Professional Documents
Culture Documents
02 - Introduction To Lean Principles - Supergraphic PDF
02 - Introduction To Lean Principles - Supergraphic PDF
Uploaded by
sendhilOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
02 - Introduction To Lean Principles - Supergraphic PDF
02 - Introduction To Lean Principles - Supergraphic PDF
Uploaded by
sendhilCopyright:
Available Formats
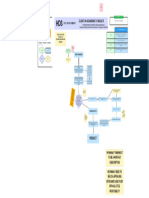
Understanding 8 Areas of Waste:
Introduction to Lean Principles WAITING:
System downtime or response time
History: Approvals from others
Process Flow: Information from customers
Henry Ford credited with starting original Look at process through Meetings starting late
Downstream Flow
movement the customer’s Late reports, paychecks, or projects
Kiichiro Toyoda and Taiichi Ohno: 1930’s Task Task B Task C perspective and identify INVENTORY: Too much of anything and any form of batch
developed the Toyota Production System. “waste” in the process. processing
Popularized by Jim Womack, author of Lean Excessive office supplies
Upstream Full “in‐boxes” (electronic or paper)
Thinking, The Machine that Changed the World
Computer files never used
and Lean Solutions
UNDERUTILIZATION OF PEOPLE
Limiting employee authority and responsibility for tasks
Why Use Lean? Inadequate business tools available
Delaying implementation of computer system components
Lean principles help to examine business processes Restricting or not offering training on technical resources
and focus on minimizing unnecessary costs, reducing
waste and improving inefficient procedures. CORRECTION/REWORK: Correction of any error
Order entry errors
Benefits: Grammar and punctuation
Identifies problem areas and bottlenecks Inaccurate reports or data
Lack of standardized work
Increases business efficiencies – make sure staff
Incomplete communications
time is spent on value‐added activities.
OVERPRODUCTION: Producing more sooner or faster than is
Save money – reduce overhead in paperwork required for the next process
Simplify processes
Printing hardcopies of forms
Purchasing items just in case they are needed
Conform to rules & regulations and codes of Processing paperwork before the next person in the process is
conduct – standardizing processes using Lean ready
Preparing reports that are not used or read
What is Lean? MOTION: Unnecessary physical movement
Copy machine too far away from users
Lean consists of proven tools and techniques that Digging through stacks of paper
focus on minimizing wasteful activity and adding Reaching for commonly used tools
value to the end product to meet customer needs. Misplacing equipment/items
Lean Terminology/Metrics: Using too many layers for electronic folders
The 8 areas of waste can be used to understand the
inefficiencies: Non‐value added: Activities or actions taken that add no real Kaizen Philosophy: Japanese for “improvement” or “change MATERIAL MOVEMENT/TRANSPORTATION (transporting, sorting,
Waiting Inventory Under
Correction / value to the product or service, making the activity or action a for the better”. Frequent small improvements, the cycle is: or arranging items unnecessarily)
Rework Filing papers that will never be used again
form of waste.
Standardize an operation Stock piling supplies far from their point of use
Material Value‐added: Activities or actions taken that add real value to Measure the standardized operation
Burying extra supplies in drawers or storerooms
Extra
Overproduction Motion Movement / Gauge measurements against requirements
Processing the product or service. Requiring multiple approvals
Transportation Innovate to meet requirements and increase productivity
Standardize the new, improved operations
Hand Delivery
Incidental Work: Activities needed to stay in business legally. Late reports, paychecks, or projects
A mapping method called Value‐Stream mapping is Lean Metrics:
Internal Customer: Receiver of the product or service inside EXTRA PROCESSING: Extra mental or physical non‐value added
typically used to capture the “current state” process, 1. Process Time (P/T) – actual “touch time” of one work item; exclude
the organization, often the individual downstream process. interruptions steps
including both the value‐added and non‐value added
2. Delay Time (D/T) – time work item is delayed or not touched Producing repetitive documents from scratch
steps. Value‐stream mapping provides an overall External Customer: Receiver of the product or service outside
3. Lead Time (L/T) – start time to finish time; L/T=P/T + D/T Poor filing system
view of business processes as they are now, mapping the organization. 4. % Complete and Accurate (%C/A) ‐ % of work entering a process that is Lack of visual controls
complete and accurate.
the material and information flows and can be used Too many approvals required for action
to create the “future state” process after the Unclear reports/memos published
Designed by Alexis Naiknimbalkar, CSU Quality Initiatives,
“leaning” has taken place. permission required for duplication outside of the CSU system (anaik@calstate.edu)
Reviewing a document multiple times to determine action
Meetings without agendas for action
WASTE WALK 5S ORGANIZATION SYSTEM
Audit questions to determine “pain points” in Tool to organize spaces and introduce Lean concepts
Audit questions for 5S area.
an area to be Leaned Description of conducting 5S
Ratings: No problems – 0, 1 problem – 1, 2 problems – 2,
improvement:
3 problems – 3, and 4 or more problems ‐4.
WAITING OVERPRODUCTION – Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain Goal is to have a low total number. Correct problems immediately.
1. Are making extra copies, more than needed?
1. Are there excessive signatures or approvals required?
2. Are we printing, faxing, e‐mailing more than what is ‐‐‐‐‐ Excess/unneeded equipment, tools, furniture in area
2. Is there too much dependency on others to complete a
needed?
SORT – When in doubt, sort it out!
task? Ask questions about use ___Unneeded/outdated items on walls
3. Are we entering repetitive information on multiple work
3. Are there delays in receiving information? Set Criteria for sorting
documents or forms? ___ Items are present in aisle ways, corners, etc.
4. Are there computer program version problems causing Place items in holding until all have had a chance
4. Are we ordering more tests or services than what is
delays? to review items being discarded ___ Excess/unneeded inventory, supplies, material in area
required by the customer?
5. System downtime or response time causing delays?
5. Are we purchasing items just in‐case they are needed?
6. Are there cross‐departmental resource commitment
6. Are we preparing reports that are not used or read?
issues?
7. Are we having meetings without the necessary
information for action? SET IN ORDER – A place for everything and ___ Correct places for items are not clearly marked or labeled
INVENTORY –
everything in its place! ___ Items are not marked or labeled with “return addresses”
1. Are files (or work) awaiting excessive signatures or MOTION – Identify location for items ___ Aisle ways, workplace, equipment locations are not marked
approvals? Relocated items
1. Are you searching for computer files on your desktop or
2. Are files awaiting task completion by other? ___ Items are not put away immediately after use
using too many layers for electronic folders? Use visual controls – labels
3. Are there delays in receiving information? 2. Are you searching for work documents (files) in cabinets Logical design flow ___ Height and quantity limits are not clearly marked
4. Are we purchasing excessive supplies of any kind? and/or drawers?
5. Do we have any obsolete files (electronic or hardcopy) in 3. Are you constantly reviewing the same manuals for
information?
the area?
6. Do we have obsolete equipment in the area? 4. Are you hand‐carrying paper work to another process or SHINE – Inspection through cleaning! ___ Floors, walls, stairs, and surfaces are dirty
department regularly?
7. Is there batch processing of transactions or reports? Clean ___ Equipment is dirty
5. Are you misplacing equipment/items?
Organize loose cords ___ Appropriate cleaning materials are not available in area
6. Are you reaching for commonly used tools?
Replace damaged items
UNDERUTILIZATION OF PEOPLE – ___ Lines, labels, signs, etc. are dirty and hard to see
Place small items on trays for easy cleaning
MATERIAL MOVEMENT/TRANSPORTATION – ___ Other cleaning problems are present
1. Are we in positions we were trained to do?
2. Can we assist other areas when work is slow in an area? 1. Are you delivering documents that are not required?
3. Can we be trained to do more within the organization? 2. Are you doing excessive filing of work documents or filing
STANDARDIZE – Everything in a state of ___ Standards to maintain sort and set in order do not exist
4. Are the business tools adequate for the job? documents that will never be used again?
readiness! ___ Checklist for all cleaning and maintenance jobs do not exist
5. Are you restricting or not offering training on technical 3. Are you requiring multiple approvals?
resources? Rules to maintain and control system (checklist, audits, ___ Standards are not visible in the area and know to area stakeholders
4. Are you hand delivering items that can be sent in and visual controls)
6. Are you delaying implementation of computer ___ Quantities and limits cannot easily be seen
components or software?
interoffice mail? Minimum and maximum limits
Quick reference checklist ___ Items needed to do job function cannot be located in 30 seconds
EXTRA PROCESSING –
CORRECTION/REWORK –
1. Are we producing repetitive documents from scratch?
1. Do we have any data entry errors?
2. Do we have a poor filing system? SUSTAIN – Training, reinforcement and ___ Workers in area have not been trained in 5S
2. Do we have pricing, quoting, billing, or coding errors?
3. Is there a lack of visual controls? measurement! ___ Daily 5S was not done this week
3. Do we forward partial documentation?
4. Are we too many approvals required for action? Communicate importance ___ Personal belongings cannot be easily stored
4. Do we ever lose files or records?
5. Are we entering repetitive information? Train on rules
5. Do we ever encounter incorrect information on a ___ 5S checklist/standards are not available or up‐to‐date
document? 6. Are we doing more work than is required for that Share success in meetings
___ Scheduled 5S audits have not been completed this week
6. Is there a lack of standardized work? process? Effective visual controls
Designed by Alexis Naiknimbalkar, CSU Quality Initiatives,
permission required for duplication outside of the CSU system (anaik@calstate.edu)
You might also like
- Citizen CharterDocument1 pageCitizen CharterReynalisa MonencilloNo ratings yet
- BP040 Current Process ModelDocument12 pagesBP040 Current Process ModelarubharraniNo ratings yet
- Taproot®: Version 5 Software TutorialDocument38 pagesTaproot®: Version 5 Software TutorialEmilNo ratings yet
- Client ON-BOARDDocument1 pageClient ON-BOARDrealxpmythNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Japanese Words Meaning in TPSDocument16 pages3.0 Japanese Words Meaning in TPSShashi Kant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Concurrent Managers SolutionDocument2 pagesConcurrent Managers SolutionMukarram KhanNo ratings yet
- 2022-06-29 Method Statement of Construction of Odor Control System Rev. ADocument71 pages2022-06-29 Method Statement of Construction of Odor Control System Rev. AMeng PamplonaNo ratings yet
- LA 21 Laws of Governance: SynonymsDocument39 pagesLA 21 Laws of Governance: SynonymsROLIPOPSTERNo ratings yet
- Globalization: Redesigning Your Chart of AccountsDocument1 pageGlobalization: Redesigning Your Chart of AccountsNatarajan AgoramNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Audit KA IQ Forms and TemplateDocument10 pagesKnowledge Audit KA IQ Forms and Templatetamrat g.meskelNo ratings yet
- Ap - Export - k2 User Manual (Miti)Document24 pagesAp - Export - k2 User Manual (Miti)makhsmyNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Object Technology: The Traditional ApproachDocument35 pagesAn Introduction To Object Technology: The Traditional ApproachBharathi IndhuNo ratings yet
- HP Jet Fusion 3D Printing Solution: Reinventing Prototyping and ManufacturingDocument3 pagesHP Jet Fusion 3D Printing Solution: Reinventing Prototyping and ManufacturingElias ImuchacNo ratings yet
- Introduction Top OmDocument30 pagesIntroduction Top OmVinuthan VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- T24 Close of Business (COB) - T24 HelperDocument17 pagesT24 Close of Business (COB) - T24 HelperNett2k100% (9)
- Don Tapping, Tom Shuker-Value Stream Management For The Lean Office - Eight Steps To Planning, Mapping, & Sustaining Lean Improvements in Administrative Areas-Productivity Press (2003)Document163 pagesDon Tapping, Tom Shuker-Value Stream Management For The Lean Office - Eight Steps To Planning, Mapping, & Sustaining Lean Improvements in Administrative Areas-Productivity Press (2003)Ronald Pedroza Rodriguez100% (4)
- BPMN Poster v1.0.10 (A2)Document1 pageBPMN Poster v1.0.10 (A2)calypso342No ratings yet
- RPA Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageRPA Cheat Sheet PDFearnestgoh3635No ratings yet
- Disclosure Summary Page DR-2: Reset FormDocument21 pagesDisclosure Summary Page DR-2: Reset FormZach EdwardsNo ratings yet
- BPMN Poster A4 Ver 1.0.10 PDFDocument1 pageBPMN Poster A4 Ver 1.0.10 PDFSatrio N. W. NotoamidjojoNo ratings yet
- Khadka 2013Document8 pagesKhadka 2013nkiran022No ratings yet
- Attendance FormDocument2 pagesAttendance FormNadjib DHMNo ratings yet
- Srinivasa Rao 2016Document4 pagesSrinivasa Rao 2016Shashi KantNo ratings yet
- The Purchasing Process PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download - ID - 6520285Document1 pageThe Purchasing Process PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download - ID - 6520285mdurre82No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionmonitoring suhu ruanganNo ratings yet
- Presentation EMPADocument13 pagesPresentation EMPAapi-26219976No ratings yet
- 02 Lean ManufacturingDocument32 pages02 Lean ManufacturingKristine Mae CabreraNo ratings yet
- 1.1.3.11 Lab - Draw A Process DiagramDocument4 pages1.1.3.11 Lab - Draw A Process DiagramJoshua ManalotoNo ratings yet
- The Relevance of Auditing in A Computerized Accounting SystemDocument5 pagesThe Relevance of Auditing in A Computerized Accounting SystemEmebet TesemaNo ratings yet
- Toyota Quiz #2 - OverviewDocument8 pagesToyota Quiz #2 - OverviewKenzie PawelczykNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document41 pagesLecture 1Mai Uyên MyNo ratings yet
- Application Handbook VM005 Option Selection Mining Value ManagementDocument8 pagesApplication Handbook VM005 Option Selection Mining Value Managementsopon567No ratings yet
- 2020 Raconteur Procurement-Supply-Chain-Innovation-2020Document16 pages2020 Raconteur Procurement-Supply-Chain-Innovation-2020CarlosBritoVonBodenburgNo ratings yet
- Workflow of Injection Molding Simulation & Verification: Ffinno-Technologies-Co-LtdDocument6 pagesWorkflow of Injection Molding Simulation & Verification: Ffinno-Technologies-Co-Ltdluan_ba100% (1)
- Sammler Jim - 1672 - ScannedDocument3 pagesSammler Jim - 1672 - ScannedZach EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Miller Thomas J - 5064 - ScannedDocument8 pagesMiller Thomas J - 5064 - ScannedZach EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Removing File Extensions Using Htaccess - InMotion HostingDocument14 pagesRemoving File Extensions Using Htaccess - InMotion HostingPradyumna Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- 2021-10-13 Project Quality Plan Rev. ADocument1 page2021-10-13 Project Quality Plan Rev. AjaymarNo ratings yet
- Python-Project-Report For Study Python-Project-Report For StudyDocument16 pagesPython-Project-Report For Study Python-Project-Report For StudyTahesin TNo ratings yet
- t24 Close of Business Cob t24 HelperDocument17 pagest24 Close of Business Cob t24 HelperAswani MucharlaNo ratings yet
- Conversation Two (Questions 5 - 8) Part One Questions 1 - 12Document7 pagesConversation Two (Questions 5 - 8) Part One Questions 1 - 12Gaais TrotNo ratings yet
- Stakeholders Register: Wilmont's Drone Project 001 Wilmont's Pharmacy Diogo Pimenta Concept 01 30/04/2020Document3 pagesStakeholders Register: Wilmont's Drone Project 001 Wilmont's Pharmacy Diogo Pimenta Concept 01 30/04/2020freddy ramdinNo ratings yet
- Lyco Manufacturing, Inc.: Offers A Full Line of World-Class Food Processing Equipment IncludingDocument4 pagesLyco Manufacturing, Inc.: Offers A Full Line of World-Class Food Processing Equipment IncludingMelissa ZelayaNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Defi., Responsibility ScopeDocument8 pagesIntroduction, Defi., Responsibility ScopeManpreet Singh SainiNo ratings yet
- Citizen'S Charter Frontline Services Personnel SectionDocument1 pageCitizen'S Charter Frontline Services Personnel SectionLyn RuizNo ratings yet
- 056 Evento ITS 2014Document7 pages056 Evento ITS 2014Ugs nguNo ratings yet
- IT4IT Reference Card4Document1 pageIT4IT Reference Card4GuillermoVillalonNo ratings yet
- Disclosure Summary Page I ®'177?. I ') NN DR-2: Statement of Cash On HandDocument5 pagesDisclosure Summary Page I ®'177?. I ') NN DR-2: Statement of Cash On HandZach EdwardsNo ratings yet
- SSRN-id3626589 (Sample ISDP)Document6 pagesSSRN-id3626589 (Sample ISDP)Ericka DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- CH 1 2 Company LawDocument22 pagesCH 1 2 Company Lawrishita mittalNo ratings yet
- AWS Periodic TableDocument1 pageAWS Periodic Tabledouglas.dvferreiraNo ratings yet
- Lean Manufacturing Chapter 2Document14 pagesLean Manufacturing Chapter 2WinterMist11No ratings yet
- CF Meridium Binder1Document89 pagesCF Meridium Binder1TommyNo ratings yet
- Disclosure Summary Page DR-2: Holh For House eDocument5 pagesDisclosure Summary Page DR-2: Holh For House eZach EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Lean Management AssignmentDocument14 pagesLean Management AssignmentNatala WillzNo ratings yet
- Ginlong - LAN Stick Quick User Guide-Ver1,3Document1 pageGinlong - LAN Stick Quick User Guide-Ver1,3Petflo FloNo ratings yet
- JITfinalDocument32 pagesJITfinalPradeepNo ratings yet
- Batch ProcessingDocument3 pagesBatch ProcessingNiño Rey LopezNo ratings yet
- Tables of International Standards, A ComparisonDocument22 pagesTables of International Standards, A ComparisonViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Araldite Ay 103 1Document1 pageAraldite Ay 103 1Viswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- 316 PDFDocument1 page316 PDFViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- SW InsightDocument13 pagesSW InsightViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Araldite Ay103 1hy991 PDFDocument4 pagesAraldite Ay103 1hy991 PDFViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- SW DailyDocument32 pagesSW DailyViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- SSWWWWDocument6 pagesSSWWWWViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Antelope 21 December 2015Document3 pagesAntelope 21 December 2015Viswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Wi 2015 12Document64 pagesWi 2015 12Viswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Design Approval ProcessDocument1 pageDesign Approval ProcessViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Shaper Tool Head AssemblyDocument6 pagesShaper Tool Head Assemblyjagadeesh01No ratings yet
- Working Mind and The Thinking Mind - Lifestyle Article On SpeakingtreeDocument3 pagesWorking Mind and The Thinking Mind - Lifestyle Article On SpeakingtreeViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Classification of CompositesDocument2 pagesClassification of CompositesViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Present Value (P.V.) Calculator: (Pvif) (Pvifa) 1,000 1,000 1,000 1,000Document1 pagePresent Value (P.V.) Calculator: (Pvif) (Pvifa) 1,000 1,000 1,000 1,000Viswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Costing Formulae Topic WiseDocument83 pagesCosting Formulae Topic WiseViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Short Notes CostingDocument32 pagesShort Notes CostingViswanathan Srk100% (1)
- International Supply Chain Management HKT1.2023 (EN)Document8 pagesInternational Supply Chain Management HKT1.2023 (EN)Thanh Trúc Nguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- A Simulation-Enhanced Lean Design Process PDFDocument24 pagesA Simulation-Enhanced Lean Design Process PDFAngela CastilloNo ratings yet
- Reduce The Cycle Time of Galvanizing by Applying Kaizen ApproachDocument5 pagesReduce The Cycle Time of Galvanizing by Applying Kaizen ApproachIJRASETPublications100% (1)
- Implementing A Mixed Model Kanban System The Lean Replenishment Technique For Pull Production-Productivity Press (2005)Document126 pagesImplementing A Mixed Model Kanban System The Lean Replenishment Technique For Pull Production-Productivity Press (2005)Chandan SkNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2352710221010548 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S2352710221010548 MainLucia QuispeNo ratings yet
- VK - 15 Years Exp in Process & Production EngineeringDocument1 pageVK - 15 Years Exp in Process & Production Engineeringjprabhu81No ratings yet
- CCA LVL 3 Simex QAsDocument14 pagesCCA LVL 3 Simex QAsRob De CastroNo ratings yet
- Managing For Daily Improvement Paul ToddDocument22 pagesManaging For Daily Improvement Paul ToddHari Krishna100% (1)
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB)Document3 pagesLean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB)شادي الاخرسNo ratings yet
- Coursera - 6 Sigma Black BeltDocument51 pagesCoursera - 6 Sigma Black Beltmusmansalim101No ratings yet
- 5 SDocument28 pages5 SHittendra Singh100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines1Document7 pagesRepublic of The Philippines1Clyde X2600No ratings yet
- Aml Murc 2020Document4 pagesAml Murc 2020sunandar HlaingNo ratings yet
- Paradigma LeanDocument29 pagesParadigma LeanLupis GlxNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect Sciencedirect SciencedirectDocument6 pagesSciencedirect Sciencedirect SciencedirectlizbethNo ratings yet
- Complementing Agile Software Project Management Methods With Plan-Driven ComponentsDocument53 pagesComplementing Agile Software Project Management Methods With Plan-Driven ComponentsAlina IliseiNo ratings yet
- Innovation Management: Session: LeanDocument29 pagesInnovation Management: Session: LeanAamiTataiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Assignment - History of Design - Roundabout MonumentDocument7 pages2nd Assignment - History of Design - Roundabout MonumentIqra 2000No ratings yet
- Akshay InternshipreportDocument72 pagesAkshay InternshipreportIshu MahajanNo ratings yet
- Basic TPS HandbookDocument33 pagesBasic TPS HandbookSumith KobewattaNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument20 pagesOperations ManagementRoyal National UniversityNo ratings yet
- Health MaxhxchxhnagementDocument448 pagesHealth MaxhxchxhnagementAlexandr TrotskyNo ratings yet
- Mulugeta EjiguDocument18 pagesMulugeta Ejiguseble hailemariamNo ratings yet
- A. Background of The StudyDocument30 pagesA. Background of The StudyCharlene MaderazoNo ratings yet
- Lean Management AssignmentDocument14 pagesLean Management AssignmentNatala WillzNo ratings yet
- Applying Lean Six SigmaDocument52 pagesApplying Lean Six Sigmajames007spyNo ratings yet
- Lean Manufacturing Implementation Problems in Beverage Production SystemsDocument6 pagesLean Manufacturing Implementation Problems in Beverage Production SystemsJerome BayocbocNo ratings yet
- Interface Management On Megaprojects: A Case StudyDocument6 pagesInterface Management On Megaprojects: A Case StudyYao SanianNo ratings yet
- ToyotaDocument2 pagesToyotaKumar HarshNo ratings yet
- Moretta AntonucciDocument17 pagesMoretta AntonucciLeyton MisterNo ratings yet