Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 10 - Deformation of Earth's Crust
Uploaded by
lesly Anne0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pageshandouts
Original Title
Topic 10_Deformation of Earth's Crust
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenthandouts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pagesTopic 10 - Deformation of Earth's Crust
Uploaded by
lesly Annehandouts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Page 9
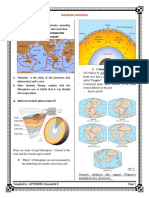
TOPIC: Deformation of Earth’s Crust
- once located near the South Pole, and
I. Theory of Continental Drift
had drifted away from each other.
It states that a giant landmass are slowly broke into
In 1919, Sir Arthur Holmes, an English geologist,
smaller land pieces, then eventually drifted away
proposed the presence of convection in the Earth’s
from each other which made the seven continents.
mantle.
Seven Continents:
When the rocks in the Earth’s interior are heated by
1. Asia 4. Europe
radioactivity, they become less dense, and they rise
2. Africa 5. Antarctic
toward the surface of the Earth. When they cool down,
3. North America 6. Australia
they become denser and sink.
4. South America
The continuous process of rising and sinking of rocks
In 1912, German meteorologist Alfred
produces mantle convection. These currents cause
Wegener proposed that in the beginning, the Earth
the tectonic plates, which include the crust, to move and
has only one giant landmass called Pangaea,
drift.
which means "all land”.
II. Theory of Plate Tectonics
It states that the Earth’s crust is divided into plates,
known as tectonic plates, and these plates move
due to the convection currents in the Earth’s
interior.
* Seven Major Plates * Seven Minor Plates
1. Pacific Plate 1. Philippine Plate
2. Eurasian Plate 2. Nazca Plate
3. African Plate 3. Arabian Plate
Alfred Wegener presented the following pieces of
4. North American Plate 4. Caribbean Plate
evidence to support his theory: 5. South American Plate 5. Cocos Plate
1. The continents fit together like a jigsaw 6. Antarctic Plate 6. Juan de Fuca Plate
puzzle. 7. Australian-Indian Plate 7. Scotia Plate
- This is most evident in the matching Plate Movements
coastlines of South America and Africa. - The movement of the plates depends on the
2. Similar animal and plant fossils were found in boundaries between them. These boundaries
different continents. can be convergent, divergent, or transform.
- The fossils of the a) Convergent Plate Boundary
reptile mesosaurus were found along the - the plates move or collide to each other
coastlines of South America and Africa caused by compressional stress.
which are separated by the Atlantic b) Divergent Plate Boundary
Ocean. - When the plates move away from each
- Moreover, the fossil of a fern- like other caused by tensional stress.
plant glossopteris was found distributed c) Transform Plate Boundary
in all the continents. - When plates slide past each other due to
3. The rocks are of the same type and age. shear stress.
- Geologic features such as mountain
ranges are found along matching Fracture
coastlines like that of the Appalachian - Since the pressure and temperature are
Mountains low at the Earth’s surface, rocks tend to
4. Presence of coal in Antartica. break or fracture when subjected to
- Coal is produced from organic matter like compressional and tensional stresses.
dead plants and animals. In a very cold - This means that the pressure exerted in
place like Antarctica, it would be the blocks of rocks exceeds the rock's
impossible for most organisms to survive. internal strength.
- The presence of coal indicates that the - Fractures can either be a fault or a
continent was once inhabited by many joint. A fault is a break in the rock where
organisms. It also gives a clue that there is considerable movement on the
Antarctica was once located near the fracture surface while a joint is a break
equator where abundant animal and plant where there is no considerable
organisms could be found. movement.
5. Presence of Glacial Deposits.
- Tillites, which are deposits of rock debris Two Types of Fault
left by glaciers, were found in Africa, 1. Dip-slip Fault
South America, India, and Australia. They - Dip-slip faults can either be a normal or a
were of the same age and type. reverse fault.
- The presence of tillites indicates that a) A normal fault is caused by tensional
those places had glaciers in the past, were stress it is characterized by the hanging
-
Page 10
wall moving downward with respect to the
footwall.
b) A reverse fault, wherein the hanging wall
moves upward, is formed by
compressional stress New oceanic crust is formed from the outpouring
of the molten materials, and as the process
continues, oceanic ridges or underwater mountain
ranges are built.
Oceanic ridges are composed of volcanic rocks.
As the molten materials continuously flow out from
the ridges, the seafloor also keeps on spreading
forming a central valley, or a rift valley, at the
2. Strike-slip Fault summit of the oceanic ridges.
- Strike-slip fault involves a horizontal
movement of blocks of rock and is caused The molten materials push the seafloor away from
by shear stress. the ridges and towards the trenches. Trenches are
depressions on the ocean floor.
Folds
- Deep within the crust, where pressure Oceanic ridges are formed at divergent
and temperature are high, rocks are boundaries, where plates move away from each
plastic-like; thus, they do not break but other;
they tend to bend or fold.
- When rocks in this area are compressed, Trenches are formed at subduction zones
they become thicker. When rocks where plates collide with each other or
become thinner, they are pulled apart. at convergent boundaries.
Types of Fold
a) When blocks of rock are bent upwards, they
form anticline structures.
b) Synclines are formed when blocks of rock
bend downwards.
c) A slightly bent rock from the parallel
undeformed layers forms monoclines.
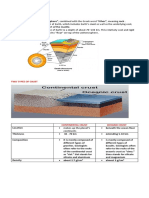
III. Theory of Seafloor Spreading
It states that convection currents in the Earth’s
interior make the seafloor spread.
Convection currents carry heat from the molten
materials in the mantle and core towards the
lithosphere
It was proposed in 1960 by Harry Hess, an
American geophysicist.
Because of seafloor spreading, the molten
materials flow out to form mid-oceanic ridges,
spread sideways to form seafloor, and disappear
into the ocean trenches.
You might also like
- Techcombank Tower Project Team StrategiesDocument5 pagesTechcombank Tower Project Team StrategiesNguyên Trịnh CaoNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift Theory and Plate TectonicsDocument3 pagesContinental Drift Theory and Plate TectonicsAndrea Mae CamachoNo ratings yet
- Plate Movements and Boundaries Science Presentation in Dark Blue Teal StyleDocument48 pagesPlate Movements and Boundaries Science Presentation in Dark Blue Teal StyleAngeline AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 - Deformation of Earth's CrustDocument2 pagesTopic 10 - Deformation of Earth's Crustlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- 1st Fact Sheets Grade 10 074123Document8 pages1st Fact Sheets Grade 10 074123Jalillah Bint Mohammad JamilNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewerMelody Bong ZitaNo ratings yet
- Movements in The EarthDocument4 pagesMovements in The EarthJoepeteNo ratings yet
- The Continental Drift Theory HandoutsDocument3 pagesThe Continental Drift Theory Handoutslorraine baysicNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument4 pagesEarth SciencerichtellegNo ratings yet
- SCIREV2Document3 pagesSCIREV2kurtdash16No ratings yet
- Earth Science Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesEarth Science Plate TectonicsKeesha MendozaNo ratings yet
- Continantal Drift TheoryDocument4 pagesContinantal Drift TheoryBasetsana BoikanyoNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 1 Reviewer G10Document12 pagesScience Quarter 1 Reviewer G10jahri ruzeraNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics ExplainedDocument4 pagesContinental Drift and Plate Tectonics ExplainedCHRISTIAN NATHANIEL PALMANo ratings yet
- Lesson 10: Plate Tectonics and Palaeogeography Shaped Early Dinosaur EvolutionDocument14 pagesLesson 10: Plate Tectonics and Palaeogeography Shaped Early Dinosaur EvolutionGuilherme Campos PereiraNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift Theory NotesDocument3 pagesContinental Drift Theory NotesGirli JoseeNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document9 pagesDocument 1NADIAHTUL MARYAM BINTI RUSYDI RUSNo ratings yet
- ZIMSEC Geography Notes Form 2Document93 pagesZIMSEC Geography Notes Form 2violetcuchNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 Tectonic Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesActivity 5 Tectonic Plate BoundariesaiahNo ratings yet
- Geog 1 - FinalsDocument10 pagesGeog 1 - FinalsAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Sci 4thDocument3 pagesSci 4thhrptqph9skNo ratings yet
- I. Definition:: Endogenic ProcessesDocument10 pagesI. Definition:: Endogenic ProcessesJepoy Nisperos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Earth'S Mechanism: (Continental Drift Theory)Document32 pagesEarth'S Mechanism: (Continental Drift Theory)Bublee NeeNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Theory Hand-OutDocument4 pagesContinental Drift and Plate Tectonics Theory Hand-OutalyssaNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz 1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesLong Quiz 1 ReviewerBianca RabeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science: LithosphereDocument3 pagesReviewer in Science: LithosphereNatasha Loujille Collado100% (1)
- Reviewer For Science Test 1Document4 pagesReviewer For Science Test 1Mudzna MusahariNo ratings yet
- CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY AND EVIDENCES THAT SUPPORT CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORYDocument11 pagesCONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY AND EVIDENCES THAT SUPPORT CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORYChad Laurence Vinson CandelonNo ratings yet
- LANDFORMS and GEOGRAPHIC PLACEMENTDocument4 pagesLANDFORMS and GEOGRAPHIC PLACEMENTElmar AlataNo ratings yet
- Science 10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 10 ReviewerAmber RamosNo ratings yet
- What Is Plate Tectonics? History:: How Plate Tectonic Work ?Document2 pagesWhat Is Plate Tectonics? History:: How Plate Tectonic Work ?Klyde Cedrick Vibal SapinNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document7 pagesScience 10Anonymous t2Y8WBZGNo ratings yet
- Earth's Major PlatesDocument4 pagesEarth's Major PlatesJosette BonadorNo ratings yet
- PTR in Sci 10Document5 pagesPTR in Sci 10IanNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics by Zeeshan AnsariDocument21 pagesPlate Tectonics by Zeeshan AnsariZeeshan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Module 2Document1 pageUnit 1 Module 2heideNo ratings yet
- Science 1st PeriodicalDocument2 pagesScience 1st PeriodicalAgatha AquinoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Reviewer LT 1.2: I. Plate Tectonics A. Plate MotionDocument5 pagesEarth and Life Reviewer LT 1.2: I. Plate Tectonics A. Plate MotionEryka FloresNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift Theory EvidenceDocument4 pagesContinental Drift Theory EvidenceJaspher Dabuet CamilonNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Earths CrustDocument3 pagesChanges in The Earths CrustMayda ValgardssonNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 4: The Earth'S MechanismDocument3 pagesLecture No. 4: The Earth'S MechanismGlenmar Alejandro VinegasNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: The Ever-Changing EarthDocument1 pagePlate Tectonics: The Ever-Changing Earthjasmine's filesNo ratings yet
- Environment 1Document12 pagesEnvironment 1soundu ranganathNo ratings yet
- Geology Notes 102 - Second Major.Document42 pagesGeology Notes 102 - Second Major.Bilal KhattabNo ratings yet
- Types of Plate BoundariesDocument1 pageTypes of Plate BoundariesJuhlia UsonNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument4 pagesPlate Tectonic TheoryMargarette MartinNo ratings yet
- Core Science 5 - Chapter 8 (The Dynamic Earth)Document30 pagesCore Science 5 - Chapter 8 (The Dynamic Earth)CrazyCat DancerNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Plate TectonicsDocument10 pages2.2 Plate TectonicsMaria KhanNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Quarter 1Document3 pagesScience 10 - Quarter 1Prestela Leona DeatrasNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesEarth ScienceakosimanihulloNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument6 pagesScienceArsheil Lavein R. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Earth QuestionsDocument2 pagesDynamic Earth QuestionsDrew ClaryNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - First Quarter NotesDocument6 pagesScience 10 - First Quarter NotesJulienne Nicole AmularNo ratings yet
- Daniel 9Document1 pageDaniel 9api-3848758No ratings yet
- Reviewer 8 ScienceDocument16 pagesReviewer 8 ScienceJhanna Gil BuctolanNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Reference MaterialDocument30 pagesCh4 Reference MaterialdrishtiNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Concepts and EvidenceDocument26 pagesPlate Tectonics Concepts and EvidenceshifatNo ratings yet
- Geology Summarize NotesDocument12 pagesGeology Summarize NotesShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Lithosphere and Plate TectonicsDocument15 pagesLithosphere and Plate TectonicsJoshua DaywanNo ratings yet
- Made by Yas - Personal Science NotesDocument15 pagesMade by Yas - Personal Science NotesMara Emira MiguelNo ratings yet
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Remedial Life QuizDocument3 pagesRemedial Life Quizlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Stoichiometry CalculationsDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry Stoichiometry Calculationslesly AnneNo ratings yet
- PhySci Module 1 Week1&2Document9 pagesPhySci Module 1 Week1&2lesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Universal Laws in Physics: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. KDocument73 pagesUniversal Laws in Physics: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. Klesly Anne100% (1)
- Topic 11 - History of The EarthDocument3 pagesTopic 11 - History of The Earthlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Iso PhysicsDocument4 pagesIso Physicslesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Kinship, Marriage Etc. PowerpointDocument34 pagesKinship, Marriage Etc. Powerpointlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Bataan Nuclear Power PlantDocument15 pagesBataan Nuclear Power Plantlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Explained: How Plants Make Food from SunlightDocument1 pagePhotosynthesis Explained: How Plants Make Food from Sunlightlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Field Biology - LESLY ANN DE VERADocument3 pagesField Biology - LESLY ANN DE VERAlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Topic 12-14 - Manifestation of Life, Origin of Life, and Cell TheoryDocument2 pagesTopic 12-14 - Manifestation of Life, Origin of Life, and Cell Theorylesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Detrailed LP in Physci2Document3 pagesDetrailed LP in Physci2lesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Biological Techniques - LESLY ANN DE VERADocument3 pagesBiological Techniques - LESLY ANN DE VERAlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Origin of The UniverseDocument2 pagesTopic 1 Origin of The Universelesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP in ELS1Document4 pagesDetailed LP in ELS1lesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Life (2016 - 08 - 21 00 - 09 - 04 UTC)Document20 pagesCharacteristics of Life (2016 - 08 - 21 00 - 09 - 04 UTC)lesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Kinship, Marriage Etc. PowerpointDocument34 pagesKinship, Marriage Etc. Powerpointlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 - History of The EarthDocument3 pagesTopic 11 - History of The Earthlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Exogenic and Endogenic Earth ProcessesDocument2 pagesExogenic and Endogenic Earth Processeslesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP in ChemDocument11 pagesDetailed LP in Chemlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Rock Cycle1Document44 pagesRocks and Rock Cycle1lesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Rocket speed = 10 km/s* Distance = 30 km * Speed = Distance / Time* Time = Distance / Speed* Time = 30,000 m / 10,000 m/s = 3 sDocument31 pagesRocket speed = 10 km/s* Distance = 30 km * Speed = Distance / Time* Time = Distance / Speed* Time = 30,000 m / 10,000 m/s = 3 slesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 The Solar SystemDocument2 pagesTopic 3 The Solar Systemlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Origin of The UniverseDocument2 pagesTopic 1 Origin of The Universelesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Origin of The Solar SystemDocument2 pagesTopic 2 Origin of The Solar Systemlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Minerals and Its PropertiesDocument1 pageTopic 6 - Minerals and Its Propertieslesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Origin of The Solar SystemDocument2 pagesTopic 2 Origin of The Solar Systemlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Gene MutationDocument21 pagesGene Mutationlesly AnneNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3: Presenter: Shelamie Joy M. AbundioDocument31 pagesQuarter 3: Presenter: Shelamie Joy M. Abundioclark cabaralNo ratings yet
- THEME 4 Writing HandoutDocument11 pagesTHEME 4 Writing HandoutMai Anh PhanNo ratings yet
- CH 6 - Periodic PropertiesDocument5 pagesCH 6 - Periodic PropertiesKakashi HowardNo ratings yet
- Meghalaya H.E. Project Progress ReportDocument13 pagesMeghalaya H.E. Project Progress ReportmadhueeNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Feeders - InstrumentationDocument15 pagesGravimetric Feeders - InstrumentationAakanksha GahlautNo ratings yet
- Landscape Narrative Design Approaches A Chinese A-Groen Kennisnet 501709 PDFDocument40 pagesLandscape Narrative Design Approaches A Chinese A-Groen Kennisnet 501709 PDFAr Nathar ShaNo ratings yet
- Heat Chap14 119Document16 pagesHeat Chap14 119Kerem GönceNo ratings yet
- Gravitation - Oneshot SSC 10th BoardDocument115 pagesGravitation - Oneshot SSC 10th BoardAditya PatilNo ratings yet
- UniversityPhysicsVolume2 WEB 5eNhMSaDocument805 pagesUniversityPhysicsVolume2 WEB 5eNhMSaTrong Nhan Do100% (1)
- Pollution and Environment Lesson for Class 5Document2 pagesPollution and Environment Lesson for Class 5Rakesh Agarwal57% (7)
- Energy Efficiency in BuildingsDocument72 pagesEnergy Efficiency in Buildingsahtin618100% (1)
- Lecture 6 Dta & Dsc01Document22 pagesLecture 6 Dta & Dsc01ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- 9780855836252Document70 pages9780855836252eibsourceNo ratings yet
- People and Ecosystem InteractionsDocument30 pagesPeople and Ecosystem InteractionsRhiena Joy Bosque100% (1)
- FM Question PaperDocument50 pagesFM Question PapervijaykhannaNo ratings yet
- PLN Berita SatuDocument25 pagesPLN Berita SatuAndre SNo ratings yet
- ManometersDocument18 pagesManometersshehzadshk01_3996181No ratings yet
- Issuance of Energy Label For Refrigerating Appliances 2023Document23 pagesIssuance of Energy Label For Refrigerating Appliances 2023ASYA ElectricalNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam (NSCI 111 - People & The Earth's Ecosystem)Document10 pagesMidterm Exam (NSCI 111 - People & The Earth's Ecosystem)Jov Soyom100% (1)
- Solid Waste Incinerator ManufacturersDocument2 pagesSolid Waste Incinerator Manufacturersbl engineeringNo ratings yet
- FESTO - Case - StudyDocument2 pagesFESTO - Case - StudyI'm 27 year old, and a Graphic Designer by profession.100% (2)
- Applied Energy: Jasim M. Mahdi, Emmanuel C. NsoforDocument12 pagesApplied Energy: Jasim M. Mahdi, Emmanuel C. Nsoforanil_stephenNo ratings yet
- Traditional Knowledge For Sustainable Living PPT 1'Document8 pagesTraditional Knowledge For Sustainable Living PPT 1'Maitri VyasNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems: Structure, Functioning & TypesDocument49 pagesEcosystems: Structure, Functioning & TypesMehul VermaNo ratings yet
- 2022 ABELE Recalled Questions1Document13 pages2022 ABELE Recalled Questions1Ailene del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic Cycle and Water Budget EquationDocument14 pagesHydrologic Cycle and Water Budget EquationShafizatulNo ratings yet
- Design Principles For Ocean VehiclesDocument7 pagesDesign Principles For Ocean VehiclesMiguelPacheecoAgamezNo ratings yet
- Timetable For Interruptions in Power Supply in AccraDocument1 pageTimetable For Interruptions in Power Supply in AccraMichael Creg AffulNo ratings yet
- WWW - The-Bac - Edu / Green: Spring 2011: Session TwoDocument12 pagesWWW - The-Bac - Edu / Green: Spring 2011: Session TwoEstrella Peñalba de GómezNo ratings yet