Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fan Engineering PDF
Fan Engineering PDF
Uploaded by
shant_mOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fan Engineering PDF
Fan Engineering PDF
Uploaded by
shant_mCopyright:
Available Formats
FAN ENGINEERING
SECTION INDEX
01. FAN BASICS
02. ABBREVIATIONS
03. SYMOBLS / NOTATIONS / UNITS
04. DEFINATIONS & TERMINOLOGY
05. METRIC / FPS CONVERSIONS
06. USEFUL FORMULAS & FAN LAWS
PFCSL /01 Page 1 of 9
01. FAN BASICS
Axial Flow Fans : A Fan is a device that is designed to move a specified volume of
air (flow) against moderate pressure (resistance). A fan induces an airflow by virtue of
its blades; a blade moves air by generating a lift force when in motion through the air.
An axial flow fan is a fan in which the flow of air is substantially parallel to the axis of
rotation.
Static Pressure : A Fan moving air must work to overcome resistance to the flow that
arises due to various obstructions in the flow path. This works is termed as velocity
pressure and is expressed as mm of wg.
Velocity Pressure : In addition to the above, a fan must also work to accumulate air
to its suction side and move it to the discharge side. This work is termed as velocity
pressure and is expressed as mm wg.
Total Pressure : The total work a fan must do to move a specified volume of air
against the static pressure plus the velocity pressure is defined as total pressure of the
system and is expressed in millimeters or mm wg.
Efficiency : The measure of how well a fan does work against the total pressure to
move a given volume of air is termed as Fan Total Efficiency. In general, a non –
uniform air stream(flow) results in a less efficient fan. A fan equipped with a duct
having proper inlet and outlet shapes, allows for a more uniform air stream (flow) and
thus dramatically improves the efficiency of the fan; in fact, if properly designed, a
ducted fan can achieve efficiencies up to 85%.
PFCSL /01 Page 2 of 9
02. ABBREVIATIONS
ABBREVIATION TERMS
bhp BRAKE HORSE POWER
bkW BREAK KILOWATTS
0
C CELCIUS
CFM CUBIC FEET PER MINUTE
cm CENTIMETER
o
F FAHRENHEIT
FPM FEET PER MINUTE
ft FEET
Hg MERCURY COLUMN
hp HORSE POWER
in INCH
kg KILOGRAM
kW KILOWATT
lb (lbs) POUND (POUNDS)
m METER
min MINUTES
mm MILIMETER
Pa PASCAL
rpm REVOLUTIONS PER MINUTE
rps REVOLUTIONS PER SECOND
s SECOND
W WATT
wg WATER GAUGE / WATER COLUMN
PFCSL /01 Page 3 of 9
03. SYMOBLS / NOTATIONS / UNITS
SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION UNITS
METRIC FPS
A NET FREE FAN AREA m2 ft2
D FAN DIAMETERER m ft
d SEAL DISC DIAMETER mm in
Hi FAN INPUT POWER kW hp
H1 FAN INPUT POWER AT DUTY POINT 1 kW hp
H2 FAN INPUT POWER AT DUTY POINT 2 kW hp
HO FAN OUTPUT POWER kW hp
HoS FAN OUTPUT POWER (STATIC) kW hp
HP HORSE POWER hp hp
N FAN SPEED rpm rpm
N1 FAN SPEED AT DUTY POINT 1 rpm rpm
N2 FAN SPEED AT DUTY POINT 2 rpm rpm
ηt FAN TOTAL EFFICIENCY % %
ηs FAN STATIC EFFICIENCY % %
Pt TOTAL PRESSURE mm wg in. wg
Ps STATIC PRESSURE mm wg in. wg
Pv VELOCITY PRESSURE mm wg in. wg
P1 PRESSURE AT DUTY POINT1 mm wg in. wg
P2 PRESSURE AT DUTY POINT 2 mm wg in. wg
ρ AIR DENSITY mm / m3 lbs /ft3
ρ1 AIR DENSITY DUTY POINT 1 kg / m3 lbs /ft3
ρ2 AIR DENSITY DUTY POINT 2 kg / m3 lbs /ft3
Q AIR FLOW RATE m3 / s CFM
Q1 AIR FLOW RATE AT DUTY POINT 1 m3 / s CFM
Q2 AIR FLOW RATE AT DUTY POINT 2 m3 / s CFM
TS FAN TIP SPEED m/s FPM
V AIR VELOCITY m/s FPM
V1 AIR VELOCITY AT PLANE 1 m/s FPM
V2 AIR VELOCITY AT PLANE 2 m/s FPM
PFCSL /01 Page 4 of 9
04. DEFINITIONS & TERMINOLOGY
Air Density (ρ) : The mass per unit volume of the air, expressed in kg/m3 or lb / ft3
Air Flow Rate (Q) : The volume of air moved by the fan per unit of time, expressed in
CFM (cubic feet per minute) or m3 /s.
Air Power (Static) : That part of the energy, per unit time, imparted by the fan to the
air in overcoming static pressure (Ps) from that at the inlet to that at the outlet.
Air Power (Total) : That part of the energy, per unit time, imparted by the fan to the
air by increasing its total pressure (Pt) from that at the inlet to that at the outlet.
Fan: A device for moving air, which utilizes a power driven rotating impeller. A fan
shall have at least one inlet and one outlet.
Axial Flow Fan : A fan in which the flow of air is substantially parallel to the axis the
impeller rotation.
Fan Characteristics: The curves depicting the relationship between air flow rate, total
pressure, fan power input and fan total efficiency at a specified angle and RPM
Fan Duty (Static) : The volume of air to be moved, by the fan at a specified static
pressure (Ps).
Fan Duty (Total) : The volume of air to be moved, by fan at a specified total pressure
(Pt)
Fan Power Input(H1) : The energy input, per unit time, required to drive a fan,
expressed in Break Horse Power (bhp) or Break Kilowatt (bkW).
Fan Speed (N) : The number of revolutions of the fan about its axis per unit time,
expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM)
Fan Total Efficiency (ηt): The ratio of air power (total) to the fan power input
PFCSL /01 Page 5 of 9
…… 04 DEFINITIONS & TERMINOLOGY
Fan Static Efficiency (ηs) : The ratio of the air power (static) to the fan power .
Stall : The region of instability in fan performance caused by the separation of the air
flow from the surface of the fan blade. The stall condition is depicted by a dip in the
performance curve.
Standard Air : Atmospheric air having a specific weight of 1.2 kg / m3 which is dry air at 20o
C and 50% relative humidity with a barometric pressure of 760 mm Hg.
Static Pressure Margin : The pitch angle margin available between the selected operating
point and stall point on the performance curve.
Static Pressure (Ps) : The sum of all resistance to the path of air flow in a given
system which a fan must overcome to move a specific volume of air, expressed in
mm wg or in wg or Pascal (Pa).
Tip Clearance : The clearance between the fan blade tip and the fan casing wall.
Total Speed (Ts) : The linear speed at the fan blade tip at a given fan rpm, expressed
in ft./min. or m/s.
Total Pressure (Pt) : The air pressure, which exists by virtue of the degree of
compression and the rate of motion. It is the sum of the static pressure and velocity
pressure at any given point in a system.
Velocity (V) : The rate of air flow divided by the net area of the air flow, and is
expressed in m/s or ft /min.
Velocity Pressure (Pv) : The portion of air pressure which exists by virtue of the rate
of motion only, expressed in mm or in wg or Pascal (Pa).
PFCSL /01 Page 6 of 9
05. METRIC / FPS CONVERSIONS
METRIC TO FPS
EQUIVALENT
PARAMETER METRIC UNIT CONVERSION
FPS UNITS
FORMULA
LENGTH 1m x 3.2802 3.2802 ft
MASS 1 kg x 2.2046 2.2046 lbs
TEMPERATURE 0o C 1.8 x oC +32 32o F
FORCE 1N x 0.22481 0.22481 lbs.
1 m3/s x 2118.9 2118.9 CFM
FLOW RATE
1 m3/hr x 0.58858 0.5884 CFM
x 32.8083 32.8083 ft / s
VELOCITY 1 m/s
x 196.85 196.85 FPM
x 0.00402264 0.00402264 in. wg
PRESSURE 1 N/m2
x 0.00029530 0.00029530 in. Hg
1 Pa x 0.0040264 0.0040264 in. wg
POWER 1W x 0.0013410 0.0013410 hp
TORQUE 1 N-m x 8.8507 8.8507 lb - in
SPEED 1 rps x 60 60 rpm
DENSITY 1 kg/m3 x 0.062428 0.062428 lbs / ft3
PFCSL /01 Page 7 of 9
06. USEFUL FORMULAS & FAN LAWS
A. USEFUL FORMULAS
• AIR VELOCITY V = Q /A
• TOTAL PRESSURE : Pt = Ps + Pv
• VELOCITY PRESSURE : Pv = (V /4.04)2 mm wg for metric, Pv
= (V / 4009)2 in wg for FPS
FAN OUTPUT POWER(TOTAL) : = Pt x Q x 9.81 / 1000 kW for metric
Ho = Pt x Q /6360 hp for FPS
FAN OUTPUT POWER (STATIC) : Hos = Ps x Q x 9.81 /1000 kW for metric,
Hos = Ps x Q x 9.81 /6360 hp for FPS
• TOTAL EFFICIENCY % : ηt = (Ho / Hi x 100)
• STATIC EFFICIENCY% : ηS = (HoS / Hi ) x 100
• TIP SPEED : TS = (π x D x N) / 60 m/s for metric, TS = π x D x N ft/min for FPS
• NET FREE AREA : A = π / 4 (D2 – d2)
• SOLIDITY RATIO = SUM OF FAN BLADE TIP CHORDS / ( π x D)
PFCSL /01 Page 8 of 9
…. 06. USEFUL FORMULAS & FAN LAWS
B. BASIC FAN LAWS
Effect of Fan Speed
a. FAN AIR FLOW RATE VARIES DIRECTLY WITH FAN SPEED RATIO:
b. Q2 = Q1 x (N2/N1)2
c. FAN PRESSURE VARIES WITH THE SQUARE OF FAN SPEED RATIO:
d. P2 = P1 x (N2/N1) 2
e. FAN INPUT POWER VARIES WITH CUBE OF FAN SPEED RATIO :
f. H2 = H1 x (N2/N1) 3
Effect of Air Density
a. AIR FLOW RATE REMAINS THE SAME WITH A CHANGE IN AIR DENSITY
b. PRESSURE VARIES IN PROPORTION TO THE AIR DENSITY
c. P2 = P1 x (ρ2/ρ1)
d. FAN INPUT POWER VARIES IN PROPORTION TO THE AIR DENSITY
e. H2 = H1 x (ρ2/ρ1)
PFCSL /01 Page 9 of 9
You might also like
- Steam Ejector CalculationsDocument11 pagesSteam Ejector Calculationsrashm006ranjan100% (1)
- Fans and Blowers Part I ModuleDocument26 pagesFans and Blowers Part I ModuleCharlyn Flores67% (3)
- Centrifugal FansDocument19 pagesCentrifugal FansMark John Santos67% (6)
- The Myth About Fan Static PressureDocument5 pagesThe Myth About Fan Static Pressurebetos013No ratings yet
- Fan TheoryDocument8 pagesFan TheoryUtsavNo ratings yet
- AMCA Fan Performance PDFDocument16 pagesAMCA Fan Performance PDFthevellin154No ratings yet
- Machinery Lubrication I IIDocument12 pagesMachinery Lubrication I IIrashm006ranjan50% (2)
- Fan PDFDocument28 pagesFan PDFpequenita34No ratings yet
- Fan BasicsDocument6 pagesFan BasicsPankaj Patil100% (1)
- Fans and Blowers: Learning OutcomesDocument17 pagesFans and Blowers: Learning OutcomesRyan CalicaNo ratings yet
- 4 Performance of A Centrifugal FanDocument7 pages4 Performance of A Centrifugal Fanfinix33No ratings yet
- Vent Axia Vent GuideDocument23 pagesVent Axia Vent GuideblasderNo ratings yet
- Fan Basics: What Is A Fan?Document6 pagesFan Basics: What Is A Fan?Rahul JaganNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor System Compressor Fundamentals: IntercoolingDocument56 pagesAir Compressor System Compressor Fundamentals: IntercoolingAmarendra Mani TiwariNo ratings yet
- Fan Terminology and Definitions: Technical Bulletin TBN002.2/2003Document4 pagesFan Terminology and Definitions: Technical Bulletin TBN002.2/2003Ngoc Vũ TrầnNo ratings yet
- Workshop On FAN Engineering For Hvac&R: Sushil K. ChoudhuryDocument85 pagesWorkshop On FAN Engineering For Hvac&R: Sushil K. ChoudhurySadique ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Fan Power ConsumptionDocument8 pagesFan Power Consumptionchilamkurti_sivasankararaoNo ratings yet
- Cermak AMCA Web FanDocument6 pagesCermak AMCA Web Fanbigi1234No ratings yet
- Fan Engineering Guide - Twin City FansDocument12 pagesFan Engineering Guide - Twin City FansHafiz KamalNo ratings yet
- 08 Ventilatorgrundlagen FantechnologyDocument37 pages08 Ventilatorgrundlagen FantechnologySsheshan PugazhendhiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Tip Clearance On Performace of Axial Flow FanDocument9 pagesEffect of Tip Clearance On Performace of Axial Flow Fancalcy4meNo ratings yet
- Fans and Air Movement Essentials Properties of AirDocument12 pagesFans and Air Movement Essentials Properties of Airricha-BNo ratings yet
- Mod 5-Fan Measurement and TestingDocument227 pagesMod 5-Fan Measurement and TestinglovjnxNo ratings yet
- All You Need To Know About FansDocument10 pagesAll You Need To Know About FansgertibajNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - Fundamentals of Airflow, Fans & DuctDocument49 pagesPart 1 - Fundamentals of Airflow, Fans & Ductkhanh.vecNo ratings yet
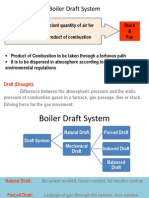
- Boiler Draft SystemDocument56 pagesBoiler Draft SystemAmit Chauhan78% (9)
- Fan Types: 1) AXIAL FLOW FANS - The Flow of The Gases Is Parallel To The Fan ShaftDocument35 pagesFan Types: 1) AXIAL FLOW FANS - The Flow of The Gases Is Parallel To The Fan ShaftKarthikRajuNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Air Compressor BasicsDocument7 pagesCentrifugal Air Compressor BasicsCésarNo ratings yet
- Fans and Blowers LectureDocument11 pagesFans and Blowers LectureVincentNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Procedure To Do Shortcut Sizing For Air Cooled Heat Exchanger and Estimate Finned Area and Power RequiredDocument5 pagesStep by Step Procedure To Do Shortcut Sizing For Air Cooled Heat Exchanger and Estimate Finned Area and Power RequiredkarthickNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger - ChE GuideDocument5 pagesAir Cooled Heat Exchanger - ChE GuideAnonymous KpVxNXsNo ratings yet
- ALUP Compressed Air Fundamentals-Part1 - GBDocument50 pagesALUP Compressed Air Fundamentals-Part1 - GBmbrijbhushan75% (4)
- 11 FanDocument5 pages11 Faniso026No ratings yet
- Fan PerformanceDocument8 pagesFan PerformanceRajeevAgrawalNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics 5Document10 pagesAerodynamics 5Mohammed AbdoNo ratings yet
- Air CompressorDocument31 pagesAir CompressorEr Bali Pandhare50% (4)
- Fan Selection: Specifying RequirementsDocument26 pagesFan Selection: Specifying Requirementsvalerio.garibayNo ratings yet
- Env Slb002 enDocument8 pagesEnv Slb002 enEduardo LegorretaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentMohamed Gamal GemyNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Variable Area NozzlesDocument18 pagesBenefits of Variable Area Nozzlesivillen001No ratings yet
- Airflow - Engineering - 101 PDFDocument5 pagesAirflow - Engineering - 101 PDFlawwumcNo ratings yet
- Fan Basics: What Is A Fan?Document6 pagesFan Basics: What Is A Fan?Tanuj Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument6 pagesHeat ExchangerAfif FakhrurNo ratings yet
- γ γ × ∆ × × × × P 81 - 9 2 Cp A: Selected questionsDocument6 pagesγ γ × ∆ × × × × P 81 - 9 2 Cp A: Selected questionsHhaabbde SybaritzNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Performance of Centrifugal Compressor: A. ObjectiveDocument6 pagesExperiment 6 Performance of Centrifugal Compressor: A. ObjectiveSurjit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics II (Chapter 5)Document10 pagesFluid Mechanics II (Chapter 5)Kaffel100% (1)
- Basic Fan Engineering NotesDocument5 pagesBasic Fan Engineering NotesrentboyrodriguezNo ratings yet
- Theory of Rating: 800 S. Missouri Avenue MARCELINE, MISSOURI 64658-1602 PHONE (660) 376-3575 FAX (660) 376-2909Document10 pagesTheory of Rating: 800 S. Missouri Avenue MARCELINE, MISSOURI 64658-1602 PHONE (660) 376-3575 FAX (660) 376-2909dfmolinaNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Fan Energy CostsDocument9 pagesMinimizing Fan Energy Costsmemep1No ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsFrom EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management (EVM)Document8 pagesEarned Value Management (EVM)rashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- 03 - Confined Space EntryDocument18 pages03 - Confined Space Entryrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- New Book Launch Schedule 36 Days: Planning Complete!Document1 pageNew Book Launch Schedule 36 Days: Planning Complete!rashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- 3rd Floor Service Bldg. Intercom List 2nd Floor Service Bldg. Intercom ListDocument2 pages3rd Floor Service Bldg. Intercom List 2nd Floor Service Bldg. Intercom Listrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Simple FormattingDocument1 pageSimple Formattingrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Energy Audit For Electric MotorDocument4 pagesEnergy Audit For Electric Motorrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- NCQC 2016 RaipurDocument8 pagesNCQC 2016 Raipurrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Turbine Cooling TemperaturesDocument12 pagesTurbine Cooling Temperaturesrashm006ranjan0% (1)
- Annemometer and ThermometerDocument1 pageAnnemometer and Thermometerrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- HyperGraph3D TutorialsDocument41 pagesHyperGraph3D Tutorialsrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Coal Mill Heat BalanceDocument2 pagesCoal Mill Heat Balancerashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Bevel & Hypoid Gears:: Measuring BacklashDocument3 pagesBevel & Hypoid Gears:: Measuring Backlashrashm006ranjan100% (1)
- 790Document5 pages790rashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Compressor and Compressed Air SystemDocument34 pagesCompressor and Compressed Air Systemrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- SKF Dry Lubricated Bearings 11358 3 enDocument28 pagesSKF Dry Lubricated Bearings 11358 3 enrashm006ranjan100% (1)
- Paper 2 - Set B Solutions: General InstructionsDocument14 pagesPaper 2 - Set B Solutions: General Instructionsrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Loss Optimisation in BoilersDocument50 pagesLoss Optimisation in Boilersrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- The Condenser Performance Test and Thermal Performance Analysis of Variable Conditions in TQNPCDocument4 pagesThe Condenser Performance Test and Thermal Performance Analysis of Variable Conditions in TQNPCrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology CalicutDocument14 pagesNational Institute of Technology Calicutrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Coal Mill Heat BalanceDocument2 pagesCoal Mill Heat Balancerashm006ranjanNo ratings yet