Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydrocarbons ChapterNotes-JEEMAIN - GURU
Uploaded by
RaagOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydrocarbons ChapterNotes-JEEMAIN - GURU
Uploaded by
RaagCopyright:
Available Formats
Downloaded from jeemain.
guru
1
Class XI
Chemistry
Ch 13: Hydrocarbons
TOP Concepts:
1. Alkanes: General formula: CnH2n+2
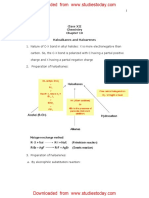
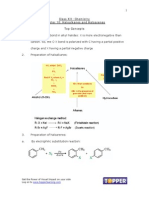
2. Preparation of alkanes:
3. Kolbe’s electrolytic method: Alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids
undergo decarboxylation on electrolysis of their aqueous solutions and form
hydrocarbons having twice the number of carbon atoms present in the alkyl
group of the acid.
Electrolysis
2CH3COO Na 2H2O CH3 CH3 2CO2 H2 2 NaOH
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
Downloaded from jeemain.guru
2
4. Physical properties of alkanes:
a. Physical state: C1 to C4 are gases, C5 to C17 are liquids and those
containing 18 carbon atoms or more are solids at 298 K.
Reason: Hydrocarbons are non- polar because of the covalent nature of C-C
and C-H bonds. Thus, they have weak van der Waals forces.
b. Boiling points: Alkanes have low boiling points because they have weak
van der Waals forces.
Higher alkanes with higher molecular masses have high boiling points than
lower alkanes with low molecular masses. This is because magnitude of van
der Waals forces increases with increase in molecular mass or increase in
surface area.
Boiling points of branched chain alkanes are lower than the corresponding
straight chain alkanes. This is because with branching the molecules become
more compact and hence the surface area decreases.
c. Melting points: The alkanes with even number of carbon atoms have
higher melting points as compared to the immediately next lower alkane with
odd number of carbon atoms. This is because alkanes with even number of
carbon atoms have symmetrical structure and hence it results in closer
packing in the crystal structure.
d. Solubility: Alkanes are soluble in non- polar solvents and are insoluble in
polar solvents since alkanes are non- polar molecules.
5. Chemical properties of alkanes:
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
Downloaded from jeemain.guru
3
Aromatization or reforming:
Isomerisation:
Pyrolysis or cracking:
A decomposition reaction in which higher alkanes on heating to higher
temperature decompose into lower alkanes, alkenes etc. is called pyrolysis or
cracking.
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
Downloaded from jeemain.guru
4
6. Conformations or conformers or rotamers or conformational
isomers:
The spatial arrangements of atoms which can be converted into one another
by rotation around a C-C single bond are called conformations or conformers
or rotamers.
7. Conformations of ethane:
Conformations → Eclipsed Staggered Skew
Conformation in Conformation in Any other
which hydrogen which hydrogen intermediate
atoms attached to atoms are as far conformation
two carbons are as apart as possible in between
closed together as eclipsed and
possible sawhorse
Sawhorse
projection
Newman projection
8. Geometrical isomers of alkenes:
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
Downloaded from jeemain.guru
5
Trans isomer is non- polar and has zero dipole moment where as cis isomer
is polar.
cis isomer has higher boiling points than trans isomer because it is polar.
In case of solids, cis isomer has a lower melting point than trans isomer. This
is because trans isomer is symmetrical and fits well into the crystal lattice.
9. Preparation of alkenes:
10. Physical properties of alkenes:
a. Physical state: The first three members are gases, the next fourteen are
liquids and the higher ones are solids.
b. Boiling points: The boiling points of alkenes increase with the increase in
molecular mass.
Boiling points of branched chain alkenes are lower than the corresponding
straight chain alkenes. This is because with branching the molecules become
more compact and hence the surface area decreases.
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
Downloaded from jeemain.guru
6
c. Solubility: Alkenes are soluble in non- polar solvents and are insoluble in
polar solvents.
11. Chemical properties of alkenes:
12. Test for Unsaturation: There are two tests to know whether a
compound is unsaturated or not:
a. Bromine water test: When an unsaturated compound is reacted with
bromine solution in carbon tetrachloride, the reddish orange colour of
bromine solution in carbon tetrachloride is discharged.
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
Downloaded from jeemain.guru
7
b. Baeyer’s reagent test: When an unsaturated compound is reacted with
cold, dilute, aqueous solution of potassium permanganate (Baeyer’s reagent,
the pink colour of KMnO4 solution is discharged.
13. Preparation of alkynes:
14. Physical properties of alkynes:
a. Solubility: Alkynes are weakly polar in nature. They are lighter than
water and immiscible with water but soluble in organic solvents like ethers,
carbon tetrachloride and benzene.
b. Melting and boiling point:
The melting and boiling points of the members of the alkyne family are
slightly higher as compared to those of corresponding alkanes and alkenes.
This is because alkynes have a linear structure and therefore their molecules
are more closely packed as compared to alkanes and alkenes. The magnitude
of attractive forces among them is higher and therefore, the melting and
boiling points are also higher.
The melting point, boiling point and density of alkynes increase with increase
in molar mass. This is because magnitude of van der Waals forces increases
with increase in molecular mass or increase in surface area.
15. Acidic nature of alkynes: Hydrogen atoms of ethyne attached to triply
bonded carbon atom are acidic in nature.
Example:
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
Downloaded from jeemain.guru
8
1
HC C Na
HC CH Na H2
Monosodium
ethynide
2
1
HC C Na Na
NaC C Na H2
disodium
ethynide
2
Reason:
Alkyne Alkene Alkane
Hybridisation of sp sp2 sp3
carbon to which
H atom is
attached
Percentage s 50% 66.6 % 25%
character of (maximum) (minimum)
carbon
Electronegativity Highest Less than alkyne lowest
of carbon atom and more than
alkane
Extent of Highest Less than alkyne lowest
attraction of and more than
hydrogen atoms alkane
of C-H bonds
towards C
Ease of liberation Highest Less than alkyne lowest
of H atoms as and more than
protons alkane
Acidic character Highest Less than alkyne lowest
and more than
alkane
16. Chemical properties of alkynes:
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
Downloaded from jeemain.guru
9
17. Conditions for aromaticity:
a. Planarity: The ring should be planar. In simple words, all the carbons
of the ring should be sp2 hybridised.
b. Complete delocalisation of the electrons in the ring: The electrons
should be completely delocalized. In simple words, in the ring
alternate single and double bonds should exist.
c. Hückel Rule: Presence of (4n + 2) electrons in the ring where n is an
integer (n = 0, 1, 2, . . .)
18. Preparation of benzene:
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
Downloaded from jeemain.guru
10
19. Chemical properties of benzene:
20. Directive influence of a functional group in monosubstituted
benzene:
a. Ortho para directing groups: Groups which direct the incoming group to
ortho and para positions.
Activating groups: Groups which increase the electron density on ortho and
para positions of the benzene ring.
Example: –NH2, –NHR, –NHCOCH3, –OCH3, –CH3, –C2H5,
Deactivating groups: Groups which decrease the electron density on ortho
and para positions of the benzene ring.
Example: -X
Halogens are moderately deactivating groups because they have strong – I
effect (electron withdrawing effect). Due to this the overall electron density
on benzene ring decreases. It makes further substitution difficult. However,
due to resonance the electron density on o– and p– positions is greater than
that at the m-position. Hence, they are also o– and p– directing groups.
b. Meta directing groups: The groups which direct the incoming group to
meta position.
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
Downloaded from jeemain.guru
11
Example: –NO2, –CN, –CHO, –COR, –COOH, –COOR, –SO3H
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
You might also like
- XI Chem Ch13 Hydrocarbons ChapterNotesDocument11 pagesXI Chem Ch13 Hydrocarbons ChapterNotesAbhyuday BharatNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Lab: Reactions of Alkanes, Alkenes, and CycloalkanesDocument27 pagesOrganic Chemistry Lab: Reactions of Alkanes, Alkenes, and CycloalkaneszazoNo ratings yet
- Coek - Info AlkynesDocument12 pagesCoek - Info AlkynesDũng NgôNo ratings yet
- of HydrocarbonsDocument45 pagesof HydrocarbonsSneha KediaNo ratings yet
- Reactions of AlkenesDocument22 pagesReactions of Alkenesdela2No ratings yet
- Chem Lec Week 5Document4 pagesChem Lec Week 5Alexandra Nicole EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Lab on HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Lab on HydrocarbonsKit GabrielNo ratings yet
- Properties and Reactions of AlkanesDocument25 pagesProperties and Reactions of AlkanesFrancine MaramagNo ratings yet
- 14.2 AlkenesDocument26 pages14.2 Alkenessafiya_91No ratings yet
- 13.HYDROCARBONS Full Chapter 2021Document14 pages13.HYDROCARBONS Full Chapter 2021raziabegum03761No ratings yet
- Lecture On Organic Chemistry Part 3Document7 pagesLecture On Organic Chemistry Part 3ARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument9 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesManish kumarNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes PropertiesDocument22 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes PropertiesAlessandra MercadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument19 pagesChapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesSujithNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument81 pagesHydrocarbonmerlinNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons (Alkanes and Alkenes)Document16 pagesHydrocarbons (Alkanes and Alkenes)Soham NagNo ratings yet
- Alkynes: Properties, Reactions and UsesDocument33 pagesAlkynes: Properties, Reactions and UsesAlvis MwangiNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds: Homologous Series, Alkanes and AlkenesDocument22 pagesCarbon Compounds: Homologous Series, Alkanes and Alkenesdr lailaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Hybridisation of OrbitalsDocument11 pagesAlkanes: Hybridisation of OrbitalsIsaa gabNo ratings yet
- Class XII Chemistry Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument9 pagesClass XII Chemistry Haloalkanes and HaloarenesamitNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument27 pagesChemistryAditya ChawlaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY OF ALIPHATIC HYDROCARBONSDocument8 pagesCHEMISTRY OF ALIPHATIC HYDROCARBONSHibba IsrarNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument33 pagesHydrocarbonaleenashaji.abraham1No ratings yet
- STPM CHEMISTRY TERM 3: HYDROCARBONSDocument16 pagesSTPM CHEMISTRY TERM 3: HYDROCARBONSVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Organic Chemistry 1Document7 pages1.2 Organic Chemistry 1zedrickNo ratings yet
- Userfiles XII Chem Ch10 HaloalkanesAndHaloarenes ConceptsDocument8 pagesUserfiles XII Chem Ch10 HaloalkanesAndHaloarenes ConceptsSandesh Kamble100% (2)
- Class 11 Chapter 13 HydrocarbonsDocument159 pagesClass 11 Chapter 13 HydrocarbonsAnkita ChandaNo ratings yet
- A3 CosepeDocument4 pagesA3 CosepeSean Jodi CosepeNo ratings yet
- NCERT Unit 12 Hydrocarbon by Manoj YadavDocument19 pagesNCERT Unit 12 Hydrocarbon by Manoj YadavKunaL VrmaNo ratings yet
- Alkyne Chemistry EEEDocument42 pagesAlkyne Chemistry EEEVictor MutugiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document24 pagesChapter 4Quỳnh Anh TrầnNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Topic 5: AlkenesDocument7 pagesEdexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Topic 5: AlkenesBara' HammadehNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of AlkenesDocument16 pagesNomenclature of AlkenesДмитрий ЛегаNo ratings yet
- Notes 2.3 - Properties of AlkanesDocument16 pagesNotes 2.3 - Properties of AlkanesNaseeb AliiNo ratings yet
- EXPE222Document6 pagesEXPE222K-yanVehraaYomomaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument21 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsrahNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons and Benzene: MVPS (2020)Document4 pagesHydrocarbons and Benzene: MVPS (2020)Paul Alfred SoNo ratings yet
- Mnar Owe SvapDocument10 pagesMnar Owe SvapAl7amdlellahNo ratings yet
- Formulae For: Haloalkane & Hal OarenesDocument9 pagesFormulae For: Haloalkane & Hal OarenesSâmïr Kumar MundariNo ratings yet
- AlkenesDocument16 pagesAlkenesVijay Kumar NatteyNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition ReactionsDocument1 pageAldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition ReactionsSandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons NCERTDocument35 pagesHydrocarbons NCERTSuman MondalNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds (One Shot) - Class Notes - (Olympiad Challengers)Document83 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds (One Shot) - Class Notes - (Olympiad Challengers)anantsinghalktp21No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReviewerDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reviewerenriquezchloe167No ratings yet
- Chapter 9: AlkynesDocument8 pagesChapter 9: AlkyneswaefsNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons UnitDocument29 pagesHydrocarbons UnitBhavesh KNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons-1Document159 pagesClass 11 Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons-1chandrika1417fgNo ratings yet
- Org 2Document30 pagesOrg 2rearachel25No ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument30 pagesHydrocarbonsSneha AunttyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 AlkenesDocument10 pagesLesson 8 AlkenesSideka ResalsinghNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds ExplainedDocument13 pagesCarbon Compounds ExplainedCT SectionNo ratings yet
- 5. AlkenesDocument7 pages5. AlkenesNisaka ChotsarangkoolNo ratings yet
- C9 - Crude Oil and FuelsDocument3 pagesC9 - Crude Oil and FuelsAbdul-Muizz KhanNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Paraffins: Preparation (I) From Grignard ReagentDocument25 pagesAlkanes Paraffins: Preparation (I) From Grignard ReagentShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- General DescriptionDocument12 pagesGeneral DescriptionMariel VillaNo ratings yet
- Lec 6C Alkyne Structure and ReactivityDocument37 pagesLec 6C Alkyne Structure and Reactivityseanroi.villas.lawNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMS CHEM - MazonDocument10 pagesMIDTERMS CHEM - MazonMazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- Radical ReactionsDocument36 pagesRadical ReactionsNimra KhanNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument7 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesShouvik sinhaNo ratings yet
- JEEMAIN.GURU Periodic Table GuideDocument26 pagesJEEMAIN.GURU Periodic Table GuideRethikNo ratings yet
- Jee Advanced 2018 Solution p1Document29 pagesJee Advanced 2018 Solution p1senthilNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2020 Jan 9 Second Shift Chemistry Resonance Answer Key PDFDocument13 pagesJEE Main 2020 Jan 9 Second Shift Chemistry Resonance Answer Key PDFRaagNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2020 Jan 9 Second Shift Chemistry Resonance Answer Key PDFDocument13 pagesJEE Main 2020 Jan 9 Second Shift Chemistry Resonance Answer Key PDFRaagNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding-Jeemain - Guru PDFDocument30 pagesChemical Bonding-Jeemain - Guru PDFFlorin RotaruNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2020 Jan 9 Second Shift Chemistry Resonance Answer Key PDFDocument13 pagesJEE Main 2020 Jan 9 Second Shift Chemistry Resonance Answer Key PDFRaagNo ratings yet
- General Theory of RelativityDocument45 pagesGeneral Theory of RelativityPoulami ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Unit 14Document22 pagesUnit 14asnaph9No ratings yet
- X-Ray Fluorescence - C MillerDocument24 pagesX-Ray Fluorescence - C MillerRodrigo AndradeNo ratings yet
- Resistance, Ohm's Law, and The Temperature of A Light Bulb FilamentDocument8 pagesResistance, Ohm's Law, and The Temperature of A Light Bulb FilamentDanno NNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map Reading GuideDocument21 pagesTopographic Map Reading GuidegopeNo ratings yet
- Measuring Viscosity Using Poiseuille's MethodDocument8 pagesMeasuring Viscosity Using Poiseuille's MethodAagam ShahNo ratings yet
- Melting Boiling Condensation SolidificationDocument12 pagesMelting Boiling Condensation Solidificationsalmanismart123No ratings yet
- Question Bank HMTDocument18 pagesQuestion Bank HMTBhavesh KapilNo ratings yet
- Homework 6 For Physics ClassDocument3 pagesHomework 6 For Physics ClassrubbadashwubbaNo ratings yet
- Mathcad Regression SolutionDocument14 pagesMathcad Regression SolutionWelsinsin Kevin SinNo ratings yet
- ASTM D4648-D4648M - 13, Laboratory Miniature Vane Shear Test For Saturated Fine-Grained Clayey Soil PDFDocument7 pagesASTM D4648-D4648M - 13, Laboratory Miniature Vane Shear Test For Saturated Fine-Grained Clayey Soil PDFMarcosNo ratings yet
- Quiz in Chemistry On DensityDocument2 pagesQuiz in Chemistry On Densitypflorendo_1No ratings yet
- Physics 101 Midterm Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesPhysics 101 Midterm Exam QuestionsbnfxnNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Classifying Matter NotesDocument5 pages3.1 Classifying Matter NotesJam Uly GastyNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double Indicator Titration Chem 28Document2 pagesQuantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double Indicator Titration Chem 28Frances Abegail QuezonNo ratings yet
- Topper Sample Paper Science Class 9Document16 pagesTopper Sample Paper Science Class 9Ankur DuttaNo ratings yet
- Period #8 Notes: Aggregates: A. A Quick Look at Aggregates 1. OverviewDocument13 pagesPeriod #8 Notes: Aggregates: A. A Quick Look at Aggregates 1. OverviewDebendra Dev KhanalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 23 Sample ExamDocument11 pagesMathematics 23 Sample ExamDominic YapNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-04: Moving Charges and Magnetism Force On A Straight ConductorDocument2 pagesCBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-04: Moving Charges and Magnetism Force On A Straight ConductorsumitNo ratings yet
- Goldstein 21 7 12 PDFDocument8 pagesGoldstein 21 7 12 PDFbgiangre8372100% (2)
- Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Second EditionDocument88 pagesChemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Second Editionchingy100% (2)
- Light Bending Refraction GuideDocument7 pagesLight Bending Refraction GuideJohn Benedict DimailigNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mineralogy Vol. 3Document343 pagesAdvanced Mineralogy Vol. 3Violeta Reyes OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws ChapterDocument20 pagesNewton's Laws ChapterRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical EngineeringDocument19 pagesElectrochemical EngineeringMolu VarchaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential 1Document2 pagesElectrostatic Potential 1Athiya ZainabNo ratings yet
- Beam Shear Force Bending Moment Stress Deflection ProblemsDocument9 pagesBeam Shear Force Bending Moment Stress Deflection ProblemsManjunatha S SheemandanavarNo ratings yet
- MiCOM P122 & P123Document3 pagesMiCOM P122 & P123Hari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Mock Exam PCPDocument10 pagesProblem Set Mock Exam PCPJeremy Allan Bartolo0% (1)
- Exam 2 - MAE 3344 - Fall 2017Document4 pagesExam 2 - MAE 3344 - Fall 2017Eseosa MusaNo ratings yet