Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 6 Chapter 4
Uploaded by
Steven MananingCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 6 Chapter 4
Uploaded by
Steven MananingCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
The flow of fluid with an abrupt change, smoothly contoured change, and for the
overall change of direction was observed to determine the experimental head loss for each
changes. The results of the experiment showed that the head loss in an abrupt change of
direction was greater than the head loss in a smoothly contoured change. The head loss
observed in the experiment incorporates the loss of energy due to the sudden change in
direction of flow of fluid. This loss of energy is mostly due to the flow separation caused by
the sudden changes of the flow in the pipe. In this experimentation, the researchers used the
elbow and tee fittings to change the direction of the flow of the fluid.
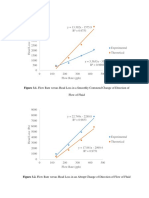
It is observed that increasing the flow rate results to a greater turbulence in the pipe
thus, making a larger head loss. Graphing the flow rate versus the head loss in a smoothly
contoured change, abrupt change, and for the overall change showed a directly proportional
relationship to each other. As the flow rate increases, the head loss also increases. The increase
in flow rate also increases the Reynolds number thus, making the flow turbulent.
The experimenters recommend to the future researchers to execute the experiment
properly to avoid the errors and lessen the difference between the theoretical and experimental
values. It is important to check the fluid flow apparatus if there are no leakages, loose fittings,
and air in the pipeline. Lastly, the researchers must also be cautious when reading the flow
rate and when reading the manometer in order to lessen the source of error.
You might also like
- CH E 512 EXPERIMENT 1 GraphsDocument2 pagesCH E 512 EXPERIMENT 1 GraphsSteven MananingNo ratings yet
- Expt 6 Chapter 2Document3 pagesExpt 6 Chapter 2Steven MananingNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 GraphsDocument3 pagesExperiment 6 GraphsSteven MananingNo ratings yet
- Expt 6 Chapter 1Document3 pagesExpt 6 Chapter 1Steven MananingNo ratings yet
- Expt 6 Appendix A and BDocument2 pagesExpt 6 Appendix A and BSteven MananingNo ratings yet
- CH E 425 Midterm ReportsDocument15 pagesCH E 425 Midterm ReportsSteven MananingNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Laboratory Experiment 4Document23 pagesEnvironmental Science Laboratory Experiment 4Steven MananingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3Steven MananingNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Laboratory Experiment 5Document17 pagesEnvironmental Science Laboratory Experiment 5Steven MananingNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Laboratory Experiment 6Document26 pagesEnvironmental Science Laboratory Experiment 6Steven MananingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3Steven MananingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3Steven MananingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3Steven MananingNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Simulation of Kaduna Refining and Petrochemical Company (KRPC) Crude Distillation Unit (CDU I) Using HysysDocument7 pagesSimulation of Kaduna Refining and Petrochemical Company (KRPC) Crude Distillation Unit (CDU I) Using HysysAdhityaEkoBagusNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering NotesDocument216 pagesMechanical Engineering NotesvelavansuNo ratings yet
- The Viability of Snail Shell Suso As An Additive in Making Cemented Pots Final DaftDocument29 pagesThe Viability of Snail Shell Suso As An Additive in Making Cemented Pots Final DaftRhaziela Eunika MalabagNo ratings yet
- Name of DefectDocument3 pagesName of DefectJana EncaboNo ratings yet
- Paul DiracDocument6 pagesPaul DiracLeonNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesThermal Power Plantshamna AbdullaNo ratings yet
- lt2 Science 3Document4 pageslt2 Science 3katherine corveraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Basic Terminology and ConceptsDocument160 pagesLesson 1: Basic Terminology and Conceptsdiala alazraiNo ratings yet
- Steam Generation - Distribution 2023Document64 pagesSteam Generation - Distribution 2023Aaqil cassimNo ratings yet
- Shuttlecock DynamicsDocument6 pagesShuttlecock Dynamicshokl88No ratings yet
- EXP-10 Pressure Drop in Packed BedDocument23 pagesEXP-10 Pressure Drop in Packed BedZakwan HanifNo ratings yet
- Physics HL p2Document415 pagesPhysics HL p22025snehithNo ratings yet
- C184 E037bDocument48 pagesC184 E037bNeyda Flores VasquezNo ratings yet
- Heat FlowDocument22 pagesHeat FlowIshita MongaNo ratings yet
- Isobutylene: CAS N°: 115-11-7Document102 pagesIsobutylene: CAS N°: 115-11-7javNo ratings yet
- Astronomy FormulaeDocument36 pagesAstronomy Formulaeescherer1099100% (3)
- IULTCS-IsO-En Leather Test MethodsDocument6 pagesIULTCS-IsO-En Leather Test MethodsTekstil DpeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FileDocument9 pagesChemistry Filemrharshityadav01No ratings yet
- Test QuestionsDocument2 pagesTest QuestionsMOHANAPRIYANo ratings yet
- Corrosion Monitoring Methods (Chevron)Document65 pagesCorrosion Monitoring Methods (Chevron)Sergey KichenkoNo ratings yet
- Sensors Evaluation 2019 Oct 19 (19) - DOC#NDL:NDA:DGA:ON:072002 PDFDocument1 pageSensors Evaluation 2019 Oct 19 (19) - DOC#NDL:NDA:DGA:ON:072002 PDFDivyansh KohliNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLab ReportShashaNo ratings yet
- KSSM Science Form 4 Chapter 9 9.1Document47 pagesKSSM Science Form 4 Chapter 9 9.1TSE100% (1)
- Chemistry Project Work: CertificateDocument6 pagesChemistry Project Work: CertificateShreya Rajpal67% (3)
- Complex Formation Between Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) and Borate IonDocument3 pagesComplex Formation Between Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) and Borate IonHaroon RashidNo ratings yet
- TEMP ABB Guide PDFDocument323 pagesTEMP ABB Guide PDFjavad4531No ratings yet
- D3S08 Volpe 508Document20 pagesD3S08 Volpe 508Madhu Chandra LNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Molecular and Cell BiochemistryDocument7 pagesBiochemistry: Molecular and Cell BiochemistryKHIENT CARLO MARTINNo ratings yet
- Ch02 QuestionsDocument8 pagesCh02 QuestionsAdliNo ratings yet
- Nickel Alloy (182, 112, 141) Electrodes For Arc WeldingDocument1 pageNickel Alloy (182, 112, 141) Electrodes For Arc WeldingMus LimNo ratings yet