Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aida Model
Uploaded by
Shreya DasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aida Model
Uploaded by
Shreya DasCopyright:
Available Formats
AIDA MODEL
AIDA is an acronym that stands for Attention or Awareness, Interest, Desire and Action. The AIDA model
is widely used in marketing and advertising to describe the steps or stages that occur from the time when a
consumer first becomes aware of a product or brand through to when the consumer trials a product or makes
a purchase decision. Given that many consumers become aware of brands via advertising or marketing
communications, the AIDA model helps to explain how an advertisement or marketing communications
message engages and involves consumers in brand choice. In essence, the AIDA model proposes that
advertising messages need to accomplish a number of tasks in order to move the consumer through a series
of sequential steps from brand awareness through to action (purchase and consumption).
The term, AIDA and the overall approach are commonly attributed to American advertising and sales
pioneer, E. St. Elmo Lewis.[23] In one of his publications on advertising, Lewis postulated at least three
principles to which an advertisement should conform:
The mission of an advertisement is to attract a reader, so that he will look at the advertisement and start to
read it; then to interest him, so that he will continue to read it; then to convince him, so that when he has
read it he will believe it. If an advertisement contains these three qualities of success, it is a successful
advertisement
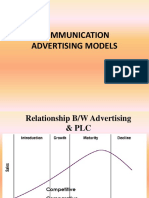
The AIDA model[edit]
Generalised hierarchy of effects sequence
The AIDA model is just one of a class of models known as hierarchy of effects models or hierarchical
models, all of which imply that consumers move through a series of steps or stages when they make
purchase decisions. These models are linear, sequential models built on an assumption that consumers
move through a series of cognitive (thinking) and affective (feeling) stages culminating in a behavioural
stage (doing e.g. purchase or trial) stage.[1]
The steps proposed by the AIDA model are as follows:[2][3]
Attention – The consumer becomes aware of a category, product or brand (usually through
advertising)
↓
Interest – The consumer becomes interested by learning about brand benefits & how the
brand fits with lifestyle
↓
Desire – The consumer develops a favorable disposition towards the brand
↓
Action – The consumer forms a purchase intention, shops around, engages in trial or makes a
purchase.
The basic AIDA model is one of the longest serving hierarchical models, having been in use for
more than a century. Using a hierarchical system, such as AIDA, provides the marketer with a
detailed understanding of how target audiences change over time, and provides insights as to which
types of advertising messages are likely to be more effective at different junctures. Moving from
step to step, the total number of prospects diminishes. This phenomenon is sometimes described as
a "purchase funnel". A relatively large number of potential purchasers become aware of a product
or brand, then a smaller subset becomes interested, with only a relatively small proportion moving
through to the actual purchase. This effect is also known as a "customer funnel", "marketing
funnel", or "sales funnel".
The model is also used extensively in selling and advertising. According to the original model, "the
steps to be taken by the seller at each stage are as follows:
Stage I. Secure attention.
Stage II. Hold attention Through Interest.
Stage III. Arouse Desire.
Stage IV. Create Confidence and Belief.
Stage V. Secure Decision and Action.
Stage VI. Create Satisfaction.
CRITICISM
A major deficiency of the AIDA model, and other hierarchical models, is the absence of post-purchase
effects such as satisfaction, consumption, repeat patronage behaviour and other post-purchase behavioural
intentions such as referrals or participating in the preparation of online product reviews.[10] Other criticisms
include the model's reliance on a linear nature, hierarchical sequence. In empirical studies, the model has
been found to be a poor predictor of actual consumer behaviour.
You might also like
- Role of Creative StrategiesDocument40 pagesRole of Creative StrategiesSunil Bhamu67% (3)
- Are Social Media Replacing Traditional Media in Terms of Brand Equity CreationDocument22 pagesAre Social Media Replacing Traditional Media in Terms of Brand Equity CreationAloysius IvanNo ratings yet
- Social Media's Key Success FactorsDocument15 pagesSocial Media's Key Success Factorsscarscar123No ratings yet
- Hierarchy of Effects ModelDocument6 pagesHierarchy of Effects ModelSawma Pautu100% (1)
- P3 Past Papers Model AnswersDocument211 pagesP3 Past Papers Model AnswersEyad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Sprinkler Sizing en v1Document12 pagesSprinkler Sizing en v1CristianDumitru0% (1)
- Bring Your Gear 2010: Safely, Easily and in StyleDocument76 pagesBring Your Gear 2010: Safely, Easily and in StyleAkoumpakoula TampaoulatoumpaNo ratings yet
- AIDA Model in AdvertisingDocument3 pagesAIDA Model in AdvertisingHằng PhạmNo ratings yet
- Using Social Media For Social Change: Susan MernitDocument30 pagesUsing Social Media For Social Change: Susan MernitodayakaNo ratings yet
- Ethics in AdvertisingDocument26 pagesEthics in AdvertisingJustGKNo ratings yet
- Celebrity Endorsement Impact in MalaysiaDocument14 pagesCelebrity Endorsement Impact in MalaysiaWengSeng WsNo ratings yet
- BUILD PR CampaignDocument27 pagesBUILD PR CampaignRussell DickersonNo ratings yet
- National BrandingDocument35 pagesNational BrandingMonoarul Islam PiashNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument53 pagesConsumer Behavioursoma sekarNo ratings yet
- Advertising Research and Copy TestingDocument15 pagesAdvertising Research and Copy TestingMahantesh KodliNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Name: Viraj S Wadkar DateDocument67 pagesAcknowledgement: Name: Viraj S Wadkar DateViraj WadkarNo ratings yet
- Ca 310 Final Paper-ProjectDocument14 pagesCa 310 Final Paper-Projectapi-282728061No ratings yet
- Campaign Analysis 5 Minute GuideDocument11 pagesCampaign Analysis 5 Minute GuideCarolina Perez GuttNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour: Session 1 Introduction To Consumer Behaviour & Importance To Marketing Management Amir HashmiDocument42 pagesConsumer Behaviour: Session 1 Introduction To Consumer Behaviour & Importance To Marketing Management Amir HashmiSalman ButtNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument6 pagesResearch ProposalAsad Ullah KhalidNo ratings yet
- Consumer Decision Making and Diffusion of InnovationDocument23 pagesConsumer Decision Making and Diffusion of InnovationArham WaseemNo ratings yet
- Unethical Practices in AdvertisingDocument34 pagesUnethical Practices in AdvertisingAyushi Aggarwal100% (1)
- Effectiveness of Online Marketing On ImcDocument6 pagesEffectiveness of Online Marketing On ImcPooja BirajdarNo ratings yet
- Creative Brief of Daia DetergentDocument3 pagesCreative Brief of Daia DetergentrozellynieweeNo ratings yet
- Importance of Branding-NewDocument24 pagesImportance of Branding-NewSri Vidya - PlacementNo ratings yet
- Advertising and Public RelationsDocument34 pagesAdvertising and Public RelationsTahmidur Rahman TonmoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Research Methodology: There Are Two Methods of Collecting Data. They Are: Primary DataDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Research Methodology: There Are Two Methods of Collecting Data. They Are: Primary DataAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Integrated Marketing CommunicationDocument4 pagesIntegrated Marketing Communicationankit20100% (1)
- Bcom 314 - Final Communication PlanDocument11 pagesBcom 314 - Final Communication Planapi-379785768No ratings yet
- AIDA Model of Marketing Student Name Student ID Professor Name DateDocument7 pagesAIDA Model of Marketing Student Name Student ID Professor Name DateGohar MalikNo ratings yet
- What Is The AIDA Model in AdvertisingDocument3 pagesWhat Is The AIDA Model in AdvertisingHằng PhạmNo ratings yet
- Applied Marketing Notes 2Document18 pagesApplied Marketing Notes 2Mobeen KhanNo ratings yet
- Aidas ModelDocument4 pagesAidas ModelShruti HarlalkaNo ratings yet
- Advertising Manegement Sem 3Document9 pagesAdvertising Manegement Sem 3Chaitali Suvagiya SolankiNo ratings yet
- Importance of Measuring The Effectiveness of AdvertisingDocument11 pagesImportance of Measuring The Effectiveness of AdvertisingAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-3: Consumer Behaviour: Service Marketing, MKT 541Document5 pagesUnit-3: Consumer Behaviour: Service Marketing, MKT 541Umesh kathariyaNo ratings yet
- Models of Marketing CommunicationDocument6 pagesModels of Marketing CommunicationRenjul Paravur100% (2)
- TextDocument7 pagesTextGithesh NairNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Notes - BBAD601M - A+BDocument10 pagesModule 2 - Notes - BBAD601M - A+BBunty GhoshNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and Innovation (Rameez Mukhtar)Document1 pageEntrepreneurship and Innovation (Rameez Mukhtar)rameez mukhtarNo ratings yet
- IMC - Unit 2Document30 pagesIMC - Unit 2Yashika TayalNo ratings yet
- Advertising & Sales ManagementDocument78 pagesAdvertising & Sales ManagementKishor Patel90% (10)
- ADVERTISINGDocument90 pagesADVERTISINGPratham SharmaNo ratings yet
- AIDAS ModelDocument5 pagesAIDAS ModelSiddharth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Loyalty SystemDocument3 pagesLoyalty SystemMerveille KalomboNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy of Effects Briefing PaperDocument9 pagesHierarchy of Effects Briefing PaperDana VanDen HeuvelNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing: BY William Asamoah-AppiahDocument64 pagesPrinciples of Marketing: BY William Asamoah-AppiahDaniel RizviNo ratings yet
- Needs: Citation NeededDocument9 pagesNeeds: Citation NeededLaura Maria GalanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Questions: What Is The Difference Between Sales and Marketing?Document2 pagesMarketing Questions: What Is The Difference Between Sales and Marketing?monikam meshramNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On Retail Marketing of Pragati Bakery Ltd. AmrvattiDocument43 pagesDissertation On Retail Marketing of Pragati Bakery Ltd. AmrvattiSandip NaradNo ratings yet
- Marketing Communication StrategyDocument17 pagesMarketing Communication StrategySunil Kumar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- MM Upadeted One 1-5Document5 pagesMM Upadeted One 1-5Vishal AnandNo ratings yet
- Advertising ModelDocument14 pagesAdvertising ModeljaweriaNo ratings yet
- Piyush Consumer BehaviourDocument19 pagesPiyush Consumer BehaviourNehal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction: Executive SummaryDocument31 pagesCustomer Satisfaction: Executive SummaryChandrashekar AkkiyavarNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument48 pagesInternational BusinessANJAN GOGOINo ratings yet
- AIDADocument1 pageAIDAAndy GianNo ratings yet
- Response Hierarchy: ModelDocument32 pagesResponse Hierarchy: ModelAkash GoreNo ratings yet
- Impact of AdvertisingDocument13 pagesImpact of AdvertisingRajanVermaNo ratings yet
- Sales and Marketing ConceptDocument20 pagesSales and Marketing ConceptSarvesh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- List of Useful Related Sales & Marketing TerminologyDocument16 pagesList of Useful Related Sales & Marketing TerminologyyeswanthNo ratings yet
- Model of Buyer Behaviour For A Sports FootwearDocument5 pagesModel of Buyer Behaviour For A Sports FootwearKESS DEAMETANo ratings yet
- Advertising UNIT - IIDocument13 pagesAdvertising UNIT - IIDr.B.R. kumarNo ratings yet
- Pyramid Type Plate Bending MachineDocument10 pagesPyramid Type Plate Bending MachineAswin JosephNo ratings yet
- PTW Site Instruction NewDocument17 pagesPTW Site Instruction NewAnonymous JtYvKt5XENo ratings yet
- Construction Project - Life Cycle PhasesDocument4 pagesConstruction Project - Life Cycle Phasesaymanmomani2111No ratings yet
- MATH CIDAM - PRECALCULUS (Midterm)Document4 pagesMATH CIDAM - PRECALCULUS (Midterm)Amy MendiolaNo ratings yet
- KRAS QC12K-4X2500 Hydraulic Shearing Machine With E21S ControllerDocument3 pagesKRAS QC12K-4X2500 Hydraulic Shearing Machine With E21S ControllerJohan Sneider100% (1)
- File RecordsDocument161 pagesFile RecordsAtharva Thite100% (2)
- Civil Rights Vocabulary Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesCivil Rights Vocabulary Lesson PlanKati ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Engineering Ethics in Practice ShorterDocument79 pagesEngineering Ethics in Practice ShorterPrashanta NaikNo ratings yet
- Atoma Amd Mol&Us CCTK) : 2Nd ErmDocument4 pagesAtoma Amd Mol&Us CCTK) : 2Nd ErmjanviNo ratings yet
- Cap1 - Engineering in TimeDocument12 pagesCap1 - Engineering in TimeHair Lopez100% (1)
- 5620 SAM Rel 14 License Point Configuration ToolDocument416 pages5620 SAM Rel 14 License Point Configuration Toolluis100% (1)
- ISO Position ToleranceDocument15 pagesISO Position ToleranceНиколай КалугинNo ratings yet
- Diverging Lenses - Object-Image Relations: Previously in Lesson 5 Double Concave LensesDocument2 pagesDiverging Lenses - Object-Image Relations: Previously in Lesson 5 Double Concave LensesleonNo ratings yet
- Superlab Manual PDFDocument76 pagesSuperlab Manual PDFGabriela Soares100% (1)
- Section 1 Company Overview StandardsDocument34 pagesSection 1 Company Overview StandardsChris MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Glass - ENDocument2 pagesAcoustic Glass - ENpeterandreaNo ratings yet
- Blackberry: Terms of Use Find Out MoreDocument21 pagesBlackberry: Terms of Use Find Out MoreSonu SarswatNo ratings yet
- Puma PypDocument20 pagesPuma PypPrashanshaBahetiNo ratings yet
- Does Adding Salt To Water Makes It Boil FasterDocument1 pageDoes Adding Salt To Water Makes It Boil Fasterfelixcouture2007No ratings yet
- How To Install Metal LathDocument2 pagesHow To Install Metal LathKfir BenishtiNo ratings yet
- Topic One ProcurementDocument35 pagesTopic One ProcurementSaid Sabri KibwanaNo ratings yet
- Rsi r2 Super Rsi FaqDocument14 pagesRsi r2 Super Rsi FaqChandrasekar Chandramohan100% (1)
- WWW Ranker Com List Best-Isekai-Manga-Recommendations Ranker-AnimeDocument8 pagesWWW Ranker Com List Best-Isekai-Manga-Recommendations Ranker-AnimeDestiny EasonNo ratings yet
- L 11Document3 pagesL 11trangNo ratings yet
- .CLP Delta - DVP-ES2 - EX2 - SS2 - SA2 - SX2 - SE&TP-Program - O - EN - 20130222 EDITADODocument782 pages.CLP Delta - DVP-ES2 - EX2 - SS2 - SA2 - SX2 - SE&TP-Program - O - EN - 20130222 EDITADOMarcelo JesusNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Part2 csc159Document26 pagesCHAPTER 2 Part2 csc159Wan Syazwan ImanNo ratings yet
- Importance of Porosity - Permeability Relationship in Sandstone Petrophysical PropertiesDocument61 pagesImportance of Porosity - Permeability Relationship in Sandstone Petrophysical PropertiesjrtnNo ratings yet