Professional Documents
Culture Documents
13 Cycles - PPSX
13 Cycles - PPSX
Uploaded by
BETHUEL P. ALQUIROZ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views14 pagesOriginal Title
13 Cycles.ppsx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views14 pages13 Cycles - PPSX
13 Cycles - PPSX
Uploaded by
BETHUEL P. ALQUIROZCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
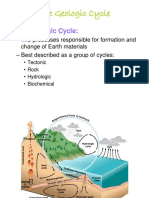
Cycles
Water, Carbon, Nitrogen
Oxygen and Phosphorus
Water (hydrologic) Cycle
Plants absorb water from the soil
Transpiration and respiration return
water to the atmosphere
Precipitation returns water to the soil
Nonmetal oxides in the atmosphere
combine with water to form acid rain
The Carbon Cycle
• Carbon is fixed by plants
– 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2
• Carbon is given off by consumers
– C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O
• Organisms containing carbon form fossil
fuels
• Burning fossil fuels releases carbon
– 2 C8H18 + 25 O2 16 CO2 + 18 H2O
Carbon Cycle
Arctic Carbon Cycling
The Nitrogen Cycle
Bacteria fix nitrogen from the air
Consumers and producers incorporate
nitrogen into their tissues
Nitrogen can be fixed industrially from
the air
Production of ammonia
Decay processes return nitrogen to the air
Nitrogen from fertilizers may contaminate
water sources
Aquarium Nitrogen Cycle
The Oxygen Cycle
• Oxygen is produced by photosynthesis
– 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2
– The largest chemical process on earth!
• Oxygen is sequestered by respiration
– C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O
6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2
The Phosphorus Cycle
• The element phosphorus (P)is released in
the form of ionic phosphate (PO43-)
– Weathering of rock, mining, some detergents
and fertilizers
• Phosphate is taken up by plants and fungi
• Consumers absorb phosphate from plants
• Decomposers return phosphate to soil
• Phosphate leaches into water supply
– May form new phosphate containing rock
You might also like
- Pocket Manual in Critical CareDocument356 pagesPocket Manual in Critical CareTahir Uddin Qazi86% (7)
- Lec 7 Biogeochemical CyclesDocument12 pagesLec 7 Biogeochemical CyclesKhaled Hasan Khan100% (1)
- Fermentationprocessesandtheirapplication 150211190135 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument31 pagesFermentationprocessesandtheirapplication 150211190135 Conversion Gate02 PDFPatricia GabonNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycle: Environmental CyclesDocument21 pagesBiogeochemical Cycle: Environmental CyclesAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Cycle of MatterDocument28 pagesCHAPTER 2 Cycle of MatterRamil NacarioNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 5Document36 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 5Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 4Document67 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 4Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- The Carbon Cycle UpdatedDocument15 pagesThe Carbon Cycle UpdatedFoisal SwarupNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process IndustriesDocument78 pagesChemical Process IndustriesaaaNo ratings yet
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Practice TestDocument51 pagesMidwifery Practice TestDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- Bod and CodDocument66 pagesBod and CodKamlesh Kamlesh EtwaroNo ratings yet
- Environmental and Applied MicrobiologyDocument68 pagesEnvironmental and Applied MicrobiologyDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- The Gram-Negative Bacilli of Medical ImportanceDocument54 pagesThe Gram-Negative Bacilli of Medical ImportanceAna-Maria Nicolae100% (1)
- Foundations in Microbiology: Microbial Metabolism: The Chemical Crossroads of Life TalaroDocument48 pagesFoundations in Microbiology: Microbial Metabolism: The Chemical Crossroads of Life TalaroDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Cycles: Water, Carbon, Nitrogen Oxygen and PhosphorusDocument14 pagesCycles: Water, Carbon, Nitrogen Oxygen and Phosphorus没言No ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument10 pagesThe Carbon CycleFoisal SwarupNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide-Oxygen CycleDocument18 pagesCarbon Dioxide-Oxygen CycleNorman Honorio Aguila CelesteNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide: CarbohydrateDocument14 pagesCarbon Dioxide: CarbohydratePratik AgajNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of The EnviromentDocument32 pagesChemistry of The Enviromentsalman ahsanNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument17 pagesCarbon CycleJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle PowerpointDocument17 pagesCarbon Cycle PowerpointJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument31 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesJessica OliverNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cyle1Document17 pagesCarbon Cyle1Kurniawan RizkiNo ratings yet
- CH215 Industrial Organic Chemistry II 24-12-2021Document229 pagesCH215 Industrial Organic Chemistry II 24-12-2021Fortune VusheNo ratings yet
- Earth's Natural Cycles: Water (H O) Cycle Carbon Dioxide/Oxygen (CO /O) Cycle Nitrogen CycleDocument18 pagesEarth's Natural Cycles: Water (H O) Cycle Carbon Dioxide/Oxygen (CO /O) Cycle Nitrogen CycleMarj Jermaine M. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Lect. 2Document5 pagesLect. 2xa53dasNo ratings yet
- Jaglerod Mono-Di OksidDocument10 pagesJaglerod Mono-Di OksidLiljana DimeskaNo ratings yet
- Key Wodrs For Environmental Engineering: Limited CompanyDocument24 pagesKey Wodrs For Environmental Engineering: Limited CompanyNazar Abdul KareemNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles 2Document58 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles 2waranya kasemchittNo ratings yet
- Carbonated Drinks: Western WorldDocument11 pagesCarbonated Drinks: Western WorldJanno GironellaNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument12 pagesThe Carbon CycleClariene CaburnayNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument13 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesisaiahdesNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering - 1 (Chemical Concentrations in Water, Air and Soil)Document20 pagesEnvironmental Engineering - 1 (Chemical Concentrations in Water, Air and Soil)m abdullah m akmalNo ratings yet
- The Oxygen CycleDocument25 pagesThe Oxygen CycleDeepakKumarJINo ratings yet
- Oxygen Carbon CycleDocument24 pagesOxygen Carbon CycleDezzalyn D. GabrielNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument12 pagesThe Carbon CycleClariene CaburnayNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle and Global WarmingDocument23 pagesCarbon Cycle and Global WarmingTayson PreteNo ratings yet
- Energy & Climate Change - Lect-6 (28.09.2021)Document25 pagesEnergy & Climate Change - Lect-6 (28.09.2021)humza abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument12 pagesCarbon CyclePorco dioNo ratings yet
- Carbonate SystemDocument64 pagesCarbonate Systemmohan kumarNo ratings yet
- Cloze Cycles in NatureDocument3 pagesCloze Cycles in NatureMheyMartinezNo ratings yet
- Nutrient CyclesDocument29 pagesNutrient CyclesMajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Cycles in Ecosystems BIODocument5 pagesCycles in Ecosystems BIOItsspongoNo ratings yet
- Earths Cycles (Lecture 06) - Part 02Document39 pagesEarths Cycles (Lecture 06) - Part 02Binthan RamzeeniNo ratings yet
- SIH1001 Population Biology: Nutrient CyclesDocument36 pagesSIH1001 Population Biology: Nutrient CyclesFatma AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Sulfur Nitrogen Cycle.Document32 pagesSulfur Nitrogen Cycle.zyrha paradoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of The EnvironmentDocument7 pagesChemistry of The Environmentmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles-SummaryDocument2 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles-Summaryapi-326622735No ratings yet
- Air and Atmosphere: Class 6 by Aditi PandeyDocument14 pagesAir and Atmosphere: Class 6 by Aditi PandeyNeha TiwariNo ratings yet
- Oxygen 150509081746 Lva1 App6891Document16 pagesOxygen 150509081746 Lva1 App6891erparshotamNo ratings yet
- Isolation and ProductionDocument4 pagesIsolation and ProductiontinkuNo ratings yet
- Hydrochloric Acid Regeneration - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesHydrochloric Acid Regeneration - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediazamburittiNo ratings yet
- Bio - HydrogenDocument18 pagesBio - HydrogenHarsh Vinay SinghNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources Biogeochemical CyclesDocument4 pagesNatural Resources Biogeochemical Cyclesboris pocusNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ramakrishna Bag Dept of Civil Engineering NIT RourkelaDocument18 pagesDr. Ramakrishna Bag Dept of Civil Engineering NIT RourkelaJon JimmyNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles - 1: Class Lecture GoalsDocument21 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles - 1: Class Lecture GoalssunilkumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Igcse Chemistry Carbon CycleDocument35 pagesLesson 2 Igcse Chemistry Carbon Cycledanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Air and Water IGCSE NotesDocument26 pagesAir and Water IGCSE NotesMisbah Kamran100% (1)
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument28 pagesWaste Water TreatmentRoseNavyaNo ratings yet
- Terjemah Karya Tulis RIKADocument17 pagesTerjemah Karya Tulis RIKAKeyla AishaNo ratings yet
- Ecology: All Ecosystems Need Certain MaterialsDocument5 pagesEcology: All Ecosystems Need Certain MaterialsHiten AhujaNo ratings yet
- NO NO R NH NO: Siklus KarbonDocument3 pagesNO NO R NH NO: Siklus KarbonAzriel BryanNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle 2020Document13 pagesCarbon Cycle 2020Shavane DavisNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument25 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesAlokfriNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument43 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 2Document18 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 2Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
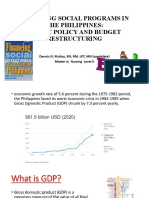
- Financing Social Programs in The Philippines: Public Policy and Budget RestructuringDocument78 pagesFinancing Social Programs in The Philippines: Public Policy and Budget RestructuringDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Covid 19: Dennis N. Muñoz, RN, RM, LPTDocument103 pagesCovid 19: Dennis N. Muñoz, RN, RM, LPTDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Davao University Graduate SchoolDocument4 pagesAteneo de Davao University Graduate SchoolDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet