Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Civil Engineering Nov 2020 Review Innovations Structural Analysis 2 Double Integration Method
Uploaded by
Eugenio Genesis AbadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Civil Engineering Nov 2020 Review Innovations Structural Analysis 2 Double Integration Method
Uploaded by
Eugenio Genesis AbadCopyright:
Available Formats
Civil Engineering Nov 2020 Review Innovations Structural Analysis 2
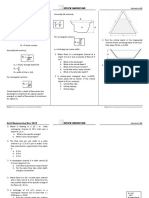
DOUBLE INTEGRATION METHOD Basic Principles 300 N/m
From flexure From Calculus, 1. The resultant bending moment at any section
1 M 1 y" caused by any load system is the algebraic sum of
= = the bending moments at that section caused by
EI [1 + (y')2 ]3/2
each load acting separately. 2m 2m
For beams, y’ is very small and (y’)2 → 0 2. The moment effect of any single specified loading R1 R2
M y" is always some variation of the general equation 1. the rotation at the right support.
= y = kxn.
EI 13/2 2. the deflection at midspan
Hence, x x
EI y " = M Note: Situation 3. (For Practice) A 5 m simply supported
M = -Mo w
y’ = slope of beam L M = -wx2/2 beam is loaded with a 200 kN-m concentrated
EI y ' = Mdx + C1 y = beam deflection Mo
b=L
L
moment placed 3.5m from the left support. The
b=L
h = -Mo
flexural rigidity of the beam is EI. If the distance
EI y = (Mdx)dx + C1 x + C2 1 2
h = -wL2/2
Area = bh x = b/2 x is measured from the left support.
Area = bh/3 x = L/4
1. Determine the equation of the slope.
x
AREA MOMENT METHOD P x
w 2. Determine the equation of the deflection
Theorems of Area Moment Method M = -Px M = -wx3/6L curve.
L L
Theorem 1: The change in slope between tangents
b=L b=L
drawn to the elastic curve at any two points A and B h = -PL h = -wL2/6 Situation 4. For the beam loaded and supported as
1 3
is equal to the product 1/EI multiplied by the area of Area = bh/2 x = L/3
shown, determine:
Area = bh/4 x = L/5
the moment diagram between these two points. 1. the rotation at the left support.
1 2. the deflection at midspan
AB = (Area)AB PROBLEMS
EI 600 N/m
1. For the beam loaded and supported as shown,
A B A B draw the moment diagram by parts at point B.
AB (+) tB/A (+)
16 kN/m
AB (-) tB/A (-) 1m 3m 2m
8 kN-m
A B B
A C R1 R2
A
B w
3m kN/
2
Theorem 2: The deviation at any point B relative to a
tangent drawn to the elastic curve at any other point m
A, in direction perpendicular to the original position Situation 1. A 6 m simply supported beam is loaded
of the beam, is equal to the product of 1/EI multiplied with a 24 kN concentrated load placed 3.5m from
by the moment of area about B of that part of the the left support. Determine:
moment diagram between points A & B. 1. the slope of the tangent at the left support.
2. the rotation at the right support.
1
t B/ A = (Area) AB xB 3. the deflection under the load.
EI 4. the maximum deflection of the beam.
MOMENT DIAGRAM BY PARTS Situation 2. (For Practice) For the beam loaded and
A method of dividing moment diagrams into parts supported as shown, determine:
whose areas and centroids are known.
Manila: https://www.facebook.com/ReviewInnovationsOfficial Cebu FB: Excel-RI CE Review Specialist Inc. Davao: https://www.facebook.com/reviewinnovations.davaobranch
You might also like
- p94-1738 Instrumentation t2000Document6 pagesp94-1738 Instrumentation t2000AaronNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument468 pagesFundamentals of Reinforced Concrete DesignZamir Mear93% (115)
- Plumbing Engineering Design Handbook - Vol 2 (2004)Document400 pagesPlumbing Engineering Design Handbook - Vol 2 (2004)Juan Carlos Mendez100% (6)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- HUD Settlement Statement - 221-1993Document4 pagesHUD Settlement Statement - 221-1993Paul GombergNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 1 PDFDocument3 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 1 PDFKristan Rae Gaetos0% (1)
- NCLEX Cram Sheet: Essential Nursing Exam Facts in <40 CharactersDocument12 pagesNCLEX Cram Sheet: Essential Nursing Exam Facts in <40 CharactersSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Year 12 - Chemistry PDFDocument108 pagesYear 12 - Chemistry PDFWill Nguyen100% (2)
- SEAFARERSDocument29 pagesSEAFARERSJohanna Arnaez100% (1)
- CE Board Nov 2020 Strength of Materials Set 1Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 Strength of Materials Set 1Eugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- Measures of Position - Calculating Quartiles Using Different MethodsDocument6 pagesMeasures of Position - Calculating Quartiles Using Different Methodssergio paulo esguerraNo ratings yet
- User Guide Varicent IcmDocument380 pagesUser Guide Varicent IcmSharad Sharma100% (3)
- Tape CorrectionsDocument82 pagesTape CorrectionsCedric Pita100% (1)
- Reading Assignment: P. 45-72 (4 Ed.) p.45-75 (Previous Ed.) in Mannering TextbookDocument26 pagesReading Assignment: P. 45-72 (4 Ed.) p.45-75 (Previous Ed.) in Mannering TextbookMohamed Imbarek EsekbiNo ratings yet
- PDF Ce Board Problems in SurveyingDocument16 pagesPDF Ce Board Problems in SurveyingBilagantol, Joriz Allen C.100% (1)
- Deflections: The Moment-Area Method Theorem 1Document24 pagesDeflections: The Moment-Area Method Theorem 1OrangeIsLemon100% (1)
- PDF Probability (Refresher) PDFDocument46 pagesPDF Probability (Refresher) PDFDivine Joy Atractivo PinedaNo ratings yet
- Past Board Objective Questions MsteDocument6 pagesPast Board Objective Questions MsteFely Joy Relatores100% (1)
- Eval 2 November 2022 Batch 1 WDDocument6 pagesEval 2 November 2022 Batch 1 WDMhiaBuenafeNo ratings yet
- Team Leader WorkbookDocument171 pagesTeam Leader Workbooktousah2010No ratings yet
- Weld Cleaning MethodsDocument7 pagesWeld Cleaning MethodsTrần Thùy LinhNo ratings yet
- 603 Quiz 5Document2 pages603 Quiz 5Cj SuarezNo ratings yet
- Techniques To Solve: - WorkDocument9 pagesTechniques To Solve: - Workarianne denice100% (1)
- STRUCTURAL TERMS REVIEWDocument6 pagesSTRUCTURAL TERMS REVIEWgarhgelhNo ratings yet
- GERTC Review November 2021 Geometry F2F Week 7: Prepared By: Engr. Jobert S. de La Cruz, CeDocument1 pageGERTC Review November 2021 Geometry F2F Week 7: Prepared By: Engr. Jobert S. de La Cruz, CeLee Ann CabuquinNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures: To Solve For Arbitrary ConstantsDocument3 pagesTheory of Structures: To Solve For Arbitrary ConstantsRj KapunanNo ratings yet
- HAU CorrelDocument3 pagesHAU CorrelCarlo Magno Olano Jr100% (1)
- Assessment Examination 01 1Document2 pagesAssessment Examination 01 1Jet JavierNo ratings yet
- Hyd 13Document2 pagesHyd 13Jocelyn CabarlesNo ratings yet
- Referece Steel DataDocument8 pagesReferece Steel DataS.M. FOYSALNo ratings yet
- Sec - PS1Document2 pagesSec - PS1Monica Amor AbengozaNo ratings yet
- REVIEW INNOVATIONS NOVEMBER 2022 CE BOARD EXAM REFRESHERDocument2 pagesREVIEW INNOVATIONS NOVEMBER 2022 CE BOARD EXAM REFRESHERAlliah Mae OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Refresher - Structural Design Ang ConstructionDocument3 pagesRefresher - Structural Design Ang Constructionmichael SonuganNo ratings yet
- Refresher MODULE - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsDocument1 pageRefresher MODULE - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsMacatangay MhorienNo ratings yet
- Structural Soln Nov 2018 PDFDocument19 pagesStructural Soln Nov 2018 PDFrey martiNo ratings yet
- 1.0-Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics CompletedDocument18 pages1.0-Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics Completedwaleed AlkaseriNo ratings yet
- Review Module - STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING (Stress-Strain)Document2 pagesReview Module - STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING (Stress-Strain)John andre MarianoNo ratings yet
- Nov23 Math 02 07 Nov 2023Document27 pagesNov23 Math 02 07 Nov 2023Jayson MariNo ratings yet
- Set Q# B A 16 16 Question Sequence of numbersDocument40 pagesSet Q# B A 16 16 Question Sequence of numberschnxyeyed14No ratings yet
- Review Module 21 Geotechnical Engineering 2 Part 1Document2 pagesReview Module 21 Geotechnical Engineering 2 Part 1Jet JavierNo ratings yet
- Hyd Ref 7Document2 pagesHyd Ref 7emielyn lafortezaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Board Part 1Document20 pages2018 Board Part 1Ira MejiaNo ratings yet
- Review Module 1 Algebra 1 Combined Part 1 and Part 2Document2 pagesReview Module 1 Algebra 1 Combined Part 1 and Part 2Esmeralda RapingNo ratings yet
- Part1 06Document2 pagesPart1 06aliscribd46No ratings yet
- Alejandro 1 - Refresher MATH PDFDocument2 pagesAlejandro 1 - Refresher MATH PDFAlliah Mae OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Review Module - Structural Engineering: Rass TeelDocument2 pagesReview Module - Structural Engineering: Rass TeelJohn andre Mariano100% (1)
- Diagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Document4 pagesDiagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Yoshjordan LambNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 9 LectureDocument5 pagesProblem Set 9 LectureAraiza FloresNo ratings yet
- Concrete Beam AnalysisDocument1 pageConcrete Beam AnalysisDale MalazzabNo ratings yet
- CE Refresher Nov 2022 - Tuzon - Set 7 F2FDocument2 pagesCE Refresher Nov 2022 - Tuzon - Set 7 F2Femielyn lafortezaNo ratings yet
- Excel Review Center FB 10 - GEAS Practice Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesExcel Review Center FB 10 - GEAS Practice Exam QuestionsKei DeeNo ratings yet
- Math Terms 1 RefresherDocument4 pagesMath Terms 1 Refreshercat buenafeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy Module Problems SolutionsDocument2 pagesEngineering Economy Module Problems Solutionscat buenafeNo ratings yet
- Centroid and Moment of InertiaDocument12 pagesCentroid and Moment of Inertiarobertjohnsanchez4No ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Document3 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Eugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- Math Terms 2 RefresherDocument3 pagesMath Terms 2 Refreshercat buenafeNo ratings yet
- CE527 Correlation Course Structural Engi PDFDocument2 pagesCE527 Correlation Course Structural Engi PDFjunNo ratings yet
- REVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAM REVIEWDocument3 pagesREVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAM REVIEWKian InductivoNo ratings yet
- Alejandro 4 MsteDocument2 pagesAlejandro 4 MsteMyra ComiaNo ratings yet
- Strength 4 May 2021Document3 pagesStrength 4 May 2021Jon SnowNo ratings yet
- Review Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Document2 pagesReview Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Mark Daren Patrona RamonNo ratings yet
- Right Triangle Trigonometry LessonDocument13 pagesRight Triangle Trigonometry LessonDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 23 M4 Data Analysis 1Document1 pageRefresher Module 23 M4 Data Analysis 1Esther Faith AbadNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 03 (M2) - Integral CalculusDocument1 pageRefresher Module 03 (M2) - Integral CalculusJessa Mae CabusNo ratings yet
- Esplana SteelDesign2Document1 pageEsplana SteelDesign2Naigell SolomonNo ratings yet
- Refresher MATH Part5Document2 pagesRefresher MATH Part5Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- Nov23 Hydraulics 01 06 Nov 2023Document16 pagesNov23 Hydraulics 01 06 Nov 2023Jayson Mari100% (1)
- Rendon 4 - Refresher HYDDocument2 pagesRendon 4 - Refresher HYDMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Excel Review Center - Manila Ece Review For October 2019 Board Exam Refresher Exam - ElecDocument4 pagesExcel Review Center - Manila Ece Review For October 2019 Board Exam Refresher Exam - ElecTintin DalatenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Strain Energy 2024Document39 pagesChapter 3 - Strain Energy 2024patriquembeleonokokoNo ratings yet
- CALCULATING BEAM SLOPES AND DEFLECTIONSDocument47 pagesCALCULATING BEAM SLOPES AND DEFLECTIONSMasithembe Tera DumezweniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document20 pagesChapter 5yousifNo ratings yet
- SSE Sub-Frame Analysisv1 - 07 - F1 - 20211109 - 2238 - 11Document1 pageSSE Sub-Frame Analysisv1 - 07 - F1 - 20211109 - 2238 - 11SES DESIGNNo ratings yet
- Sample ProblemsDocument3 pagesSample Problemsalagarg137691No ratings yet
- Deflection of Beams and Trusses 1Document9 pagesDeflection of Beams and Trusses 1nickxnickNo ratings yet
- GEOTECHNICAL AND HYDRAULICS ENGINEERING EVALUATION EXAMDocument2 pagesGEOTECHNICAL AND HYDRAULICS ENGINEERING EVALUATION EXAMArianna Denyse Gasgonia100% (1)
- Steel Design: Steel Connections - Bolted or Riveted ConnectionsDocument37 pagesSteel Design: Steel Connections - Bolted or Riveted ConnectionsEugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- Steel Design: Column and Other Compression MembersDocument14 pagesSteel Design: Column and Other Compression MembersEugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- Steel Design: Steel Connections - Welded ConnectionsDocument16 pagesSteel Design: Steel Connections - Welded ConnectionsEugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 1Document1 pageCE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 1Froilan Balumbago Monikas100% (2)
- Practical Plumbing Engineering Design Vol 4 2004 PDFDocument288 pagesPractical Plumbing Engineering Design Vol 4 2004 PDFmimahmoudNo ratings yet
- PI DesignDocument10 pagesPI DesignKarlNo ratings yet
- Stability of Structures Determinacy of Structures: Civil Engineering Nov 2020 Review Innovations Structural Analysis 1Document2 pagesStability of Structures Determinacy of Structures: Civil Engineering Nov 2020 Review Innovations Structural Analysis 1Eugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 Plane Trigonometry Set 1Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 Plane Trigonometry Set 1Eugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Document3 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Eugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- Traffic TermsDocument4 pagesTraffic TermsEugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- NRSG 5800 SyllabusDocument5 pagesNRSG 5800 Syllabusapi-310557802No ratings yet
- Coa - Resolution No. 2017-023 Dtd.12.21.2017 - Intosai Sai Qms Cert.Document2 pagesCoa - Resolution No. 2017-023 Dtd.12.21.2017 - Intosai Sai Qms Cert.Anie Guiling-Hadji GaffarNo ratings yet
- CUMINDocument17 pagesCUMIN19BFT Food TechnologyNo ratings yet
- CH 6 SandwichesDocument10 pagesCH 6 SandwichesKrishna ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- NTSE MAT Maharashtra 2011Document38 pagesNTSE MAT Maharashtra 2011Edward FieldNo ratings yet
- HAM Processing Technique for Ocular Surface ReconstructionDocument4 pagesHAM Processing Technique for Ocular Surface ReconstructionJoel JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Code: Final Exam in English: Grade 8Document7 pagesCode: Final Exam in English: Grade 8Luka EradzeNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet ToeicDocument2 pagesAnswer Sheet ToeicNgọc PhanNo ratings yet
- EZPC/SC FAQ Covers Installation and Use of Smart Card ReadersDocument7 pagesEZPC/SC FAQ Covers Installation and Use of Smart Card ReadersDjuroLjPosticNo ratings yet
- Man 040 0001Document42 pagesMan 040 0001arturo tuñoque effioNo ratings yet
- UEM Sol To Exerc Chap 097Document11 pagesUEM Sol To Exerc Chap 097sibieNo ratings yet
- Smoothed Bootstrap Nelson-Siegel Revisited June 2010Document38 pagesSmoothed Bootstrap Nelson-Siegel Revisited June 2010Jaime MaihuireNo ratings yet
- Principles of Synthetic BiologyDocument21 pagesPrinciples of Synthetic BiologyOpale PapaleNo ratings yet
- Macquarie Capital Cover LetterDocument1 pageMacquarie Capital Cover LetterDylan AdrianNo ratings yet
- PearsonDocument7 pagesPearsonJimmy M TaopanNo ratings yet
- Lovacka Kamera UputstvoDocument24 pagesLovacka Kamera UputstvoEmir MusijaNo ratings yet
- Veego Software Selected As One of Asia's 30 Best Tech CompaniesDocument3 pagesVeego Software Selected As One of Asia's 30 Best Tech CompaniesPR.comNo ratings yet
- Airworthiness StandardsDocument15 pagesAirworthiness StandardsJason RossNo ratings yet
- 9A01709 Advanced Structural Analysis PDFDocument8 pages9A01709 Advanced Structural Analysis PDFReddy Kiran KDNo ratings yet
- 6 1 Reducing Rational Expressions To Lowest TermsDocument21 pages6 1 Reducing Rational Expressions To Lowest Termsapi-233527181No ratings yet
- Garmin Etrex 30Document2 pagesGarmin Etrex 30Desli MunarsaNo ratings yet