Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reflection What Part of Plant Does
Reflection What Part of Plant Does
Uploaded by
Maitha ACopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reflection What Part of Plant Does
Reflection What Part of Plant Does
Uploaded by
Maitha ACopyright:
Available Formats
AAWC Lesson Reflection
School: Shaikha Bint Suroor Class: 1 A Date of Observation: 22/10
Select:
Identify a specific feature of the lesson:
The lesson was about plants, and the outline was to identify what part of plant does.
Describe:
Who is the lesson for?
Where did the lesson take place?
What were you trying to achieve in your lesson?
What did the students do?
The lesson was about Identify what each part of plant does. I taught the lesson in the
classroom. The previous lesson the students learned about Part of the plant, in this lesson,
she taught them to Identify what each part of plant does.
A teacher was trying to achieve goals, like Implementing Learning and to go through the
learning outcome and always look for where the student has trouble and work on it to
make it improve by a variety of strategies.
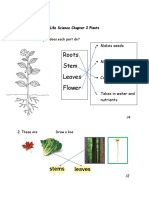
In the starter, the teacher tell the students what each part of plant job
Flower: This part makes seeds.
Leaf : This part makes food for the plant.
Stem: This part carries food and water through the plant and holds the plant up.
Root: This part soaks up water from the soil to the plant and holds it in the ground.
Then, she will ask students to repeat after her and check for comprehension.
Analyze:
Why do you think the students responded the way that they did?
How well did your teaching relate to the students’ prior understanding?
How well did you engage the students?
I think that students responded to this activity the way that they did because a teacher
introduces and model then practice. So, the learner did understand the concept and
answer the right answer. A teacher use drawing the plant with writing the parts of the
plant job, explaining all of the parts and Thumbs up and down to answer. For example,
she pointed to the roots and ask the student does this part suck the water? If you think yes
thumbs up if you think it’s not thumbs down, students make thumbs down and the teacher
asks: Hmm if it’s does not suck the water then what is it?
The learner answer: carries food and water
A teacher linked the prior knowledge by telling a short story and show them the plants
and whenever we saw it we know that this is plant but we don’t know the parts of it.
The teacher engaged the students with a game because it allows the student to
comprehends the parts of the plant job with pointing and telling the names and job.
Students enjoyed it a lot.
Appraise:
Explain the nature of the experience from the students’ perspective
Did your lesson meet your teaching goals? Why?/Why not?
The educator used hands-on activity to engage the students. According to Thankful, Fast
forward to the early 2000's, and increasing pressure for drastic improvements on
national test scores led to a nationwide shift in education. Schools were faced with the
challenge of improving test scores while also staying under budget. They were ultimately
forced to cut programs like sewing and home economics, and focus their attention on
creating a more lecture based curriculum geared towards improving test scores and
decreasing spending. Later, after STEM classes were deemed more desirable and
ultimately affordable, arts programs, once part of schools' core class offerings, were cut.
The teacher used hands-on activity for the learner. Students were learning by using
real materials like straw, cupcake plastic and wool to create a plant it improv es the
student cognitive and fine-motor skills.
I met my goals because I used check list to check for students comprehension and it
shows that everyone understands.
Transform:
How might you enhance student learning of this lesson in the future?
What are the implications for your professional practice?
In the future, I would like to introduce model learning in a way that I’ll take the students
to see the plants, trees and flower in outside environment to feel and watch the plant in
real.
As the Responsive Classroom argues that, “Interactive Modeling is a simple, quickly
paced way of teaching that can lead students to a stronger mastery of skills than
traditional modeling. It’s effective for teaching any skill or procedure that students need to
do in a specific way, such as filling out an answer sheet or talking with a partner about a
reading selection. Interactive Modeling works because, in contrast to lecturing or
traditional modeling, it creates a clear mental image of the expected behavior for students,
fully engages them in noticing details about it, and immediately gives them a chance to
practice and receive teacher feedback (ResponsiveClassroom, 2013).
A teacher developing idea and practices about science performance assessment:
Successes, stumbling blocks, and implications for professional development. Since it’s
little bit harder for them because of the vocabs that they don’t know.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 5CO03 - Assessment Brief and MarkSheet OCT 22Document21 pages5CO03 - Assessment Brief and MarkSheet OCT 22Neelam MehtabNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Organisational Behavior Lo1,2Document24 pagesOrganisational Behavior Lo1,2Muhammed Musthafa86% (7)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Wigfield & Eccles - 35 Years of Research On Students'Document38 pagesWigfield & Eccles - 35 Years of Research On Students'Rubén Páez DíazNo ratings yet
- Online Teaching Practicum GuidelinesDocument11 pagesOnline Teaching Practicum GuidelinesMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Estimate Quotient ReflectionDocument2 pagesEstimate Quotient ReflectionMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Estimate QuotientDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Estimate QuotientMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Appendix 2 Feedback Observation (Time)Document2 pagesAppendix 2 Feedback Observation (Time)Maitha ANo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Template: Identify Patterns and Use Procedures in Division ToDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Template: Identify Patterns and Use Procedures in Division ToMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Appendix 2: MCT/MST Formative Teaching Observation Feedback & Assessment RubricDocument3 pagesAppendix 2: MCT/MST Formative Teaching Observation Feedback & Assessment RubricMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Appendix 2: MCT/MST Formative Teaching Observation Feedback & Assessment RubricDocument2 pagesAppendix 2: MCT/MST Formative Teaching Observation Feedback & Assessment RubricMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Appendix 2 Feedback Observation (Time)Document2 pagesAppendix 2 Feedback Observation (Time)Maitha ANo ratings yet
- MST/MCT Holistic Grade C+Document14 pagesMST/MCT Holistic Grade C+Maitha ANo ratings yet
- Maitha Abdulazeez Hasan: Personal InformationDocument2 pagesMaitha Abdulazeez Hasan: Personal InformationMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Appendix 2 Feedback Observation (Fractions)Document2 pagesAppendix 2 Feedback Observation (Fractions)Maitha ANo ratings yet
- Appendix 2 Feedback Observation (Intervals)Document2 pagesAppendix 2 Feedback Observation (Intervals)Maitha ANo ratings yet
- Evaluate Expressions GR 3Document5 pagesEvaluate Expressions GR 3Maitha ANo ratings yet
- 3 Factors Lesson PlanDocument6 pages3 Factors Lesson PlanMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Fraction On Number LineDocument6 pagesFraction On Number LineMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Answer Keys Plant ExamDocument4 pagesAnswer Keys Plant ExamMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Appendix 1: Lesson Plan (Template) : I Am Working On: Classroom Management, Implementing LearningDocument11 pagesAppendix 1: Lesson Plan (Template) : I Am Working On: Classroom Management, Implementing LearningMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Reflection Subtraction 3.2Document2 pagesReflection Subtraction 3.2Maitha ANo ratings yet
- Part of Plant Reflection 3.2Document3 pagesPart of Plant Reflection 3.2Maitha ANo ratings yet
- Reflection 3.2 Letter WWDocument2 pagesReflection 3.2 Letter WWMaitha ANo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Discussion Method of TeachingDocument18 pagesLaboratory and Discussion Method of TeachingEmmanuel OrimogunjeNo ratings yet
- JamaMusse J Somali Corpus StateOfTheArt PDFDocument8 pagesJamaMusse J Somali Corpus StateOfTheArt PDFAhmedNo ratings yet
- Revista Stiinte Politice Issue 42Document264 pagesRevista Stiinte Politice Issue 42Costel111No ratings yet
- 2023 BUSINESS STUDIES GRADE 1O TERM 3 SBA TASK PROJECT (Afrikaans)Document15 pages2023 BUSINESS STUDIES GRADE 1O TERM 3 SBA TASK PROJECT (Afrikaans)Anika Du PreezNo ratings yet
- Ieo Sample Paper Class-10Document2 pagesIeo Sample Paper Class-10name nameNo ratings yet
- Lpe2501 SCL Worksheet 2 (Week 4)Document4 pagesLpe2501 SCL Worksheet 2 (Week 4)yifei YanNo ratings yet
- Teachers Guidelines On Incentive and RewardDocument3 pagesTeachers Guidelines On Incentive and RewardReggie Regalado100% (21)
- SIS QuestionnaireDocument6 pagesSIS QuestionnaireDanielicah CruzNo ratings yet
- Developmental Model of Intercultural Sensitivity. PerceptionsDocument3 pagesDevelopmental Model of Intercultural Sensitivity. PerceptionsErwejkNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing-Lecture NoteDocument36 pagesCreative Writing-Lecture NoteBedada NigusieNo ratings yet
- Kallidus Insight Guide Learning ArchitectureDocument4 pagesKallidus Insight Guide Learning ArchitectureCoolminded CoolmindedNo ratings yet
- Opcrf 2021Document98 pagesOpcrf 2021BrianSantiagoNo ratings yet
- Rules of LifeDocument20 pagesRules of LifeUmamaheswarKA100% (1)
- Decision-Forcing CasesDocument12 pagesDecision-Forcing CasesBruce Ivar GudmundssonNo ratings yet
- Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Lac 2: Department of EducationDocument4 pagesMost Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Lac 2: Department of EducationDaniel DarantinaoNo ratings yet
- Turner Pascoe Online Projects WeeblyDocument2 pagesTurner Pascoe Online Projects Weeblyapi-594503997No ratings yet
- Curriculum StudiesDocument12 pagesCurriculum StudiesBonnieArmstrongGreeneNo ratings yet
- Constraints N 2Document4 pagesConstraints N 2linguist_nNo ratings yet
- Sense Memory 11: Private MomentDocument5 pagesSense Memory 11: Private MomentJonathan Samarro100% (4)
- Podcast Rubric Y7Document1 pagePodcast Rubric Y7owenmccNo ratings yet
- Discipline Vs Punishment & Reinforcement - Catuira IvyDocument16 pagesDiscipline Vs Punishment & Reinforcement - Catuira IvyIvy Guillarte CatuiraNo ratings yet
- Motivational Interviewing ManualDocument206 pagesMotivational Interviewing ManualSean Cho100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: Block 1 Informal AssessmentDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Block 1 Informal AssessmentTSS DTNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan For COT WEEK 27Document14 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan For COT WEEK 27Aivan Chris M RielNo ratings yet
- Preceptor Handbook For Nursing EducationDocument41 pagesPreceptor Handbook For Nursing EducationBryan Mae H. Degorio0% (1)
- 2022 Year 2nd Semester Syllabus: Basic InformationDocument4 pages2022 Year 2nd Semester Syllabus: Basic InformationSaddiq Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Direction of FitDocument4 pagesDirection of FitMatheus de BritoNo ratings yet