Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pedia Recalls 2015
Uploaded by
deevonc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesOriginal Title
PEDIA-RECALLS-2015.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesPedia Recalls 2015
Uploaded by
deevoncCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
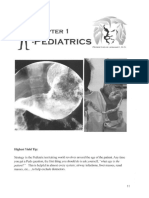
PEDIATRIC SURGERY RECALLS 1
SECTION C 2015
1. visceral pain b. seldom done in children
A. Colicky abdominal c. antero posterior cross table lateral view to
B. Burning epigastric demonstrate air fluid level
C. Vague abdominal? d. routine ______(forgot the word) radiation is
D. Mild... relatively low and not cumulative.
2. Example of referred pain 16. 20 cc/kg volume resuscitation in children.
Answer: C. Abdominal pain from a pulmonary A. A magical number without scientific basis.
pathology B. Equivalent to 20% of cardiac output
(Sorry nakalimutan ko choices) C. Amt that nearly increase bp.
D. Almost always given to all pediactric patients
4. Apley's rule
Answer - the likelihood of organic pathology is 17. Clinical manifestation of Choledochal cyst?
directly proportional to the distance of pain from a. jaundice, fever, hepatomegaly
the umbilicus b. hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, acholic stool
(Nalimutan ko yung choices saka letter sorry) c. jaundice, abdominal pain, RUQ mass
d. jaundice, acholic stools, hepatomegaly
5. True in incidence of pyloric stenosis
a. increase in asians 18. PE findings of pyloric stenosis:
b. increase in male a. scaphoid abdomen
c. male has increased index of transmission to b. adbominal distention
offspring c. visible peristaltic wave
d. isolated disease
19. Biliary vomiting in malrotation is associated
9. 10 month old bb girl well with bright red blood with:
around stool a. Abdominal distention
A. Intussusception b. Abd fullnesss
B. Meckel's diverticulum c. Intrstinal loops
C. Volvulus d. Peristaltic wave
D. Anal fissure
20. 1 year old, down syndrome, sudden
11. Etiology of biliary atresia abdominal pain with vomiting. Healthy. Bloody
A. Virus stools. Slight abdominal distention with guarding.
B. maternal illness A. Delayed malrotation
C. No known b. Fenestrated duodenal atresia
D. Genetics c. Intussuception
15. abdominal radiograph in AP d. Intestinal atresia
a. almost universally done to demonstrate fecalith
PEDIATRIC SURGERY RECALLS 2
SECTION C 2015
21. 2 year old girl down facie billous vominintg B.obesity
a.doundenal atresia C.chronic abdominal pain
b. intestinal atresia D.frequent stooling
c .malrotation
33. 8mos. Old, babyboy. W/ recent viral infection,
26. A condition that will less likely need further sick looking w/ blood & mucus in diarrhea?
investigation if diagnosed prenatally. A. Gastroenteritis
a. Duodenal atresia B. Intussusception
b. Intestinal atresia C. Midgut volvulus
c. CDH D. Anal fissure
d. Intrauterine growth restriction
34. In malrotation, timing of intervention is
27. Type 1 Choledochal cyst - choices: essential due to possible complication of:
A. Fusiform Cyst a. Midgut volvulus
B. Diverticular cyst b. Intestinal necrosis
C. Choledocolithiasis c. Dehydration
D. Caroli's Cyst d. Electrolyte imbalance
28. Etiology of biliary atresia. 36. Pedia. pathphysiology of intestinal atresia?
A. Probably viral in nature. a. completer resorption of ischemic segment b.
B. Linked to maternal illness during pregnancy. usually occurs in the 1st trimester c. etiology
C. Unlikely to occur more than once in the family. unknown d. not occuring with other anomalies
D. Purely Genetic.
37. Intestinal atresia as an isolated
29. Lost in the vomitus from pyloric stenosis? syndrome..which of the ff is assoc.with familial
A. Potassium occurence and other anomalies?
B. Chloride a.I
C. Bicarbonate b.II
D. Sodium c.IIIa
d.IIIb
30. Clinical manifestation of malrotation
A. Bilous vomiting 38. most common type of choledochal cyst?
B. Abd. Distention a.I
C. Loose stool b.II
D. Projectile vomiting c.III
32. In an older patient with malrotation,the usual d.IV
presenting symptom is
A.recurrent bilous vomiting 44. PE findings in pyloric stenosis.
PEDIATRIC SURGERY RECALLS 3
SECTION C 2015
A. Scaphoid abdomen a. follows typical epigastric pain --> RLQ
B. Abdominal distention b. anorexia is seen in significantly obese children
C. Peristaltic wave c. high rate of perforation
D. Hypoactive bowel sound. d. vague pain
45. Preparation for pedia with abdominal pain.
A. Dress me slowly, im in a hurry
B. Common things are more common
C. How did we get here?
D. We have arrived
46. Examination of pedia patient w/ abd pain
A. Secondary survey is important
B. Examine on mother's lap even if it's awkward
C. Pount tenderness is not important and
frustrating
D. Doctors have cold hands, ...use ball of hands
47. Lab examination in children with abdominal
pain
A. It is use as adjunct to history taking in the
diagnosis of children with abdominal pain
B. It is helpful with the diagnosis in children with
abdominal pain (not sure)
C. Routine cbc and ua is indicated for dx of AA
D. It is helpful in the management rather than
diagnosis
48. Urinalysis is routinely done in cases of
ruptured AP
A. To assess irritative bladder infection due to
rupture pelvic AP
B. To r/o synchronous UTI especially in female
patients
C. ......because of low cost and nonivasiveness
D. Not important in GI diseases like AP
49. acute appendicitis in children
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Continuity of CareDocument1 pageContinuity of CaredeevoncNo ratings yet
- FMCH Family Health CareDocument3 pagesFMCH Family Health CaredeevoncNo ratings yet
- Uhc Ra 11223Document8 pagesUhc Ra 11223deevoncNo ratings yet
- RA 11223 + F1 For HealthDocument3 pagesRA 11223 + F1 For HealthdeevoncNo ratings yet
- PEDTRIC SURGERY Dr. Isabedra - PDF Notes - 201702082201Document25 pagesPEDTRIC SURGERY Dr. Isabedra - PDF Notes - 201702082201deevonc100% (1)
- Asphyxia and BarotraumaDocument10 pagesAsphyxia and BarotraumadeevoncNo ratings yet
- RA 11223 + F1 For HealthDocument3 pagesRA 11223 + F1 For HealthdeevoncNo ratings yet
- Trainee EvaluationDocument2 pagesTrainee EvaluationdeevoncNo ratings yet
- Ent Midterms SamplexDocument7 pagesEnt Midterms SamplexdeevoncNo ratings yet
- CARIAGA Pharmacological TXDocument1 pageCARIAGA Pharmacological TXdeevoncNo ratings yet
- Clinical Psychiatric Signs and Symptoms Group 1 (Section L)Document9 pagesClinical Psychiatric Signs and Symptoms Group 1 (Section L)deevoncNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Duodenal ObstructionDocument53 pagesDuodenal ObstructionBoby ChandraNo ratings yet
- Malrotation and Volvulus Great Ormond Street HospitalDocument1 pageMalrotation and Volvulus Great Ormond Street Hospitalghy7jbj96sNo ratings yet
- A Pattern Based Approach To The Bowel Obstruction in The NewbornDocument12 pagesA Pattern Based Approach To The Bowel Obstruction in The Newborntiosam59100% (1)
- Pediatrics Acute AbdomenDocument67 pagesPediatrics Acute AbdomenCabdi IshakNo ratings yet
- 6255 24879 1 PBDocument2 pages6255 24879 1 PBSyafatesia nicky pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric GI RadiologyDocument6 pagesPediatric GI Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- Malrotation of Gut: Pravin NarkhedeDocument44 pagesMalrotation of Gut: Pravin Narkhedepravin narkhede0% (1)
- Intestinal Malrotation - A Common Yet Deadly Cause of Neonatal Small Bowel ObstructionDocument4 pagesIntestinal Malrotation - A Common Yet Deadly Cause of Neonatal Small Bowel ObstructionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction in Pediatric PatientsDocument25 pagesIntestinal Obstruction in Pediatric PatientsHaryo Priambodo100% (1)
- Intestinal Ischemia in Neonates and Children: ReviewDocument5 pagesIntestinal Ischemia in Neonates and Children: Reviewriri siahaanNo ratings yet
- Ocluzie Intestinala Prin Stenoza Extrinseca de Colon TransversDocument8 pagesOcluzie Intestinala Prin Stenoza Extrinseca de Colon TransversClaudia DanielaNo ratings yet
- Malrotation and Midgut VolvulusDocument4 pagesMalrotation and Midgut VolvulusFendyJonathanNo ratings yet
- Neorev - Emergencias Quirúrgicas Abdominales en NeoDocument10 pagesNeorev - Emergencias Quirúrgicas Abdominales en NeoLuis Ruelas SanchezNo ratings yet
- Multiple Associated Anomalies in Patients of Duodenal Atresia: A Case SeriesDocument2 pagesMultiple Associated Anomalies in Patients of Duodenal Atresia: A Case SeriesMuhammad Bilal MirzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31 - Duodenal and Intestinal Atresia and Stenosis PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 31 - Duodenal and Intestinal Atresia and Stenosis PDFArdi SuhardjoNo ratings yet
- Case Report Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome ADocument5 pagesCase Report Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome AGunduz AgaNo ratings yet
- Poster MidgutDocument1 pagePoster MidgutMuruga PrakashNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics - Baby Emesis PDFDocument2 pagesPediatrics - Baby Emesis PDFDaniel FischerNo ratings yet
- 2-Acute Abdominal PainDocument24 pages2-Acute Abdominal Painabdalmajeed alshammaryNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Malrotation and Volvulus: Luisa Ferrero, François Becmeur, and Olivier ReinbergDocument15 pagesIntestinal Malrotation and Volvulus: Luisa Ferrero, François Becmeur, and Olivier ReinbergIván Castellares RojasNo ratings yet
- Ajr 17 19378Document13 pagesAjr 17 19378heryanggunNo ratings yet
- Case Study SurgeryDocument12 pagesCase Study SurgeryrupaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31 - Duodenal and Intestinal Atresia and Stenosis PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 31 - Duodenal and Intestinal Atresia and Stenosis PDFArdi SuhardjoNo ratings yet
- 01 - PediatricsDocument74 pages01 - Pediatricscore radiologyNo ratings yet
- Duodenal Stenosis in A Child: A. Y. Kshirsagar, Sanjitsingh R. Sulhyan, Gaurav Vasisth, Yogesh P. NikamDocument3 pagesDuodenal Stenosis in A Child: A. Y. Kshirsagar, Sanjitsingh R. Sulhyan, Gaurav Vasisth, Yogesh P. Nikameka nurjanahNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Imaging A Core Review PDFDocument767 pagesPediatric Imaging A Core Review PDFBeatriz100% (3)
- Association of Duodenal Atresia, Malrotation, Ventricular Septal Defect, Endocardial Cushion Defect, Atrial Septal Defect, and Patent Ductus Arteriosus in A Down Syndrome PatientDocument3 pagesAssociation of Duodenal Atresia, Malrotation, Ventricular Septal Defect, Endocardial Cushion Defect, Atrial Septal Defect, and Patent Ductus Arteriosus in A Down Syndrome PatientasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Nausa Vomiting Children PDFDocument36 pagesNausa Vomiting Children PDFNie's Pastries-PartyNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Billious VomitingDocument42 pagesNeonatal Billious Vomitinghayssam rashwan100% (1)
- WJR 8 656Document13 pagesWJR 8 656aldosaputraNo ratings yet