Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Radio Finals
Radio Finals
Uploaded by
Chethran0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Radio-Finals.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesRadio Finals
Radio Finals
Uploaded by
ChethranCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Radiology Finals Pointers as noted by microadenomas seek medical attention
Samira V. bec of abnormal hormone secretion
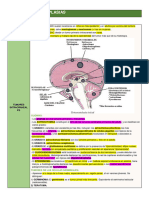
19. Craniopharyngoma – most are suprasellar
NERVOUS SYSTEM within the pituitary fossa (Rathke’s area)
20. Schwannoma – most common tumor of
1. CT scan is the technique of choice for… cerebellopontine angle
2. X-ray & UTZ in neonates & infants, use 21. Metastasis – hematogenous spread
the open fontanels 22. Primary possible sites of Metastasis –
3. Physiologic intracranial calcifications melanoma, lung, breast, colon, kidney
4. Pineal gland calcification – almost always 23. Subdural hematoma – crescentic
present in the adult configuration
5. Choroid plexus calcification – frequently 24. Epidural hematoma – result of injury to
seen at the glomera (atria of L ventricles) meningeal vessels (arterial); it is a
6. Dural calcification – plaque like neurosurgical emergency; occur between
calcification; maybe part of the basal cell the dura and calvaria – constrained
nevus syndrome resulting in biconvex configuration
7. Study the difference of Cytotoxic Edema & 25. Subdural & epidural empyema – may
Vasogenic Edema extend to interhemispheric fissure
8. Cytotoxic Edema – seen in strokes, 26. Cerebritis and brain abscess – most often
hypoxemic injury, cortical edema from from hematogenous dissemination of
status epilepticus; seen in gray matter infectious agent, often from the lung; ring
9. Vasogenic edema – seen in metastatic or enhancement become apparent
primary neoplasm, infections; primarily a 27. Atypical bacteria, fungi & parasites: Taenia
white matter phenomenon solium – encysted larvae dies eliciting
10. Neoplasm Incidence: gliomas – 43%; inflammatory reaction leading to seizures
meningiomas – 15% and ring enhancing brain lesions
11. Gliomas – Grade 4 are gliobastoma 28. Cerebral infarction: MRI findings –
multiforme (most malignant) demonstrates ischemic changes earlier
12. Glioblastoma multiforme – most common than CT
supratentorial glioma 29. Saccular Aneurysms: Most common sites –
13. Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma – low grade proximal segment of MCA, anterior
astrocytoma that occurs in children communicating artery, junction between
14. Meningioma – extraaxial tumors that arise the internal carotid & posterior cerebral
from the arachnoid artery
15. Meningioma common sites: superior 30. Multiple Myeloma – salt and pepper
sagittal sinus, region of tuberculum sellae, appearance
edge of sphenoidal ridge, margin of falx
cerebri & tentorium OSSEOUS SYSTEM
16. Meningioma – derived blood supply from
1. Traumatic Lesions of Bones: Incomplete
arteries supplying the dura
fractures – greenstick (hickory stick or
17. Meningioma – sand like deposits
willowy) perforates cortex & ramify
(psammoma bodies)
within the medullary bone; torus
18. Pituitary adenoma – macroadenomas are
(buckling) insufficient in force to create
usually hormonally inactive;
a complete discontinuity of bone, but hyperostosis chronic osteomyelitis;
sufficient to produce buckling Layered/laminated/ onion-skin Ewing’s
2. Traumatic Lesions of Bones: Linear – tumor; hair on end Ewing’s tumor;
segmental fracture lines isolate a sunburst osteosarcoma; buttress
segment of the shaft of a tubular bone aneurismal bone cyst
3. Terminology: Alignment – longitudinal 17. Endochondroma – most common tumor
relationship of one fragment to another; encountered in the bones of the hand
Apposition – degree of bone contact at 18. Ollier’s dse – congenital osseous dysplasia,
the fracture site; Avulsion – osseus multiple endochondromas at the ends of
fragment is pulled from the parent bone long bones
by a tendon or ligament 19. Mafucci’s syndrome – assoc with multiple
4. Special Types of Fractures: Pathologic cavernous hemangiomas
fracture – done is disrupted at the site of 20. Osteochondroma (Exostosis) – cauliflower
preexisting abnormality, frequently by a shaped
stress that would NOT have a fractured a 21. Osteoma: skull – frontal & ethmoid sinus;
normal bone Gardner’s syndrome – osteomas w/
5. Fatigue fractures – aka march fractures colonic polyposis
6. Monteggia’s fracture – fracture of the 22. Unicameral or Solitary Bone Cyst – fallen
proximal ulna, associated with dislocation fragment sign
of the proximal radius at the elbow joint 23. Neurofibroma of the spinal nerve root –
7. Galeazzi’s fracture – fracture radial shaft dumbbell type
w/ dislocation of inf. Radioulnar joint 24. Metastatic carcinoma – present as pain
8. Colle’s fracture – fracture of distal radius 25. Multiple myeloma – most common
with dorsal angulation of the distal primary tumor arising within bone
fragment; most common fracture in the 26. Osteosarcoma – most common primary
wrist malignant tumor of bone; Osteoblastic –
9. Smith’s fracture – fracture of distal radius most common histologic type of
with palmar/ventral displacement osteosarcoma; Mixed – most common
10. Compression fractures – most frequent radiographic form of osteosarcoma
type of vertebral injury 27. Codman’s triangle – irregular/sunburst
11. STUDY Salter-Harris Classification periosteal reaction
12. Scaphoid fracture – most common 28. Ewing’s tumor – primary malignant tumor
fracture of the carpus arising from red bone marrow
13. Fracture of the patella – transverse & 29. Solitary bone lesions: most common
vertical solitary lesion = cortical defect or non
14. Bone Tumors – most commonly ossifying fibroma (children before closure
METASTATIC of epiphyses)
15. Age: <1y/o – metastatic neuroblastoma; 30. Staph aureus – most frequently involved
1-20y/o – Ewing’s tumor in tubular bones; organism in bone infxn
10-30y/o – osteosarcoma; >40y/o – 31. Sequestrum – segment of cortical bone
metastatic carcinoma, multiple myeloma, isolated in the midst of a chronic infxn &
chondrosarcoma devoid of blood supply
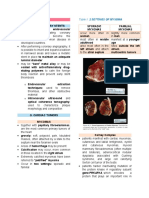
16. Periosteal new bone formation: Lamellar
acute osteomyelitis; Solid/compact
32. Involucrum – shell of bone formed by the genotype; partial H mole – contain fetal
periosteum that surrounds and enclose tissue or amniotic membranes, polyploidy
the sequestrum genotype.
33. Read Xray findings of osteoarthritis
Male & Female GUT
LOVE LOVE LOVE BIATCHES!!!
1. Transition Zone of prostate – site of
benign prostatic hyperplasia
2. Peripheral & central zones (prostate) –
primary tumor site in 70-80% cases
3. Prostatic CA – Read all
4. Scrotum: epididymal head – superior to
testis
5. Testicular Torsion (TIANGSSEN!!!!) –
diagnosis should be prompt, w/in 6 hrs to
ensure testicular viability
6. Varicocele – read all
OB Gyne Radiology
1. 1st trimester – read all
2. Blighted ovum – read all
3. Ectopic pregnancy – test for quantitative
serum β-HCG determination (lower than
normal pregnancy and plateaus rather
than rise with time)
4. Fetal death – read all
5. Placenta previa – most common cause of
vaginal bleeding in 2nd or 3rd trimester
6. Abruptio placenta – painful vaginal
bleeding
7. Leiomyoma – most common benign
neoplasm of the uterus
8. Adenomyosis – deposits of endometrial
glands within the myometrium
9. Endometrial CA – most common
malignant neoplasm of the uterine body
10. Cervical CA – second most common
uterine neoplasm
11. Gestational Trophoblastic Dse: increased
serum β-HCG level; clinical hallmark –
vaginal bleeding in 1st tri or early 2nd
trimester; complete or classic H mole – no
fetal tissue or amniotic membranes, 46 XX
You might also like
- Vaginal/Cervical Examination: Cristin G. Ungab, MNDocument21 pagesVaginal/Cervical Examination: Cristin G. Ungab, MNCristin Ungab100% (1)
- Brain TumorsDocument72 pagesBrain Tumorsmo_mibNo ratings yet
- Flakes Teachings About Astral ProjectionDocument33 pagesFlakes Teachings About Astral ProjectionsimionNo ratings yet
- Msds NaclDocument6 pagesMsds NaclNur Oktri Mulya DewiNo ratings yet
- Algunas NeoplasiasDocument13 pagesAlgunas Neoplasiasjose colon machucaNo ratings yet
- Table 1. 2 Settings of MyxomaDocument8 pagesTable 1. 2 Settings of MyxomaGlenda DavisNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Bone Tumours: 1. Age of Patient 2. Location of Tumour 3. Radiological Appearance 4. Histological FeaturesDocument69 pagesDiagnosis of Bone Tumours: 1. Age of Patient 2. Location of Tumour 3. Radiological Appearance 4. Histological FeaturesMochammad Fariz AmsalNo ratings yet
- Bone TumorsDocument80 pagesBone TumorsbucculuNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708Document3 pagesTumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708CitrusNo ratings yet
- Pediatr Clin N Am 50 - 2003 - 149 - 172Document24 pagesPediatr Clin N Am 50 - 2003 - 149 - 172HemerobibliotecaHospitalNo ratings yet
- Adult Brain Tumours: DR M.P. Okemwa PathologistDocument39 pagesAdult Brain Tumours: DR M.P. Okemwa PathologistSalman MajidNo ratings yet
- Spinaltumors Copy 160925185617Document122 pagesSpinaltumors Copy 160925185617Irving H Torres LopezNo ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma DR: Gehan MohamedDocument19 pagesOsteosarcoma DR: Gehan MohamedDimas BagusNo ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma DR: Gehan MohamedDocument19 pagesOsteosarcoma DR: Gehan MohamedNico DougaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Feature - PDF Version 1Document3 pagesDiagnostic Feature - PDF Version 1hassanenterprises9907No ratings yet
- Bone and Cartilage Tumors Benign and MalignantDocument92 pagesBone and Cartilage Tumors Benign and MalignantMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma DR: Gehan MohamedDocument19 pagesOsteosarcoma DR: Gehan MohamedInge Dackrisna DaudNo ratings yet
- Tumors of Auditory Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesTumors of Auditory Nervous SystemgitengeorgeNo ratings yet
- Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors: Clinical PresentationDocument15 pagesIntramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors: Clinical Presentationmetasoniko81No ratings yet
- Most Comon Questions Asked in NEET PG and DNBDocument12 pagesMost Comon Questions Asked in NEET PG and DNBSubhajitPaul100% (2)
- SCHWANNOMADocument4 pagesSCHWANNOMAAshwani Kumar Pati TripathiNo ratings yet
- 13-Benign Bone TumorsDocument18 pages13-Benign Bone Tumorsفراس الموسويNo ratings yet
- SynoviomaDocument28 pagesSynoviomaAnonymous bE4VegCcNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 MuskDocument8 pagesLecture 3 MuskElgilani zaherNo ratings yet
- Tumors of Head and Neck RegionDocument94 pagesTumors of Head and Neck Regionpoornima vNo ratings yet
- Meningiomas DR David CuencaDocument43 pagesMeningiomas DR David CuencatramperoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Bone Tumours: 1. Age of Patient 2. Location of Tumour 3. Radiological Appearance 4. Histological FeaturesDocument69 pagesDiagnosis of Bone Tumours: 1. Age of Patient 2. Location of Tumour 3. Radiological Appearance 4. Histological Featuresyurie_ameliaNo ratings yet
- Hand Tumours: Allens TestDocument74 pagesHand Tumours: Allens TestfiestaNo ratings yet
- Bone Tumors: Prepared by DR Pgr.2 Ortho Unit 3 BMCHDocument47 pagesBone Tumors: Prepared by DR Pgr.2 Ortho Unit 3 BMCHMohamed Al-zichrawyNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - Cardiac Microbes, Tumors, Heart FailureDocument20 pagesWeek 11 - Cardiac Microbes, Tumors, Heart Failureshivani patelNo ratings yet
- Intramedullary Osteosarcoma - Pathology - OrthobulletsDocument6 pagesIntramedullary Osteosarcoma - Pathology - OrthobulletsEmiel AwadNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The SpineDocument31 pagesTumors of The Spinetalk2 mohanNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology Lec6a81fe1b A65f 4c85 9e9d 4f9e299f7ba5 - 1Document10 pagesOral Pathology Lec6a81fe1b A65f 4c85 9e9d 4f9e299f7ba5 - 1مصطفى محمدNo ratings yet
- 08 Bone TumorsDocument94 pages08 Bone TumorsSara FoudaNo ratings yet
- Bone TheoryDocument19 pagesBone Theoryسہاجہدةه لہلہهNo ratings yet
- Flashcard PADocument6 pagesFlashcard PAAlif AlifNo ratings yet
- PROPTOSISDocument26 pagesPROPTOSISAhmad fayazNo ratings yet
- Bone 2Document43 pagesBone 2kazelio2017No ratings yet
- Bone TumorsDocument43 pagesBone TumorsIsaac MwangiNo ratings yet
- 5 - Bone Tumour 24 PDFDocument38 pages5 - Bone Tumour 24 PDFnoreentamer20No ratings yet
- RCSD or RCCD Peripheral WITHDocument2 pagesRCSD or RCCD Peripheral WITHEmma LiamNo ratings yet
- Proptosis: How To Approach?: History, Clinical Examination, Investigations and Differntial DiagnosisDocument27 pagesProptosis: How To Approach?: History, Clinical Examination, Investigations and Differntial Diagnosisdrkshitij100% (1)
- 3 So Called Fibrius Histiocytic TumorsDocument18 pages3 So Called Fibrius Histiocytic Tumorsgururaj patilNo ratings yet
- Practical 19 HistoDocument12 pagesPractical 19 HistoarjunNo ratings yet
- Cartilage Forming TumorsDocument10 pagesCartilage Forming TumorsRavikiran NandirajuNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman TumorDocument31 pagesRangkuman TumorraishapiNo ratings yet
- Bone TumorsDocument15 pagesBone Tumorssarguss1450% (2)
- Non Odontogenic Tumours of JawDocument22 pagesNon Odontogenic Tumours of JawDrMuskan AroraNo ratings yet
- Cong Anomalies and Tumors of SpineDocument120 pagesCong Anomalies and Tumors of SpineSunny SbaNo ratings yet
- L75 - Pathology of CNS TumorsDocument73 pagesL75 - Pathology of CNS Tumorsb deepthiNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument17 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDinesh RajputNo ratings yet
- Chondroma: X-Ray ShowsDocument2 pagesChondroma: X-Ray ShowsMd Ahsanuzzaman PinkuNo ratings yet
- OPHTHALMOPLEGIADocument58 pagesOPHTHALMOPLEGIAAryo Handoko SitorusNo ratings yet
- (10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Surgical Management of Posterior Petrous MeningiomasDocument7 pages(10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Surgical Management of Posterior Petrous MeningiomasAri MartanusaNo ratings yet
- Salivary Gland TumorsDocument12 pagesSalivary Gland TumorsDurga VoraNo ratings yet
- BONE - 09 - Bone TumorsDocument68 pagesBONE - 09 - Bone TumorsAmrit GautamNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tumours - SreejaDocument184 pagesEpithelial Tumours - SreejaaakiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Tumors of The Eye and OrbitDocument60 pagesPediatric Tumors of The Eye and OrbitDMdewiNo ratings yet
- Patologi Anatomi Sistem Kardiovaskular - Dr. NarisDocument24 pagesPatologi Anatomi Sistem Kardiovaskular - Dr. NarisGalih rarang gatiNo ratings yet
- Malignant Bone TumoursDocument52 pagesMalignant Bone Tumourscromwellopoku42No ratings yet
- Tumor Jar. Lunak, Tulang Dan Saraf1Document92 pagesTumor Jar. Lunak, Tulang Dan Saraf1FaerusNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Cysts and Benign Tumours of The Neck: Matti AnnikoDocument2 pages9.1 Cysts and Benign Tumours of The Neck: Matti AnnikoDevi DaryaningsihNo ratings yet
- 01 Integration of Primary Care and Oh ServicesDocument5 pages01 Integration of Primary Care and Oh ServicesChethranNo ratings yet
- AllergicDocument18 pagesAllergicChethranNo ratings yet
- Temporary - BbbhbRegistration - Non Schedule 7A FTPDocument8 pagesTemporary - BbbhbRegistration - Non Schedule 7A FTPChethranNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-10-23 15.16.57 - 20191023151720Document1 pageNew Doc 2019-10-23 15.16.57 - 20191023151720ChethranNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-10-23 15.15.15 - 20191023151531Document1 pageNew Doc 2019-10-23 15.15.15 - 20191023151531ChethranNo ratings yet
- SS Plastic - General Principles (2014)Document11 pagesSS Plastic - General Principles (2014)ChethranNo ratings yet
- Definitions:: Impotence Here Means Incapable of Having Sexual RelationDocument2 pagesDefinitions:: Impotence Here Means Incapable of Having Sexual RelationChethranNo ratings yet
- BREECH 2nijnjinijnuihiuhDocument7 pagesBREECH 2nijnjinijnuihiuhChethranNo ratings yet
- Answer: FDocument8 pagesAnswer: FChethranNo ratings yet
- Rvrtv5tgt5Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument4 pagesRvrtv5tgt5Abnormal Uterine BleedingChethranNo ratings yet
- Rvrtv5tgt5Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument4 pagesRvrtv5tgt5Abnormal Uterine BleedingChethranNo ratings yet
- A GYNE PrelimsuyguvuybDocument3 pagesA GYNE PrelimsuyguvuybChethranNo ratings yet
- My Note (2) BB Gubtuvuvt7Document19 pagesMy Note (2) BB Gubtuvuvt7ChethranNo ratings yet
- Traumassee 2 Notes - 20171202083816850Document14 pagesTraumassee 2 Notes - 20171202083816850ChethranNo ratings yet
- Optha Midterm: Saturday, May 16, 2015 10:59 PMDocument7 pagesOptha Midterm: Saturday, May 16, 2015 10:59 PMChethranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFChethranNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis: Adenocarcinoma of Colon FOBT Positive Black Stool May Be Metastasis Has Gone To Form Liver AbcessDocument3 pagesDifferential Diagnosis: Adenocarcinoma of Colon FOBT Positive Black Stool May Be Metastasis Has Gone To Form Liver AbcessChethranNo ratings yet
- 255067, Hibuinoubounojnounoun852 Cvs Clinical NotesDocument38 pages255067, Hibuinoubounojnounoun852 Cvs Clinical NotesChethranNo ratings yet
- Sunuohouhouhafari - 28 Feb 2019 at 11:19 Ouh0uhhDocument1 pageSunuohouhouhafari - 28 Feb 2019 at 11:19 Ouh0uhhChethranNo ratings yet
- Bakdjdjedjnk Receipt - 20180910223833350Document2 pagesBakdjdjedjnk Receipt - 20180910223833350ChethranNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Solutions Manual For Welding Principles and Practices 5Th Edition BohnartDocument7 pagesSolutions: Solutions Manual For Welding Principles and Practices 5Th Edition BohnartBassel AlshamiNo ratings yet
- CSSD EvaluationDocument6 pagesCSSD EvaluationFouzia ShariqNo ratings yet
- Technical CS: Parameters CG Power NTPL Yeoman Electrical & ElectronicsDocument2 pagesTechnical CS: Parameters CG Power NTPL Yeoman Electrical & ElectronicsStephen BridgesNo ratings yet
- Aspire S7-191 Wistron Helium UMADocument103 pagesAspire S7-191 Wistron Helium UMAWieslaw ZadenkoNo ratings yet
- M (V) - 8 Er CraneDocument41 pagesM (V) - 8 Er CranehamzehNo ratings yet
- AlfettaDocument110 pagesAlfettaSebasthian AlbaNo ratings yet
- 3-Stresses in TrackDocument49 pages3-Stresses in Trackarpit_089No ratings yet
- CraniotomyDocument5 pagesCraniotomyReylan AtcNo ratings yet
- Robert S de Ropp The Master GameDocument132 pagesRobert S de Ropp The Master GameConnor Woolf100% (1)
- Layher Event Catalogue 2022Document40 pagesLayher Event Catalogue 2022anilNo ratings yet
- News Letter SEPTEMBER 2023Document1 pageNews Letter SEPTEMBER 2023AS VIJAY RATHAN LINGAANo ratings yet
- GEA Standomat Automatic Standardization Unit Tcm25 67307Document16 pagesGEA Standomat Automatic Standardization Unit Tcm25 67307hozhabrNo ratings yet
- LTJournal V20N4 02 DF LT3652 Jay - CelaniDocument6 pagesLTJournal V20N4 02 DF LT3652 Jay - CelaniCanerNo ratings yet
- Tax Types QuestionsDocument5 pagesTax Types QuestionsJoseph Tinio CruzNo ratings yet
- The History of Money in The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesThe History of Money in The PhilippinesShareen BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Swami SivanandaDocument276 pagesSwami SivanandaJames Herring100% (1)
- Plug Valve Repair KitDocument1 pagePlug Valve Repair Kitcmrig74No ratings yet
- Buxton and Its Medicinal WatersDocument32 pagesBuxton and Its Medicinal WatersMotea IoanaNo ratings yet
- Vadiraja Life and WorksDocument12 pagesVadiraja Life and WorksKeshav Bhat100% (1)
- Indonesia Batik: A Cultural BeautyDocument60 pagesIndonesia Batik: A Cultural BeautyIndoplaces100% (2)
- ISCP Aerospace Handbook 19 21Document33 pagesISCP Aerospace Handbook 19 21Dibya DillipNo ratings yet
- The Gods Never Left Us - The Long Awaited Sequel To The Worldwide Best-Seller Chariots of The Gods (PDFDrive)Document155 pagesThe Gods Never Left Us - The Long Awaited Sequel To The Worldwide Best-Seller Chariots of The Gods (PDFDrive)Jake AmbersonNo ratings yet
- 3rd Periodical Exam GenPhy2Document2 pages3rd Periodical Exam GenPhy2VincentNo ratings yet
- Redx LogisticsDocument29 pagesRedx Logisticsbabu chyNo ratings yet
- DT128-155-128HLC v51xx OpGdDocument174 pagesDT128-155-128HLC v51xx OpGdJEEVAN KUMAR MNo ratings yet
- TransferirDocument15 pagesTransferirigorNo ratings yet
- Michael Dear - The Postmodern Challenge: Reconstructing Human GeographyDocument14 pagesMichael Dear - The Postmodern Challenge: Reconstructing Human GeographyJoão VictorNo ratings yet