Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 viewsReviewFinal 2
ReviewFinal 2
Uploaded by
Shriya VenkataramanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
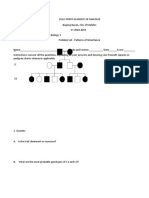
- NCP in POC Module (Bernales)Document11 pagesNCP in POC Module (Bernales)Jan Lianne BernalesNo ratings yet
- BelgeDocument11 pagesBelgeRoyalNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Patterns of InheritanceDocument5 pagesProblem Set Patterns of InheritanceKarl RochaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal G&DDocument75 pagesAssessment of Fetal G&DHillary Praise AquinoNo ratings yet
- LeukorrheaDocument29 pagesLeukorrheaThorsang Chayovan100% (1)
- Sample Ayurvedic Cooking PDFDocument15 pagesSample Ayurvedic Cooking PDFSurya Nap HercegNo ratings yet
- Fitness Manual IFADocument128 pagesFitness Manual IFAAlejandro BalcazarNo ratings yet
- Important Endocrine Glands, The Hormone They Secrete & Their FunctionDocument50 pagesImportant Endocrine Glands, The Hormone They Secrete & Their FunctionSiva SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGDocument76 pagesElectrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGInnocent Clifford MaranduNo ratings yet
- Mirela Ibrahimovic CV 1Document3 pagesMirela Ibrahimovic CV 1api-454732066No ratings yet
- Set A - Tunas Cemerlang PemahamanDocument18 pagesSet A - Tunas Cemerlang PemahamanrafaelzalaqueNo ratings yet
- Consciously Control Your Immune System With The Wim Hof Method - Earth. We Are OneDocument5 pagesConsciously Control Your Immune System With The Wim Hof Method - Earth. We Are OneGian Prit Singh Khalsa100% (5)
- Equipo de Contrapulsacion Arrow-KaatDocument103 pagesEquipo de Contrapulsacion Arrow-KaatCarito HernandezNo ratings yet
- Community PsychologyDocument20 pagesCommunity PsychologyMaePornelaGomezNo ratings yet
- MyocarditisDocument52 pagesMyocarditis7337man100% (1)
- Psychiatric Aspects of Liver DiseaseDocument8 pagesPsychiatric Aspects of Liver DiseaseBrian AsayasNo ratings yet
- Food For DogsDocument5 pagesFood For DogsPaul LuschwitzNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Potential of Heterocyclic Pyrimidine Scaffolds: Review Open AccessDocument29 pagesTherapeutic Potential of Heterocyclic Pyrimidine Scaffolds: Review Open AccessWalid EbaiedNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Universitas Kristen MaranathaDocument10 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Universitas Kristen MaranathaUlfa Kaka' TersaiiankNo ratings yet
- Monalisa ManurungDocument13 pagesMonalisa ManurungPradinta BayuNo ratings yet
- 6.1 MicrobiologyDocument32 pages6.1 MicrobiologyYsabelle BautistaNo ratings yet
- General Examination For CVSDocument29 pagesGeneral Examination For CVSstudymedic100% (1)
- Writing Sub-Test: Nursing Time AllowedDocument2 pagesWriting Sub-Test: Nursing Time AllowedAnit XingNo ratings yet
- HPCT-1-Intro To General Pathology PDFDocument6 pagesHPCT-1-Intro To General Pathology PDFRochellane Ramos PlasabasNo ratings yet
- The Lac Operon: (BIOT 4006: Genetics and Molecular Biology)Document8 pagesThe Lac Operon: (BIOT 4006: Genetics and Molecular Biology)Alina RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Department of Health (Repaired)Document48 pagesDepartment of Health (Repaired)Vanito SwabeNo ratings yet
- Ra 9211 Tobacco Regulation ActDocument10 pagesRa 9211 Tobacco Regulation Actrocky inthesea2No ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For A Patient With B ThalassaemiaDocument4 pagesAnaesthesia For A Patient With B ThalassaemiaGanesh HansdahNo ratings yet
- Akema Brochure 2011Document19 pagesAkema Brochure 2011J C Torres FormalabNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Polymyalgia Rheumatica Usually Means A Favourable Outcome For Your PatientDocument8 pagesDiagnosis of Polymyalgia Rheumatica Usually Means A Favourable Outcome For Your PatientPrakashNo ratings yet
ReviewFinal 2
ReviewFinal 2
Uploaded by
Shriya Venkataraman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesReviewFinal 2
ReviewFinal 2
Uploaded by
Shriya VenkataramanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
BIOLOGY-9th grade Year
SEMESTER II FINAL EXAM review
1) The following could be on your Exam-
2) Unifying themes of biology – Cellular structure and function, reproduction,
metabolism, homeostasis, heredity, evolution, interdependence
3) Solving world problems – preserving our environment, improving food supply,
understanding the human genome, fighting diseases (AIDS, cancer, emerging
diseases)
4) Stages of a scientific investigation
5) Atoms, Subatomic particles, Elements, Isotopes, Molecules, Compounds
6) Bonding – covalent, ionic, hydrogen
7) Acids, Bases, Buffers, pH – their properties and examples
8) Biomolecules - carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids – properties, uses and
examples
9) Enzymes – properties, activation energy, enzyme action, factors affecting
enzymes
10) Compare and contrast prokaryotes and eukaryotes
11) Cell organelles and function of each organelle
12) Active transport- Sodium potassium pump
13) Passive transport-Osmosis, Diffusion, Facilitated diffusion
14) Movement in vesicles-endocytosis, exocytosis
15) Calvin cycle
16) Pigments
17) Factors affecting photosynthesis
18) Glycolysis
19) Kreb’s cycle
20) Respiration in absence of oxygen (fermentation)
21) Chromosome structure: Chromatids, Centromere etc.
22) Stages of Mitosis
23) What happens in Cytokinesis?
24) Stages of Meiosis
25) Seven characters/traits Mendel studied in Peas
26) Three steps of Mendel’s experiments
27) Examples of dominant and recessive characters
28) The Laws of Heredity: The law of segregation, The law of independent
assortment
29) Punnett squares – Monohybrid crosses, Dihybrid crosses
30) Test cross, Pedigree
31) Polygenic inheritance, Incomplete dominance, Multiple alleles, Codominance,
Environmental influence on characters
32) Griffiths experiment -transformation
33) Hershey Chase experiment
34) Contributions of various scientists in the field of DNA research – Avery,
Chargaff, Wilkins and Franklin, Watson and Crick
35) Structure of DNA
36) Base pairing rules
37) DNA replication
38) Central dogma
39) Three types of RNA
40) Transcription
41) Translation
42) Genetic code, codons; Interpreting the genetic code
43) Steps in genetic engineering – cutting DNA, making recombinant DNA, Cloning,
Screening
44) Confirmation of a cloned gene – Southern blot method
45) Facts about the human genome project
46) 5 genetically engineered medicines and their basic uses
47) 5 ways to improve crops by manipulating genes
48) 5 applications of genetic engineering to animal farming
49) Earth’s formation and events that followed
50) Radiometric dating, half life
51) Primordial soup model
52) Miller Urey experiment
53) Lerman’s bubble model
54) Evolution of cellular life – prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their examples
55) Theory of endosymbiosis
56) 6 kingdoms of life
57) Food chains, food webs, trophic levels (producers, herbivores, small carnivores, large
carnivores)
58) Omnivores, Decomposers, Detritivores
59) Energy flow in an ecosystem
60) Biotic and abiotic factors, examples
61) Community interactions and their examples – competition, predation, parasitism,
symbiosis, mutualism, commensalisms
62) Acid rain, Ozone layer depletion, Global warming, Greenhouse effect
63) Classification of organisms (8 categories in the correct order)
64) What are the 6 kingdoms of life with examples
65) Examples of non vascular plants
66) Examples of seedless vascular plants
67) Types of seeded vascular plants - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms and their basic
difference
68) Types of angiosperms (Monocots vs. Dicots and examples)
69) Four parts of a flower
70) Role of Major nutrients required by plants(Table 1,page 579)
71) Hormones in plants –auxins, gibberrlins, cytokinins
72) Basic characteristics AND Examples of organisms belonging to each of the phyla/class –
Porifera, Cnidaria, Annelida, Arthropods, Echinodermata, Molluska, Chondrichthyes,
Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, Mammals
a. For the following chapters, please read the notes given to you in class and your
textbook also.
73) Ch 27 –Introduction to animals
74) Ch 37 –Introduction to body structure
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- NCP in POC Module (Bernales)Document11 pagesNCP in POC Module (Bernales)Jan Lianne BernalesNo ratings yet
- BelgeDocument11 pagesBelgeRoyalNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Patterns of InheritanceDocument5 pagesProblem Set Patterns of InheritanceKarl RochaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal G&DDocument75 pagesAssessment of Fetal G&DHillary Praise AquinoNo ratings yet
- LeukorrheaDocument29 pagesLeukorrheaThorsang Chayovan100% (1)
- Sample Ayurvedic Cooking PDFDocument15 pagesSample Ayurvedic Cooking PDFSurya Nap HercegNo ratings yet
- Fitness Manual IFADocument128 pagesFitness Manual IFAAlejandro BalcazarNo ratings yet
- Important Endocrine Glands, The Hormone They Secrete & Their FunctionDocument50 pagesImportant Endocrine Glands, The Hormone They Secrete & Their FunctionSiva SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGDocument76 pagesElectrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGInnocent Clifford MaranduNo ratings yet
- Mirela Ibrahimovic CV 1Document3 pagesMirela Ibrahimovic CV 1api-454732066No ratings yet
- Set A - Tunas Cemerlang PemahamanDocument18 pagesSet A - Tunas Cemerlang PemahamanrafaelzalaqueNo ratings yet
- Consciously Control Your Immune System With The Wim Hof Method - Earth. We Are OneDocument5 pagesConsciously Control Your Immune System With The Wim Hof Method - Earth. We Are OneGian Prit Singh Khalsa100% (5)
- Equipo de Contrapulsacion Arrow-KaatDocument103 pagesEquipo de Contrapulsacion Arrow-KaatCarito HernandezNo ratings yet
- Community PsychologyDocument20 pagesCommunity PsychologyMaePornelaGomezNo ratings yet
- MyocarditisDocument52 pagesMyocarditis7337man100% (1)
- Psychiatric Aspects of Liver DiseaseDocument8 pagesPsychiatric Aspects of Liver DiseaseBrian AsayasNo ratings yet
- Food For DogsDocument5 pagesFood For DogsPaul LuschwitzNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Potential of Heterocyclic Pyrimidine Scaffolds: Review Open AccessDocument29 pagesTherapeutic Potential of Heterocyclic Pyrimidine Scaffolds: Review Open AccessWalid EbaiedNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Universitas Kristen MaranathaDocument10 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Universitas Kristen MaranathaUlfa Kaka' TersaiiankNo ratings yet
- Monalisa ManurungDocument13 pagesMonalisa ManurungPradinta BayuNo ratings yet
- 6.1 MicrobiologyDocument32 pages6.1 MicrobiologyYsabelle BautistaNo ratings yet
- General Examination For CVSDocument29 pagesGeneral Examination For CVSstudymedic100% (1)
- Writing Sub-Test: Nursing Time AllowedDocument2 pagesWriting Sub-Test: Nursing Time AllowedAnit XingNo ratings yet
- HPCT-1-Intro To General Pathology PDFDocument6 pagesHPCT-1-Intro To General Pathology PDFRochellane Ramos PlasabasNo ratings yet
- The Lac Operon: (BIOT 4006: Genetics and Molecular Biology)Document8 pagesThe Lac Operon: (BIOT 4006: Genetics and Molecular Biology)Alina RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Department of Health (Repaired)Document48 pagesDepartment of Health (Repaired)Vanito SwabeNo ratings yet
- Ra 9211 Tobacco Regulation ActDocument10 pagesRa 9211 Tobacco Regulation Actrocky inthesea2No ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For A Patient With B ThalassaemiaDocument4 pagesAnaesthesia For A Patient With B ThalassaemiaGanesh HansdahNo ratings yet
- Akema Brochure 2011Document19 pagesAkema Brochure 2011J C Torres FormalabNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Polymyalgia Rheumatica Usually Means A Favourable Outcome For Your PatientDocument8 pagesDiagnosis of Polymyalgia Rheumatica Usually Means A Favourable Outcome For Your PatientPrakashNo ratings yet