Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4 Electricity Exam Questions
Uploaded by
Noor Ulain NabeelaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4 Electricity Exam Questions
Uploaded by
Noor Ulain NabeelaCopyright:
Available Formats
P2, Chapter 4
Name …………………………………………………….………… Class …………………………..
Current electricity
1 A plastic rod is rubbed with a dry cloth.
a Explain how the rod becomes negatively charged.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(3)
b What charge is left on the cloth?
....................................................................................................................................
(1)
c What happens if the negatively charged rod is brought close to another
negatively charged rod?
....................................................................................................................................
(1)
2 a Complete the table of circuit symbols and their names. (5)
Circuit symbol Name
ii ammeter
iii
New AQA GCSE Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2011 1
P2, Chapter 4
Name …………………………………………………….………… Class …………………………..
iv LDR
b Copy and complete the following sentences using the list of words and
phrases below. Each word can be used once, more than once or not at all.
energy transferred charge resistance voltage
Electric current is a flow of ……………………
The potential difference between two points in a circuit is the
…………………… per unit of …………………… that passes between the
points.
The greater the …………………… the lower the current for a given potential
difference. (4)
3 Complete the following calculations. Write down the equation you use. Show clearly
how you work out your answer and give the unit.
a i What is the potential difference between A and B?
....................................................................................................................................
(1)
ii The potential difference across the 15 Ω resistor is 5 V.
What is the potential difference across the 12 Ω resistor?
New AQA GCSE Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2011 2
P2, Chapter 4
Name …………………………………………………….………… Class …………………………..
....................................................................................................................................
(1)
b i Calculate the combined resistance of the 12 Ω and the 15 Ω resistors in
series.
....................................................................................................................................
(1)
ii Calculate the current that flows through the circuit at X.
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
iii Calculate the current flowing through the circuit at Y.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(1)
c Calculate the resistance of the resistor labelled R.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
d Calculate the charge that flows through resistor R in 2 minutes.
....................................................................................................................................
New AQA GCSE Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2011 3
P2, Chapter 4
Name …………………………………………………….………… Class …………………………..
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(3)
e Calculate the work done (energy transferred) by the cell if the total charge
that has flowed through it is 3000 C.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
New AQA GCSE Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2011 4
P2, Chapter 4
Name …………………………………………………….………… Class …………………………..
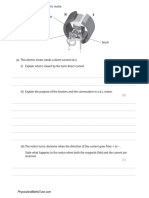
4 a Sketch and label a graph of current against potential difference for a diode.
....................................................................................................................................
(3)
b The graph of current against potential difference for a filament bulb is shown.
i Calculate the potential difference when the resistance of the filament bulb is 2 Ω
when the current is 1.6 A. Write down the equation you use. Show clearly how you
work out your answer and give the unit.
....................................................................................................................................
New AQA GCSE Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2011 5
P2, Chapter 4
Name …………………………………………………….………… Class …………………………..
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
ii Calculate the resistance at a potential difference of 12 V. Write down the
equation you use. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(3)
c In this question you will be assessed on using good English, organising
information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate.
Explain the change in resistance of the filament bulb in terms of ions and
electrons.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
New AQA GCSE Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2011 6
P2, Chapter 4
Name …………………………………………………….………… Class …………………………..
....................................................................................................................................
[H] (6)
New AQA GCSE Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2011 7
You might also like
- All-Inclusive Calculations in PhysicsDocument484 pagesAll-Inclusive Calculations in PhysicsMuhammad Olushola80% (98)
- Year 7 and 8 Textbooks and Websites.96222304 PDFDocument4 pagesYear 7 and 8 Textbooks and Websites.96222304 PDFNoor Ulain Nabeela17% (6)
- SDTS-15 Digital Timer Manual V2Document2 pagesSDTS-15 Digital Timer Manual V2mica50% (2)
- PCA-4125 Manual Rev 021Document139 pagesPCA-4125 Manual Rev 021Sergio Medina0% (1)
- Critical Thinking WorkbookDocument32 pagesCritical Thinking Workbookajmcrae0% (1)
- Physics Grade 10Document228 pagesPhysics Grade 10Jan92% (26)
- Test 104Document45 pagesTest 104Rinalyn-Oscar Gamboa Magtibay56% (9)
- Xeno ManualDocument122 pagesXeno Manualzbhp z100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Mains Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapter 5 Mains Exam QuestionsNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Forces Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Forces Exam QuestionsNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Current, Potential Difference - Resistance 1 QPDocument19 pagesCurrent, Potential Difference - Resistance 1 QPSheikhNo ratings yet
- Electromotive Force & Internal Resistance QPDocument10 pagesElectromotive Force & Internal Resistance QPcrochetbyellaa4No ratings yet
- Current, Potential Difference & Resistance 2 QPDocument17 pagesCurrent, Potential Difference & Resistance 2 QPXuan HouNo ratings yet
- Capacitors Revision Worksheet: Addu High School Hithadhoo/AdduDocument8 pagesCapacitors Revision Worksheet: Addu High School Hithadhoo/AdduDhan Bahadhur Mr.Dhan Bahadur BoharaNo ratings yet
- Current, Potential Difference & Resistance 1Document17 pagesCurrent, Potential Difference & Resistance 1Juyeon NamNo ratings yet
- Y8 EyaDocument12 pagesY8 Eyatella idrisNo ratings yet
- Electro ChemistryDocument13 pagesElectro ChemistryRameenNo ratings yet
- Arenes QuestionsDocument18 pagesArenes Questionscare3ashNo ratings yet
- Year-7-Science-revision 2Document17 pagesYear-7-Science-revision 2Cally ChewNo ratings yet
- Potential Divider QDocument9 pagesPotential Divider QJellyfishNo ratings yet
- 3.7.4.4 Capacitor Charge and DischargeDocument83 pages3.7.4.4 Capacitor Charge and DischargeModathir salimNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Internal Resistance PDFDocument16 pages2.4 Internal Resistance PDFschlemielzNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper TwoDocument11 pagesPhysics Paper Twohmatara8No ratings yet
- WCH06 01 Que 20140514Document12 pagesWCH06 01 Que 20140514Paras AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Energy Change in A System QPDocument14 pagesEnergy Change in A System QPxshahadxsaadx2009No ratings yet
- P1 3 The Usefulness of Electrical Appliances StandDocument59 pagesP1 3 The Usefulness of Electrical Appliances StandjesudassajNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic Capacitor For Pulse GenerationDocument148 pagesElectrolytic Capacitor For Pulse Generationmohi jefriNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Solar Energy Conversion-CRC PressDocument491 pagesThe Physics of Solar Energy Conversion-CRC PressgerardoNo ratings yet
- Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table Chemistry Form 2 Topical Questions and AnswersDocument27 pagesStructure of the Atom and the Periodic Table Chemistry Form 2 Topical Questions and Answersdonaldsonvincent9No ratings yet
- P2 Revision Booklet Static Electricity: Medium (Grade C)Document10 pagesP2 Revision Booklet Static Electricity: Medium (Grade C)Prarthana VinothNo ratings yet
- Week 19 Questions (FF)Document4 pagesWeek 19 Questions (FF)Solace HusseinNo ratings yet
- P3 10 Motor EffectDocument58 pagesP3 10 Motor EffectHiruni FernandoNo ratings yet
- EScholarship UC Item 9sr0c5sxDocument136 pagesEScholarship UC Item 9sr0c5sxLiviu BadeaNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Semester 1 Exam ReviewDocument280 pagesIB Physics Semester 1 Exam Reviewaryamandoc100% (3)
- 360 Sci / P1a.10 You're in Charge SQ 09 - 10Document7 pages360 Sci / P1a.10 You're in Charge SQ 09 - 10Paul BurgessNo ratings yet
- Electro ChemistryDocument0 pagesElectro ChemistryseekforheavenNo ratings yet
- Design Substrate Integrated Waveguide Slot ArrayDocument40 pagesDesign Substrate Integrated Waveguide Slot ArraybluewolfNo ratings yet
- 20.5 Electromagnetic InductionDocument41 pages20.5 Electromagnetic InductionRageifyNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 15Document26 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 15Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- HW On Energy and PhotonDocument8 pagesHW On Energy and PhotonTony CliftonNo ratings yet
- Sphere Technical GuideDocument22 pagesSphere Technical GuidePrabhu Raj HarakangiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atomic Structure QSDocument51 pages1.1 Atomic Structure QSakilNo ratings yet
- Defstan 61-12PT5Document24 pagesDefstan 61-12PT5Hattar MNo ratings yet
- P4.3 Evaporation QuestionsDocument9 pagesP4.3 Evaporation QuestionsAndreas LambriasNo ratings yet
- Circuit QuestionsDocument36 pagesCircuit QuestionsMuhammad TauseefNo ratings yet
- Energy Changesina SystemDocument74 pagesEnergy Changesina SystemCally ChewNo ratings yet
- GroupIV WSDocument14 pagesGroupIV WSMaryam RaiNo ratings yet
- Discovery of the Electron ChargeDocument23 pagesDiscovery of the Electron ChargePa GesNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Exam Questions AS: Minutes MarksDocument75 pagesMechanics Exam Questions AS: Minutes MarksSheikh SamirNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions PDFDocument9 pagesRevision Questions PDFmwagweNo ratings yet
- 5054 s12 QP 22Document16 pages5054 s12 QP 22xiaokiaNo ratings yet
- 2004-Bruckner_Thesis_Simulation and Modeling of the HD, Thrml Beh of FoilDocument163 pages2004-Bruckner_Thesis_Simulation and Modeling of the HD, Thrml Beh of FoilAlex CooperNo ratings yet
- Simplified Constructibility.1.0Document71 pagesSimplified Constructibility.1.0mikeNo ratings yet
- Using electromagnets investigationDocument10 pagesUsing electromagnets investigationAyesha HussainNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Questions NO MOMENTUM and Answers in One FileDocument92 pagesMechanics Questions NO MOMENTUM and Answers in One FileFin Brickman100% (1)
- Internal ResistanceDocument4 pagesInternal Resistancenewabrown1012No ratings yet
- UdkdfhvkdhfnfDocument12 pagesUdkdfhvkdhfnfG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Steam TablesDocument45 pagesSteam Tablesabdalfadel younisNo ratings yet
- Q1. The Diagram Below Shows Part of An Energy Level Diagram For A Hydrogen AtomDocument8 pagesQ1. The Diagram Below Shows Part of An Energy Level Diagram For A Hydrogen AtomTony CliftonNo ratings yet
- Current-Voltage Characteristics QPDocument12 pagesCurrent-Voltage Characteristics QPJohnNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties & CalorimetryDocument3 pagesThermal Properties & CalorimetryGajendraNo ratings yet
- Nodal and Mesh Equations - Circuit TheoremsDocument2 pagesNodal and Mesh Equations - Circuit TheoremsRoberto Carlos Urquiola AyalaNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry: Topic 15 - Transition Metals and Complex IonsDocument15 pagesA Level Chemistry: Topic 15 - Transition Metals and Complex IonsKizzy-Anne BoatswainNo ratings yet
- Ls Dyna Theory Manual 2006Document680 pagesLs Dyna Theory Manual 2006Gerardo FranckNo ratings yet
- Platform Interference in Wireless Systems: Models, Measurement, and MitigationFrom EverandPlatform Interference in Wireless Systems: Models, Measurement, and MitigationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Science 9 Chemistry Topic 3Document19 pagesScience 9 Chemistry Topic 3Noor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Physical ScienceDocument9 pagesGrade 8 Physical ScienceNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Electronic Configuration BC Science - AnsDocument2 pagesWorksheet Electronic Configuration BC Science - AnsNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Year 11 GCSE Revision Guidance and Exam Booklet Solihull PDFDocument27 pagesYear 11 GCSE Revision Guidance and Exam Booklet Solihull PDFNoor Ulain Nabeela83% (6)
- Yellowstone Story and WorksheetDocument4 pagesYellowstone Story and WorksheetNoor Ulain Nabeela0% (1)
- Ecology Unit PacketDocument30 pagesEcology Unit PacketNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Density and Volume - 1Document3 pagesDensity and Volume - 1Noor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- 7a Summary SheetDocument2 pages7a Summary SheetNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Target Aqa Gcse Combined Science Grade 5 Physics Unit 6 Graph SkillsDocument8 pagesTarget Aqa Gcse Combined Science Grade 5 Physics Unit 6 Graph SkillsNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Target 7 Edexcel Single Science Chem WB Unit 7Document8 pagesTarget 7 Edexcel Single Science Chem WB Unit 7Noor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Physics Separate Particle ModelDocument13 pagesPhysics Separate Particle ModelNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- IBT 2012 Science Year 3 PDFDocument1 pageIBT 2012 Science Year 3 PDFNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Wave MotionDocument41 pagesWave MotionyididiyayibNo ratings yet
- 9HW Knowing The Periodic TableDocument1 page9HW Knowing The Periodic TableNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines Unit PacketDocument24 pagesSimple Machines Unit PacketNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganisationDocument1 pageLevels of OrganisationNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Wave Speed Equation PracticeDocument3 pagesWave Speed Equation Practicechristiecherry100% (1)
- CBSE Class 8 Science WorksheetDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science WorksheetNoor Ulain Nabeela100% (1)
- GPFY Chapter 4 Molecules ATDocument2 pagesGPFY Chapter 4 Molecules ATNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions For Chapter 5, ExpansionDocument1 pageAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions For Chapter 5, ExpansionclydeNo ratings yet
- GPFY Chapter 34 Magnetism ATDocument2 pagesGPFY Chapter 34 Magnetism ATNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Table - Atoms-And-Elements-Questions.137948609Document2 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodic Table - Atoms-And-Elements-Questions.137948609Noor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- GPFY Chapter 26 Lenses ATDocument2 pagesGPFY Chapter 26 Lenses ATNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- GPFY Chapter 21 Waves ATDocument1 pageGPFY Chapter 21 Waves ATNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- 2007SciKS3T3 6paper2 PrimaryTools - Co.ukDocument36 pages2007SciKS3T3 6paper2 PrimaryTools - Co.ukNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- 153D3F2BFF7CFF0729EB5088345643CE.docxDocument10 pages153D3F2BFF7CFF0729EB5088345643CE.docxNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- DD8B00CA674E7B18535C51A13DF62FDFDocument2 pagesDD8B00CA674E7B18535C51A13DF62FDFNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Panasonic - VRLA Handbook 2013Document70 pagesPanasonic - VRLA Handbook 2013hendra20No ratings yet
- Service Manual: Micro-Tech - 1200Document43 pagesService Manual: Micro-Tech - 1200ALEJANDRONo ratings yet
- Water Leak Detection SystemsDocument9 pagesWater Leak Detection SystemsAnitha JebarajNo ratings yet
- Fna41560 1008744 PDFDocument18 pagesFna41560 1008744 PDFLeandro RibeiroNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument23 pagesSeminaraartitomar47_8332176No ratings yet
- Water Saturation From Electric Logs TotalDocument12 pagesWater Saturation From Electric Logs TotalAlfredo SGNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Conical ScanDocument11 pagesBlock Diagram of Conical Scanvasudeva sharmaNo ratings yet
- HT33-TX Series Tower Online UPS: 10-40kVA (380V/400V/415V)Document1 pageHT33-TX Series Tower Online UPS: 10-40kVA (380V/400V/415V)dhaferNo ratings yet
- Filler Wire For MIG/MAG Welding IRS M-46-2003 (With Amendment No.1)Document1 pageFiller Wire For MIG/MAG Welding IRS M-46-2003 (With Amendment No.1)Lakhwant Singh KhalsaNo ratings yet
- Ancillary Services NotesDocument31 pagesAncillary Services NotesRick JordanNo ratings yet
- SWCNT ScapsDocument10 pagesSWCNT ScapsMd Arif Ul Islam-KowshikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Network TheoremsDocument79 pagesChapter 9 Network TheoremsShajahan ShariefNo ratings yet
- Gestra Level Control Monitoring LimitationDocument7 pagesGestra Level Control Monitoring LimitationVoicu StaneseNo ratings yet
- Datasheet - Sun (5 25) K sg01hp3 Eu - 230626 - enDocument2 pagesDatasheet - Sun (5 25) K sg01hp3 Eu - 230626 - enPhyo WaiNo ratings yet
- The Need For Harmonic Modeling and Mitigation of Generator ApplicationsDocument8 pagesThe Need For Harmonic Modeling and Mitigation of Generator ApplicationssnfulNo ratings yet
- Control Exercise Sheets 2021Document13 pagesControl Exercise Sheets 2021周暐凱No ratings yet
- Is 2259 1963 PDFDocument23 pagesIs 2259 1963 PDFrohanmanimaniNo ratings yet
- V. Mosfet PDFDocument33 pagesV. Mosfet PDFleeminho_janxiNo ratings yet
- EasyRET Low-Band 2-Port Antenna with 1 Integrated RCU - 1.4m SpecsDocument1 pageEasyRET Low-Band 2-Port Antenna with 1 Integrated RCU - 1.4m SpecsWaleed HasNo ratings yet
- 1 The Diagram Shows An Electric Motor. N SDocument13 pages1 The Diagram Shows An Electric Motor. N SGema Putra MahardhikaNo ratings yet
- Labtech Basic Electricity Experiment ResultsDocument143 pagesLabtech Basic Electricity Experiment ResultsMayang Enggar KusumastutiNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Specifications and CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesDC Motor Specifications and Characteristicsjonoc90No ratings yet
- Nikola Tesla DC Power Supplies (PDFDrive)Document132 pagesNikola Tesla DC Power Supplies (PDFDrive)charlyvegaNo ratings yet
- Poster FDTD PDFDocument1 pagePoster FDTD PDFabdallah meziti-proNo ratings yet
- Access Full Complete Solution Manual Here: Chapter 1 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAccess Full Complete Solution Manual Here: Chapter 1 SolutionsAnanna TithiNo ratings yet
- Application Guide: Application Guide P12X/En Ap/G75 Micom P120/P121/P122/P123Document78 pagesApplication Guide: Application Guide P12X/En Ap/G75 Micom P120/P121/P122/P123JonatanNo ratings yet