Professional Documents
Culture Documents
More Di Erentiation Practice: Di Erentiate ( ND The Derivative Of) The Following Func-Tions With Respect To X
Uploaded by
Irene Lyu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagescalculus_practice
Original Title
Calculus Practice
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcalculus_practice
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesMore Di Erentiation Practice: Di Erentiate ( ND The Derivative Of) The Following Func-Tions With Respect To X
Uploaded by
Irene Lyucalculus_practice
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
More Di¤erentiation Practice
Di¤erentiate (…nd the derivative of) the following func-
tions with respect to x.
a) f (x) = 1x 3
3
b) f (x) = ln(500000 2x)
1 2
c) f (x) = e 2x
What x maximizes each of the following functions?
d) f (x) = 5 + 12x 2x2
e) f (x) = x 1 + (0:9) (150000 1:5x) 1
Solutions
a) Start by considering the product rule and set g (x) =
1 and h (x) = x 3 . Using the di¤erentiation rule for
3
constants, g 0 (x) = 0: Using the polynomial rule h0 (x) =
3x 3 1 = 3x 4. Substituting these pieces into
the product rule. f 0(x) = g (x) h0 (x) + h (x) g 0 (x) =
1 3x 4 + x 3 (0) = x 4
3
b) Start by considering the chain rule and set h (:) =
ln (:) and g (x) = 500000 2x. Using the di¤erentiation
rule for constants, the polynomial rule, and the addition
rule, g 0 (x) = 0 2x1 1 = 2. Using the logarithm rule,
h0 (:) = (:)1 . Substituting these pieces into the chain rule,
1
f 0(x) = h0 (g (x)) g 0 (x) = 500000 2x ( 2).
c) Start by considering the chain rule and set h (:) = e(:)
and g (x) = 12 x 2. Using the polynomial rule and the
product rule, g 0 (x) = 1 ( 2) x 2 1 = x 3. Using
2
the exponential rule h0 (:) = e(:). Substituting these
pieces into the chain rule, f 0(x) = h0 (g (x)) g 0 (x) =
1 2
e 2x x 3 .
d) The function f (x) is called the objective function.
To …nd its maximum (or minimum) set the deriviative
of the function equal to zero (the …rst order condition)
and solve for x. In this case the function is a sum of a
constant and two polynomials. Using the di¤erentiation
rule for constants, the polynomial rule, and the addition
rule, f 0 (x) = 0 + 12 4x = 0. The addition rule allows
the separate calculation of the derivative for each term
of f (x). Solving for x, we …nd that x = 3 maximizes
the objective function.
e) In this case the function is a sum of two polynomi-
als with negative exponents where the second polyno-
mial is itself a function of x. Let g (x) = x 1 ,
the …rst polynomial. Using the polynomial rule, g 0 (x) =
( 1) ( 1) x 2 = x 2. Let the second polynomial be
h (x) = (0:9) (150000 1:5x) 1
and consider the chain rule. Set k (:) = (0:9) (:) 1
and q (x) = 150000 1:5x. Using the rule for constants,
the addition rule, and the polynomial rule, q 0 (x) = 1:5.
Using the polynomial rule, k (:) = (0:9) ( 1) ( 1) (:) 2 =
(0:9) (:) 2. The chain rule for the second polynomial is
given by h0 (x) = k0 (q (x)) q 0 (x). Substituting,
h0 (x) = (0:9) ( 1) ( 1) (150000 1:5x) 2 ( 1:5) :
After putting the pieces together, the …rst order condition
is
f 0 (x) = x 2 + (0:9) (150000 1:5x) 2 ( 1:5) = 0.
Rearrange, and solve for x.
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Rules of Differentiation of Functions in CalculusDocument7 pagesRules of Differentiation of Functions in CalculusOyedotun TundeNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of Algebraic Functions Theorems On Differentiation of Algebraic Functions and Higher-Order DerivativesDocument12 pagesDerivatives of Algebraic Functions Theorems On Differentiation of Algebraic Functions and Higher-Order DerivativeshappyfacerocksNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Differentiation RulesDocument7 pagesDifferentiation Ruleszidminhcd1992No ratings yet
- Business33 Derivatives For Composite Functions The Chain RuleDocument2 pagesBusiness33 Derivatives For Composite Functions The Chain Rulemarchelo_cheloNo ratings yet
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
- Rules for DerivativesDocument1 pageRules for DerivativesKristhel Pecolados RombaoaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document2 pagesLecture 14Syahir IshakNo ratings yet
- Find derivatives using differentiation rulesDocument2 pagesFind derivatives using differentiation rulesSumit PolNo ratings yet
- 18 GenfuncDocument20 pages18 GenfuncDương Minh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Basic Differentiation FormulasDocument3 pages2.3 Basic Differentiation FormulastinasheembofanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 3 Derivative of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Dr. Ghada AbdelhadyDocument32 pagesLecture # 3 Derivative of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Dr. Ghada AbdelhadyEsraa AhmadNo ratings yet
- Higher Order Derivatives of The Inverse Function - Version 2Document6 pagesHigher Order Derivatives of The Inverse Function - Version 2andrej_liptajNo ratings yet
- Using a table of derivatives to master differentiation techniquesDocument7 pagesUsing a table of derivatives to master differentiation techniquesBuniappa IyyerNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 4.4 - D-1Document7 pagesThe Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 4.4 - D-1alexlhhcasNo ratings yet
- Taylor ExpansionDocument8 pagesTaylor ExpansionJammy4411No ratings yet
- Lecture17 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture17 PDFreshmeNo ratings yet
- Prop DerivDocument1 pageProp DerivEloi Rubio GarciaNo ratings yet
- MA2213 SummaryDocument2 pagesMA2213 SummaryKhor Shi-JieNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Polynomials: 1-1 Introduction Definition 1.1: A Monomial in Variable X Is An Expression of The Form C XDocument28 pagesChapter One Polynomials: 1-1 Introduction Definition 1.1: A Monomial in Variable X Is An Expression of The Form C Xعبداللە عمر ابراهیمNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Functions: (Represents Real-Life Situations Using Rational Functions)Document33 pagesBasic Concepts of Functions: (Represents Real-Life Situations Using Rational Functions)Gerlie Jay-ann Ramos100% (1)
- MATH 31B Week 1 Examines Exponential, Inverse, and Logarithmic Functions and Their DerivativesDocument3 pagesMATH 31B Week 1 Examines Exponential, Inverse, and Logarithmic Functions and Their DerivativesAgus LeonardiNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Exercises 8.1: Section 8.1 Partial Differential Equations in Physics and EngineeringDocument21 pagesSolutions To Exercises 8.1: Section 8.1 Partial Differential Equations in Physics and EngineeringTri Phương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Rumus Matematika Sma InterDocument19 pagesRumus Matematika Sma InterAde JayusNo ratings yet
- C1 Functions CompleteDocument51 pagesC1 Functions CompleteZaxyln Zen ArchiliasNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument2 pagesSummaryZainariah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS FOR MICROECONOMICS SOLUTIONSDocument8 pagesMATHEMATICS FOR MICROECONOMICS SOLUTIONSAsia ButtNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Theorem of CalculusDocument5 pagesThe Fundamental Theorem of CalculusDaiszyBarakaNo ratings yet
- 11.8 Constraint Optimization: Lagrange's MultipliersDocument4 pages11.8 Constraint Optimization: Lagrange's MultipliersAlexander MonroeNo ratings yet
- Basic Differentiation Rules and ApplicationsDocument19 pagesBasic Differentiation Rules and Applicationsramasamy_lNo ratings yet
- ME Lecture NoteDocument65 pagesME Lecture Noteasu manNo ratings yet
- Limit of A FunctionDocument30 pagesLimit of A FunctionhamZaNo ratings yet
- 0st DerivativeDocument2 pages0st DerivativeHua Tien DungNo ratings yet
- 1 Mathematical Preliminaries 2Document17 pages1 Mathematical Preliminaries 2shubhamNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedShahnaz GazalNo ratings yet
- Notes Day 18-22Document12 pagesNotes Day 18-22api-272815616No ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Functions (Sect. 7.7) : RemarkDocument8 pagesHyperbolic Functions (Sect. 7.7) : RemarkCole Wong Kai KitNo ratings yet
- Basic Rules of DifferentiationDocument3 pagesBasic Rules of DifferentiationPrincessdy CocadizNo ratings yet
- Basic Rules of DifferentiationDocument33 pagesBasic Rules of DifferentiationGhulam Mohey Ud DinNo ratings yet
- 1 D Greens FunctionsDocument4 pages1 D Greens Functionsss_nainamohammedNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument44 pagesDifferentiationnaseem113No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Differentiation NotesDocument17 pagesFundamentals of Differentiation NotesGary TeongNo ratings yet
- Calculating LimitsDocument5 pagesCalculating LimitsanthonykogeyNo ratings yet
- Differentiation of Exponential FunctionsDocument20 pagesDifferentiation of Exponential FunctionsPrya Suthan SathiananthanNo ratings yet
- Topics Entry Test IBEB NonCD Version 2014Document5 pagesTopics Entry Test IBEB NonCD Version 2014YonYonNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Introduction of Optimal Economic Dispatch of GenerationDocument36 pages7.1 Introduction of Optimal Economic Dispatch of GenerationSwathi PrasadNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Fourier Transform Definition. The Fourier Transform (FT) Relates A Function To Its Frequency Domain EquivalentDocument23 pagesNotes On The Fourier Transform Definition. The Fourier Transform (FT) Relates A Function To Its Frequency Domain EquivalentRajas KhokleNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedFadzilah YayaNo ratings yet
- D DX C) 0: Rules of Derivatives Constant RuleDocument4 pagesD DX C) 0: Rules of Derivatives Constant Ruleruthanne022No ratings yet
- MAT060 12 Differential Notation and Trigonometric FunctionsDocument52 pagesMAT060 12 Differential Notation and Trigonometric FunctionsShine Ibarra AlabaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Functions. Essential Functions: Nguyen Thu HuongDocument27 pagesChapter 1: Functions. Essential Functions: Nguyen Thu HuongMai LinhNo ratings yet
- 5.integral Calculus Objectives:: DX DyDocument16 pages5.integral Calculus Objectives:: DX DyAndyMavia100% (1)
- MATH21Document11 pagesMATH21NilushaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Integration and DifferentiationDocument2 pagesNumerical Integration and DifferentiationGaurav UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Business34 The Product and Quotient RulesDocument2 pagesBusiness34 The Product and Quotient Rulesmarchelo_cheloNo ratings yet
- Roots of Equations SolvedDocument21 pagesRoots of Equations SolvedRibesha MushNo ratings yet
- Busa130 L8Document138 pagesBusa130 L811 MIPA 7 : 06 - BILQIS WISAM YASMINNo ratings yet
- Newtons Method of Root Finding SciLab Co PDFDocument1 pageNewtons Method of Root Finding SciLab Co PDFMiguel HinojosaNo ratings yet
- Least-Squares Circle Fit (Bullock 2006)Document3 pagesLeast-Squares Circle Fit (Bullock 2006)bigfigus100% (1)
- Social Network AnalysisDocument40 pagesSocial Network AnalysisLorraine D'AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Level - 1 (Problems Based On Fundamentals)Document19 pagesExercises: Level - 1 (Problems Based On Fundamentals)Shashank KumarNo ratings yet
- Triangular NumbersDocument2 pagesTriangular Numbersayu7kajiNo ratings yet
- 2014 Cape Unit 1 Paper 2 SolutionsDocument8 pages2014 Cape Unit 1 Paper 2 Solutionslindon9000No ratings yet
- C ProblemsDocument9 pagesC ProblemsggyuuouNo ratings yet
- Coe Bsee Syl Math34Document11 pagesCoe Bsee Syl Math34Darrel Damo PasaloNo ratings yet
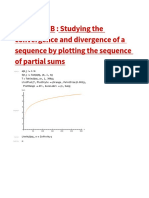
- Studying the convergence and divergence of sequences by plotting partial sumsDocument3 pagesStudying the convergence and divergence of sequences by plotting partial sumsPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- FSA MMW AnswerKeyDocument24 pagesFSA MMW AnswerKeysddsdssds100% (2)
- Math 10Document3 pagesMath 10Mary Joselyn BodionganNo ratings yet
- Mathanati : Discrete 3 (1981) 163-174 North-Holland Publishing CompanyDocument12 pagesMathanati : Discrete 3 (1981) 163-174 North-Holland Publishing Companyzabroma1717No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJemuel FraneNo ratings yet
- Kudelic R. Feedback Arc Set... Problem and Algorithms 2022Document134 pagesKudelic R. Feedback Arc Set... Problem and Algorithms 2022LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Isometric and Orthographic ProjectionDocument11 pagesIsometric and Orthographic Projectionanimeshdorugade244No ratings yet
- A PAIR CORRELATION PROBLEM, AND COUNTING LATTICE POINTS WITH THE ZETA FUNCTION CHRISTOPH AISTLEITNER, DANIEL EL-BAZ, MARC MUNSCH-Technau-Rudnick-SarnakDocument25 pagesA PAIR CORRELATION PROBLEM, AND COUNTING LATTICE POINTS WITH THE ZETA FUNCTION CHRISTOPH AISTLEITNER, DANIEL EL-BAZ, MARC MUNSCH-Technau-Rudnick-SarnakSam TaylorNo ratings yet
- DT DT+ DX: 1.3 First Order Partial Differential EquationsDocument3 pagesDT DT+ DX: 1.3 First Order Partial Differential EquationsSyed Beeban BashaNo ratings yet
- Hermite PolynomialsDocument6 pagesHermite PolynomialsJhon Bladimir Caicedo PortillaNo ratings yet
- NMTC Primary PDocument10 pagesNMTC Primary PSindujaNo ratings yet
- Qqad - 2008Document71 pagesQqad - 2008api-19818421No ratings yet
- Aleph NumbersDocument4 pagesAleph NumbersAvicena AlbiruniNo ratings yet
- Public Chow Et Al 43 5Document5 pagesPublic Chow Et Al 43 5PobretanoNo ratings yet
- Numerics Chapter 2Document90 pagesNumerics Chapter 2Matusal GizawNo ratings yet
- MAST20026 Real Analysis With Applications, August 10, 2011. This Document Was Produced by Steve Carnie and Adapted by Alex GhitzaDocument2 pagesMAST20026 Real Analysis With Applications, August 10, 2011. This Document Was Produced by Steve Carnie and Adapted by Alex Ghitzavanessa8pangestuNo ratings yet
- Multi Variable Optimization: Min F (X, X, X, - X)Document38 pagesMulti Variable Optimization: Min F (X, X, X, - X)Saheera HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Chap08-Discrete Markov ChainsDocument20 pagesChap08-Discrete Markov ChainsDian Muhtar BudiasaNo ratings yet
- Curve TracingDocument4 pagesCurve Tracingsurekha surekha0% (1)
- Chapter Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesChapter Practice ProblemsNavras MridangNo ratings yet
- Polar Form of Complex Numbers 8Document25 pagesPolar Form of Complex Numbers 8Amy CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Mrinal Kalakrishnan: CHOMP Motion PlannerDocument15 pagesMrinal Kalakrishnan: CHOMP Motion PlannerWillow GarageNo ratings yet
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceFrom EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- Assessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6From EverandAssessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)