Pre-charge - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.
org/wiki/Pre-charge
Pre-charge
Pre-charge of the powerline voltages in a high voltage
DC application is a preliminary mode which limits the
inrush current during the power up procedure.
A high-voltage system with a large capacitive load can be
exposed to high electric current during initial turn-on.
This current, if not limited, can cause considerable stress
or damage to the system components. In some
applications, the occasion to activate the system is a rare
occurrence, such as in commercial utility power
distribution. In other systems such as vehicle
applications, pre-charge will occur with each use of the
Peak inrush current into a high voltage capacitor
system, multiple times per day. Precharging is upon power up can stress the component,
implemented to increase the lifespan of electronic reducing its reliability.
components and increase reliability of the high voltage
system.
Contents
1 Background: inrush currents into capacitors
2 Definition of a pre-charge function
3 Benefits of pre-charging
4 Applications in high voltage power systems
5 References
6 Notes
Background: inrush currents into capacitors
Inrush currents into capacitive components are a key concern in power-up stress to components. When DC input
power is applied to a capacitive load, the step response of the voltage input will cause the input capacitor to charge.
The capacitor charging starts with an inrush current and ends with an exponential decay down to the steady state
condition. When the magnitude of the inrush peak is very large compared to the maximum rating of the
components, then component stress is to be expected. The current into a capacitor is known to be :
the peak inrush current will depend upon the capacitance C and the rate of change of the voltage (dV/dT). The
inrush current will increase as the capacitance value increases, and the inrush current will increase as the voltage
of the power source increases. This second parameter is of primary concern in high voltage power distribution
systems. By their nature, high voltage power sources will deliver high voltage into the distribution system.
Capacitive loads will then be subject to high inrush currents upon power-up. The stress to the components must be
understood and minimized.
The objective of a pre-charge function is to limit the magnitude of the inrush current into capacitive loads during
1 of 4 13/11/2017, 12:08 PM
�Pre-charge - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pre-charge
power-up. This may take several seconds depending on the system. In general, higher voltage systems benefit from
longer pre-charge times during power-up.
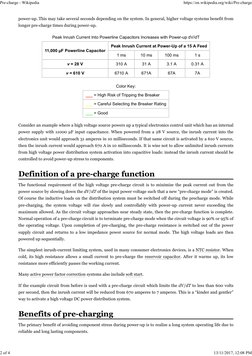
Peak Inrush Current Into Powerline Capacitors Increases with Power-up dV/dT
Peak Inrush Current at Power-Up of a 15 A Feed
11,000 µF Powerline Capacitor
1 ms 10 ms 100 ms 1s
v = 28 V 310 A 31 A 3.1 A 0.31 A
v = 610 V 6710 A 671A 67A 7A
Color Key:
___ = High Risk of Tripping the Breaker
___ = Careful Selecting the Breaker Rating
___ = Good
Consider an example where a high voltage source powers up a typical electronics control unit which has an internal
power supply with 11000 µF input capacitance. When powered from a 28 V source, the inrush current into the
electronics unit would approach 31 amperes in 10 milliseconds. If that same circuit is activated by a 610 V source,
then the inrush current would approach 670 A in 10 milliseconds. It is wise not to allow unlimited inrush currents
from high voltage power distribution system activation into capacitive loads: instead the inrush current should be
controlled to avoid power-up stress to components.
Definition of a pre-charge function
The functional requirement of the high voltage pre-charge circuit is to minimize the peak current out from the
power source by slowing down the dV/dT of the input power voltage such that a new “pre-charge mode” is created.
Of course the inductive loads on the distribution system must be switched off during the precharge mode. While
pre-charging, the system voltage will rise slowly and controllably with power-up current never exceeding the
maximum allowed. As the circuit voltage approaches near steady state, then the pre-charge function is complete.
Normal operation of a pre-charge circuit is to terminate pre-charge mode when the circuit voltage is 90% or 95% of
the operating voltage. Upon completion of pre-charging, the pre-charge resistance is switched out of the power
supply circuit and returns to a low impedance power source for normal mode. The high voltage loads are then
powered up sequentially.
The simplest inrush-current limiting system, used in many consumer electronics devices, is a NTC resistor. When
cold, its high resistance allows a small current to pre-charge the reservoir capacitor. After it warms up, its low
resistance more efficiently passes the working current.
Many active power factor correction systems also include soft start.
If the example circuit from before is used with a pre-charge circuit which limits the dV/dT to less than 600 volts
per second, then the inrush current will be reduced from 670 amperes to 7 amperes. This is a “kinder and gentler”
way to activate a high voltage DC power distribution system.
Benefits of pre-charging
The primary benefit of avoiding component stress during power-up is to realize a long system operating life due to
reliable and long lasting components.
2 of 4 13/11/2017, 12:08 PM
�Pre-charge - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pre-charge
There are additional
benefits: pre-charging
reduces the electrical
hazards which may occur
when the system integrity
is compromised due to
hardware damage or
failure. Activating the high
voltage DC system into a
short circuit or a ground
fault or into unsuspecting
personnel and their
equipment can have
undesired effects. Arc flash
will be minimized if a pre-
charge function slows
down the activation time of
a high voltage power-up. A
slow pre-charge will also
reduce the voltage into a
faulty circuit which builds
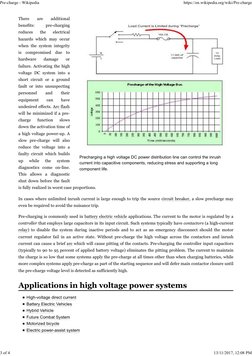
Precharging a high voltage DC power distribution line can control the inrush
up while the system
current into capacitive components, reducing stress and supporting a long
diagnostics come on-line. component life.
This allows a diagnostic
shut down before the fault
is fully realized in worst case proportions.
In cases where unlimited inrush current is large enough to trip the source circuit breaker, a slow precharge may
even be required to avoid the nuisance trip.
Pre-charging is commonly used in battery electric vehicle applications. The current to the motor is regulated by a
controller that employs large capacitors in its input circuit. Such systems typically have contactors (a high-current
relay) to disable the system during inactive periods and to act as an emergency disconnect should the motor
current regulator fail in an active state. Without pre-charge the high voltage across the contactors and inrush
current can cause a brief arc which will cause pitting of the contacts. Pre-charging the controller input capacitors
(typically to 90 to 95 percent of applied battery voltage) eliminates the pitting problem. The current to maintain
the charge is so low that some systems apply the pre-charge at all times other than when charging batteries, while
more complex systems apply pre-charge as part of the starting sequence and will defer main contactor closure until
the pre-charge voltage level is detected as sufficiently high.
Applications in high voltage power systems
High-voltage direct current
Battery Electric Vehicles
Hybrid Vehicle
Future Combat System
Motorized bicycle
Electric power-assist system
3 of 4 13/11/2017, 12:08 PM
�Pre-charge - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pre-charge
References
Ametherm - Inrush Current Limiters (http://www.ametherm.com/Inrush_Current/) NTC Thermistors -
Application Notes and Inrush Energy Calculator
Notes
Retrieved from "https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Pre-charge&oldid=795540111"
This page was last edited on 14 August 2017, at 21:57.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. By
using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the
Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
4 of 4 13/11/2017, 12:08 PM