − 𝑥1 )2 + (𝑦2 − 𝑦1 )2 Given: a = x intercept
b = y intercept Angle Between Two Lines:
Midpoint Formula: Then, L2
𝑥 𝑦
+ =1 L1 𝑚2 − 𝑚1
𝑎 𝑏 θ 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝜃 =
If M(xm, ym) is the midpoint of P1P2, then, 1 + 𝑚2 𝑚1
𝑥1 +𝑥2 𝑦1 +𝑦2 β
𝑥𝑚 = ; 𝑦𝑚 = E. General Form: 𝑚1 − 𝑚2
2 2 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝛽 =
𝐴𝑥 + 𝐵𝑦 + 𝐶 = 0 Note: m = 1 + 𝑚1 𝑚2
Division of a Line Segment: -A/B
P2(x2, y2) Parallel Lines: Two lines, L1& L2, are parallel if: Area of Triangle:
𝑃1 𝑃 𝑚
𝐼𝑓 = , 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛 m1 = m2
n 𝑃𝑃2 𝑛
A(x1, y1)
P (x, y)
𝑚𝑥2 + 𝑛𝑥1 Perpendicular Lines: Two lines, L1& L2, are
𝑥=
m 𝑚+𝑛 perpendicular if
B(x2, y2) C(x3, y3)
𝑚𝑦2 + 𝑛𝑦1 m1 m2 = -1 or m1 = -1/m2
P1(x1, y1) 𝑦=
𝑚+𝑛
1 𝑥1 𝑥2 𝑥3 𝑥1
Equation of a Line: Distance Between Point & Line: 𝐴= { }
2 𝑦1 𝑦2 𝑦3 𝑦1
A. Point-Slope Form • P1(x1, y1) 1 (𝑥 𝑦 + 𝑥2 𝑦3 + 𝑥3 𝑦1 )
Given: m = slope and a point P1(x1,y1)
𝐴= [ 1 2 ]
d 𝐴𝑥1 + 𝐵𝑦1 + 𝐶 2 − (𝑦1 𝑥2 + 𝑦2 𝑥3 + 𝑦3 𝑥1 )
Then, 𝑦 − 𝑦1 = 𝑚(𝑥 − 𝑥1 ) 𝑑=
±√𝐴2 + 𝐵2
B. Slope-Intercept Form L: Ax + By + C = 0 Centroid of Triangle:
Given: m = slope
b = y-intercept Use + if the point is above the line provided B is 𝑥1 + 𝑥2 + 𝑥3 𝑦1 + 𝑦2 + 𝑦3
𝑥̅ = ; 𝑦̅ =
Then, 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑏 positive; use – if the point is below the line provided 3 3
B is positive. L: 4x – 3y – 6 = 0
C. Two-Point Form Ex: L: 4x + 3y – 6 = 0 Point above → -
Given: P1(x1,y1) & P2(x2,y2) Point above → + Point below → +
Then, Point below → -
𝑦 − 𝑦1 𝑦2 − 𝑦1
=
𝑥 − 𝑥1 𝑥2 − 𝑥1
Manila FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
(02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
Civil Engineering November 2021 Review Innovations Analytic Geometry 1
The Circle: 3. Given the triangle with vertices at A(9, 6), B(1, 4) Problems for Practice:
y and C(7, 2). Find: 1. Find the coordinates of the point which is 3/8 of
a. the equation of the line through (0, -3) and the way from the point A(-1, 3) to the point B(4, -2).
P(x,y) parallel to BC, and Answer: (7/8, 9/8)
b. the equation of the perpendicular bisector of 2. Find the equation of the line passing through the
r side AC. point A(2, -3) and perpendicular to the line having
C(h,k) the parametric equations:
4. Find the coordinates of the point which is 3/8 of 5x = 3t + 4 and 3y = 4t – 6
O(0,0) the way from the point A(-1, 3) to the point B(4, -2). Answer: 9x + 20y + 42 = 0
x
3. Determine the equations of the lines (two
A locus of a point which moves at a constant 5. The equation of the Euler’s line of triangle ABC answers) passing through (-2, 4) and forming with
distance from a fixed point called center and the is 51x – 71y – 122 = 0. The vertices of the triangle the axes a triangle having an area of 9 square units.
constant distance of any point from the center is are: A(-2, 3), B(1, -7) and C(x, 1). Locate the Answers: x + 2y = 6 and 8x + y = -12
called the radius. triangle’s orthocenter. 4. Find the farthest distance from the point (12, 2) to
Center at C (h, k): the circle x2 + y2 + 6x – 16y + 24 = 0.
(𝑥 − ℎ)2 + (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 𝑟 2 Sample Problems (CIRCLES) Answer: 23.16 units
Center at O (0, 0): 6. Find the equation of the circle having its center 5. The two points on the line 2x + 3y + 4 = 0 which
𝑥 2 + 𝑦2 = 𝑟2 on the line 4x – y = 7 and passing through the points are at distance 2 from the line 3x + 4y – 6 = 0
General Form: (-2, 4) and (5, 5). Answer: (64, - 44) and (4, -4)
𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 + 𝐷𝑥 + 𝐸𝑦 + 𝐹 = 0 6. A line has an equation of x + 5y + 5 = 0. Find the
7. Find the equation of the circle a diameter of equation of the line through (3, 1) that makes an
*Center(h,k): h = -D/2 k = -E/2 which is the line segment connecting the centers of angle of 450 clockwise from the line that is
the following circles: perpendicular to the line x + 5y + 5 = 0 at that point.
RADICAL AXIS - is always perpendicular to the x2 + y2 + 2x + 2y – 7 = 0 and
Answer: 2x – 3y = 3
line joining the centers of the given circles. x2 + y2 - 4x + 8y – 5 = 0
7. Find the equation of the circle circumscribing the
RADICAL CENTER - is the point of intersection of triangle with vertices at A(-1, -4), B(3, -2) and C(5,
8. Find an equation(s) of the circle(s) tangent to both
radical axes. 2).
axes and containing the point (-8, -1).
Answer: (x + 2)2 + (y – 3)2 = 50
8. Determine the length of the tangent to the circle
9. Find the radical center of the following circles:
Sample Problems (LINES) x2 + y2 – 4x – 5 = 0 from (8, -2).
x2 + y2 - 4x + 2y – 1 = 0
1. Find the abscissa of a point whose ordinate is 5 if Answer: 5.57 units
x2 + y2 + 2x + 4y + 1 = 0
this point is collinear with points A(1, -2) and B(4, x2 + y2 - 6x - 4y + 9 = 0
2).
2. Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are at
A(2, -5), B(6, 2) and C(4, 1). Locate the point of
intersection of its medians.
Manila FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
(02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
You might also like
- A Manual of Machine Drawing and Design - David Allan Low, Alfred William BevisDocument416 pagesA Manual of Machine Drawing and Design - David Allan Low, Alfred William Bevismrafiq9002100% (1)
- Steel Design 5 Nov 2021Document3 pagesSteel Design 5 Nov 2021Lemuel Teope100% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Column DesignThe following provides a concise title for the given document:DOCUMENT REINFORCED CONCRETE COLUMN DESIGN PRINCIPLESDocument26 pagesReinforced Concrete Column DesignThe following provides a concise title for the given document:DOCUMENT REINFORCED CONCRETE COLUMN DESIGN PRINCIPLESJohn Cedric GarganeraNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Column DesignThe following provides a concise title for the given document:DOCUMENT REINFORCED CONCRETE COLUMN DESIGN PRINCIPLESDocument26 pagesReinforced Concrete Column DesignThe following provides a concise title for the given document:DOCUMENT REINFORCED CONCRETE COLUMN DESIGN PRINCIPLESJohn Cedric GarganeraNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math Exam Review - CirclesDocument16 pagesGrade 9 Math Exam Review - Circlesazetinasjc100% (1)
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Hydraulics - Set 8Document3 pagesCE Board Nov 2021 - Hydraulics - Set 8Lemuel Teope100% (1)
- Handouts - Differential Equation and Advanced MathematicsDocument7 pagesHandouts - Differential Equation and Advanced MathematicsLexter QuitaraNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Hydraulics - Set 6Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2021 - Hydraulics - Set 6Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Workbench TutorialDocument25 pagesANSYS Workbench TutorialRitesh Sharma60% (5)
- Lines & AnglesDocument15 pagesLines & AnglesSMK100% (1)
- Analytic Geometry 1Document2 pagesAnalytic Geometry 1Wayne VillarozaNo ratings yet
- SFTY 100 - Questions With AnswersDocument5 pagesSFTY 100 - Questions With AnswersLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Solutions of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument12 pagesLesson 3: Solutions of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering November 2021 Review Innovations Concrete 4 AnalysisDocument3 pagesCivil Engineering November 2021 Review Innovations Concrete 4 AnalysisLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- CE Board Problems in SurveyingDocument13 pagesCE Board Problems in SurveyingHomer Batalao33% (9)
- Sunday Problems - Week 1 Refresher Course For May 2020 Ce Board ExamDocument4 pagesSunday Problems - Week 1 Refresher Course For May 2020 Ce Board ExamJerome YangaNo ratings yet
- Review Innovations Measures of Central Tendency FRACTILES: Percentiles, Deciles, and QuartilesDocument1 pageReview Innovations Measures of Central Tendency FRACTILES: Percentiles, Deciles, and QuartilesLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 3Document2 pagesAnalytic Geometry 3Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Review Module 22 Geotechnical Engineering 3 Part 2Document2 pagesReview Module 22 Geotechnical Engineering 3 Part 2John Andre MarianoNo ratings yet
- Alejandro 6 MsteDocument2 pagesAlejandro 6 MsteBack UpNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering May 2022 Review Analyzes Hyperbolas and Conic SectionsDocument2 pagesCivil Engineering May 2022 Review Analyzes Hyperbolas and Conic SectionsEd Vincent PabloNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry review module with applications problemsDocument1 pageTrigonometry review module with applications problemsYeddaMIlaganNo ratings yet
- Eval Exam 1Document3 pagesEval Exam 1Krisia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Review Module 1 Algebra 1 Combined Part 1 and Part 2Document2 pagesReview Module 1 Algebra 1 Combined Part 1 and Part 2Esmeralda RapingNo ratings yet
- 10 5 13 Surveying Refresher Module 1Document2 pages10 5 13 Surveying Refresher Module 1Walter CatapangNo ratings yet
- Mste 5Document4 pagesMste 5Lynea AlbaytarNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 36 Nov 2021Document2 pagesRefresher Module 36 Nov 2021Joshua Lacaña SaltivanNo ratings yet
- Refresher MODULE - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsDocument1 pageRefresher MODULE - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsMacatangay MhorienNo ratings yet
- PDF Advanced Math (Refresher) PDFDocument51 pagesPDF Advanced Math (Refresher) PDFDivine Joy Atractivo PinedaNo ratings yet
- Review Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Document2 pagesReview Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Mark Daren Patrona RamonNo ratings yet
- Review Module: - Analytic GeometryDocument2 pagesReview Module: - Analytic GeometryChristian Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 3Document2 pagesHydraulics 3IZNo ratings yet
- Review Module 3 Trigonometry Part 1Document1 pageReview Module 3 Trigonometry Part 1KrishaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Nov Algebra 3 PDFDocument1 page2020 Nov Algebra 3 PDFJoshua CalaNo ratings yet
- Math Terms 2 RefresherDocument3 pagesMath Terms 2 Refreshercat buenafeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy Problems on Simple and Compound Interest, Annuities, Uniform and Geometric GradientsDocument2 pagesEngineering Economy Problems on Simple and Compound Interest, Annuities, Uniform and Geometric GradientsKrisia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Math Terms 1 RefresherDocument4 pagesMath Terms 1 Refreshercat buenafeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy Module Problems SolutionsDocument2 pagesEngineering Economy Module Problems Solutionscat buenafeNo ratings yet
- 10 5 13 SURVEYING Refresher Module 1Document2 pages10 5 13 SURVEYING Refresher Module 1Jan Chris VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- GERTC Review November 2021 Geometry F2F Week 7: Prepared By: Engr. Jobert S. de La Cruz, CeDocument1 pageGERTC Review November 2021 Geometry F2F Week 7: Prepared By: Engr. Jobert S. de La Cruz, CeLee Ann CabuquinNo ratings yet
- Algebra Set 1Document2 pagesAlgebra Set 1Albert PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Review Module - Structural Engineering: Rass TeelDocument2 pagesReview Module - Structural Engineering: Rass TeelJohn andre Mariano100% (1)
- Final PreboardDocument2 pagesFinal PreboardKrisia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Techniques To Solve: - WorkDocument9 pagesTechniques To Solve: - Workarianne denice100% (1)
- STRUCTURAL TERMS REVIEWDocument6 pagesSTRUCTURAL TERMS REVIEWgarhgelhNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Nov 2020 Review Innovations Structural Analysis 2 Double Integration MethodDocument1 pageCivil Engineering Nov 2020 Review Innovations Structural Analysis 2 Double Integration MethodEugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 13 Nov 2021Document1 pageRefresher Module 13 Nov 2021JaydeeLove AlconeraNo ratings yet
- Hyd 13Document2 pagesHyd 13Jocelyn CabarlesNo ratings yet
- REVIEW INNOVATIONS NOVEMBER 2022 CE BOARD EXAM REFRESHERDocument2 pagesREVIEW INNOVATIONS NOVEMBER 2022 CE BOARD EXAM REFRESHERAlliah Mae OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Eval Exam 4 Review Nov 2021Document5 pagesEval Exam 4 Review Nov 2021Iris FloresNo ratings yet
- Review Module: - Hydraulics 4Document2 pagesReview Module: - Hydraulics 4YeddaMIlaganNo ratings yet
- Right Triangle Trigonometry LessonDocument13 pagesRight Triangle Trigonometry LessonDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- Excel Review Center FB 10 - GEAS Practice Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesExcel Review Center FB 10 - GEAS Practice Exam QuestionsKei DeeNo ratings yet
- Practical Question in Design and Construction - Set 2 - 08 April 2022Document1 pagePractical Question in Design and Construction - Set 2 - 08 April 2022Abubakar SalikNo ratings yet
- Kippap CE Final Coaching 6 Presentation Marjes-1Document28 pagesKippap CE Final Coaching 6 Presentation Marjes-1Jae HanNo ratings yet
- Reinforced concrete beam design reviewDocument2 pagesReinforced concrete beam design reviewDale MalazzabNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Retaining Wall ProblemsDocument1 pageReinforced Concrete Retaining Wall ProblemsDale MalazzabNo ratings yet
- Alejandro 3 MsteDocument2 pagesAlejandro 3 MsteBack UpNo ratings yet
- Part1 06Document2 pagesPart1 06aliscribd46No ratings yet
- Civil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Concrete 2 Flexural MembersDocument2 pagesCivil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Concrete 2 Flexural MembersDale MalazzabNo ratings yet
- Rendon 1Document2 pagesRendon 1ryanNo ratings yet
- Math Practice Problems Part 2 2018Document4 pagesMath Practice Problems Part 2 2018Rommel RaferNo ratings yet
- 1.0-Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics CompletedDocument18 pages1.0-Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics Completedwaleed AlkaseriNo ratings yet
- HAU CorrelDocument3 pagesHAU CorrelCarlo Magno Olano Jr100% (1)
- Review Module - STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING (Stress-Strain)Document2 pagesReview Module - STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING (Stress-Strain)John andre MarianoNo ratings yet
- Eng Eco Set 2Document2 pagesEng Eco Set 2Krisia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lesson notes for weeks 1 and 2Document30 pagesLesson notes for weeks 1 and 2wisdomonuoha867No ratings yet
- Act Math Formulas Interactive 1Document2 pagesAct Math Formulas Interactive 1Isley Quintine YutucNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (YDocument12 pagesMathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (Yvzimak2355No ratings yet
- III Applications of DerivativesDocument21 pagesIII Applications of DerivativesHyacinth FarinasNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concepts of Analytic GeometryDocument11 pagesFundamental Concepts of Analytic GeometryShela RamosNo ratings yet
- Review - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringDocument6 pagesReview - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringJustine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Questions With Answers G3Document2 pagesQuestions With Answers G3Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- OSH Standards 2017Document422 pagesOSH Standards 2017Kap LackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- HW EssayDocument1 pageHW EssayLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Phy12 Exit Exam ReviewDocument9 pagesPhy12 Exit Exam ReviewAngelo Joshua De LeonNo ratings yet
- Physics Exit 8Document2 pagesPhysics Exit 8Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To EstimatingDocument13 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To EstimatingLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula (Basic)Document12 pagesPhysics Formula (Basic)GaiusChrisA.EvaNo ratings yet
- Physics Exit 9Document3 pagesPhysics Exit 9Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Plane Geometry: CE Correlation 1Document16 pagesPlane Geometry: CE Correlation 1Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 2 SolutionDocument5 pagesCE Board Nov 2021 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 2 SolutionLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Wednesday, 25 November 2020 9:01 AMDocument20 pagesAlgebra: Wednesday, 25 November 2020 9:01 AMLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Solid Geometry 2Q2021Document31 pagesSolid Geometry 2Q2021Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Graph of Trigo Functions by Engr. JuneDocument6 pagesGraph of Trigo Functions by Engr. JuneLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- SMAT4a - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument6 pagesSMAT4a - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- SMAT4b - Simple StrainDocument4 pagesSMAT4b - Simple StrainLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- SMAT1 - Simple Stress - 2 PDFDocument9 pagesSMAT1 - Simple Stress - 2 PDFLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Example 11 - One-Way Slab & SW InstructionsDocument9 pagesExample 11 - One-Way Slab & SW InstructionsLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Shear Stress and Bearing Stress ExamplesDocument7 pagesShear Stress and Bearing Stress ExamplesLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Maths LL PracticalsDocument14 pagesMaths LL PracticalsHemantkumar GosaviNo ratings yet
- 5.conic Section (English)Document67 pages5.conic Section (English)Shival KatheNo ratings yet
- Std06 Maths EMDocument223 pagesStd06 Maths EMrajiniNo ratings yet
- Definition of Symmetry and Line of SymmetryDocument3 pagesDefinition of Symmetry and Line of SymmetryJasvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- ISOMETRIC DRAWING CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONSDocument32 pagesISOMETRIC DRAWING CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONSNajed SallehNo ratings yet
- Philippine Grade 7 Summative Math TestDocument6 pagesPhilippine Grade 7 Summative Math TestMonicLizaBergonioNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS FUNDAMENTALS REVIEWDocument102 pagesMATHEMATICS FUNDAMENTALS REVIEWFghhNo ratings yet
- Geometry Basics: Concepts You Must Know!Document25 pagesGeometry Basics: Concepts You Must Know!Muhammad Waseem AbbasNo ratings yet
- 9th Maths 2 Digest (ByRobert)Document124 pages9th Maths 2 Digest (ByRobert)Krishna NikamNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 09 Geometry ConceptsDocument20 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 09 Geometry ConceptsPrimoNo ratings yet
- Vertical Learning Progression Map for Mathematics Geometry Strands Across Grade LevelsDocument2 pagesVertical Learning Progression Map for Mathematics Geometry Strands Across Grade LevelsReyboy TagsipNo ratings yet
- LOCI IN TWO DIMENSION Form2Document10 pagesLOCI IN TWO DIMENSION Form2Rosmah Abdullah100% (16)
- UKMT - BMO Round 1 - British Mathematical Olympiad 2021 - ReportDocument15 pagesUKMT - BMO Round 1 - British Mathematical Olympiad 2021 - ReportArsh TewariNo ratings yet
- Math Vii Learners Material Module 4 - Algebra Quarter 4Document54 pagesMath Vii Learners Material Module 4 - Algebra Quarter 4sualeperaltajhNo ratings yet
- 312SM 31203 02 Parabola 2222Document19 pages312SM 31203 02 Parabola 2222Anonymous kY9YQYNED8No ratings yet
- Project On Properties and Application of Parabola and EllipseDocument9 pagesProject On Properties and Application of Parabola and Ellipse(11-A) SUMIT SINGH (5194)100% (3)
- Transformations Unit PlanDocument27 pagesTransformations Unit Planerdawati nurdinNo ratings yet
- XII - Maths - CirclesDocument12 pagesXII - Maths - CirclesNaveen GargNo ratings yet
- Yield Line Analysis For Slabs: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurDocument31 pagesYield Line Analysis For Slabs: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurkvrgmsNo ratings yet
- Course Outline MMWDocument3 pagesCourse Outline MMWSRANo ratings yet
- Math 9-Summative Week 1-4 With KeyDocument3 pagesMath 9-Summative Week 1-4 With KeyPedro LeycoNo ratings yet
- Math concepts and skillsDocument2 pagesMath concepts and skillsNANCITA O. PERLASNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 10- Circle Objective QuestionsDocument28 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 10- Circle Objective QuestionsAdhi AdhiNo ratings yet
- RegshDocument3 pagesRegshWorse To Worst Satittamajitra0% (1)
- CONSTRUCTDocument30 pagesCONSTRUCTPhoebe Imee ThomasNo ratings yet