Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thyroid Cancer
Uploaded by
Zed P. EstalillaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thyroid Cancer
Uploaded by
Zed P. EstalillaCopyright:
Available Formats
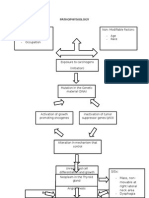
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THYROID CANCER
MODIFIABLE NON-MODIFIABLE
RADIATION DAMAGE AND FAILURE OF REPAIR DNA INHERITED MUTATION;GENETIC
LOW DIETARY IODINE FEMALE
AGE
MUTATION IN GENOME
HORMONAL CHANGES
ALTERATION IN GENES
INACTIVATION OF TUMOR THAT REGULATE
ACTIVATION OF GROWTH SUPRESSOR GENES APOPTOSIS
PROMOTING ONCOGENES
DECREASED APOPTOSIS
UNREGULATED CELL PROLIFERATION
COLONIAL EXPANSION
TUMOR PROGRESSION
MALIGNANT NEOPLASM
DIFFERENTIATED THYROID CARCINOMAS MEDULLARY THYROID ANAPLASTIC THYROID
CARCINOMAS CARCINOMAS
PAPILLARY CARCINOMAS FOLLICULAR HURTHLE CELL
CARCINOMAS CARCINOMAS
THYROID CANCER Fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB)
Is a disease in which the cells of the thyroid Neck ultrasonography
gland become abnormal, grow uncontrollably
Thyroid radioiodine imaging
and form a mass of cells called a tumor.
Neck computed tomography scanning
Complication
Signs and symptoms
Dysphagia
Painless
Stridor
Palpable
Hormone alteration
Solitary thyroid nodule
Distant metastases
Hard and fixed nodules
Prevention
Changes to your voice
Adult and children with and inherited
Causes
gene mutation that increases the risk of
Inherited gene mutation medullary thyroid cancer are often
advised to have thyroid surgery
Exposure to radiation in the neck area
(prophylactic thyroidectomy).
Prolonged secretion of
To the people who are near in nuclear
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
power plants may be eligible to receive a
Risk factor medication (potassium iodide)
Female sex
Exposure to high levels of radiation Treatment
(childhood)
Surgery
Certain inherited genetic syndromes
Removing all or most of the
Diagnosis thyroid (thyroidectomy)
History taking Removing lympnodes in the neck
Physical examination Removing a portion of the thyroid
Laboratory evaluation (Thyroidlobectomy)
Serum thyroid-stimulating hormone Risk for thyroid surgery
concentration, serum calcitonin
Bleeding
/pentagastrin-stimulated calcitonin level
and polymerase chain reaction (PRC) Infection
Indirect laryngoscopy
Damage can also occur to your
parathyroid glands, which can
lead to low calcium levels
Damage to nerves connected to
your vocal cord, which can cause
vocal cord paralysis, horseness,
soft voice or difficulty breathing.
Thyroid hormone therapy
After thyroidectomy, thyroid
hormone medication
levothyroxine for life.
Radioactive iodine
To destroy any remaining healthy
thyroid tissue,after thyroidectomy
External radiation therapy
May be an option if cancer
continues to grow after radioactive
iodine treatment
Chemotherapy
Is not commonly used in the treatment of
thyroid cancer but it may benefit some
people who don’t respond to other
therapies.
Combined with radiation theraphy
Drug theraphy
Cabozantinib(cometriq)
Sorafenib(nexavar)
Vandetanib(caprelsa)
Types of thyroid cancer aggressive and less differentiated than
papillary or follicular cancers. These cancers
Papillary carcinomas are slow-growing, are more likely to spread to lymph nodes and
differentiated cancers that develop from other organs, compared with the more
follicular cells and can develop in one or both differentiated thyroid cancers. They also
lobes of the thyroid gland. This type of frequently release high levels calcitonin and
cancer may spread to nearby lymph nodes in carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), which can
the neck, but it is generally treatable with a be detected by blood tests.
good prognosis. Under the microscope, the
nuclei of papillary carcinomas cells contain Anaplastic carcinoma is the most
very few proteins and small amount of DNA. undifferentiated type of thyroid cancer,
meaning that it looks the least like normal
Follicular carcinoma is the second most cells of the thyroid gland. As a result, it is a
common type of thyroid cancer, and accounts very aggressive form of cancer that quickly
for approximately one out of 10 cases. It is spreads to other parts of the neck and body.
found more frequently in countries with an
inadequate dietary intake of iodine. Follicular Stages for thyroid cancer
carcinoma is also a differentiated form of
thyroid cancer. In most cases, it is associated Stage I (stage 1 thyroid cancer): The tumor is
with a good prognosis, although it is 2 cm or smaller (less than an inch wide), and
somewhat more aggressive than papillary has not grown outside the thyroid. It has not
cancer. Follicular carcinomas do not usually spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant sites.
spread to nearby lymph nodes, but they are Stage II (stage 2 thyroid cancer): The cancer
more likely than papillary cancers to spread meets one of the following criteria:
to other organs, like the lungs or the bones.
The diameter of the primary tumor ranges
Hürthle cell carcinoma, also known as from 2 to 4 cm. There are no cancer cells in
oxyphil cell carcinoma, is a subtype of regional lymph nodes or distant sites in the
follicular carcinoma, and can often cause body.
immune cell to attack it causing inflammation.
Follicular cells in thyroid become adapt to The primary tumor is larger than four cm in
cellular stress like inflammation by becoming diameter or has started to grow outside of the
hurthle cells. they do so by increase the thyroid gland. No cancer was found in the
production of mitochondria which fills up lymph nodes or other parts of the body
(medullary thyroid cancer only).
their cytoplasm and gives a granular
appearance and stains pink. Stage III (stage 3 thyroid cancer): The cancer
meets one of the following criteria:
Medullary thyroid carcinoma develops
from C cells in the thyroid gland, and is more
The primary tumor is larger than 4 cm, or has may not have been found in regional lymph
grown outside the thyroid, but has not spread nodes, but have not reached distant sites.
to nearby lymph nodes or beyond
(differentiated cancers only). Stage IVC: The cancer cells have spread
beyond the thyroid gland to more distant
The tumor can be any size or be growing parts of the body.
outside the thyroid, and has spread to lymph
nodes in the neck but no farther. Nursing considerations
Stage IV (stage 4 thyroid cancer): This is the Before surgery, tell the patients to expect
most advanced stage of thyroid cancer, is horseness ( but not voice loss) lasting
further subdivided depending on where the several days after surgery
cancer has spread: After sugery, provide appropriate post
operative care:
Stage IVA: Cancers at this stage have grown Keep patient in semi-fowler’s position
beyond the thyroid gland and may have after he regains consciousness make sure
spread into nearby tissue, or they may have his head is neither hyperextended nor
spread to lymph nodes in the neck and upper flexed, to avoid pressure on the suture
chest, but not to distant sites. line.
Monitor vital sign’s, and then check
Stage IVB: The primary tumor has grown the patient’s dressing neck and back for
into the spine or into nearby large blood bleeding; loosen the dressing and call the
vessels. In this thyroid cancer stage, the physician immidiately if the patient
disease may or may not have spread to lymph complains that the dressings feels tight.
nodes, but has not reached distant sites. Keep a tracheostomy set and oxygen
equipment handy in case of respiratory
Stage IVC: The thyroid cancer cells have
obstruction
metastasized, or spread to distant sites.
Check serum calcium levels every 12
Stage IV anaplastic thyroid cancer (stage 4 hrs because hypocalcemia may develop if
anaplastic thyroid cancer): the parathyroid have been removed.
Anaplastic/undifferentiated thyroid cancers Monitor and observe for potential
are much more aggressive than the other complication such as hemorrhage,
subtypes and are all considered stage IV: hematoma formation, edema of the glottis
and injury to recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Stage IVA: The primary tumor is contained Teach the patient and family about the
within the thyroid gland, although it may or possible signs and symptoms of possible
may not have spread to nearby lymph nodes. complication and those should be
It has not spread to distant organs. reported.
Explained to the patient and family
Stage IVB: The tumor has spread outside of the need for rest, relaxation, and nutrition.
the thyroid gland, and cancer cells may or
You might also like
- Thyroid Cancer Pathophysio WinjDocument4 pagesThyroid Cancer Pathophysio WinjgeejeiNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology and NCP Lung CancerDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology and NCP Lung CancerAlleizarg EuqorNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Carcinoma Case PreDocument22 pagesThyroid Carcinoma Case PreTabrrett Bethel100% (1)
- Malignant MelanomaDocument31 pagesMalignant MelanomakityamuwesiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle Acena100% (2)
- Blunt Abdominal TraumaDocument24 pagesBlunt Abdominal TraumaDen SinyoNo ratings yet
- Chest TraumaDocument9 pagesChest Traumaapi-3838240100% (7)
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Breast Cancerpauline mangadaNo ratings yet
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocument2 pagesPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Case Study 3 - HCVDDocument12 pagesCase Study 3 - HCVDJilkiah Mae Alfoja CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Lung CancerDocument25 pagesLung CancerCarla Mae Guillermo NavarroNo ratings yet
- Modified Radical MastectomyDocument6 pagesModified Radical Mastectomymetch isulatNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Lung CA FinalDocument102 pagesCase Presentation Lung CA FinalMinerva Joan Escobido50% (2)
- Cervical Cancer Patho.2Document2 pagesCervical Cancer Patho.2Verni Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Modified Radical MastectomyDocument47 pagesModified Radical MastectomyErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD86% (7)
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyElmer Balgos Alinsog50% (4)
- Causes and Stages of Cervical Cancer DevelopmentDocument1 pageCauses and Stages of Cervical Cancer DevelopmentJanice MǾntañǾ100% (1)
- Lung Cancer Concept Map-Group 2Document2 pagesLung Cancer Concept Map-Group 2Maria Cristina100% (2)
- Thoracic Aortic AneurysmDocument17 pagesThoracic Aortic AneurysmGlyssa CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Dengue PoathoDocument6 pagesDengue PoathoCleobebs Agustin100% (1)
- Pathophysiology ARDSDocument1 pagePathophysiology ARDSRoderick Agbuya100% (1)
- Case Study Colorectal CancerDocument23 pagesCase Study Colorectal CancerLeogalvez BedanoNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - PathophysiologyJoann67% (3)
- Patho of MIDocument2 pagesPatho of MIInchan Montesines0% (1)
- A Case Study On Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument19 pagesA Case Study On Systemic Lupus ErythematosusIrah GatchoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Cervical Cancer) Case StudyDocument7 pagesPathophysiology (Cervical Cancer) Case StudyRosalie Valdez Espiritu100% (2)
- Lung CancerDocument4 pagesLung CancerKrizia TepootNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMarynette MapaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pulmonary Edema PDFDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pulmonary Edema PDFAsmaa100% (1)
- Oral RevalidaDocument98 pagesOral RevalidaJay ArNo ratings yet
- Case Study MM-2Document40 pagesCase Study MM-2Aya Sayed100% (1)
- Prostate Cancer Risk Factors & Stages ExplainedDocument1 pageProstate Cancer Risk Factors & Stages ExplainedEggy Pascual100% (1)
- Papillary Carcinoma Case StudyDocument29 pagesPapillary Carcinoma Case StudyKatrene LequiganNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Angina PectorisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Angina PectorisCheryl100% (1)
- CardiomyopathyDocument18 pagesCardiomyopathyDimpal Choudhary100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHSarah Lim100% (1)
- Colon Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Stages & TreatmentDocument17 pagesColon Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Stages & TreatmentYaska MusaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGy Thyroid CancerDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGy Thyroid Cancerjaenarose75% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal Failurenosevad88850% (2)
- Liver CancerDocument44 pagesLiver CancerEjay Jacob Ricamara50% (2)
- Papillary Thyroid CarcinomaDocument17 pagesPapillary Thyroid CarcinomaEster Sibarani100% (2)
- ARDS Pathophysiology and EtiologyDocument3 pagesARDS Pathophysiology and EtiologyJorie Roco100% (1)
- Acute PancreatitisDocument7 pagesAcute PancreatitisVytheeshwaran Vedagiri100% (9)
- Pleural Effusion-Individual CPDocument42 pagesPleural Effusion-Individual CPKristine Mae Sugarol100% (1)
- Case Study Lung Adenocarcinoma PDFDocument43 pagesCase Study Lung Adenocarcinoma PDFFrancis Anthony LoslosoNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction: Yohannes TDocument34 pagesIntestinal Obstruction: Yohannes TVincent Ser100% (1)
- Thyroid Cancer Types, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentDocument2 pagesThyroid Cancer Types, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentEl FaroukNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Wilms TumorDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Wilms TumorNikki Ricafrente100% (3)
- Lung CancerDocument11 pagesLung CancerNader Smadi100% (2)
- Rectal Cancer Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument15 pagesRectal Cancer Diagnosis and TreatmentTarquin TomadaNo ratings yet
- Group-1b Myocardial InfarctionDocument39 pagesGroup-1b Myocardial InfarctionJean ReyesNo ratings yet
- Physiological ChangesDocument1 pagePhysiological ChangesJilian McGuganNo ratings yet
- Thrombophlebitis Pathophysiology ExplainedDocument2 pagesThrombophlebitis Pathophysiology ExplainedKartika YuliantiNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary HypertensionDocument35 pagesPulmonary HypertensionKea Keleste DetablanNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument15 pagesCongestive Heart FailureChiraz Mwangi100% (1)
- DCM - Heart Failure Due to Dilated CardiomyopathyDocument13 pagesDCM - Heart Failure Due to Dilated CardiomyopathyPrincysuzine PintoNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument43 pagesThyroidchowhan04No ratings yet
- Oncology AssignmentDocument18 pagesOncology AssignmentAngeline EspinasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aberrations Guide to Cancer DiagnosisDocument5 pagesCellular Aberrations Guide to Cancer DiagnosisIrish Eunice Felix100% (1)
- CookfestDocument3 pagesCookfestZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Final NCP (Jannel)Document6 pagesFinal NCP (Jannel)Zed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ArfDocument28 pagesDrug Study ArfZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan HeadnursingDocument14 pagesTeaching Plan HeadnursingZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- RIzal AssignmentDocument3 pagesRIzal AssignmentZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching Plan - Medical Ward Jenny SalongaDocument13 pagesClinical Teaching Plan - Medical Ward Jenny SalongaZed P. Estalilla100% (1)
- Lactose Intolerance JournalDocument14 pagesLactose Intolerance JournalZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- LOGIC OF LANGUAGEDocument12 pagesLOGIC OF LANGUAGEZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Jxym 02 24Document11 pagesJxym 02 24Zed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Bilirubin Levels During First 48 Hours of Life in Healthy InfantsDocument10 pagesFactors Affecting Bilirubin Levels During First 48 Hours of Life in Healthy InfantsZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- NeuroSensory - Eye Part 2Document38 pagesNeuroSensory - Eye Part 2Zed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- COLORECTALShainapptDocument25 pagesCOLORECTALShainapptZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- CookfestDocument3 pagesCookfestZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Compliance Matrix Case StudyDocument2 pagesCompliance Matrix Case StudyZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Compliance Matrix Case StudyDocument2 pagesCompliance Matrix Case StudyZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of action and nursing considerations for paracetamolDocument2 pagesMechanism of action and nursing considerations for paracetamolAbdelmar SusulanNo ratings yet
- LOGIC OF LANGUAGEDocument12 pagesLOGIC OF LANGUAGEZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- EpilepsDocument1 pageEpilepsZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4Document8 pagesCase Study 4api-310029384100% (1)
- Asia Alternative Child Care and Deinstitutionalisation ReportDocument56 pagesAsia Alternative Child Care and Deinstitutionalisation ReportZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- ProfileDocument1 pageProfileZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Proper Handwashing Guide for Health & SafetyDocument3 pagesProper Handwashing Guide for Health & SafetyZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Individual Case Study On Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument53 pagesIndividual Case Study On Cerebrovascular Accidentemman_m92% (13)
- Asia Alternative Child Care and Deinstitutionalisation ReportDocument56 pagesAsia Alternative Child Care and Deinstitutionalisation ReportZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid CancerDocument5 pagesThyroid CancerZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Training Design AprilDocument3 pagesTraining Design AprilZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Ca IIDocument1 pageCa IIZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Sah CPDocument25 pagesSah CPZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Non HodgkinsDocument16 pagesNon HodgkinsZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Manual Sensor Anemómetro WindSonic GPADocument30 pagesManual Sensor Anemómetro WindSonic GPApevalpevalNo ratings yet
- Commercial Invoice: Exporter/Shipper Importer/ConsigneeDocument1 pageCommercial Invoice: Exporter/Shipper Importer/ConsigneePrem ChanderNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Neuroanatomical ResearchDocument404 pagesTechniques in Neuroanatomical ResearchVlad TomaNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Fourth CircuitDocument4 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Fourth CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Burwitz Teaching ResumeDocument2 pagesBurwitz Teaching Resumeapi-300437677No ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics at Columbia University - Calculus II Sample Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesDepartment of Mathematics at Columbia University - Calculus II Sample Syllabus PDFKaka AsefNo ratings yet
- Skinhead Groups in IndonesiaDocument4 pagesSkinhead Groups in IndonesiaJhanna Baitiez RezqiNo ratings yet
- 11Document24 pages11anil.gelra5140100% (1)
- Jee Advanced Sample PaperDocument24 pagesJee Advanced Sample PaperDark Knight0% (1)
- Mutagenic Effects of Sodium Azide On The Quality of Maize SeedsDocument7 pagesMutagenic Effects of Sodium Azide On The Quality of Maize SeedsKanhiya MahourNo ratings yet
- Test Tenses en AnswersDocument4 pagesTest Tenses en AnswersAmit Kumar LalNo ratings yet
- Soderstrom - Circuit Modeling of Cyanex 272Document17 pagesSoderstrom - Circuit Modeling of Cyanex 272Anonymous OnoowoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Arabic LiteratureDocument26 pagesModule 6 - Arabic LiteratureFrancis TatelNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Framework and ProcessDocument16 pagesRisk Management Framework and ProcessIuliana T.No ratings yet
- Labman PDFDocument76 pagesLabman PDFJames OnsachiNo ratings yet
- Surviving A Zombie ApocalypseDocument4 pagesSurviving A Zombie ApocalypseSarah SmithNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Service ExcellenceDocument18 pagesOperations Management Service ExcellenceParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Tang Re CIA 2 enDocument20 pagesTang Re CIA 2 enDimitris TsagkoudisNo ratings yet
- Racionalidad Acotada 1Document4 pagesRacionalidad Acotada 1Hector J. RubiniNo ratings yet
- Mama and Mommy and Me in The Middle Press ReleaseDocument2 pagesMama and Mommy and Me in The Middle Press ReleaseCandlewick Press0% (1)
- Isc at The Receiving End of A Feeder As A Function of The Isc at Its Sending End - Electrical Installation GuideDocument3 pagesIsc at The Receiving End of A Feeder As A Function of The Isc at Its Sending End - Electrical Installation GuidedhruvNo ratings yet
- Mercyhurst Magazine - Winter 1989-90Document36 pagesMercyhurst Magazine - Winter 1989-90hurstalumniNo ratings yet
- English Revision Notes XIIDocument41 pagesEnglish Revision Notes XIIRämíz MêmóñNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro I - 2011 TahaDocument27 pagesCiv Pro I - 2011 TahaACDCNo ratings yet
- BS en 01062-3-2008 PDFDocument12 pagesBS en 01062-3-2008 PDFjohnNo ratings yet
- Anthony Andreas Vass, Barbara Harrison Social Work Competences Core Knowledge, Values and SkillsDocument248 pagesAnthony Andreas Vass, Barbara Harrison Social Work Competences Core Knowledge, Values and SkillsAhmad Syifa100% (2)
- CHAPTER 7 - Combination and ExamplesDocument31 pagesCHAPTER 7 - Combination and ExamplesMikeMoralesNo ratings yet
- Status Signalling and Conspicuous Consumption: The Demand For Counterfeit Status GoodDocument5 pagesStatus Signalling and Conspicuous Consumption: The Demand For Counterfeit Status GoodMarliezel CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Unified LSG Code 1Document12 pagesUnified LSG Code 1Kerby Kent RetazoNo ratings yet
- WtA - 01 - Forgotten Lessons PDFDocument8 pagesWtA - 01 - Forgotten Lessons PDFHyperion DriverNo ratings yet