Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trig Cheat Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
Steven TruongOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trig Cheat Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
Steven TruongCopyright:
Available Formats
Trig Cheat Sheet
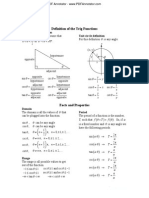
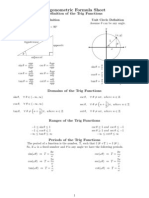
Definition of the Trig Functions
Right triangle definition
For this definition we assume that Unit circle definition
p For this definition q is any angle.
0 < q < or 0° < q < 90° .
2 y
( x, y )
hypotenuse 1
y q
opposite x
x
q
adjacent
opposite hypotenuse y 1
sin q = csc q = sin q = =y csc q =
hypotenuse opposite 1 y
adjacent hypotenuse x 1
cos q = sec q = cos q = = x sec q =
hypotenuse adjacent 1 x
opposite adjacent y x
tan q = cot q = tan q = cot q =
adjacent opposite x y
Facts and Properties
Domain
The domain is all the values of q that Period
can be plugged into the function. The period of a function is the number,
T, such that f (q + T ) = f (q ) . So, if w
sin q , q can be any angle is a fixed number and q is any angle we
cos q , q can be any angle have the following periods.
æ 1ö
tan q , q ¹ ç n + ÷ p , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,K
è 2ø 2p
sin ( wq ) ® T=
csc q , q ¹ n p , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,K w
æ 1ö 2p
sec q , q ¹ ç n + ÷ p , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,K cos (wq ) ® T =
è 2ø w
cot q , q ¹ n p , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,K p
tan (wq ) ® T =
w
Range 2p
csc (wq ) ® T =
The range is all possible values to get w
out of the function. 2p
-1 £ sin q £ 1 csc q ³ 1 and csc q £ -1 sec (wq ) ® T =
w
-1 £ cos q £ 1 sec q ³ 1 and sec q £ -1 p
-¥ < tan q < ¥ -¥ < cot q < ¥ cot (wq ) ® T =
w
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
Formulas and Identities
Tangent and Cotangent Identities Half Angle Formulas (alternate form)
sin q cos q q 1 - cos q 1
tan q = cot q = sin = ± sin 2 q = (1 - cos ( 2q ) )
cos q sin q 2 2 2
Reciprocal Identities
q 1 + cos q 1
csc q =
1
sin q =
1 cos
2
=±
2
cos 2 q =
2
(1 + cos ( 2q ) )
sin q csc q
1 1 q 1 - cos q 1 - cos ( 2q )
sec q = cos q = tan = ± tan 2 q =
cos q sec q 2 1 + cos q 1 + cos ( 2q )
1 1 Sum and Difference Formulas
cot q = tan q =
tan q cot q sin (a ± b ) = sin a cos b ± cos a sin b
Pythagorean Identities cos (a ± b ) = cos a cos b m sin a sin b
sin 2 q + cos 2 q = 1
tan a ± tan b
tan 2 q + 1 = sec 2 q tan (a ± b ) =
1 m tan a tan b
1 + cot 2 q = csc 2 q Product to Sum Formulas
1
Even/Odd Formulas sin a sin b = éëcos (a - b ) - cos (a + b ) ùû
sin ( -q ) = - sin q csc ( -q ) = - csc q 2
1
cos ( -q ) = cos q sec ( -q ) = sec q cos a cos b = éë cos (a - b ) + cos (a + b ) ùû
2
tan ( -q ) = - tan q cot ( -q ) = - cot q 1
sin a cos b = éësin (a + b ) + sin (a - b ) ùû
Periodic Formulas 2
If n is an integer. 1
cos a sin b = éësin (a + b ) - sin (a - b ) ùû
sin (q + 2p n ) = sin q csc (q + 2p n ) = csc q 2
Sum to Product Formulas
cos (q + 2p n ) = cos q sec (q + 2p n ) = sec q
æa + b ö æa - b ö
tan (q + p n ) = tan q cot (q + p n ) = cot q sin a + sin b = 2sin ç ÷ cos ç ÷
è 2 ø è 2 ø
Double Angle Formulas
æa + b ö æa - b ö
sin a - sin b = 2 cos ç ÷ sin ç ÷
sin ( 2q ) = 2sin q cos q è 2 ø è 2 ø
cos ( 2q ) = cos 2 q - sin 2 q cos a + cos b = 2 cos ç
æa + b ö æa - b ö
÷ cos ç ÷
= 2 cos 2 q - 1 è 2 ø è 2 ø
æa + b ö æa - b ö
= 1 - 2sin 2 q cos a - cos b = -2sin ç ÷ sin ç ÷
è 2 ø è 2 ø
2 tan q
tan ( 2q ) = Cofunction Formulas
1 - tan 2 q
æp ö æp ö
Degrees to Radians Formulas sin ç - q ÷ = cos q cos ç - q ÷ = sin q
è2 ø è2 ø
If x is an angle in degrees and t is an
angle in radians then æp ö æp ö
csc ç - q ÷ = sec q sec ç - q ÷ = csc q
p t px 180t è2 ø è2 ø
= Þ t= and x = æp ö æp ö
180 x 180 p tan ç - q ÷ = cot q cot ç - q ÷ = tan q
è2 ø è2 ø
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
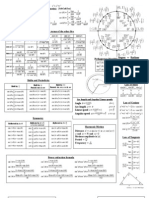
Unit Circle
y
( 0,1)
p æ1 3ö
æ 1 3ö çç 2 , 2 ÷÷
ç- , ÷ 2 è ø
è 2 2 ø p æ 2 2ö
2p 90° çç , ÷÷
æ 2 2ö 3 è 2 2 ø
ç- , ÷ 3
è 2 2 ø 120° p
3p 60° æ 3 1ö
4 çç 2 , 2 ÷÷
æ 3 1ö 4 45° p è ø
ç- , ÷ 135°
è 2 2ø 5p
6
6 30°
150°
( -1,0 ) p 180° 0° 0 (1,0 )
360° 2p x
210°
7p 330°
11p
6 225°
æ 3 1ö 6 æ 3 1ö
ç - ,- ÷ 5p 315° ç ,- ÷
è 2 2ø è 2 2ø
4 240° 300° 7p
æ 2ö 4p 270°
ç-
2
,- ÷ 5p 4 æ 2 2ö
è 2 2 ø 3 3p ç
2
,-
2
÷
3 è ø
æ 1 3ö 2 æ
ç - ,- ÷ 1 3ö
2 2 ç ,- ÷
è ø è2 2 ø
( 0,-1)
For any ordered pair on the unit circle ( x, y ) : cos q = x and sin q = y
Example
æ 5p ö 1 æ 5p ö 3
cos ç ÷= sin ç ÷=-
è 3 ø 2 è 3 ø 2
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
Inverse Trig Functions
Definition Inverse Properties
y = sin -1 x is equivalent to x = sin y cos ( cos -1 ( x ) ) = x cos -1 ( cos (q ) ) = q
y = cos -1 x is equivalent to x = cos y sin ( sin -1 ( x ) ) = x sin -1 ( sin (q ) ) = q
y = tan -1 x is equivalent to x = tan y
tan ( tan -1 ( x ) ) = x tan -1 ( tan (q ) ) = q
Domain and Range
Function Domain Range Alternate Notation
p p sin -1 x = arcsin x
y = sin -1 x -1 £ x £ 1 - £ y£
2 2 cos -1 x = arccos x
y = cos -1 x -1 £ x £ 1 0£ y £p tan -1 x = arctan x
p p
y = tan -1 x -¥ < x < ¥ - < y<
2 2
Law of Sines, Cosines and Tangents
c b a
a g
Law of Sines Law of Tangents
sin a sin b sin g
= = a - b tan 12 (a - b )
=
a b c a + b tan 12 (a + b )
Law of Cosines b - c tan 12 ( b - g )
=
a 2 = b2 + c 2 - 2bc cos a b + c tan 12 ( b + g )
b 2 = a 2 + c 2 - 2ac cos b a - c tan 12 (a - g )
=
c = a + b - 2ab cos g a + c tan 12 (a + g )
2 2 2
Mollweide’s Formula
a + b cos 12 (a - b )
=
c sin 12 g
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
You might also like
- Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet ReducedMritunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Trigonometry Condensed Formula SheetDocument2 pagesTrigonometry Condensed Formula SheetRiza Azari0% (1)
- Trig Cheat Sheet: Formulas and IdentitiesDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet: Formulas and IdentitiesMuzamilNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Motion in A PlaneDocument3 pagesMotion in A PlanePilotsaicharan AirbusNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law of MotionDocument25 pagesNewtons Law of MotionJoca RiveraNo ratings yet
- 25 Even and Odd FunctionsDocument4 pages25 Even and Odd Functionsapi-299265916No ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Circles: Chapter HighlightsDocument55 pagesCircles: Chapter HighlightsAditya WanwadeNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines Slides-239Document465 pagesStraight Lines Slides-239Siddharth Rajendran100% (1)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Integration SummaryDocument5 pagesIntegration SummarySweekrut SahooNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Solutions of 5 Online Physics BrawlDocument45 pagesSolutions of 5 Online Physics BrawlKetul ShahNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Must Know Formula On Physics For AIPMT NewDocument78 pagesMust Know Formula On Physics For AIPMT Newanshul sharma33% (3)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Math.lamar - Edu PDF Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedDocument2 pagesTutorial - Math.lamar - Edu PDF Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedAnonymous vyXcR9No ratings yet
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet ReducedPhirak KhimNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument4 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsMihir SethiNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument3 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionstripathi_girishNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- EquationsDocument17 pagesEquationshasanmt23100% (1)
- Mathematics???Document6 pagesMathematics???DEFRON GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Mathematics TrigonometryDocument129 pagesMathematics TrigonometryUdayveerSinghNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet 1.4Document2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet 1.4agentc0re0% (1)
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. Hons Mathematics-2 PDFDocument47 pagesB.Sc. Hons Mathematics-2 PDFFirdous AhmadNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Calculus Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Story of TrigonometryDocument16 pagesStory of TrigonometryAkshat Jain100% (1)
- Trig Cheat Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet PDFRiham Salah Mustafa100% (1)
- Derivative Worksheet 1Document1 pageDerivative Worksheet 1Kasun TudugalaNo ratings yet
- SPB AddMaths Answer SPM 2009Document19 pagesSPB AddMaths Answer SPM 2009murulikrishanNo ratings yet
- CVT 2marks - 21Document23 pagesCVT 2marks - 21Pasupuleti Venkata RamanaNo ratings yet
- Sweet Baby Dresses in Crochet: 4 Dresses in Sizes Newborn to 24 Months, with Matching AccessoriesFrom EverandSweet Baby Dresses in Crochet: 4 Dresses in Sizes Newborn to 24 Months, with Matching AccessoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Syllabus PDFDocument34 pagesSyllabus PDFTazel Hossan100% (1)
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Table: Let A, N & C Are Constant, F F (X)Document3 pagesDifferentiation Table: Let A, N & C Are Constant, F F (X)alexandra owNo ratings yet
- Complex AnalysisDocument9 pagesComplex AnalysisSuman BasakNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical Trigonometry SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesPlane and Spherical Trigonometry SYLLABUSCAHEL ALFONSONo ratings yet
- Complex Analytic and Differential Geometry - J. DemaillyDocument518 pagesComplex Analytic and Differential Geometry - J. DemaillyShahenaz KassemNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Measurement of AnglesDocument57 pagesTrigonometry: Measurement of AnglesLeo V. Baker100% (2)
- List of Logarithmic IdentitiesDocument7 pagesList of Logarithmic IdentitiesMuhammedNayeemNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- MAT060 - 27 Integration Involvin Quadratic FunctionsDocument11 pagesMAT060 - 27 Integration Involvin Quadratic FunctionsHassan GandamraNo ratings yet
- Power SeriesDocument33 pagesPower SeriesAlfiyah An-NajmNo ratings yet
- Productivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionFrom EverandProductivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionNo ratings yet
- B Sc-Maths PDFDocument34 pagesB Sc-Maths PDFNunna MaheshbabuNo ratings yet
- Water RudinDocument7 pagesWater Rudintgabi2012No ratings yet
- Yibeltal Irrational NumbersDocument20 pagesYibeltal Irrational NumbersMiliyon TilahunNo ratings yet
- 77 89Document9 pages77 89deresNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P2 Feb-March 2014 Memo Afr & EngDocument14 pagesMathematics P2 Feb-March 2014 Memo Afr & Engaleck mthethwaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P2 Feb-March 2018 Memo Afr & EngDocument22 pagesMathematics P2 Feb-March 2018 Memo Afr & EngPeter Ng'ambiNo ratings yet
- BesintDocument457 pagesBesintccNo ratings yet
- Tabel Laplace PDFDocument2 pagesTabel Laplace PDFIlham Hendratama100% (1)
- Beta FunctionDocument4 pagesBeta FunctionSindhubairaviNo ratings yet
- Detailed Proof For Chudnovski's Formula For PiDocument120 pagesDetailed Proof For Chudnovski's Formula For PijeamichelNo ratings yet
- CalcI ChainRule SolutionsDocument19 pagesCalcI ChainRule SolutionsFajrul Islam RamdhanNo ratings yet
- Diferensial Dan Integral BakuDocument1 pageDiferensial Dan Integral BakuAufa ArdNo ratings yet
- Mind Action Series: Mathematics Grade 10 New Edition Textbook Launch - Sample ChaptersDocument64 pagesMind Action Series: Mathematics Grade 10 New Edition Textbook Launch - Sample ChaptersHarvest SoulsNo ratings yet
- This Page Is About The Trigonometric Functions ofDocument37 pagesThis Page Is About The Trigonometric Functions ofSilvio MadetyNo ratings yet
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet