Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Report of Platelet
Uploaded by
Shweta PatilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Report of Platelet
Uploaded by
Shweta PatilCopyright:
Available Formats
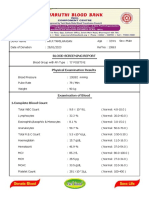
AARTI JAISWAL Reference: VID: 11196397318
Sample Collected At: Registered On:
CARDINAL GRACIAS MEMORIAL HOSP
21/08/2019 03:52 PM
TRUST 12
PID NO: P11190492409 BANGLI , SANDOR POST OFFICE VASAI Collected On:
Age: 27 Year(s) Sex: Female THANE 21/08/2019
Zone: W-26A(12)401201 Reported On:
22/08/2019 02:31 PM
Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference Interval
Immature Platelet fraction
(EDTA Whole Blood)
Immature Platelet fraction 50.9 % 0.70-4.30
Platelet count 84 10^3 / µl 140-440
Medical Remarks: Platelet reduced on smear.
Method:
• Automated CBC counter based on Flow Cytometry principle
• IPF have a greater RNA content, are measured by automated hematology analyzers equipped with a reticulocyte detection
channel, and are reported as percentage of the total platelet count (%-IPF).
Clinical Background:
• Circulating immature platelets, also known as the immature platelet fraction (IPF), is the term that defines much larger
platelets that have been recently released from the bone marrow, presence of which show the thrombopoietic activity of the
marrow.
CLINICAL UTILITY:
It can help to distinguish between causes of thrombocytopenia due to
• Increased consumption/destruction (ITP) - High IPF
• Decreased production (marrow failure) – Low IPF
• It predicts the timing of platelet recovery (in Dengue, Malaria, after transplantation or chemotherapy)
• It can save platelet transfusions
◦ help to save a precious resource
◦ help to avoid potential infection risk
• IPF estimation can be used as guide for decisions concerning platelet transfusions & recovery of platelets in patients with
Dengue, Malaria, etc.
• The IPF% can predict the timing of platelet recovery. The platelet recovery time is 1-2 days of IPF increase.
• It was found that when the IPF starts going up (rising trend), 93.75% of the patients showed recovery within 24–48 h of the
rise. After a certain point when the IPF has peaked, then the platelets start coming up and IPF starts falling. This fall in the
IPF is a strong predictor of an impending rise in platelet count.
• As on most clinical scenarios follow-up IPF data for patients is not available, it has been shown in various studies that use of
a single time point IPF with cut-off value of 10% and above can be considered a good predictor for platelet recovery.
References:
• Assessment of an immature platelet fraction (IPF) in peripheral thrombocytopenia, Carol Briggs, Stefan Kunka,Dan Hart,
Shinichiro Oguni and Samuel J. Machin, British Journal of Haematology, 126, 93–99
• Dadu, T., Sehgal, K., Joshi, M, Khodaiji, S. Evaluation of the immature platelet fraction as an indicator of platelet recovery in
dengue patients. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology, 2013; 2013; 49(7)10.
Page 1 of 3 Dr. Rina Shah
M.D (Pathology)
Consulting Pathologist
AARTI JAISWAL Reference: VID: 11196397318
Sample Collected At: Registered On:
CARDINAL GRACIAS MEMORIAL HOSP
21/08/2019 03:52 PM
TRUST 12
PID NO: P11190492409 BANGLI , SANDOR POST OFFICE VASAI Collected On:
Age: 27 Year(s) Sex: Female THANE 21/08/2019
Zone: W-26A(12)401201 Reported On:
22/08/2019 02:31 PM
Investigation Observed Value Biological Reference Interval
Anti Nuclear Antibody by IFA
(Serum,Immunofluorescence)
Result Negative Negative
Pattern - -
Grade - -
Estimated Titre - -
Interpretation Guidelines (Sample screening Dilution - 1:100):
Negative : No Immunofluorescence
+ : Weak Positive (1:100)
++ : Moderate Positive (1:320)
+++ : Strong Positive (1:1000)
++++ : Very strong Positive (1:3200)
Test Description:
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs) are unusual antibodies, detectable in the blood, that have the capability of binding to certain
structures within the nucleus of the cells. ANAs indicate the possible presence of autoimmunity & provide, therefore, an indication of
autoimmune illness. Fluorescence tech. are frequently used to actually detect the antibodies in the cells, thus ANA testing is
sometimes referred to as fluorescent antinuclear antibody test (FANA). The ANA test is a sensitive screening test used to detect
autoimmune diseases.
Technique:
Indirect Immunofluorescence - Automated IF Processor (AP 16 IF Plus)
The BIOCHIP Slide is a combination of Hep-20-10 cells and primate liver and has the following advantages.
• It is a global standard tech. with a natural antigen spectrum capable of detecting more than 30 diagnostically relevant auto
antibodies.
• Hep 20-10 cell lines contain 40% mitotic cells, facilitating easier identification of rare patterns.
• If the test is negative, detectable level of auto antibodies is ruled out. In case of a positive result, autoantibodies against any
one or in some cases simultaneously against more than one antigens may be present and further monospecific tests or
panel of profiles can be used to determine the specific autoantibodies present.
• NOTE- All weak positive (+) results may be repeated after 6 - 8 weeks.
Associated Tests: Monospecific ELISA to define single antigens, ANA Immunoblot assay.
Abbreviations: SLE: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, SCL: Scleroderma, MCTD: Mixed Connective Tissue Disease; CFS: Chronic
Fatigue Syndrome; AIH: Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC: Primary Bilary Cirrhosis, PM:Polymyositis, DM:Dermatomyositis, SS: Systemic
sclerosis, RA:Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Please view next page for co-relation table including various single antigens with their Immunoflourescence patterns and
clinical associations.
Page 2 of 3 Dr. Rina Shah
M.D (Pathology)
Consulting Pathologist
AARTI JAISWAL Reference: VID: 11196397318
Sample Collected At: Registered On:
CARDINAL GRACIAS MEMORIAL HOSP
21/08/2019 03:52 PM
TRUST 12
PID NO: P11190492409 BANGLI , SANDOR POST OFFICE VASAI Collected On:
Age: 27 Year(s) Sex: Female THANE 21/08/2019
Zone: W-26A(12)401201 Reported On:
22/08/2019 02:31 PM
Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference Interval
Location Pattern Target Antigen Clinical Association
Nucleus Homogeneous Double strand DNA SLE
Histones Drug Induced Lupus, SLE ,
Nucleosome, RNA,Single RA
Strand DNA SLE, MCTD,RA, PM, DM, SS
Speckled Sm SLE
U1-snRNP MCTD,SLE,RA, sharp
SSA/Ro syndrome
SSB/La Sjogren`s syndromes
Ku (SS)/SLE/Neonatal Lupus
Cyclin1(PCNA) PM/DM/SLE/SS
Mitosin/Cyclin II SLE/Overlap Syndromes
DM
Dense Fine Speckled(DFS) Lens epithelium-derived Healthy individuals, Various
growth factor (LEDGF), DNA Inflammatory conditions like
binding transcription atopic dermatitis, interstitial
coactivator p75.(DFS-70) cystitis, Asthma.
Centomeres Proteins of Kinetochores CREST syndrome, PSS
limited form
Nuclear Dots Sp-100 , NDP53 PBC,Rheumatic Disease
Nuclear Membrane Lamins, gp210, p62 CFS,Collagenoses,PBC,AIH
Nucleolus Nucleolar homogeneous PM-Scl PM, DM, PSS(Diffuse)
Scl-70 PSS(Diffuse)
Nucleolar speckled RNA-Polymerase I / NOR-90 Progressive Systemic
Sclerosis(Diffuse)
Nucleolar Pattern Fibrillarin Progressive Systemic
Sclerosis(Diffuse)
Cytoplasm Cytoplasmic speckled Mitochondrial PBC,
Lysosomal Unknown
Golgi Complex SS/SLE/RA
Ribosome P SLE
Jo -1 Polymyositis (PM),
SRP, PL12, TIF1-Gamma PM/ DM, Myositis
Cytoplasmic filament F-Actin AIH
Vimentin Unknown
Tropomyosin Unknown
Cytoplasmic Rings & rods HCV Infection- on therapy
Cell Cycle (mitotic cells) Centriole -- Unknown
Mid-Body -- Unknown
Spindle Fibres -- Rheumatic Disease
-- End of Report --
Page 3 of 3 Dr. Rina Shah
M.D (Pathology)
Consulting Pathologist
You might also like
- Essentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationFrom EverandEssentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Report HB ELECTROPHORESISDocument2 pagesReport HB ELECTROPHORESISShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Haematology: Complete Blood Cell CountDocument5 pagesHaematology: Complete Blood Cell CountSenthil RajaNo ratings yet
- Erythrocytes: Reference: DR - NAINI SETALVAD Abhishek Khemka VID: 106191000857Document11 pagesErythrocytes: Reference: DR - NAINI SETALVAD Abhishek Khemka VID: 106191000857Abhishek KhemkaNo ratings yet
- 52 1023122 0 1Document7 pages52 1023122 0 1Kula Segara PandiyanNo ratings yet
- Wwiy4300 PDFDocument6 pagesWwiy4300 PDFShobhit MishraNo ratings yet
- Saatvik.A:::: Patient Age / Sex 8 M / Male BranchDocument3 pagesSaatvik.A:::: Patient Age / Sex 8 M / Male BranchNaveen GaneshNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Picture (CBP), EDTA Whole Blood: Master - SushanthDocument4 pagesComplete Blood Picture (CBP), EDTA Whole Blood: Master - SushanthAbdul MuqeemNo ratings yet
- Master Anshu Jha 18 12 2023 05 29 03 PMDocument2 pagesMaster Anshu Jha 18 12 2023 05 29 03 PMVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Wwiy4300 PDFDocument3 pagesWwiy4300 PDFRani reddy45% (42)
- Fnac Results - 31 - 08 - 2023 - 05 - 44 - 51 - AmDocument1 pageFnac Results - 31 - 08 - 2023 - 05 - 44 - 51 - AmClan of comedyNo ratings yet
- Int J Lab Hematology - 2023 - Adir - The Role of Blood Inflammatory Markers in The Preoperative Diagnosis of AcuteDocument5 pagesInt J Lab Hematology - 2023 - Adir - The Role of Blood Inflammatory Markers in The Preoperative Diagnosis of AcuteOncología CdsNo ratings yet
- K SadanandamDocument1 pageK SadanandamAnonymous toGGtuxMACNo ratings yet
- Haematology: Complete Blood Count With - ESRDocument3 pagesHaematology: Complete Blood Count With - ESRshakthi thiNo ratings yet
- Haematology: Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesHaematology: Laboratory ReportChithraa KarthikNo ratings yet
- PdfText - 2021-11-11T202745.532Document1 pagePdfText - 2021-11-11T202745.532Murtaza AhmarNo ratings yet
- Department of Laboratory Medicine: Immunology Test Result Unit Biological Reference IntervalDocument2 pagesDepartment of Laboratory Medicine: Immunology Test Result Unit Biological Reference IntervalRajesh MondalNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry: MR Ankit JainDocument10 pagesClinical Biochemistry: MR Ankit JainAnkit Jain chinese interpreterNo ratings yet
- TyphoidDocument3 pagesTyphoidShivam Tomar83% (6)
- Anti HCVDocument5 pagesAnti HCVFaisal JamshedNo ratings yet
- Glucose, Fasting (FBS) : Req. No: 031903144201Document17 pagesGlucose, Fasting (FBS) : Req. No: 031903144201SRIPERAMBHUDURI KRISHNANo ratings yet
- Fully Automated Lab Accurate Reports Reports Verified by PathologistDocument3 pagesFully Automated Lab Accurate Reports Reports Verified by PathologistRiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- This Is An Electronic Report & Not: To Be Used For Any Legal PurposesDocument1 pageThis Is An Electronic Report & Not: To Be Used For Any Legal PurposesZia Wains RoseNo ratings yet
- LabReport L14 Mrs - RAJESHWARI60YRS F 06 04 202420240406 2 E38fgDocument3 pagesLabReport L14 Mrs - RAJESHWARI60YRS F 06 04 202420240406 2 E38fgAnkit GairolaNo ratings yet
- DESHMUKHDocument8 pagesDESHMUKHUmesh BansodeNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument10 pagesReportAnkita GoyalNo ratings yet
- Sacchi Dan andDocument2 pagesSacchi Dan andVINAYNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Pathology: Ena Quantrix 25 IggDocument2 pagesDepartment of Chemical Pathology: Ena Quantrix 25 IggKhurram ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Ramki REPORTSDocument2 pagesRamki REPORTSDumpali Sharath Chandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Sumaira CBC Test Case # 44010-26-08 Chughtai Lab PDFDocument1 pageSumaira CBC Test Case # 44010-26-08 Chughtai Lab PDFAnonymous zXF5UgqP833% (3)
- Department of Hematology: Blood C/E (Complete, CBC)Document2 pagesDepartment of Hematology: Blood C/E (Complete, CBC)Abdul Karim Chaudhry0% (1)
- Autoimmune - Hemolytic - Anemia - Mixed - Type-A - Case - Repo 2Document5 pagesAutoimmune - Hemolytic - Anemia - Mixed - Type-A - Case - Repo 2Afsha AnishNo ratings yet
- Brain Abscess: JUNE 2020Document38 pagesBrain Abscess: JUNE 2020Bochand CoolNo ratings yet
- Erythrocytes: Reference: DR - ADITI SINHA Ms. Diya Aravind VID: 63180121715Document10 pagesErythrocytes: Reference: DR - ADITI SINHA Ms. Diya Aravind VID: 63180121715Suganthi AravindNo ratings yet
- CLL PatientReportDocument1 pageCLL PatientReportAmeer AslamNo ratings yet
- Automated Versus Manual Platelet Count in Aden 2161 0681-3-149Document4 pagesAutomated Versus Manual Platelet Count in Aden 2161 0681-3-149Jeffry MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Report of CA 15.3Document1 pageReport of CA 15.3Shweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Blood Screening ReportDocument2 pagesBlood Screening ReportSarathNo ratings yet
- Results Are To Be Correlated Clinically: Page 1 of 2Document10 pagesResults Are To Be Correlated Clinically: Page 1 of 2rajeshkv1No ratings yet
- ReportViewer 1Document4 pagesReportViewer 1Shehriyar KhanNo ratings yet
- This Is An Electronic Report & Not: To Be Used For Any Legal PurposesDocument1 pageThis Is An Electronic Report & Not: To Be Used For Any Legal PurposesTahaNo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology: Coagulation ProfileDocument2 pagesDepartment of Hematology: Coagulation ProfileShaikh Muhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Indra Lal - (MRN 1006076) - 1023001085Document3 pagesIndra Lal - (MRN 1006076) - 1023001085yukeonnaNo ratings yet
- Erythrocytes: Reference: DR - SELF Mrs. Rashmi VID: 15821730013744Document6 pagesErythrocytes: Reference: DR - SELF Mrs. Rashmi VID: 15821730013744Senthil VelNo ratings yet
- Aplasia Medular Adquirida. Blood. 2017 129 (11) 1428-1436.Document9 pagesAplasia Medular Adquirida. Blood. 2017 129 (11) 1428-1436.VirginiaÁlvarezYepesNo ratings yet
- Test Results Units Biological Reference Range Hematology:::::: Ms. Farha MemonDocument5 pagesTest Results Units Biological Reference Range Hematology:::::: Ms. Farha MemonKM GASTRO CENTERNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Platelet Antibody Screening in 38 840 InpatientsDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Platelet Antibody Screening in 38 840 Inpatients周富源No ratings yet
- DownloadDocument10 pagesDownloadmandapatiNo ratings yet
- SR7975632 ReportDocument6 pagesSR7975632 ReportPradipNo ratings yet
- Procalcitonin Is It The End of Road To Sepsis Diagnosis - February - 2022 - 6546541022 - 2629943Document2 pagesProcalcitonin Is It The End of Road To Sepsis Diagnosis - February - 2022 - 6546541022 - 2629943RateeshNo ratings yet
- Saniya Fathima (7G28Jy) :::: Patient Age / Sex 26 Y / Female BranchDocument3 pagesSaniya Fathima (7G28Jy) :::: Patient Age / Sex 26 Y / Female BranchShah FaisalNo ratings yet
- 14 Feb 2024Document1 page14 Feb 2024TechnetNo ratings yet
- Patient Report Direct ViewDocument2 pagesPatient Report Direct ViewSyed Tahir BukhariNo ratings yet
- Abnormal WBC Scattergram A Clue To The Diagnosis of MalariaDocument6 pagesAbnormal WBC Scattergram A Clue To The Diagnosis of Malariatufis02No ratings yet
- N KusumamdhaDocument1 pageN Kusumamdhakirankumar KavalaNo ratings yet
- 2020MB6953RDocument1 page2020MB6953RFaizan RasoolNo ratings yet
- Study of Peripheral Blood Smear Findings in Patients of Anemia and To Compare It With Automated Hematology Analyzer Generated Red Cell ParametersDocument5 pagesStudy of Peripheral Blood Smear Findings in Patients of Anemia and To Compare It With Automated Hematology Analyzer Generated Red Cell ParametersDra. Lisy BarçaNo ratings yet
- 572010000562: 57003694 20-Oct-20 11:42 AM: Master VIDHAN: 20-Oct-2020 01:07PM:: 20-Oct-2020 05:18PM: 5 Y 11 M 10 D / M: 20-Oct-2020 05:39PMDocument1 page572010000562: 57003694 20-Oct-20 11:42 AM: Master VIDHAN: 20-Oct-2020 01:07PM:: 20-Oct-2020 05:18PM: 5 Y 11 M 10 D / M: 20-Oct-2020 05:39PMseds5anuragNo ratings yet
- Haematology: Complete Blood Cell CountDocument2 pagesHaematology: Complete Blood Cell CountMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Department of Microbiology Urine Examination: Result ResultDocument3 pagesDepartment of Microbiology Urine Examination: Result ResultDanish AmanNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Class12Document10 pagesChromosomal Basis of Inheritance Class12Shweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Origin and Evolution of LifeDocument22 pagesOrigin and Evolution of LifeShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- B57a77 PDFDocument18 pagesB57a77 PDFKuldeep AshiyaNo ratings yet
- English Charakam ChikitsaDocument13 pagesEnglish Charakam ChikitsaShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument22 pagesHuman ReproductionShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Organism & Environment-2Document13 pagesOrganism & Environment-2Shweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering and Genomics Class 12Document6 pagesGenetic Engineering and Genomics Class 12Shweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Mol - Basis of InheritanceDocument21 pagesMol - Basis of InheritanceSyed Nazir AhammedNo ratings yet
- Mol - Basis of InheritanceDocument21 pagesMol - Basis of InheritanceSyed Nazir AhammedNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction 3Document8 pagesHuman Reproduction 3Manas Ranjan JenaNo ratings yet
- CH8Document12 pagesCH8Manas Ranjan JenaNo ratings yet
- ProteinreportDocument2 pagesProteinreportShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology PDFDocument165 pagesClass 12 Biology PDFShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology PDFDocument165 pagesClass 12 Biology PDFShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Acls 2011 PretestDocument32 pagesAcls 2011 PretestShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Urinealbumin 24 HrsDocument1 pageUrinealbumin 24 HrsShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Report Dengue NS1, IGM IGGDocument4 pagesReport Dengue NS1, IGM IGGShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Report of CortisolDocument1 pageReport of CortisolShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Report of CA 15.3Document1 pageReport of CA 15.3Shweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Acls CPR and Pals - Clinical Pocket GuideDocument230 pagesAcls CPR and Pals - Clinical Pocket Guideapi-275075644100% (1)
- Com&mis&cli&med&pad&1st PDFDocument294 pagesCom&mis&cli&med&pad&1st PDFJeevan Raj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Report of Patient With Liver AbscessDocument2 pagesReport of Patient With Liver AbscessShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- MOH Pocket Manual in Emergency Medicine PDFDocument244 pagesMOH Pocket Manual in Emergency Medicine PDFErandi Andrea100% (2)
- Ayurvedic Medicines Are Dangerous Than Allopathic MedicinesDocument7 pagesAyurvedic Medicines Are Dangerous Than Allopathic MedicinesShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- Report of ANADocument2 pagesReport of ANAShweta PatilNo ratings yet
- AAH v2 Acute AsthmaDocument81 pagesAAH v2 Acute AsthmaEssa SmjNo ratings yet
- Cardianix Mission Vision SlogansDocument3 pagesCardianix Mission Vision SlogansArsal KhanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTweenie DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2868Document8 pagesGenetics 2868Farrukh Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Js - Case PresentationDocument61 pagesJs - Case Presentationapi-592676308No ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Concussion and Post Concussion SydromeDocument8 pagesRehabilitation of Concussion and Post Concussion Sydromebuckley1212085No ratings yet
- Useful Websites For Medical StudentsDocument1 pageUseful Websites For Medical StudentsRakesh DudiNo ratings yet
- Long Term Care Facilities Final ReportDocument157 pagesLong Term Care Facilities Final ReportPeter YankowskiNo ratings yet
- List of ClinicDocument47 pagesList of ClinicAmie ManarpaNo ratings yet
- Acute Medicine Surgery - 2022 - Sasaki - Japanese Society For Burn Injuries JSBI Clinical Practice Guidelines ForDocument104 pagesAcute Medicine Surgery - 2022 - Sasaki - Japanese Society For Burn Injuries JSBI Clinical Practice Guidelines For白石 真土320D008No ratings yet
- Fraktur Klavikula PDFDocument15 pagesFraktur Klavikula PDFSJ Iraa100% (1)
- Safety and Efficacy Hyaluronic Acid Correction of Nasolabial Folds A Meta-Analysis - Huang, 2013Document8 pagesSafety and Efficacy Hyaluronic Acid Correction of Nasolabial Folds A Meta-Analysis - Huang, 2013Rafael Autran Cavalcante AraújoNo ratings yet
- Niña Sheena L. So Grade 12 STEM: "All About Mountaineering"Document3 pagesNiña Sheena L. So Grade 12 STEM: "All About Mountaineering"Sheena ChanNo ratings yet
- The Short Child Review Article DR Azriyanti 2021Document10 pagesThe Short Child Review Article DR Azriyanti 2021tee qarafiNo ratings yet
- Job Search-1Document2 pagesJob Search-1Prashanth RajuNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Ultrasonography: Clinical Uses and ApplicationsDocument54 pagesThoracic Ultrasonography: Clinical Uses and ApplicationsMesay AssefaNo ratings yet
- WEBINAR On PEDIATRIC TRAUMADocument44 pagesWEBINAR On PEDIATRIC TRAUMAGovindarajan HariharanNo ratings yet
- Physiology Unit 7 JournalDocument3 pagesPhysiology Unit 7 JournalRicky SinghNo ratings yet
- LacrisertDocument4 pagesLacrisertChindra Sebaly PutryNo ratings yet
- F 16 CLINNeurologicalObservationChartDocument2 pagesF 16 CLINNeurologicalObservationChartRani100% (1)
- C2 ExamDocument29 pagesC2 ExamauNo ratings yet
- Author: Tuazon, Josefina A. RN, BSN, MN, DRPH: Learning Objective 1: Appreciate OneDocument6 pagesAuthor: Tuazon, Josefina A. RN, BSN, MN, DRPH: Learning Objective 1: Appreciate OneJohn Robert PescadorNo ratings yet
- TOMS Giving-Report 2013Document13 pagesTOMS Giving-Report 2013Inglorious KunalNo ratings yet
- Forensic Age EstimationDocument10 pagesForensic Age EstimationMaría Camila ValenciaNo ratings yet
- A Moment To RememberDocument8 pagesA Moment To RememberKate Laxamana GuinaNo ratings yet
- Paramedical 1Document156 pagesParamedical 1Iswarya MohanNo ratings yet
- High Risk Babies Resuscitation Stabilitation and Management IDAIDocument23 pagesHigh Risk Babies Resuscitation Stabilitation and Management IDAIaulianaNo ratings yet
- Nephrology MCQ PDFDocument7 pagesNephrology MCQ PDFMonica J Ortiz PereiraNo ratings yet
- Seasonal InfluenzaDocument4 pagesSeasonal InfluenzaRachitNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) Is A Disease of TheDocument6 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) Is A Disease of TheDhea Fajeria FitriNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (403)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (20)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)