Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2, Problem 4P BRAJA
Uploaded by
Henry León SuárezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2, Problem 4P BRAJA
Uploaded by
Henry León SuárezCopyright:
Available Formats
NEW!
Textbook Solutions Expert Q&A Study Pack Practice Search
home / study / engineering / civil engineering / structural design / structural design solutions manuals / principles of foundation engineering,
Chapter 2, Problem 4P Bookmark Show all steps: ON
Principles of Foundation Engineering, SI Edition (8
See this solution in the app
Problem
A saturated soil specimen has w =36% and γd = 13.43 kN/m3. Determine:
a. Void ratio
b. Porosity
c. Specific gravity of soil solids
d. Saturated unit weight (in lb/ft3)
Step-by-step solution
Step 1 of 6
(a)
Calculate void ratio by using the for dry unit weight equation.
…… (1)
Here, is the unit weight of water, e is the void ratio and is the specific gravity of soil
solids.
Represent the formula for specific gravity of soil solids, for a saturated soil.
Here, w is the moisture content.
Comment
Step 2 of 6
Substitute for in equation (1).
NEW!
Textbook Solutions Expert Q&A Study Pack Practice Search
Chapter 2, Problem 4P Bookmark Show all steps: ON
Comment
Step 3 of 6
Substitute for , for w, and for .
Therefore, the obtained value of void ratio is .
The denser the soil, the less is the void ratio.
Comment
Step 4 of 6
(b)
Calculate the porosity of the soil by using the equation.
Substitute 0.97 for e.
Therefore, the porosity of the soil is .
The higher the void ratio the more will be the porosity, although the relationship is not linear.
Comment
Step 5 of 6
(c)
Calculate the specific gravity of soil solids by using the equation.
NEW!
Textbook Solutions Expert Q&A Study Pack Practice Search
Substitute 0.97 for e, and for w in equation
Chapter 2, Problem 4P Bookmark Show all steps: ON
Therefore, the specific gravity for this soil is .
The specific gravity of most soils is commonly in the range of 2.55 to 2.75.
Comment
Step 6 of 6
(d)
Calculate the saturated unit weight of the soil by using the equation.
Substitute 0.97 for e, 2.69 for , and for .
Therefore, the saturated unit weight of the soil is .
Compared to the dry unit weight and bulk unit weight, the saturated unit weight for any soil is the
highest.
Comments (1)
Was this solution helpful? 2 0
Recommended solutions for you to review
Chapter 5, Problem 15P Chapter 4, Problem 6P
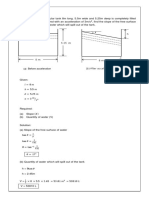
A continuous foundation For a square foundation
is to be constructed near that is B × B in plan, Df =
a slope made of granular 2 m; vertical gross
soil (see Figure 1). If B = allowable load, Qall =
1.22 m, b = 1.83 m, H =... 3330 kN, γ = 16.5 kN/m3;
ϕ =...
See solution
See solution
NEW!
Textbook Solutions Expert Q&A Study Pack Practice Search
Chapter 2, Problem 4P Bookmark Show all steps: ON
ABOUT CHEGG
LEGAL & POLICIES
CHEGG PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
CHEGG NETWORK
CUSTOMER SERVICE
© 2003-2020 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Tutorial Chapter 2Document2 pagesTutorial Chapter 2wendyNo ratings yet
- VERTICAL STRESS BELOW CIRCULAR AREADocument20 pagesVERTICAL STRESS BELOW CIRCULAR AREAJess PalmaNo ratings yet
- Relative Equilibrium of LiquidsDocument18 pagesRelative Equilibrium of LiquidsIrene Grace BatalaoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Vertical and Horizontal StressDocument12 pagesModule 4 Vertical and Horizontal StressShane IsorenaNo ratings yet
- Soil Composition AnalysisDocument9 pagesSoil Composition AnalysisThortheGreayNo ratings yet
- Answers (Open-Channel Flow Notes) AUTUMN 2022 Section 1.2 ExampleDocument39 pagesAnswers (Open-Channel Flow Notes) AUTUMN 2022 Section 1.2 ExampleAliyyi JamaalNo ratings yet
- A. Hydrostatic Force On Plane Surface: 1. FormulaDocument20 pagesA. Hydrostatic Force On Plane Surface: 1. FormulaKim Kelley AngNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Analysis of Prestressed Concrete Beams Using Combined Load ApproachDocument48 pagesModule 2 Analysis of Prestressed Concrete Beams Using Combined Load ApproachVann AlfredNo ratings yet
- CelerityDocument23 pagesCelerityswabrightNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 Lecture on Buoyancy Forces and StabilityDocument20 pagesQuiz 3 Lecture on Buoyancy Forces and StabilityAlyssa AmistosoNo ratings yet
- Hge May 2022Document21 pagesHge May 2022JOHN KEAN NIEMONo ratings yet
- Prismoidal Formula 2Document11 pagesPrismoidal Formula 2anggaxkusumaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity & Oscillations: Ut Tension, Sic Vis As Extension, So Force. Extension Is Directly Proportional To ForceDocument11 pagesElasticity & Oscillations: Ut Tension, Sic Vis As Extension, So Force. Extension Is Directly Proportional To ForceJustin Paul VallinanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Fluid StaticsDocument26 pagesChapter 2 Fluid StaticsSoban Malik100% (1)
- Appendix G Elastic and Inelastic Response SpectraDocument11 pagesAppendix G Elastic and Inelastic Response SpectracedaserdnaNo ratings yet
- Eval 2 FinalDocument4 pagesEval 2 FinalGreg Rasco, REE, RMPNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Engineering PDFDocument36 pagesHydraulic Engineering PDFZaid Hadi100% (2)
- A Sample of Wet Soil Has A Volume of 0Document8 pagesA Sample of Wet Soil Has A Volume of 0eph0% (1)
- CHAPTER 8C - SeepageDocument26 pagesCHAPTER 8C - SeepageTyn MaturanNo ratings yet
- CIVL 3210 - Assignment 2 - 2023 - SolutionDocument8 pagesCIVL 3210 - Assignment 2 - 2023 - Solutiondemar holnessNo ratings yet
- Prefi Calculus DraftDocument2 pagesPrefi Calculus Draftralph crucilloNo ratings yet
- CH 2 For PresentationDocument34 pagesCH 2 For PresentationNesru Jemal100% (1)
- Measure flow using Venturi metersDocument3 pagesMeasure flow using Venturi metersMike Mor'z0% (2)
- Soil Mechanics HandoutDocument62 pagesSoil Mechanics HandoutRenz Erick Reveche Delgado100% (1)
- Properties of Fluids: Sample Problems BDocument4 pagesProperties of Fluids: Sample Problems BFronda Jerome BlasNo ratings yet
- Assignment I Field Exploration & Soil TestingDocument12 pagesAssignment I Field Exploration & Soil TestingEphrem Bizuneh100% (1)
- Calculate volumes and surface areas of common solidsDocument17 pagesCalculate volumes and surface areas of common solidssam_raunayNo ratings yet
- 2014Document1 page2014jerold_arandiaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems in Soil Mechanics1Document31 pagesSolved Problems in Soil Mechanics1Denis Kalumba100% (3)
- Development of Gabion Walls Using Tungsten and Recycled CansDocument25 pagesDevelopment of Gabion Walls Using Tungsten and Recycled CansPaolo EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech ProbsetDocument18 pagesFluid Mech ProbsetRia Mae LauronNo ratings yet
- MorroofdDocument2 pagesMorroofdAnonymous ym7PJCj0% (1)
- HAU Structural Loads LessonDocument14 pagesHAU Structural Loads Lessoncutie4everrNo ratings yet
- Ce161p A88 q1 MakeupDocument1 pageCe161p A88 q1 MakeupRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Plane & SphericalDocument28 pagesPlane & SphericalMarcelo AbreraNo ratings yet
- Permeability Test in The Field by Pumping From WellsDocument16 pagesPermeability Test in The Field by Pumping From WellsGed CudiamatNo ratings yet
- Basics For Rural ConstructionDocument83 pagesBasics For Rural ConstructionBernard Palmer100% (1)
- 3 ChannelDocument45 pages3 ChannelPatrick YuNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Compressibility of Soil4Document14 pagesCH 11 Compressibility of Soil4Boni ClydeNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Expert AnswerDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Expert AnswerMarc Jairro GajudoNo ratings yet
- CE142P-2 / E01 Engr. Edward Monjardin 01-09-21 01-12-21: Jingona, Fatimah Rahima TDocument6 pagesCE142P-2 / E01 Engr. Edward Monjardin 01-09-21 01-12-21: Jingona, Fatimah Rahima TFatimah Rahima Jingona100% (1)
- Flow in Open Channel - Sample ProblemsDocument8 pagesFlow in Open Channel - Sample Problemsacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Sample Soil Investigation Lab ReportDocument26 pagesSample Soil Investigation Lab ReportMo-T0% (1)
- Highway Geometric Design Earthworks 2014 2015Document28 pagesHighway Geometric Design Earthworks 2014 2015Herbert MayombweNo ratings yet
- Math word problems and equationsDocument2 pagesMath word problems and equationsChan FamilyNo ratings yet
- Cebep Reviewer Set 1Document33 pagesCebep Reviewer Set 1Loysa Agtarap MataNo ratings yet
- 5 - CE 511 - Combined Axial and Bending Stresses - Handout PDFDocument16 pages5 - CE 511 - Combined Axial and Bending Stresses - Handout PDFJayson RamosNo ratings yet
- 4 Bouyancy 01Document18 pages4 Bouyancy 01Soledad AceitunoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1saedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document5 pagesTutorial 2WHfamilyNo ratings yet
- NCESQ 2018 QuestionsDocument3 pagesNCESQ 2018 QuestionsKhent Alfred B. DerechoNo ratings yet
- RCD Lesson 1b Flexural Analysis of Beams (Cracking Moment) PDFDocument14 pagesRCD Lesson 1b Flexural Analysis of Beams (Cracking Moment) PDFEduard Joseph Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PRELIM EXAM: Directions, Problems 1-4Document1 pagePRELIM EXAM: Directions, Problems 1-4Lian HebronNo ratings yet
- CE 353 Geotechnical Engineering: in Situ StressesDocument12 pagesCE 353 Geotechnical Engineering: in Situ StressesKenaouia BahaaNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Sample ProblemsDocument1 pageSoil Mechanics Sample ProblemsMarvin Bryant Medina33% (3)
- TRUSSESDocument17 pagesTRUSSESMohamedDarwishNo ratings yet
- GVF Model Question Solved PDFDocument34 pagesGVF Model Question Solved PDFJeewan75% (4)
- Chapter 2, Problem 1P BRAJADocument4 pagesChapter 2, Problem 1P BRAJAHenry León SuárezNo ratings yet
- 4 Desarrollo de Brahan DasDocument3 pages4 Desarrollo de Brahan Dascristhian zamoraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Foundation Engineering: (7th Edition)Document3 pagesPrinciples of Foundation Engineering: (7th Edition)cristhian zamoraNo ratings yet
- Word document formatting tipsDocument25 pagesWord document formatting tipsgaithiacNo ratings yet
- Ubicacion y Localizacion 1-A-0-2Document1 pageUbicacion y Localizacion 1-A-0-2Henry León SuárezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, Problem 6P BRAJADocument7 pagesChapter 2, Problem 6P BRAJAHenry León SuárezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, Problem 2P BRAJADocument3 pagesChapter 2, Problem 2P BRAJAHenry León SuárezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, Problem 5P BRAJADocument3 pagesChapter 2, Problem 5P BRAJAHenry León SuárezNo ratings yet
- Verbos Irregulares - Por GruposDocument1 pageVerbos Irregulares - Por GruposHenry León SuárezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, Problem 1P BRAJADocument4 pagesChapter 2, Problem 1P BRAJAHenry León SuárezNo ratings yet
- 1969 and Man Reached The MoonDocument1 page1969 and Man Reached The MoonHenry León SuárezNo ratings yet
- EF3e Preint Filetest 01 Answerkey PDFDocument4 pagesEF3e Preint Filetest 01 Answerkey PDFDiego Real Torres NinaNo ratings yet
- SalmonellaDocument2 pagesSalmonellaAlfarizi Julistyo S.No ratings yet
- PDF Microsite Achieve Global AG Survey of Sales EffectivenessDocument44 pagesPDF Microsite Achieve Global AG Survey of Sales Effectivenessingrid_walrabensteinNo ratings yet
- Angels in The NurseryDocument17 pagesAngels in The NurseryRoxana DincaNo ratings yet
- The Lair of Arachas - A Mausritter AdventureDocument8 pagesThe Lair of Arachas - A Mausritter AdventureGladstone PinheiroNo ratings yet
- FCE - Exam: B2 First For SchoolsDocument26 pagesFCE - Exam: B2 First For SchoolsNele Loubele PrivateNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Work Discipline and Leadership On Organizational Commitments With Work Satisfaction As Intervening Variables (Case Study at Asam Jujuhan Sub-District Office Dharmasraya Regency)Document11 pagesThe Effect of Work Discipline and Leadership On Organizational Commitments With Work Satisfaction As Intervening Variables (Case Study at Asam Jujuhan Sub-District Office Dharmasraya Regency)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Highway Construction Production Rates and Estimated Contracct TimesDocument95 pagesHighway Construction Production Rates and Estimated Contracct TimesLTE002No ratings yet
- 10 Study Hacks For Better Grades - EGBDocument41 pages10 Study Hacks For Better Grades - EGBNarimeneKahloulaNo ratings yet
- FMFM 1-ADocument35 pagesFMFM 1-AcvbnNo ratings yet
- English Revision Notes XIIDocument41 pagesEnglish Revision Notes XIIRämíz MêmóñNo ratings yet
- Labman PDFDocument76 pagesLabman PDFJames OnsachiNo ratings yet
- PBA Physics SSC-I FinalDocument7 pagesPBA Physics SSC-I Finalrayyanhashmi93No ratings yet
- Complete Oh Atlas PDFDocument63 pagesComplete Oh Atlas PDFCarmen GaborNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - Revisiting The ClassicsDocument22 pagesMODULE 3 - Revisiting The ClassicsSneha MichaelNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Framework and ProcessDocument16 pagesRisk Management Framework and ProcessIuliana T.No ratings yet
- Response To 'Enforced Sunday Law Will Soon Become The Mark of The Beast'Document22 pagesResponse To 'Enforced Sunday Law Will Soon Become The Mark of The Beast'jennywren3177No ratings yet
- Challenges in Sensory Integration and Processing in The Child WithDocument6 pagesChallenges in Sensory Integration and Processing in The Child WithDanyela SchlosserNo ratings yet
- Pityriasis Versicolor: Avoiding Pitfalls in Disease Diagnosis and TherapyDocument3 pagesPityriasis Versicolor: Avoiding Pitfalls in Disease Diagnosis and TherapypanduNo ratings yet
- Bioentrepreneurship 2018 OBTL Course Plan (Rev)Document17 pagesBioentrepreneurship 2018 OBTL Course Plan (Rev)Ellah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Measure Dark Triad Personality TraitsDocument5 pagesMeasure Dark Triad Personality TraitsLidia BorleanNo ratings yet
- 2006 Arawak Languages Encyclopedia of Language and LinguisticsDocument4 pages2006 Arawak Languages Encyclopedia of Language and LinguisticsSheldon JungleNo ratings yet
- Workbook Answer Key SEODocument2 pagesWorkbook Answer Key SEOlabNo ratings yet
- SPELLFIRE - Sets Oficiais - XLSX Versão 1Document88 pagesSPELLFIRE - Sets Oficiais - XLSX Versão 1Valdir BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Kudippaka" - in Kannur Politics An Investigation?Document8 pagesKudippaka" - in Kannur Politics An Investigation?Anonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Oracle 1z0-986 Exam: Implementation EssentialsDocument23 pagesOracle 1z0-986 Exam: Implementation Essentialslakshmanan84No ratings yet
- Overexploitation of Parrots in The NeotropicsDocument6 pagesOverexploitation of Parrots in The NeotropicsElenananaNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument10 pagesJurnalIca PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- C.R.a.P.the Four Principles of Sound DesignDocument2 pagesC.R.a.P.the Four Principles of Sound DesignkamilNo ratings yet
- Anthony Andreas Vass, Barbara Harrison Social Work Competences Core Knowledge, Values and SkillsDocument248 pagesAnthony Andreas Vass, Barbara Harrison Social Work Competences Core Knowledge, Values and SkillsAhmad Syifa100% (2)
- Competition Commission of India Economics Study Material Amp NotesDocument3 pagesCompetition Commission of India Economics Study Material Amp NotesRaghav DhillonNo ratings yet