Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Truss & Frame Course Analysis
Uploaded by
Deb Lodh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views12 pagesThis document provides an introduction to prestressed concrete design. It discusses trusses and frames, including the definition of a truss, types of trusses, truss terminology, truss analysis methods, the definition of a frame, and frame analysis. It also outlines the course details, including the course number, title, teachers, and university.
Original Description:
ffgfgfgfg
Original Title
10-131202081341-phpapp01
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an introduction to prestressed concrete design. It discusses trusses and frames, including the definition of a truss, types of trusses, truss terminology, truss analysis methods, the definition of a frame, and frame analysis. It also outlines the course details, including the course number, title, teachers, and university.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views12 pagesTruss & Frame Course Analysis
Uploaded by
Deb LodhThis document provides an introduction to prestressed concrete design. It discusses trusses and frames, including the definition of a truss, types of trusses, truss terminology, truss analysis methods, the definition of a frame, and frame analysis. It also outlines the course details, including the course number, title, teachers, and university.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
TRUSS & FRAME
Course no-CE 416
course title- Prestress Concrete Design Sessinonal
Presented by Course Teachers
MD. Mohotasimur Rahman Munshi Galib Muktadir
ID NO. 10.01.03.040
&
Sabreena Nasrin
Lecturer of Civil Engineering Department
Ahsanullah University Of Science And Tecnology
Dhaka, Bangladesh
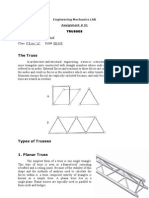
TRUSS - INTRODUCTION
A truss is a structure composed of members fastened
together in such a way to resist change in shape and it is
rigid structure.
Triangular unit
A truss is a structure comprising one or more
triangular units constructed with straight members
whose ends are connected at joints referred to as nodes.
Its purpose is to support a larger load or span a
greater distance than any individual member from
which the truss may be built
TRUSS – INTRODUCTION CONTINUE
Node External forces and reactions to those
forces are considered to act only at the
nodes.
Moments (torques) are explicitly
excluded because, and only because, all the
joints in a truss are treated as pin
joint or hinge joint .
Result in forces in the members which
Tie strut are either tensile or compressive forces.
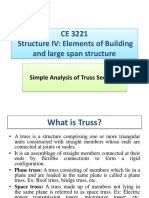
PLANE TRUSS VS SPACE TRUSS
Plane Truss Space Truss
All member of truss and applied load lie An elementary space truss consists of 6
in a same plane. members connected at 4 joints to form a
tetrahedron.
In a simple truss, m = 2n - 3 where m In a simple space truss, m = 3n - 6
is the total number of members and n is the where m is the number of members and n
number of joints. is the number of joints.
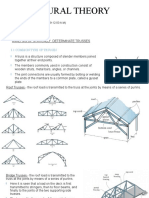
ROOF TRUSS TERMINOLOGY
ROOF TRUSS TYPE
BRIDGE TRUSS TERMINOLOGY
BRIDGE TRUSS TYPE
METHOD OF TRUSS ANALYSIS
Joint Method
Determine the Support Reaction.
Apply Fx = 0 and Fy = 0 to every node and
determine member force
Dismember the truss and create a free-body
diagram for each member and pin.
METHOD OF TRUSS ANALYSIS
Section method
Determine the Support Reaction.
To determine the force in member BD, pass a
section through the truss as shown and create a
free body diagram for the left side.
With only three members cut by the
section, the equations for static equilibrium may
be applied to determine the unknown member
forces, including FBD.
FRAME (INTRODUCTION)
Contain at least one multi-force
member, i.e., member acted upon by 3 or more
forces.
Frames are designed to support loads and are
usually stationary.
ANALYSIS OF FRAME
A free body diagram of the complete frame is
used to determine the external forces acting on
the frame.
Internal forces are determined by
dismembering the frame and creating free-body
diagrams for each component.
You might also like
- Beams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsFrom EverandBeams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- TRUSS & FRAME Course AnalysisDocument12 pagesTRUSS & FRAME Course AnalysisMir Mustafa AliNo ratings yet
- Truss AnalysisDocument11 pagesTruss AnalysisAdrian ParasNo ratings yet
- StructureDocument54 pagesStructureAnoushka BansalNo ratings yet
- BecDocument7 pagesBecron123domingoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 TOSDocument10 pagesModule 3 TOSPrince IbanezNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis of Trusses Using Method of JointsDocument46 pagesStructural Analysis of Trusses Using Method of Jointsongica jamesNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Analysis of StructureDocument42 pagesModule 5 - Analysis of StructureJazmine ValenzonaNo ratings yet
- TrussDocument13 pagesTrussArjun Sharma VNo ratings yet
- MEE 233 - Truss - FrameDocument11 pagesMEE 233 - Truss - Frameleebrown21082003No ratings yet
- Unit IIIDocument59 pagesUnit IIIShankarNo ratings yet
- Simple Truss PDFDocument14 pagesSimple Truss PDFHalesh NaikNo ratings yet
- Simple Truss PDFDocument14 pagesSimple Truss PDFHalesh NaikNo ratings yet
- 3-Analysis of StructuresDocument42 pages3-Analysis of StructuresJoylyn BeranNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 (Chapter 6)Document20 pagesLecture 12 (Chapter 6)Adam SurtiNo ratings yet
- Connected at Their Extremities Only. The Members BeingDocument13 pagesConnected at Their Extremities Only. The Members BeingSergio Sánchez SalazarNo ratings yet
- The Truss: Engineering Mechanics LAB Assignment # 01Document2 pagesThe Truss: Engineering Mechanics LAB Assignment # 01Championip4pNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Prepared by Prem Kumar Soni Asst. Prof. LNCT-SDocument34 pagesLecture Notes: Prepared by Prem Kumar Soni Asst. Prof. LNCT-SQF “QF”No ratings yet
- Analysis of Structures: Aastu (Civil Engg Department) Engineering Mechanics I (Statics) For Pre-EngineeringDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Structures: Aastu (Civil Engg Department) Engineering Mechanics I (Statics) For Pre-EngineeringGadisaNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 23 Trusses IntroDocument17 pagesLecture # 23 Trusses IntroAbdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis: Engr. John Marco I. MatiraDocument28 pagesStructural Analysis: Engr. John Marco I. MatiraAIMNo ratings yet
- Ayush Kishore 21410005 Physics ProjectDocument12 pagesAyush Kishore 21410005 Physics ProjectAYUSH KISHORENo ratings yet
- Truss Analysis and DeterminacyDocument50 pagesTruss Analysis and DeterminacyAbdelhay Mohamed Hassan100% (1)
- Analysis of StructuresDocument30 pagesAnalysis of Structurescontrax8No ratings yet
- Introduction To StructuresDocument17 pagesIntroduction To StructuresObed JimmyNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Truss StructuresDocument21 pagesAnalyzing Truss Structuresshuvo devNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Methods in 40 CharactersDocument2 pagesStructural Analysis Methods in 40 CharactersElle HeartfiliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Analysis of Structures: Connected at Their Extremities Only. The Members BeingDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Analysis of Structures: Connected at Their Extremities Only. The Members BeingBELAL ALSUBARINo ratings yet
- Mini Project Mechanic Static ROOF TRUSS Analysis and DesignDocument16 pagesMini Project Mechanic Static ROOF TRUSS Analysis and DesignFatimah Nik Mazlan0% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Structural TheoryDocument20 pagesChapter 3 - Structural TheoryServando III UyNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis and Design-III: Space Truss AnalysisDocument41 pagesStructural Analysis and Design-III: Space Truss AnalysisObak Pothik AmiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Statically Determinate TrussesDocument15 pagesAnalysis of Statically Determinate TrussesCowar D. CourageNo ratings yet
- Trusses: ENG1001 Course NotesDocument17 pagesTrusses: ENG1001 Course Notesaizaz ahmadNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis of Trusses and FramesDocument30 pagesStructural Analysis of Trusses and FramesOmar AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Analysis of StructuresDocument6 pagesAnalysis of StructuresGirlie BalabatNo ratings yet
- EM-I _ Lec-6. TrussesDocument48 pagesEM-I _ Lec-6. TrussesFAISAL TaseenNo ratings yet
- TrussesDocument21 pagesTrussesShepherd NhangaNo ratings yet
- H.J.D. Institute of Reserch and Technology, Kera: Subject Name: Plane TrussDocument23 pagesH.J.D. Institute of Reserch and Technology, Kera: Subject Name: Plane TrussDevi Bhakti SongsNo ratings yet
- Unit4 PDFDocument29 pagesUnit4 PDFAashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- MEC-107: Basic Engineering Mechanics Unit-4 Analysis of StructuresDocument29 pagesMEC-107: Basic Engineering Mechanics Unit-4 Analysis of StructuresAashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A TrussDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of A TrussManish RaturiNo ratings yet
- ES 1022y Engineering Statics Structural Analysis - TrussesDocument15 pagesES 1022y Engineering Statics Structural Analysis - TrussesErikNo ratings yet
- Structure 1 - Chapter 3Document35 pagesStructure 1 - Chapter 3ljlubrhf rjnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Analysis of StructureDocument20 pagesChapter 5 Analysis of StructureRenu SekaranNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document22 pagesPresentation 4Angelo Mike John JavinezNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document4 pagesLec 4Muhammad Suhaib Uz Zaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Truss by RJ AliDocument18 pagesTruss by RJ AliAli AhsanNo ratings yet
- Plain and Space TrussesDocument29 pagesPlain and Space TrussesYusof Asanji50% (2)
- Statics #5 - (Ch7) Trusses, Frames, and MachinesDocument8 pagesStatics #5 - (Ch7) Trusses, Frames, and MachinesAshkan MirzaiNo ratings yet
- 5 - Structural AnalysisDocument46 pages5 - Structural AnalysisHawsar Omer HamaNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Simple Structures in Engineering Mechanics (CENG1041Document9 pagesAnalyzing Simple Structures in Engineering Mechanics (CENG1041nvnrevNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis1 PDFDocument142 pagesStructural Analysis1 PDFAkshit Raj Babbar Sher100% (1)
- Chapter ThreeDocument37 pagesChapter ThreeMah MoodNo ratings yet
- 16 Lecture Notes For Sections 6.1-6.3Document11 pages16 Lecture Notes For Sections 6.1-6.3iking balonNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument69 pagesVectorsdivyaNo ratings yet
- PLANE TRUSS ANALYSISDocument14 pagesPLANE TRUSS ANALYSISPrincess SandovalNo ratings yet
- Subhan Ahmed-344776-Lab 2 and 3Document9 pagesSubhan Ahmed-344776-Lab 2 and 3Subhan Ahmed MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Analysis of Structures 1ST Sem 2019-2020Document5 pagesChapter 5. Analysis of Structures 1ST Sem 2019-2020EllaMariePaceteNo ratings yet
- L2 - Engineering Mechanics Statics: Structural Analysis Simple TrussesDocument5 pagesL2 - Engineering Mechanics Statics: Structural Analysis Simple TrussesApostle ApostleNo ratings yet
- Lab 04Document22 pagesLab 04sisacs2002No ratings yet
- IN SUNNY SPAIN, 1882-85: "My Country, My Love, My People, I Leave You Now, You Disappear, I Lose Sight of You"Document4 pagesIN SUNNY SPAIN, 1882-85: "My Country, My Love, My People, I Leave You Now, You Disappear, I Lose Sight of You"Mary Claire ComalaNo ratings yet
- Pathways Rw1 2e U7 TestDocument9 pagesPathways Rw1 2e U7 TestGrace Ann AbanteNo ratings yet
- SMEspdfDocument13 pagesSMEspdflilpumpdidnothingwrong dNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Unit IDocument14 pagesAbnormal Psychology Unit IMahadevan K V100% (1)
- Window On The Wetlands BrochureDocument2 pagesWindow On The Wetlands BrochureliquidityNo ratings yet
- Types of Motivation in Language LearningDocument8 pagesTypes of Motivation in Language LearningAlya IrmasyahNo ratings yet
- NEW HOLLAND - Trucks, Tractor & Forklift Manual PDDocument14 pagesNEW HOLLAND - Trucks, Tractor & Forklift Manual PDAjjaakka0% (2)
- Packex IndiaDocument12 pagesPackex IndiaSam DanNo ratings yet
- Scan Sep 2, 2020Document1 pageScan Sep 2, 2020Taresh MittalNo ratings yet
- A Ghost StoryDocument10 pagesA Ghost StoryTrần MạnhNo ratings yet
- Surio vs. ReyesDocument3 pagesSurio vs. ReyesAdrian FranzingisNo ratings yet
- What Is ReligionDocument15 pagesWhat Is ReligionMary Glou Melo PadilloNo ratings yet
- India-An Underdeveloped Economy: (Contd )Document6 pagesIndia-An Underdeveloped Economy: (Contd )Amrita Prashant IyerNo ratings yet
- Not Qualified (Spoken Word Poem) by JonJorgensonDocument3 pagesNot Qualified (Spoken Word Poem) by JonJorgensonKent Bryan Anderson100% (1)
- BHEL Doctors - Mobile Number and Email IdDocument11 pagesBHEL Doctors - Mobile Number and Email IdCHANDRAN MAHA100% (1)
- Teaching As Noble ProfessionDocument1 pageTeaching As Noble ProfessionJeric AcostaNo ratings yet
- SDM - Session 6Document21 pagesSDM - Session 6Rohith NairNo ratings yet
- g6 Sws ArgDocument5 pagesg6 Sws Argapi-202727113No ratings yet
- SCM Software Selection and EvaluationDocument3 pagesSCM Software Selection and EvaluationBhuwneshwar PandayNo ratings yet
- Proposal to Enhance Science InstructionDocument4 pagesProposal to Enhance Science InstructionAzzel ArietaNo ratings yet
- Touch TypingDocument49 pagesTouch TypingCris Tin100% (2)
- Talent Level 3 Grammar Tests Unit 2Document2 pagesTalent Level 3 Grammar Tests Unit 2ana maria csalinasNo ratings yet
- ResMed Case Study AnalysisDocument12 pagesResMed Case Study Analysis徐芊芊No ratings yet
- Waiters' Training ManualDocument25 pagesWaiters' Training ManualKoustav Ghosh90% (51)
- DepEd Memorandum on SHS Curriculum MappingDocument8 pagesDepEd Memorandum on SHS Curriculum MappingMichevelli RiveraNo ratings yet
- Time To Get SeriousDocument354 pagesTime To Get SeriousEdmond Blair100% (1)
- IFCRecruitment Manual 2009Document52 pagesIFCRecruitment Manual 2009Oklahoma100% (3)
- Kim Hoff PAR 117 JDF 1115 Separation AgreementDocument9 pagesKim Hoff PAR 117 JDF 1115 Separation AgreementlegalparaeagleNo ratings yet
- TenorsDocument74 pagesTenorsaris100% (1)
- Researching Indian culture and spirituality at Auroville's Centre for Research in Indian CultureDocument1 pageResearching Indian culture and spirituality at Auroville's Centre for Research in Indian CultureJithin gtNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Infinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseFrom EverandInfinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (126)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Mastering Logical Fallacies: The Definitive Guide to Flawless Rhetoric and Bulletproof LogicFrom EverandMastering Logical Fallacies: The Definitive Guide to Flawless Rhetoric and Bulletproof LogicRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (91)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsFrom EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (57)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet