Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Is The Optimal Choice For Many Reasons.: Fixatives
Uploaded by
bea gallardoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Is The Optimal Choice For Many Reasons.: Fixatives
Uploaded by
bea gallardoCopyright:
Available Formats
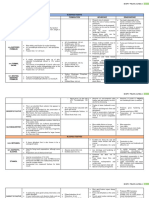
FIXATIVES
ALDEHYDES
FORM ALEDEHYDE 10% Formol Saline 10% Neutral Buffered Formol-Corrosive Alcoholic
(Formalin) Formalin (Formol-sublimate) Formalin(Gendre’s)
Fixative
× most widely × 40% saturated × is the optimal choice × recommended for × faster fixation
used Fixative is formaldehyde for many reasons. routine post- times
10% diluted with fast penetration mortem tissues × can be used
× pure stock 10%NaCl cheap & stable × penetrates small for rapid
available is 37- × Recommended prevents alterations pieces of tissues diagnosis ;
40%; for fixation of during processing rapidly fixes and
(Unsatisfactory central less shrinkage than × excellent for many dehydrates at
for routine nervous other fixatives staining the same time.
fixation: tissues and not osmotically active procedures × used to fix
should be general post × hardens tissue better including silver sputum, since
diluted to mortem × tissue can be stored in reticulin methods it coagulates
1:10 ratio ) tissues formalin indefinitely × cytological mucus.
× Formaldehyde × Fixation times: × fixative of choice for structures and × good for
= colorless 24 hrs at 35C Immunohistochemistry blood cells are well preservation of
gas commonly 48 hrs at 20- & molecular tests preserved glycogen and
obtained in 25C × Most widely used × No need of for micro-
histopathology solution for routine washing –out, can incineration
laboratory as a formalin fixation. be transfer directly technique.
37% to 40% × Has a pH of from fixative to × Disadvantage:
solution in approximately 6.8 and alcohol -gross
water. it is hypotonic in the hardening of
× Commercial × buffer ions present tissues
solutions are (approximately 165 -causes partial
37% to 40% mOsm). lysis of RBC
formaldehyde -preservation
but are of iron-containing
considered to pigments is poor
be 100%
formalin.
DISADVANTAGE: forms
mercuric chloride
deposits; doesn’t allow
frozen tissue sections
to be made; tissue
section should not be
more than 1cm thick
JAPOY ZARATE 4MT-1 1
FIXATIVES
GLUTARALDEHYDE
Made up of two formaldehyde residue
More stable effect on tissue especially on central nervous tissue
Preserves plasma CHON better
Produces less tissue shrinkage
Preserves cellular structures better; recommended for enzyme histochemistry and electron microscopy.
Less irritating to nose
Doesn’t cause dermatitis
DISADVANTAGES:
expensive and less stable
Reduces PAS positivity of reactive mucin
Specimen vial/container must be kept refrigerated during fixation
Solution may be changed several times during fixation by swirling
CHROMATE FIXATIVES
Potassium Dichromate REGAUD’S (MULLER’S) ORTH’S FLUID Chromic acid
FLUID
used in a 3% aqueous Recommended for Recommended for used in 1-2% aqueous
solution demonstration of study of early solution
Preserves lipid and chromatin, degenerative Precipitates all
mitochondria mitochondria, mitotic processes and tissue proteins and
figures, Golgi bodies, necrosis adequately preserves
RBC and colloid Demonstrates carbohydrates
containing tissue rickettsiae and other A strong oxidizing
bacteria agent
DISADVANTAGES: Disadvantages: DISADVANTAGE:
needs freshly same in Muller’s formaldehyde must
prepared be added to chrome-
does not preserve fats containing fixatives
prolonged fixation before use
blackens tissue
pigments
should be thoroughly
washed in running
water before
dehydration
Lead Fixatives
Used in 4% aqueous solution of basic lead acetate
Recommended for acid mucopolysaccharides
Fixes connective tissue mucin
JAPOY ZARATE 4MT-1 2
FIXATIVES
PICRIC ACID FIXATIVES
Normally used in strong saturated aqueous solution
Also dyes the tissues but the yellow color may be removed by treatment with another acid dye or lithium
carbonate
Preserves glycogen well but causes considerable tissue shrinkage
Allows brilliant staining with the Trichrome method
Disadvantages:
causes RBC hemolysis
reduces the amount of demonstrable ferric iron in tissue
not suitable for frozen sections
tissues must never washed in water before dehydration; must be first rendered insoluble by
direct immersion in 70% alcohol
interferes with azure eosin method of staining; should be washed thoroughly with alcohol
Alters and dissolves lipids
Highly explosive when dry; must be kept moist with distilled water or saturated alcohol during
storage
BOUIN’S SOLUTION BRASIL’S ALCOHOLIC PICROFORMOL FIXATIVE
Recommended for fixation of embryos and pituitary Excellent fixative for glycogen
biopsy
An excellent fixative for preserving soft and delicate
structures(e.g. Endometrial curettings)
Does not need “washing out”
Preserves glycogen
Preferred fixative for tissues to be stained by
MASSON’S TRICHOME for collagen, elastic and
connective tissue
Disadvantages: Disadvantage:
penetrates large tissues POORLY Utilizes 3-4 changes of Brasil’s fixative (30-2 hrs
soluble in water; needs to be directly transferred to each); succeeded directly by Absolute aclcohol
70% alcohol when using Automatich processing technique.
Glacial acetic acid
Precipitates chromosomes and chromatin material; very useful in study of NUCLEAR COMPONENTS OF THE CELL
Disadvantage:
contraindicated for cytoplasmic fixation; - destroys mitochondria and Golgi elements of cells.
ACETONE
it is used in fixing brain tissues for the diagnosis of rabies
Recommended for study of water diffusible enzymes especially phosphatases and lipases.
DISADVANTAGES:
dissolves fat and evaporates rapidly
JAPOY ZARATE 4MT-1 3
FIXATIVES
Alcohol fixatives
Used in concentrations ranging from 70-100%
Rapidly denatures and precipitates proteins
Used both as fixative and dehydrating agent
Excellent for glycogen preservation
Disadvantage:
if tissues left in alcohol too long will shrink; making it difficult to cut
METHYL ALCOHOL ISOPROPYL ETHYL ALCOHOL CARNOY’S FLUID NEWCOMER’S FLUID
100% ALCOHOL 95%
Excellent for Used for fixing Used at Recommended Recommended for
fixing dry and touch concentrations for fixing fixing
wet smears, preparations of 70-100% chromosomes, mucopolysaccharides
blood smears Lower lymph glands and nuclear protein
and bone concentration and urgent Acts both as nuclear
marrow causes RBC’s to biopsy. and histochemical
tissues. be hemolyzed Also used to fix fixative
Fixes and and WBC’s are brain tissue for
hydrates at inadequately the diagnosis of
the same time preserved. rabies.
Excellent
fixative for
glycogen
OSMIUM TETRAOXIDE
Preserves cytoplasmic structures well
Used extensively for neurological
Fixes myelin and peripheral nerves
Produces brilliant nuclear staning with safranin
Adequately fixes materials for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy
DISADVANTAGE:
very expensive, extremely volatile and inhibits hematoxylin(makes staining difficult)
FLEMING’S SOLUTION W/ACETIC ACID FLEMING’S SOLUTION W/O ACETIC ACID
most common chrome-osmium acetic acid fixative recommended for cytoplasmic structures,
excellent fixative for nuclear structure particularly mitochondria
Permanently fixes fat.
DISADVANTAGE:
very expensive, forms artefact(needs washing-out),
poor penetrating agent
JAPOY ZARATE 4MT-1 4
You might also like
- Types of Fixatives 1Document12 pagesTypes of Fixatives 1Vince Nicole MoraNo ratings yet
- Fixatives SummaryDocument5 pagesFixatives SummaryYza RysNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lecture Ver 2.0Document78 pagesHistopath Lecture Ver 2.0Caressa Marie EstradaNo ratings yet
- Fixative TableDocument11 pagesFixative TableNicole Kimberly Yu100% (1)
- OoDocument5 pagesOoKaden MikaelNo ratings yet
- HISTOPATH (Quizlet)Document4 pagesHISTOPATH (Quizlet)Allyssa AniNo ratings yet
- Aling Vicky MergedDocument62 pagesAling Vicky MergedFeilart FerrarisNo ratings yet
- Seminar 2 Bullet Notes # 1Document3 pagesSeminar 2 Bullet Notes # 1airareotutar16No ratings yet
- Histopathology MidtermDocument2 pagesHistopathology MidtermAncestral garmentsNo ratings yet
- FixationDocument5 pagesFixationMargalet Aguinaldo100% (1)
- Fixation: Quick Review Notes in Histopath - Fixation-Dehydration-Clearing-Infiltration-Embedding-DecalcificationDocument8 pagesFixation: Quick Review Notes in Histopath - Fixation-Dehydration-Clearing-Infiltration-Embedding-DecalcificationMaikka Lorraine Melchor DoriaNo ratings yet
- Histopathology MLS 304B UpdateDocument23 pagesHistopathology MLS 304B UpdateBarakat IsmailNo ratings yet
- Histopathology Techniques UnfinishedDocument8 pagesHistopathology Techniques UnfinishedGianna SablanNo ratings yet
- ALLNOTES HistoDocument29 pagesALLNOTES HistoEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Compre HistopatDocument21 pagesCompre HistopatMark FuerteNo ratings yet
- Precautions in Handling, Acceptance & Fixation of SpecimensDocument32 pagesPrecautions in Handling, Acceptance & Fixation of SpecimensMary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- FixationDocument11 pagesFixationMary Christelle100% (1)
- (A) Fixation (Notes)Document6 pages(A) Fixation (Notes)nd1706No ratings yet
- Week 8 (For Pre-Quiz Only)Document10 pagesWeek 8 (For Pre-Quiz Only)BEVERLY JANE LLUVERASNo ratings yet
- Killing and Fixing of Plant SpecimensDocument39 pagesKilling and Fixing of Plant SpecimensSWETA MOHANTY 2147619No ratings yet
- Routine Histotechniques Staining and NotDocument19 pagesRoutine Histotechniques Staining and Notamiitan63No ratings yet
- Lab Tech Solimullah Phase ADocument30 pagesLab Tech Solimullah Phase AAbdullah Yeamin PeyalNo ratings yet
- His To PathologyDocument5 pagesHis To PathologyBloody MarieNo ratings yet
- Fixation CompleteDocument30 pagesFixation CompleteFatimaMendozaNo ratings yet
- Types of FixativesDocument43 pagesTypes of FixativesAbubakar Dahiru Usman100% (1)
- Chemical Fixatives ContinuationDocument8 pagesChemical Fixatives ContinuationKenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- Hard TissuesDocument3 pagesHard TissuesKrizza UrmazaNo ratings yet
- Fixatives For HistopathologyDocument5 pagesFixatives For HistopathologyAlyssa PelayoNo ratings yet
- Histopath e Print NiDocument6 pagesHistopath e Print NiChian Marie Pearl C. TagayloNo ratings yet
- HistoPath Lesson 4Document23 pagesHistoPath Lesson 4Mary GNo ratings yet
- Histopath LectureDocument8 pagesHistopath LectureSandhya Narag SharmaNo ratings yet
- Metallic FixativesDocument7 pagesMetallic FixativesNelcy De Los SantosNo ratings yet
- Fixation of Histology SamplesDocument25 pagesFixation of Histology Sampleslalemchanie16No ratings yet
- Fixation of Tissues: NotesDocument8 pagesFixation of Tissues: NotesKhabab AliNo ratings yet
- Decalcification: Presented By: Madhura ShekatkarDocument45 pagesDecalcification: Presented By: Madhura ShekatkarMadhura ShekatkarNo ratings yet
- I. Aldehydes: Fixatives Advantages Disadvantages Formula Fixation Time Classifica TionDocument20 pagesI. Aldehydes: Fixatives Advantages Disadvantages Formula Fixation Time Classifica TionKaty RosNo ratings yet
- Mavm HistopathologyDocument41 pagesMavm HistopathologyVirna Grace MonteroNo ratings yet
- Act. 3 - Proper Fixation of Tissue SamplesDocument8 pagesAct. 3 - Proper Fixation of Tissue SamplesBSMLS TINGZNo ratings yet
- Histology Study Material - The Paraffin TechniqueDocument4 pagesHistology Study Material - The Paraffin TechniqueYumeeeeeyNo ratings yet
- PreservativeDocument4 pagesPreservativeHayyyNakuNeilNo ratings yet
- 7 Fixation1Document100 pages7 Fixation1Bhan MallareNo ratings yet
- HistotechDocument46 pagesHistotechviolaorsino100% (1)
- Congo RedDocument3 pagesCongo RedAnnicoldjohn LariozaNo ratings yet
- Histology 1Document5 pagesHistology 1raphaelNo ratings yet
- FixationDocument3 pagesFixationachelois sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Q 1. Describe The PAS Procedure To Show Glycogens in Liver?Document18 pagesQ 1. Describe The PAS Procedure To Show Glycogens in Liver?Parveen AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Q 1. Describe The PAS Procedure To Show Glycogens in Liver?Document18 pagesQ 1. Describe The PAS Procedure To Show Glycogens in Liver?Parveen AkhtarNo ratings yet
- HP DecalcificationDocument7 pagesHP DecalcificationMalliga SundareshanNo ratings yet
- Decal-Clear NotesDocument3 pagesDecal-Clear NotesbarbiegahibNo ratings yet
- HISTOPATHOLOGY NotesDocument3 pagesHISTOPATHOLOGY NotesAndrea Faye MONTERONANo ratings yet
- Tissue Processing: Marco R. Celio March 21, 2011Document51 pagesTissue Processing: Marco R. Celio March 21, 2011Yeron CedanNo ratings yet
- FixationDocument9 pagesFixationGail SantanderNo ratings yet
- Department of Pathology Gandhi Medical College, Bhopal: SeminarDocument25 pagesDepartment of Pathology Gandhi Medical College, Bhopal: SeminarAbhinav JunwalNo ratings yet
- Fixative SDocument6 pagesFixative SGerald John Paz100% (1)
- BiotechnologyDocument64 pagesBiotechnologyyashsharmaNo ratings yet
- FixativesDocument2 pagesFixativesAngelica BayonaNo ratings yet
- FixationDocument13 pagesFixationdeblackaNo ratings yet
- Practical - 2: Preparation of The FixativeDocument14 pagesPractical - 2: Preparation of The FixativeIseth ISethNo ratings yet
- Writing A Case Study: Quick Guide For StudentsDocument3 pagesWriting A Case Study: Quick Guide For StudentsManish AhujaNo ratings yet
- Avid Vocabulary Word BankDocument17 pagesAvid Vocabulary Word Bankapi-243081850No ratings yet
- Title Eight Crimes Against Persons: Article 246. ParricideDocument27 pagesTitle Eight Crimes Against Persons: Article 246. ParricideJeric RealNo ratings yet
- PWC Orgdna The Key To Unlocking Your Companys PotentialDocument1 pagePWC Orgdna The Key To Unlocking Your Companys PotentialMinh Nguyễn TrọngNo ratings yet
- Cma Inter MCQ Booklet Financial Accounting Paper 5Document175 pagesCma Inter MCQ Booklet Financial Accounting Paper 5DGGI BPL Group1No ratings yet
- Latch Lock and Mutex Contention TroubleshootingDocument20 pagesLatch Lock and Mutex Contention Troubleshootingvippy_love100% (1)
- Fish Oil Infographic FINALDocument2 pagesFish Oil Infographic FINALpierna casa casaNo ratings yet
- CO-CURRICULAR 6th SEMESTERDocument3 pagesCO-CURRICULAR 6th SEMESTERMasood RazaNo ratings yet
- PROM-12395-002 1114007 BRO QIAstat-Dx 0518 SPREAD WWDocument3 pagesPROM-12395-002 1114007 BRO QIAstat-Dx 0518 SPREAD WWTaty ElejaldeNo ratings yet
- مذكرات كافر مغربي PDF - PDFDocument1 pageمذكرات كافر مغربي PDF - PDFYassin MejNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Greece Sec 1Document32 pagesChapter 5 Greece Sec 1missseesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals IKS SyllabusDocument2 pagesFundamentals IKS Syllabuspurushotampandit1No ratings yet
- Johnny SinsDocument9 pagesJohnny SinsEmmanuel TalamNo ratings yet
- ESP Test 1 Part 1 AnswersDocument5 pagesESP Test 1 Part 1 Answerschemistry_mwuNo ratings yet
- Filosofi Pengakuan Dan Penghormatan Negara Terhadap Masyarakat Hukum Adat Di IndonesiaDocument13 pagesFilosofi Pengakuan Dan Penghormatan Negara Terhadap Masyarakat Hukum Adat Di Indonesialisken hNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Investment DecisionsDocument5 pagesLiterature Review On Investment Decisionsc5t0jsyn100% (1)
- Art Auction Malaysia 2010 (E-Catalogue) (Encrypted) PDFDocument77 pagesArt Auction Malaysia 2010 (E-Catalogue) (Encrypted) PDFRus HanaNo ratings yet
- Islcollective Worksheets Preintermediate A2 High School Reading Speaking Adjectives To Describe Personality and Characte 881191338542ea693560488 36713719Document2 pagesIslcollective Worksheets Preintermediate A2 High School Reading Speaking Adjectives To Describe Personality and Characte 881191338542ea693560488 36713719Citra Priski Abadi33% (9)
- Sobre Nicolás Gómez DávilaDocument4 pagesSobre Nicolás Gómez DávilaDiego GarridoNo ratings yet
- Prelim Task De-Vera Angela-KyleDocument6 pagesPrelim Task De-Vera Angela-KyleJohn Francis RosasNo ratings yet
- Refutation of Catherine Emerick and Padre PioDocument12 pagesRefutation of Catherine Emerick and Padre PioMarie Julianna BoweNo ratings yet
- SWOT ANALYSIS Dumaguin Ralph Justine B.Document3 pagesSWOT ANALYSIS Dumaguin Ralph Justine B.Edmarkmoises ValdezNo ratings yet
- Graham V Blissworld, LLCDocument16 pagesGraham V Blissworld, LLCcityfileNo ratings yet
- Click On 1 4 Leaflet PDFDocument88 pagesClick On 1 4 Leaflet PDFEseniya TishkinaNo ratings yet
- Silent MuslimDocument3 pagesSilent MuslimMohamed Dameer FahdNo ratings yet
- CPP MCQ - Control Flow Statements PDFDocument2 pagesCPP MCQ - Control Flow Statements PDFBlackk WorldzNo ratings yet
- Crim DigestDocument76 pagesCrim DigestBernice joyce OliverosNo ratings yet
- Jenova Chen - Flow in Games (And Everything Else) PDFDocument4 pagesJenova Chen - Flow in Games (And Everything Else) PDFKirakirakirakiraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of ZombiesDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ZombiesdsolisNo ratings yet
- 5.0 Problem Solving in MathDocument51 pages5.0 Problem Solving in MathRose Suba100% (3)