Professional Documents
Culture Documents
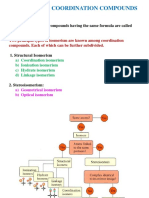
Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds) (Answer)
Uploaded by
Shreyash KolekarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds) (Answer)
Uploaded by
Shreyash KolekarCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE TEST PAPER-03
CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (coordination compounds)
[ANSWER]
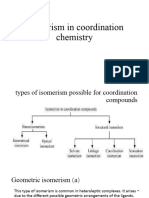
Topic:- Isomerism in coordination compounds
Ans1. Isomerism is the phenomenon of existence of two or more compounds with same
chemical formula but a different arrangement of atoms.
Ans2. The isomerism that arises in hetroleptic complexes due to different possible
geometric arrangements of the ligands is called geometric isomerism.
1) Cis and Trans isomerism can occur in square planar complexes of formula [MX2
L2] ( X&L are unidentate ligands) , square planar complexes of formula MAB X L
& octahedral complexes of formula MX2 L4 .
2) Fac and mer isomerism can occur in octahedral complexes of formula Ma3b3.
Ans3. Optical isomers differ in the direction in which they rotate the plane of polarized
light in a polarimeter.
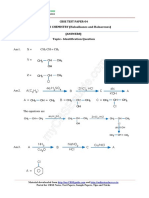
Ans4. [Cr Cl2 (en)2 ]+
Cis and trans forms.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
The cis form will be optically active.
mirror
Ans5. A complex having ambident ligand will show linkage isomerism e.g [Cr (NH3)5
(NO2) ] Cl2 has NO-2 as ambident Ligand and its Linkage isomer will be [Cr (NH3)5
(ONO) ]Cl2.
Ans6. Ionisation isomerism arises when the counter ion in a complex salt is itself a
potential Ligand and can displace a Ligand which can then become counter ion e.g.
[CO (NH3)5 SO4] Br and [CO (NH3)5 Br] SO4 are ionization isomer.
Ans7. The solvate isomers differ by wether or not a solvent molecule is directly bonded to
the metal ion or is merely present on free solvent molecules in the crystal.
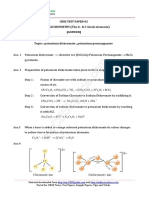
Ans8. Geometrical isomers
Ans9. Both geometrical and optical isomerisms will be present.
Ans10. Example of coordination isomerism is
[Cr (NH3)6] [Co (CN)6] and [Co (NH3)6] [Cr (CN)6]
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesNo ratings yet
- Tricks of Isomerism in Coordination Compounds Chemistry For NEET & JEE 2019Document5 pagesTricks of Isomerism in Coordination Compounds Chemistry For NEET & JEE 2019misostudy0% (1)
- Coordination CompoundsDocument15 pagesCoordination Compoundsdivanshu2006yadavNo ratings yet
- 6 2018 11 10!08 18 38 PMDocument9 pages6 2018 11 10!08 18 38 PMAlma Tyara SNo ratings yet
- Isomerism IN Compounds: CoordinationDocument19 pagesIsomerism IN Compounds: CoordinationEmilyNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH07 The P Block Elements 03Document15 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH07 The P Block Elements 03Ricky SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ma'Am Faraha Inorganic, Isomerism in Complexes, LECT-7Document16 pagesMa'Am Faraha Inorganic, Isomerism in Complexes, LECT-7Junaid BaigNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry-Intro N IsomerDocument22 pagesCoordination Chemistry-Intro N IsomerAnuragJainNo ratings yet
- Isomerism in Coordination CompoundsDocument3 pagesIsomerism in Coordination CompoundsZainab MughalNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document23 pagesUnit 5laxmanmamilwar18No ratings yet
- VBT - Theory and IsomerismDocument25 pagesVBT - Theory and Isomerismzuneid-adamoNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compound. Inorganic ChemistryDocument14 pagesCoordination Compound. Inorganic ChemistryPragyan ChutiaNo ratings yet
- Isomerism in Coordination CompoundDocument14 pagesIsomerism in Coordination CompoundPragyan ChutiaNo ratings yet
- Isomerism in Coordination Compounds: 1. StereoisomersDocument6 pagesIsomerism in Coordination Compounds: 1. StereoisomersAs if Ali LarikNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument48 pagesCoordination CompoundsK_S_Krishna0001No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 11Document15 pagesChapter 9 11Ritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Isomerism and BondingDocument61 pagesIsomerism and BondingkamoNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentNoor AlamNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Test 03 PDFDocument1 page12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Test 03 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sajjad Hussain Sumrra Isomerism (CHEM-305) Inorganic Chemistry-IIDocument48 pagesDr. Sajjad Hussain Sumrra Isomerism (CHEM-305) Inorganic Chemistry-IITanya DilshadNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds Class 12Document112 pagesCoordination Compounds Class 12nm.ananya2008No ratings yet
- Complex Forming Ability of D-Block ElementsDocument53 pagesComplex Forming Ability of D-Block Elementsaleena jayaNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundDocument19 pagesCoordination CompounddeepjoypalNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 Coordination Compounds Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument6 pagesJEE Main 2023 Coordination Compounds Revision Notes - Free PDF Downloadaryan.aru2006No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Test 03Document1 page12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Test 03Raja KushwahNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Imp Isomerism in Coordination Compounds MixDocument8 pages12 Chemistry Imp Isomerism in Coordination Compounds MixMeha JabeenNo ratings yet
- Lecture Powerpoint: ChemistryDocument54 pagesLecture Powerpoint: ChemistryHenry AlemanNo ratings yet
- Activity 22: Monodentate One With Two Such Atoms Is Bidentate, One With Three Such Atoms Is Tridentate, EtcDocument8 pagesActivity 22: Monodentate One With Two Such Atoms Is Bidentate, One With Three Such Atoms Is Tridentate, EtcAhmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Dharampeth M.P. Deo Memorial Science CollegeDocument4 pagesDharampeth M.P. Deo Memorial Science CollegeManoj KhandateNo ratings yet
- Do The Compounds Have The Same Connectivity?Document9 pagesDo The Compounds Have The Same Connectivity?Kushagra SinghNo ratings yet
- 11th Class Chemistry Chapter 12 Study MaterialDocument49 pages11th Class Chemistry Chapter 12 Study MaterialAyushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Neet Chemistry Notes-1Document37 pagesNeet Chemistry Notes-1Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Isomerism in Coordination ChemistryDocument21 pagesIsomerism in Coordination Chemistrym.nouraldenNo ratings yet
- Chem Project Term 1Document21 pagesChem Project Term 1Abishek ArunNo ratings yet
- Transition Metals and Coordination CompoundsDocument54 pagesTransition Metals and Coordination CompoundsCaryl FrancheteNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Class 9 Atoms and MoleculesDocument3 pagesModule 2 Class 9 Atoms and Moleculesmyshachaudhuri75No ratings yet
- IC Lecture1 0Document30 pagesIC Lecture1 0DusuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsDocument64 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsGaurav YadavNo ratings yet
- 10 Coordination Compound2 (1 Orang)Document11 pages10 Coordination Compound2 (1 Orang)Zakiyah Rizkah Nu'manNo ratings yet
- CAPE Unit 2 Chemistry NotesDocument207 pagesCAPE Unit 2 Chemistry NotesAshley Cunningham100% (2)
- Types of IsomerismDocument14 pagesTypes of IsomerismAbdullah MunawarNo ratings yet
- Coordination Complex: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument21 pagesCoordination Complex: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaHasnain Mohammad HanifNo ratings yet
- EXP 3 Geometrical Isomerism CHEM 333Document3 pagesEXP 3 Geometrical Isomerism CHEM 333Abambagade AberaNo ratings yet
- Very Short Answer Questions (PYQ)Document36 pagesVery Short Answer Questions (PYQ)chandra gunashekharanNo ratings yet
- Isomerism Theory Solved and Unsolved With Anwers NKBDocument42 pagesIsomerism Theory Solved and Unsolved With Anwers NKBRajeev Kaushik100% (1)
- Yasemin Celik Chapter3 2022-2023 Part1Document19 pagesYasemin Celik Chapter3 2022-2023 Part1bastezalteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsDocument37 pagesChapter 9 Coordination CompoundsNAVINNo ratings yet
- Isomers HandoutDocument5 pagesIsomers HandoutMohamed MeeranNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds IDocument58 pagesCoordination Compounds IAli Muhammad Kamba60% (5)
- Co-Ordination CompoundsDocument10 pagesCo-Ordination CompoundsTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Naming Coordination CompoundsDocument8 pagesNaming Coordination CompoundsBLi'H'AbieeNo ratings yet
- Xii - Cbse Coordination Chemistry Material (23.11.2022)Document15 pagesXii - Cbse Coordination Chemistry Material (23.11.2022)Sanjana MohanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsDocument14 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsHarry RoyNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lecture Question Isomers2Document19 pages2nd Lecture Question Isomers2Asma GulzarNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii Chemistry CH 9 Coordination Compounds by SajeevDocument2 pagesHsslive Xii Chemistry CH 9 Coordination Compounds by SajeevrasalgafoorrvgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument29 pagesChapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Formula Chapter9 Coordination CompoundsDocument15 pagesChemistry Formula Chapter9 Coordination CompoundsJeshanth JsNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundDocument24 pagesCoordination CompoundAnsari SameerNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Test 05 Answer s2l6 PDFDocument2 pages12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Test 05 Answer s2l6 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) (Answer)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) (Answer)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- CHCHCHBR X Y Z: Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Document1 pageCHCHCHBR X Y Z: Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) (Answers)Document3 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry General Principles and Processes Test 04 PDFDocument1 page12 Chemistry General Principles and Processes Test 04 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Test 04 Answer 12b3 PDFDocument3 pages12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Test 04 Answer 12b3 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds) (Answer)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds) (Answer)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Test 03 PDFDocument1 page12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Test 03 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 01Document1 page12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 01Shyan ShivaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-05 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-05 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Document3 pagesCbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer) Topic: - F-Block Elements: Lanthanoids and ActinoidsDocument1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer) Topic: - F-Block Elements: Lanthanoids and ActinoidsShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 03 PDFDocument1 page12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 03 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 02 PDFDocument2 pages12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 02 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 01 Answer 8b9m PDFDocument2 pages12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 01 Answer 8b9m PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Electrochemistry) (Answers)Document3 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Electrochemistry) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Phase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)