0% found this document useful (0 votes)
682 views19 pages10 Rayleigh Ritz Method-1
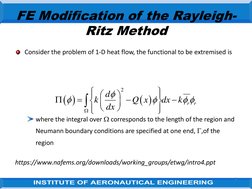
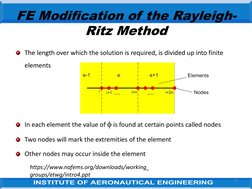
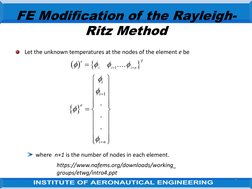
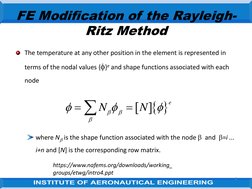
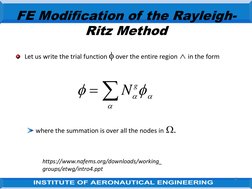
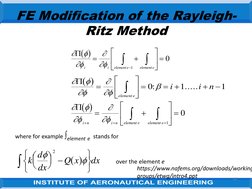
The document discusses the finite element modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz method. It describes how the Rayleigh-Ritz method uses a single trial function over the entire problem region, while finite elements divide the region into subsections and use simple trial functions piecewise over each element. Within each element, the solution is approximated at discrete nodes using shape functions. By assembling the element equations globally, the finite element approach can model complex problems using basic shape functions within each element.
Uploaded by
rashmitha chigullapallyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
682 views19 pages10 Rayleigh Ritz Method-1
The document discusses the finite element modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz method. It describes how the Rayleigh-Ritz method uses a single trial function over the entire problem region, while finite elements divide the region into subsections and use simple trial functions piecewise over each element. Within each element, the solution is approximated at discrete nodes using shape functions. By assembling the element equations globally, the finite element approach can model complex problems using basic shape functions within each element.
Uploaded by
rashmitha chigullapallyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method: Describes the modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz method for solving problems in finite elements, including mathematical formulations and application techniques over a series of steps.