Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Suhamira Nordin-Poster-Template-latest PDF
Suhamira Nordin-Poster-Template-latest PDF
Uploaded by
Suhamira NordinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Suhamira Nordin-Poster-Template-latest PDF
Suhamira Nordin-Poster-Template-latest PDF
Uploaded by
Suhamira NordinCopyright:
Available Formats
Metacognitive Awareness in Higher Order Thinking
Skills Assessment Questions
Suhamira , KamariahNordin 1 Yunus 2
1,2 Department of English, Faculty of Languages and Communication,
University of Sultan Zainal Abidin, 21300 Kuala Nerus, Terengganu
Abstract Flavell’s Model of Metacognition
Metacognition is an abstract and subjective concept The model captures all the components as they
that signifies the instrument for multidisciplinary complement one another. Cognitive goals have
field of studies. Metacognitive has becoming the important effect to activate metacognitive
imperative concern in developing the growth of experience and vice versa where the learners have
autonomous learners; one who thinks, acts, take a anxious feeling when they do not understand
stand and work on judgement based on reasons. In something and there is the need and want to
this paper, metacognition is given a functional role understand it to provide a solution to achieve the
to describe higher order thinking skills being goal. The anxious feeling also embraces the feeling
practiced in the written responses corresponding of hard to perceive, comprehend or remember and
with reading comprehension from the perspective solve. Then, these feeling that is the metacognitive
of the primary school learners. Much of the focus experience gives important impact to stimulate or
surrounding the higher order thinking skills selecting the strategy to be used in solving the task.
requirement has led the achievement gap to Finally, the process proceeds to store the Figure 2 Model of Metacognitive Strategy adapted in solving
become broader between the two distinctive knowledge in long term memory as the strategy can word physics problem
groups of learners; high and low achievers. The be used again in similar task. This type of
present paper aims to explore the empirical knowledge would be in term of declarative of HOTS in Assessment Question
research on the role of metacognitive awareness knowing that or procedural of knowing how. Thus,
involved in representing integrated HOTS in written the concept of how metacognitive process revolves
English Language Education in Malaysia integrates
response from text comprehension in language in one’s cognitive activity can be seen actively in higher order thinking skills (HOTS) for being parts of its
lesson. Into highlighting the focus of the study, it self-regulating learners. testing and assessment system. The aim is to enhance
follows the research question; what are the role of cognitive skills and ability in learning which starts at the
metacognitive awareness involved in integrating earliest age of formal education in primary schooling.
HOTS in ESL learning instruction? This review Furthermore, HOTS has been one of the 21st century
enlarge the understanding of metacognitive learners’ characteristics in order to fulfil the national
aspiration as being the global citizen with highly
knowledge and metacognitive regulation involved in
intelligent and better human values. Thus, the
written response text comprehension and will
implementation of HOTS is being distributed in all
indicate ESL learning strategy implies to all teachers subjects which also includes in the assessment.
and learners. Recommendation for future studies
are highlighted to discuss the limitation from At initial stage, LPM (2013) announced that 40% would
previous studies. be allocated for the element of HOTS in the assessment
for primary school and 60% in secondary school.
Figure 1 Flavell’s Model of Metacognition Despite the proportion has been given, Singh (2019)
examines the quality of HOTS elements in selected
Limitation and Future Research English reading comprehension examinations for
Standard 6 students in Malaysia. The study indicates
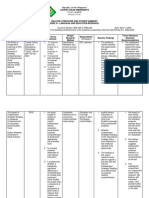
Findings from Dabarera (2014) posits positive limited number (20 percent) of higher order thinking
Introduction relationship between metacognitive awareness and questions in almost all reading comprehension papers
reading comprehension improvement in students, selected from eight different states in Malaysia.
while Soodla (2017) highlights the importance of Moreover, in Iran, Ahmed et.al (2013) and Khorsand
Metacognitive is an eminent based in education
teachers’ metacognitive knowledge in students’ (2009) analysed the cognitive level of exam questions
psychology. The research of metacognitive will always
metacognitive knowledge of reading strategies. for first and second grade are all categorized in the first
determine the positive results in study plan. To begin
three lowest level of Bloom Taxonomy. Therefore, the
with, is to define the concept of metacognitive
findings implied limited exposure of this particular
processes for all the learners. Nuhfer & Wirth (2014) Limitation Future Research aspect among English language teachers in Malaysia.
describe it as an, “internal conversation that reflects on
one’s ongoing thought” while Callan, Marchant, Holmes Instruments used are meant Developing instruments for Similar reasons are identified from the aspects of
Finch, and German (2016) agree that metacognitive is a for students teachers lacking awareness, knowledge, skills and exposure as
strategic way of thinking that leads to greater academic Exploring teachers well as teachers preference for easy marking scheme
success. Being aware in how the brain works proceed The samplings are from perception of the and scoring. Azian et al (2017) also posits teachers’
the learners to be focused with their learning goals. students significant relationship awareness in the need of HOTS inculcation in their
Kuhn (2000) believes that the first step to become a through in-depth interview teaching and learning activities, however they are
metacognitive learner is when the learner began to
Using various comparable unable to implement due to uncertainty of how to go
understand that knowledge is a product of human
Use one tool (MARSI) measures for better about it.
learning.
evaluation
Simultaneously, higher order thinking skills (HOTS) Analyze reading
assessment questions imply the process of comprehension sub-skills to
metacognitive by applying strategic thinking, particularly
in reading comprehension. In addition, many research
Reading is bi-divisible
match with metacognitive
awareness that suggest
Conclusions
construct
on metacognition relate to the learning and specific strategy to meet
achievement of reading (Channa, Nordin, & Dean, 2014; the demand each type of In conclusion, the implementation of HOTS still need to
Cubukcu, 2008; Diravidamani, 2016; Farahian, 2015; comprehension questions. be facilitated especially in term of knowledge, skills and
Jacobs & Paris, 1987; Soto et al., 2019). The Classroom observation strategies. Reading strategies need to be emphasized in
Teachers metacognitive
metacognitive process that involved in reading need to be included to the lesson as metacognitive strategies instruction aid
knowledge of reading
comprehension include metacognitive knowledge and assess their instructional the cognitive process in text comprehension. Teachers’
strategies were measured
metacognitive monitoring and control as being practices role to provide better metacognitive awareness need to
anticipated by the definition. Using multiple texts for be addressed in ESL learning instruction.
Based on one text only
reading comprehension
Table 1. Limitation and future research.
Contact 1.
References
Channa, M. A., Nordin, Z. S., & Dean, D. (2014). Identifying Metacognitive Strategies Through Learners ’ Reading Comprehension : a Review of Related Studies. Sci.Int. (Lahore), 26(5), 2457–2460.
2. Cubukcu, F. (2008). Enhancing vocabulary development and reading comprehension through metacognitive strategies. Issues in Educational Research, 18(1), 1–11.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-014-0806-4
SUHAMIRA NORDIN 3. Dabarera, C., Renandya, W. A., & Zhang, L. J. (2014). The impact of metacognitive scaffolding and monitoring on reading comprehension. System, 42(1), 462–473.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2013.12.020
UNIVERSITY SULTAN ZAINAL ABIDIN, 21300 KUALA NERUS, TERENGGANU 4. Diravidamani, S. (2016). Effectiveness of Metacognitive Strategies through Reading Comprehension of Tertiary Level Leaner’s of English. IRA International Journal of Education and
Multidisciplinary Studies (ISSN 2455–2526). https://doi.org/10.21013/jems.v4.n1.p19
Email: suhamiranordin@gmail.com 5. Farahian, M. (2015). Poor EFL Learners’ Metacognitive Reading Strategies: A Case Study. International Journal of Applied Linguistics and English Literature, 5(1).
https://doi.org/10.7575/aiac.ijalel.v.5n.1p.272
Website: 6. Jacobs, J. E., & Paris, S. G. (1987). Children’s Metacognition About Reading: Issues in Definition, Measurement, and Instruction. Educational Psychologist, 22(3–4), 255–278.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.1987.9653052
Phone:+60166400756 7. Soodla, P., Jõgi, A. L., & Kikas, E. (2017). Relationships between teachers’ metacognitive knowledge and students’ metacognitive knowledge and reading achievement. European Journal of
Psychology of Education, 32(2), 201–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-016-0293-x
8. Soto, C., Gutiérrez De Blume, A. P., Jacovina, M., Mcnamara, D., Benson, N., & Riffo, B. (2019). Reading comprehension and metacognition: The importance of inferential skills. Cogent Education,
6. https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2019.1565067
9. Kuhn, D. (2000). Metacognitive development: Current directions in psychological science. Current Directions in Psychological Science. 9(5). 178-181.
10. Nuhfer, E., & Wirth, K. (2014). Three tools for promoting metacognition for meta- understanding: Educating in fractal patterns. National Teaching & Learning Forum, 23(5), 6-9.
doi:10.1002/ntlf.20016
You might also like
- 08 LAPart 1 Literature Approved Listing Grade 68Document78 pages08 LAPart 1 Literature Approved Listing Grade 68assadjaved0% (1)
- Clinical Psychology ReportDocument33 pagesClinical Psychology Reportiqra-j75% (4)
- EDUC 5210 - Written Assignment 5Document3 pagesEDUC 5210 - Written Assignment 5Gilbert AyimanaNo ratings yet
- English Language - Teacher's Guide (Year 5) PDFDocument186 pagesEnglish Language - Teacher's Guide (Year 5) PDFlinda lom33% (3)
- Lesson Plan in English 10: MODULE 2: Establishing Solidarity Lesson 1: Sub-ThemeDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in English 10: MODULE 2: Establishing Solidarity Lesson 1: Sub-ThemeMary Anne WenceslaoNo ratings yet
- Psycholinguistics 2017 PDF FilenameDocument108 pagesPsycholinguistics 2017 PDF FilenameLawliet_LockhartNo ratings yet
- PPST 1.4 ModuleDocument15 pagesPPST 1.4 Moduleclaire cabato100% (1)
- B.ed CurriculumDocument29 pagesB.ed CurriculumAkash MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 To 3 Thesis Corrected 3Document44 pagesChapter 1 To 3 Thesis Corrected 3marleneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.TEACHING - Listening PDFDocument23 pagesChapter 2.TEACHING - Listening PDFEsther Ponmalar Charles91% (11)
- Chapter 1 06-07-22Document24 pagesChapter 1 06-07-22MARELIE GARCIANo ratings yet
- Real-Time Emotion Classification Using EEG Data STDocument26 pagesReal-Time Emotion Classification Using EEG Data STNaman KabadiNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Lilang Title Defense Dissertation PresentedDocument17 pagesJonathan Lilang Title Defense Dissertation PresentedJonathan LilangNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Matrix No. Author's Name Title Year Findings InstrumenDocument9 pagesLiterature Review Matrix No. Author's Name Title Year Findings InstrumenYONG CHIAN RU MoeNo ratings yet
- Using Metacognitive Strategies To Support Student Self-Regulation and EmpowermentDocument5 pagesUsing Metacognitive Strategies To Support Student Self-Regulation and Empowermentsugguna malarNo ratings yet
- Pedagogical Commentary and Teaching Through PandemicDocument1 pagePedagogical Commentary and Teaching Through PandemicJanet Latorre TamorNo ratings yet
- Artikel Penelitian 2Document5 pagesArtikel Penelitian 2Irwandi RahmatNo ratings yet
- Research NotesDocument6 pagesResearch NotesJoderon NimesNo ratings yet
- Research Draft FinalDocument51 pagesResearch Draft Finalsatonasatona20No ratings yet
- 2.3.6 Affective Domain: The Importance of Affect in Human Behavior The Role of Affect in LearningDocument4 pages2.3.6 Affective Domain: The Importance of Affect in Human Behavior The Role of Affect in LearningFrancis KatigmanNo ratings yet
- EJ1118705Document8 pagesEJ1118705yanirusdiantoNo ratings yet
- ORibia MetacognitionDocument5 pagesORibia MetacognitionAngelo Rebayla OribiaNo ratings yet
- Ed 105Document4 pagesEd 105Castillo LorenNo ratings yet
- HOTScompensatoryDocument5 pagesHOTScompensatoryellNo ratings yet
- F Chapter 1 3finalDocument48 pagesF Chapter 1 3finalRITCHELL ANN DEMAVIVAS GABOTNo ratings yet
- EducateDocument34 pagesEducateTrần Lê Quỳnh NhưNo ratings yet
- Samuel S. Celino Reflection 1 Reflection 2 Reflection 3 Norman G. Leaderman, A Professor at IllinoisDocument2 pagesSamuel S. Celino Reflection 1 Reflection 2 Reflection 3 Norman G. Leaderman, A Professor at IllinoisMamuNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Matrix-for-Research 2-Proposal-WritingDocument3 pagesActivity 4 - Matrix-for-Research 2-Proposal-WritingElena EscańoNo ratings yet
- Pal Inc Sar 1987Document11 pagesPal Inc Sar 1987Milena AcostaNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension and Metacognition: The Importance of Inferential SkillsDocument20 pagesReading Comprehension and Metacognition: The Importance of Inferential SkillsFebry Siicwekzlemoetz EankclalHu KcpyeAnNo ratings yet
- Metacognition in Reading: Reviewing The Literature: Abidin Pammu, Zaini Amir, Tg. Nor Rizan Tg. Mohd. MaasumDocument22 pagesMetacognition in Reading: Reviewing The Literature: Abidin Pammu, Zaini Amir, Tg. Nor Rizan Tg. Mohd. MaasumNajma FitriaNo ratings yet
- Abordo-Rawit - Quiz-Curriculum Framework of The Mtb-MleDocument4 pagesAbordo-Rawit - Quiz-Curriculum Framework of The Mtb-MleMariel AbordoNo ratings yet
- Attitudes and Feelings Influence Their Learning ExperienceDocument4 pagesAttitudes and Feelings Influence Their Learning ExperienceMaya BabaoNo ratings yet
- Preprints202310 2029 v1Document36 pagesPreprints202310 2029 v1El Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Learning Skills and Academic Performance of Senior High School Students in The Second District in The Province of BoholDocument10 pagesImplementation of Learning Skills and Academic Performance of Senior High School Students in The Second District in The Province of BoholPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Developing Eq in Students Teachers in UniversityDocument6 pagesDeveloping Eq in Students Teachers in UniversityNgọc MaiNo ratings yet
- Pedagogical Approaches in Teaching Bachelor of Elementary Education Teacher-CandidatesDocument12 pagesPedagogical Approaches in Teaching Bachelor of Elementary Education Teacher-CandidatesLee Hock SengNo ratings yet
- Teaching Competency of Secondary Teacher Education Students in Relation To Their MetacognitionDocument9 pagesTeaching Competency of Secondary Teacher Education Students in Relation To Their MetacognitionRajakumaranNo ratings yet
- Higher Order Thinking Skills, fORSTER 2004Document6 pagesHigher Order Thinking Skills, fORSTER 2004dahliafisherpmat dahliafisherpmatNo ratings yet
- A Review of Research On The Importance of Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) in Teaching English Language.Document9 pagesA Review of Research On The Importance of Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) in Teaching English Language.Widiyati RiyadiNo ratings yet
- Active Enquiry Poster PDFDocument1 pageActive Enquiry Poster PDFkhadija awanNo ratings yet
- 13 BaoD Guanc 2019 ListeningstrategiesDocument7 pages13 BaoD Guanc 2019 ListeningstrategiesCh ArmanNo ratings yet
- Pedagogical Competencies of TeachersDocument17 pagesPedagogical Competencies of TeachersHazel AbitriaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 103 Module 2 2T 2018 2019Document4 pagesEDUC 103 Module 2 2T 2018 2019Pau CervantesNo ratings yet
- Khellab 2022 - Recommended - CALLA FrameworksDocument19 pagesKhellab 2022 - Recommended - CALLA FrameworksHà Nguyễn ThanhNo ratings yet
- Ely ThesisDocument45 pagesEly ThesisEly Boy AntofinaNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Document To The FIDP in Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument10 pagesSupplementary Document To The FIDP in Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonBlue macchiatoNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Self-Directed Learning Strategies On Reading ComprehensionDocument10 pagesThe Impact of Self-Directed Learning Strategies On Reading ComprehensionDhon CaldaNo ratings yet
- Metacognicion Regulacion Metacognitiva AutoregulacionDocument35 pagesMetacognicion Regulacion Metacognitiva AutoregulacionLu GalvisNo ratings yet
- Title Related Literature Theoretical Framework The Constructivism TheoryDocument6 pagesTitle Related Literature Theoretical Framework The Constructivism TheoryAngelica Apostol GonzalesNo ratings yet
- MDW105 - Mod 6 MillanDocument4 pagesMDW105 - Mod 6 MillanTricia Anne MillanNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Education & Literacy Studies: Article InfoDocument12 pagesInternational Journal of Education & Literacy Studies: Article InfoMustafa TürkyılmazNo ratings yet
- MetacognitionDocument8 pagesMetacognitionRona de BorjaNo ratings yet
- Interrelation Between EFL Students' Metacognitive Awareness and Reading ComprehensionDocument4 pagesInterrelation Between EFL Students' Metacognitive Awareness and Reading ComprehensionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Are Observed Classroom Practices Related To Student Language Literacy AchievementDocument39 pagesAre Observed Classroom Practices Related To Student Language Literacy Achievement丽娟 黄No ratings yet
- Lyva ActDocument6 pagesLyva Actletlyvalenzuela03No ratings yet
- College Freshmen Least Mastered Higher Order Thinking Skills in Purposive Communication: Inputs For Developing and Evaluating Digitized Multimodal Learning ActivitiesDocument11 pagesCollege Freshmen Least Mastered Higher Order Thinking Skills in Purposive Communication: Inputs For Developing and Evaluating Digitized Multimodal Learning ActivitiesPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Charanjit JCRDocument9 pagesCharanjit JCRchristinasuNo ratings yet
- Reading PDFDocument6 pagesReading PDFDelia ȘipoșNo ratings yet
- Levels of Reading Comprehension in Higher Education: Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument11 pagesLevels of Reading Comprehension in Higher Education: Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisJack EckhartNo ratings yet
- Priming Adult Learners For Learning Transfer: Refereed ArticlesDocument8 pagesPriming Adult Learners For Learning Transfer: Refereed ArticlesFollet TortugaNo ratings yet
- Contextualized Module Development in Social Science For Senior High SchoolDocument15 pagesContextualized Module Development in Social Science For Senior High SchoolPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- The Correlation Between Formal Reasoning Ability and Physics Concept Mastery of Senior High School Nasrani 1 Medan Students in 20182019 Academic YearDocument8 pagesThe Correlation Between Formal Reasoning Ability and Physics Concept Mastery of Senior High School Nasrani 1 Medan Students in 20182019 Academic YearInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Literature-Summary Ricafrente, AngelicaDocument5 pagesLiterature-Summary Ricafrente, AngelicaANGELICA RICAFRENTENo ratings yet
- Executive Function and Metacognition: Relations and Measure On High Intellectual Ability and Typical SchoolchildrenDocument12 pagesExecutive Function and Metacognition: Relations and Measure On High Intellectual Ability and Typical Schoolchildrenkhushi chopra 0050No ratings yet
- Multidisciplinary Team For Taal Eruption 2021: EducationDocument5 pagesMultidisciplinary Team For Taal Eruption 2021: EducationLUNA MARIA URIEL NUÑEZNo ratings yet
- Group 9 Instructional DesignDocument19 pagesGroup 9 Instructional Designannisasalsabila2580No ratings yet
- Implementing ICT in ClassroomDocument28 pagesImplementing ICT in ClassroomSuhamira NordinNo ratings yet
- Exploring Metacognitive Awareness Among TeachersDocument12 pagesExploring Metacognitive Awareness Among TeachersSuhamira Nordin100% (1)
- Metacognitive Awareness in Malaysia Reading Research: An Suhamira NordinDocument18 pagesMetacognitive Awareness in Malaysia Reading Research: An Suhamira NordinSuhamira NordinNo ratings yet
- SECTIONC3Document1 pageSECTIONC3Suhamira NordinNo ratings yet
- ICTL Y4 SyllabusDocument14 pagesICTL Y4 SyllabusSuhamira NordinNo ratings yet
- SZRZ6014 SilibusApprovedSenate2010Document8 pagesSZRZ6014 SilibusApprovedSenate2010Suhamira NordinNo ratings yet
- 12 Reading StrategiesDocument14 pages12 Reading StrategiesAgatha Qyara AnnabellaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Template: Essential QuestionDocument9 pagesLesson Plan Template: Essential Questionapi-531359206No ratings yet
- MODULE 5 - NCDocument5 pagesMODULE 5 - NCIvy Chezka HallegadoNo ratings yet
- 2020 Teacher Guide 2nd EditionDocument50 pages2020 Teacher Guide 2nd EditionMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- 1st - Maybelle The Cable CarDocument2 pages1st - Maybelle The Cable Carapi-358681464No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan (Unit 3 Getting Started)Document8 pagesLesson Plan (Unit 3 Getting Started)Như NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Animal WorldDocument17 pagesAnimal WorldCamille MouraNo ratings yet
- SQRRR or SQ3R Is A Reading Comprehension Method Named For Its Five Steps: Survey, Question, Read, Recite, and Review. TheDocument3 pagesSQRRR or SQ3R Is A Reading Comprehension Method Named For Its Five Steps: Survey, Question, Read, Recite, and Review. TheShreyas TawareNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Lessons - 6-10 (Pp. 136-142)Document7 pagesUnit 3 - Lessons - 6-10 (Pp. 136-142)catherinerenanteNo ratings yet
- EAPPDocument3 pagesEAPPShaira WongNo ratings yet
- The Literacy Learning ProgressionsDocument32 pagesThe Literacy Learning ProgressionstestvrocNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Teaching Silent Reading (Blank)Document1 pageLesson Plan in Teaching Silent Reading (Blank)Paulo Israel Escobal RemulloNo ratings yet
- G6 English W7 - CufDocument7 pagesG6 English W7 - CufJohn Rich CaidicNo ratings yet
- 6 Lesson Writing Unit: Personal Recount For Grade 3 SEI, WIDA Level 2 Writing Kelsie Drown Boston CollegeDocument17 pages6 Lesson Writing Unit: Personal Recount For Grade 3 SEI, WIDA Level 2 Writing Kelsie Drown Boston Collegeapi-498419042No ratings yet
- What Is Your Approach To Classroom ManagementDocument5 pagesWhat Is Your Approach To Classroom ManagementHusainmh SalmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan TemplateDocument5 pagesLesson Plan TemplateSyarah ImaniNo ratings yet
- Read Aloud Study-05-02-2022Document101 pagesRead Aloud Study-05-02-2022Aprica BrownNo ratings yet
- First Additional Language Grade 3 Term 1Document16 pagesFirst Additional Language Grade 3 Term 1Koketso SekwenyaneNo ratings yet
- Check Your Comprehension: A. Choose The Correct Answers For The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesCheck Your Comprehension: A. Choose The Correct Answers For The Following Questionsdrecosh-1100% (1)
- EappDocument2 pagesEappKer SaturdayNo ratings yet
- Motor Imaging Strategy On Students' Vocabulary in Reading ComprehensionDocument19 pagesMotor Imaging Strategy On Students' Vocabulary in Reading ComprehensionRanah KabbaniNo ratings yet
- The Most Dangerous Game and The NecklaceDocument8 pagesThe Most Dangerous Game and The NecklaceCorinne BaldwinNo ratings yet