Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 5 Factors Affecting The Growth of Plant
Uploaded by
Ricardo Ricafort0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views2 pagesGrade 3 Lessons on Science
Original Title
Lesson 5 Factors Affecting the Growth of Plant
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGrade 3 Lessons on Science
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views2 pagesLesson 5 Factors Affecting The Growth of Plant
Uploaded by
Ricardo RicafortGrade 3 Lessons on Science
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Lesson 5: Environmental Factors affecting the Growth of Plants
LIGHT. Light reaching the surface of a plant is either absorbed, reflected, or
transmitted. Energy, in the form of sunlight is one of the driving forces in the chemical
reaction known as photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants
manufacture food, mainly sugars, from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of
chlorophyll (a green pigment), utilizing light energy and releasing oxygen and water.
Together the quality, quantity, and duration of light influences plant growth. Plants
grown in direct sunlight are typically compact, where as those in shade are taller and
elongated.
MOISTURE. Water is essential for life, it is one of the most important requirements
for plant growth. Water is the main component in plants cells, it keeps the plant turgid
(stiff), it is used in photosynthesis, and transports nutrients throughout the plant. Plants
also use water to lower leaf temperature, increase mineral absorption, and pull water
from the roots to the top of the plants through a process known as transpiration.
AIR One of the raw materials used in photosynthesis is carbon dioxide. The content
of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is relatively stable at about 0.03 percent, a
seemingly small amount but totaling roughly 2,000,000,000,000 tons in the atmosphere
surrounding the earth. Carbon dioxide is continually being added to the air by
respiration of plants and animals, decaying organic materials, combustion of fuels, and
volcanic activity. Carbon dioxide diffuses through the stomata (pores or openings in a
plants.
PROPER TEMPERATURE. The temperature of the atmosphere is the result of the
transfer of heat from the earth’s surface to the surrounding air. Temperature varies with
latitude, altitude, and topography. The climate and temperature of an area determines
what kinds of plants will grow. The ability of a plant to withstand cold temperatures is
known as cold hardiness while plants that cannot tolerate cool weather are known as
tender. In the natural environment, temperature is continually changing.
NUTRIENTS. In addition to carbon dioxide and water, plants need 17 different
nutrients to maintain growth. Although carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are obtained from
the air, most nutrients that a plant needs must be present in the soil or growing medium.
The soils in which plants grow consists of a mixture of mineral materials, organic matter,
water, and air in varying proportions.
MAIN PARTS OF A PLANT
Roots. A plant’s roots grow under the ground. The roots help hold the plant in the soil.
They also take in water and nutrients which the plant turns into food. Plants have
different kinds of root systems. Some plants have fibrous roots. Fibrous roots have
many branches and spread out like the branches of a tree. Plants that have fibrous root
systems include grasses, corn plants, wheat and many other crops that farmers grow.
Other plants have a tap root. This is a single, main root that grows straight down. The
tap root has smaller branches growing off of it. Examples of plants that have a tap root
are carrots, radishes and turnips.
Stems. The stem grows upward from the roots. It holds the plant up and carries water
from the roots to the other parts of the plant. Secondary stems, called petioles, grow
from the main stem. These petioles have leaves growing on them. Sometimes we eat
the stems of plants, like celery and asparagus.
Leaves. The leaves of a plant make the food the plant needs to survive. The water and
nutrients that were taken in by the roots, move upward through the stem to the leaves.
The leaves take sunlight and carbon dioxide from the air and convert the nutrients to
plant food. This process is called photosynthesis. We eat the leaves of some plants
such as lettuce and spinach.
Flowers. Fruit and Seeds When a plant receives the proper amount of water, nutrients,
air and sunlight it produces flowers. The flowers usually grow on the stems. When the
flower dies and falls off it leaves behind a fruit. The fruit contains seeds. Fruits that we
eat include apples, oranges, watermelons and tomatoes. Sometimes we let the seeds
dry out and use them for food. Things like corn, peas and beans are examples of seeds
that we eat. The seed is the part that grows a new plant. If we plant a bean seed we will
get a plant just like the one that made the seed.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Revision in History 4Document2 pagesRevision in History 4Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- 1st Term Week 8 Math 2020Document5 pages1st Term Week 8 Math 2020Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Camel LectureDocument2 pagesCamel LectureRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Grade 1 Science Review QuizDocument5 pagesGrade 1 Science Review QuizRicardo Ricafort100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Review Quiz in English1Document8 pagesReview Quiz in English1Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
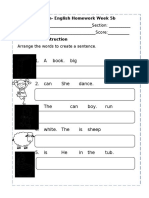
- Grade 5 English AssignmentDocument2 pagesGrade 5 English AssignmentRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 2020 WorksheetDocument6 pages2020 WorksheetRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
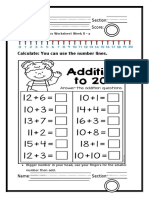
- Grade 2 Math Lesson For This WeekDocument5 pagesGrade 2 Math Lesson For This WeekRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grade 4 Science Lesson: Camel LectureDocument2 pagesGrade 4 Science Lesson: Camel LectureRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grade 1 Math Week 8Document5 pagesGrade 1 Math Week 8Ricardo Ricafort100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grade 2 Review Quiz in EnglishDocument8 pagesGrade 2 Review Quiz in EnglishRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grade 2 Worksheet English 2: Predicting EventsDocument3 pagesGrade 2 Worksheet English 2: Predicting EventsRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Floating and Sinking Property of MaterialsDocument4 pagesFloating and Sinking Property of MaterialsRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grade 2 Lessons in Math and EnglishDocument3 pagesGrade 2 Lessons in Math and EnglishRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- 2020 List of AnimalsDocument2 pages2020 List of AnimalsRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- 2020 11 Ways To Keep Your Teeth HealthyDocument2 pages2020 11 Ways To Keep Your Teeth HealthyRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- 2020 ActivitiesDocument4 pages2020 ActivitiesRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Schedule For Third Term Long Quiz 2018Document4 pagesSchedule For Third Term Long Quiz 2018Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 English LessonDocument1 pageGrade 1 English LessonRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Schedule For First Term Long Test For Grades 3 To 6Document8 pagesSchedule For First Term Long Test For Grades 3 To 6Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Outline of Grade 1 Lessons On Math, Science, and EnglishDocument1 pageOutline of Grade 1 Lessons On Math, Science, and EnglishRicardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Gr5 - 2nd Term Long Test 19Document2 pagesGr5 - 2nd Term Long Test 19Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Continuation of English Lessons For Grade 1 Pupils...Document1 pageContinuation of English Lessons For Grade 1 Pupils...Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Gr1.2-2ndt Term Long Tests 19Document1 pageGr1.2-2ndt Term Long Tests 19Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Schedule of 3rd Term Long Test For Grades 3, 4, 5 & 6Document2 pagesSchedule of 3rd Term Long Test For Grades 3, 4, 5 & 6Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Schedule of 3rd Term Long Test For Grades 1 & 2Document1 pageSchedule of 3rd Term Long Test For Grades 1 & 2Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Gr4 - 2nd Term Long Test 19Document2 pagesGr4 - 2nd Term Long Test 19Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Gr6 - 2nd Term Long Test 19Document2 pagesGr6 - 2nd Term Long Test 19Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- Gr5 - 2nd Term Long Test 19Document2 pagesGr5 - 2nd Term Long Test 19Ricardo RicafortNo ratings yet
- LoLa 42 Opening Drink List 5.12.17Document1 pageLoLa 42 Opening Drink List 5.12.17Jacqueline CainNo ratings yet
- AGC Printing Patchogue History Part 1 LayoutDocument112 pagesAGC Printing Patchogue History Part 1 Layoutlnichols6754No ratings yet
- Why You Should Never Eat High Fructose Corn Syrup - Mark Hyman, MDDocument6 pagesWhy You Should Never Eat High Fructose Corn Syrup - Mark Hyman, MDcendekiaNo ratings yet
- English Book 2-StudentDocument177 pagesEnglish Book 2-StudentMaritza RamirezNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W9Document2 pagesDLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W9Cherry ursuaNo ratings yet
- Phonetic Chart and Word MeaningsDocument76 pagesPhonetic Chart and Word Meaningsnadekaramit9122No ratings yet
- Cooking in Britain Today Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesCooking in Britain Today Lesson PlanНаталя ЩурNo ratings yet
- ST 1 GR.4 EnglishDocument2 pagesST 1 GR.4 EnglishKit Dwight Uy CapeNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Enzyme Activity and Characterization PDFDocument14 pagesEnzyme Activity and Characterization PDFpanrumb06No ratings yet
- Food Processor ManualDocument10 pagesFood Processor ManualSneha PavithranNo ratings yet
- Suomi Finland 100 YearsDocument15 pagesSuomi Finland 100 YearsYiota AchelonoudiNo ratings yet
- Fiesta Solicitation LetterDocument2 pagesFiesta Solicitation LetterPangarap Ni JuanNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Case StudyDocument3 pagesDiabetes Case Studydsaitta108No ratings yet
- Madison County ScoresDocument3 pagesMadison County ScoresMike BrownNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Buying Roles and Post Purchase - Microwave NSDocument2 pagesCase Study On Buying Roles and Post Purchase - Microwave NSMaroof BaigNo ratings yet
- Soal B. Inggris Kelas 2Document3 pagesSoal B. Inggris Kelas 2po. nusantaraNo ratings yet
- Tel Is Romero 2006Document7 pagesTel Is Romero 2006Alex Samuel SilvaNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed LP THREE BASIC COMPONENT OF SANDWICHDocument2 pagesSemi Detailed LP THREE BASIC COMPONENT OF SANDWICHChristine Jade81% (21)
- Backpacker Risk NarrativesDocument21 pagesBackpacker Risk NarrativesMaria LeiteNo ratings yet
- Native American HealthDocument20 pagesNative American Healthapi-253792021No ratings yet
- Sanitation and Disinfection in Poultry Processing PlantsDocument49 pagesSanitation and Disinfection in Poultry Processing Plantssmoubarak100% (1)
- Air Fryer 14 Day Meal PlanDocument36 pagesAir Fryer 14 Day Meal Planjgregors8683No ratings yet
- What are GMOs? The Benefits and RisksDocument13 pagesWhat are GMOs? The Benefits and RisksRocel Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Beastly BeautyDocument24 pagesBeastly BeautyI Read YANo ratings yet
- Dentists ExpensesDocument4 pagesDentists ExpensesPieNo ratings yet
- FS Template 1Document63 pagesFS Template 1JED FRANZ AKEEM DE GUIANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Extrusion TechnologyDocument46 pagesChapter 1 Extrusion TechnologychaudharymeelNo ratings yet
- Browerville Blade - 03/24/2011Document14 pagesBrowerville Blade - 03/24/2011bladepublishingNo ratings yet
- Understanding the 4Ms of OperationsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding the 4Ms of OperationsMorelei FernandezNo ratings yet
- GMP & ValidationDocument54 pagesGMP & ValidationKamal Chokshi100% (1)