Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Degree of Freedom: No. of Independent Coordinates Needed To Define Position of Body
Degree of Freedom: No. of Independent Coordinates Needed To Define Position of Body
Uploaded by
AhmedAhmed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views17 pagesOriginal Title
Lecture 2.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views17 pagesDegree of Freedom: No. of Independent Coordinates Needed To Define Position of Body
Degree of Freedom: No. of Independent Coordinates Needed To Define Position of Body
Uploaded by
AhmedAhmedCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
Degree of Freedom
No. of independent coordinates needed to define position of body
How many DOF does a body in three-space (3-D) have?
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
Definitions
All of the above contain linkages which consist of:
• Links
• Joints
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
Links
A link is a nominally rigid body that
possess at least 2 nodes.
A node is an attachment point to other
links via joints.
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
Links
- The order of a link indicates the number of
joints to which the link is connected (or the
number of nodes per link).
There are binary (2 nodes), ternary (3 nodes),
and quaternary (4 nodes) links.
- Can be any shape (not just those shown)
-Link order = number of nodes
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
Links
- Are assumed to be rigid bodies
- Have nodes for attachment
- Can be any shape (not just those shown)
-Link order = number of nodes
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
JOINTS
Joints A joint is a connection between
two or more links at their nodes,
allow which allows
DOF motion to occur between the
between links.
A pivot is a joint that allows
links rotary motion,
A slider is a joint that allows
linear motion.
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
JOINTS
Joints
allow
DOF
between
links
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
2.5: Determining DOF or Mobility
Joints Reduce
System DOF
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
2.5: Determining DOF or Mobility
Joints Reduce
System DOF
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
Kinematics Diagrams
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
Determining Mobility or DOF
Gruebler & Kutzbach Equations
Gruebler’s
Equation is the
most commonly
used equation
for evaluating
simple
linkages.
Kutzbach’s equation
is modified
Gruebler’s Equation
that takes into
consideration full (1
DOF) and half (2
DOF) joints.
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
Determining Mobility or DOF
Grubler & Kutzbach Equations
Lower pairs (first order joints) or full-joints (counts as J = 1 in
Gruebler’s Equation) have one degree of freedom (only one motion can
occur):
–- Revolute (R): Also called a pin joint or a pivot, take care to ensure that the
axle member is firmly anchored in one link, and bearing clearance is present
in the other link , washers make great thrust bearings, snap rings keep it all
together
• A rolling contact joint also counts as a one-degree-of-freedom revolute
joint
- Prismatic (P): Also called a slider or sliding joint, beware Saint-Venant!
- Helical (H): Also called a screw, beware of thread strength, friction and
efficiency
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
Determining Mobility or DOF
Gruebler & Kutzbach Equations
Joints: Multiple Degree-of-Freedom
• Lower Pair joints with multiple degrees of freedom:
– Cylindrical (C) 2 DOF
• A multiple-joint (J = 2)
– Spherical (S) 3 DOF
A multiple-joint not used in planar mechanisms (J = 3)
– Planar (F) 3 DOF
• A multiple-joint (J = 3)
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
Determining Mobility or DOF
Gruebler & Kutzbach Equations
Joints: Higher Pair Multiple Degree-of-Freedom
• Higher Pair joints with multiple degrees of freedom:
– Link against a plane and a force is required to keep the joint closed
(force closed)
– A half-joint (J 2 = 1 in Kutzbach’s equation)
• The link may also be pressed against a rotating cam to create
oscillating motion
– Pin-in-slot
• Geometry keeps the joint closed (form closed) (Slide and pin)
– A multiple-joint (J = 2 in Gruebler’s equation)
– Second order pin joint, 3 links joined, 2-DOF
• A multiple-joint (J = 2 in Gruebler’s equation)
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
Kinematics Diagrams
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
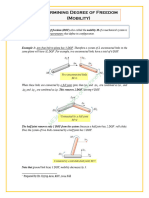
Applying Mobility Equations - 1
M = 3 (L-1) –2(J1) – J2 = 3(8-1) –2(10) – 0 = 1
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
Applying Mobility Equations - 2
M = 3 (L-1) –2(J1) – J2 = 3(6-1) –2(7) – 1 = 0
Union College MER 312: Dynamics and Kinematics
Mechanical Engineering (of Mechanisms) / AT
You might also like
- An Integrated Inverter Output Passive Sinewave Filter For Eliminating Both Common and Differential Mode PWM Motor Drive ProblemsDocument7 pagesAn Integrated Inverter Output Passive Sinewave Filter For Eliminating Both Common and Differential Mode PWM Motor Drive ProblemsdavialacerdaNo ratings yet
- Theory of MachinesDocument83 pagesTheory of MachinesVijay AnandNo ratings yet
- HYDRO POWER and Mini Hydro SystemsDocument36 pagesHYDRO POWER and Mini Hydro SystemsIndran KunusilinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Degrees of FreedomDocument105 pagesLecture 2 Degrees of FreedombourneNo ratings yet
- 24 2017 Unit1-Lecture1-7 MEC219 PDFDocument97 pages24 2017 Unit1-Lecture1-7 MEC219 PDFCorey TaylorNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument65 pagesKinematics of Machinerykumaravel07No ratings yet
- Transmission Line Parameter CalculationDocument12 pagesTransmission Line Parameter Calculationksg9731100% (4)
- Me 555 Degrees of FreedomDocument2 pagesMe 555 Degrees of FreedomkrishNo ratings yet
- Lect Degrees of FreedomDocument111 pagesLect Degrees of FreedomZeeshan Rafiq100% (1)
- Degrees of FreedomDocument9 pagesDegrees of FreedomReyner LozaNo ratings yet
- Lecture02 PDFDocument26 pagesLecture02 PDFxrx91765No ratings yet
- Cume213 L2Document80 pagesCume213 L2irvinvongiNo ratings yet
- M 1B Degrees of Freedom, InversionDocument32 pagesM 1B Degrees of Freedom, InversionRimti BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Mode-Matching Analysis of Large Aperture Coupling and Its Applications To The Design of Waveguide Directional CouplersDocument7 pagesMode-Matching Analysis of Large Aperture Coupling and Its Applications To The Design of Waveguide Directional CouplersTinhVoNo ratings yet
- MatlabDocument5 pagesMatlabhimanshuNo ratings yet
- FEM - 1 Introduction PDFDocument23 pagesFEM - 1 Introduction PDFwiyorejesend22u.infoNo ratings yet
- Fem Short AnswersDocument8 pagesFem Short Answers21k95a0324No ratings yet
- Lect 2Document47 pagesLect 2anon_672293409No ratings yet
- Trask Tem TutorialDocument5 pagesTrask Tem TutorialbangntsuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document13 pagesLecture 3Abdullah Mohammed AlsaadouniNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Inversion & Grashof's RiterionDocument10 pagesMechanism Inversion & Grashof's RiterionAHMED ghribiNo ratings yet
- Joints DOF Kinematic Pairs Mechanism Mobility: TodayDocument26 pagesJoints DOF Kinematic Pairs Mechanism Mobility: TodayMaya VargheseNo ratings yet
- 4 Mobility 1Document10 pages4 Mobility 1praiselovesscienceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document28 pagesChapter 1uccs1No ratings yet
- Three Moment EquationDocument13 pagesThree Moment EquationHan WuNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lec Theory of Machines2 - ShahDocument29 pages2nd Lec Theory of Machines2 - ShahHaroonNo ratings yet
- Heat Dynemic Gear Transmıssıon SystemDocument18 pagesHeat Dynemic Gear Transmıssıon SystemkarayagizmuhammedNo ratings yet
- 4 BarsDocument49 pages4 BarsTalha Naeem RaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 MechanismDocument44 pagesLecture 9 Mechanismaku_la100% (8)
- Bending and Axial Compression With RestraintsDocument8 pagesBending and Axial Compression With RestraintsszalaijaNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Modeling With Bond Graphs by Kevin Craig PDFDocument125 pagesMechatronics Modeling With Bond Graphs by Kevin Craig PDFAhmed H El ShaerNo ratings yet
- Kinematics and DynamicsDocument48 pagesKinematics and Dynamicsakhilesh120No ratings yet
- Ee3104 Lecture1 PDFDocument38 pagesEe3104 Lecture1 PDFAbdul Hafiz AnuarNo ratings yet
- MunjaDocument6 pagesMunjaBat MojNo ratings yet
- Lect.1. Mechanisms and DOFDocument21 pagesLect.1. Mechanisms and DOFammarfetbeNo ratings yet
- Traceable Loop Antenna Calibration Methods Using A VNADocument25 pagesTraceable Loop Antenna Calibration Methods Using A VNAAton LuanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Question BankDocument11 pagesCircuit Theory Question BankJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Structure of MechanismsDocument35 pagesChapter 1 Structure of MechanismsHuỳnh BảoNo ratings yet
- Yoo1994 HybridDocument18 pagesYoo1994 HybridBrendon MenezesNo ratings yet
- Subject: Theory of Machines and Mechanisms (ME-403)Document79 pagesSubject: Theory of Machines and Mechanisms (ME-403)amitNo ratings yet
- Mechanism: Mechanism - Part of A Machine, Which Transmit Motion and Power From Input Point To Output PointDocument68 pagesMechanism: Mechanism - Part of A Machine, Which Transmit Motion and Power From Input Point To Output PointelangandhiNo ratings yet
- CH 2: Fundamentals of Kinematics: - Topic OutlineDocument36 pagesCH 2: Fundamentals of Kinematics: - Topic OutlineJohn FiveNo ratings yet
- Jeroen J. de Jonge, Mark A. Ratner and Simon W. de Leeuw - Local Field Controlled Switching in A One-Dimensional Dipolar ArrayDocument8 pagesJeroen J. de Jonge, Mark A. Ratner and Simon W. de Leeuw - Local Field Controlled Switching in A One-Dimensional Dipolar ArrayHumdsNo ratings yet
- Machine DesigningDocument147 pagesMachine DesigningSiddharth VatsNo ratings yet
- Progress in Studies of Transients Analysis Method of Multiconductor Transmission LinesDocument5 pagesProgress in Studies of Transients Analysis Method of Multiconductor Transmission LinesKushtrim MalaNo ratings yet
- W - 1 - Mce 3513 - Lo1Document19 pagesW - 1 - Mce 3513 - Lo1Ajay SambojuNo ratings yet
- Transmission Characteristics of SMS Fiber Optic Sensor Structures 2003 Optics CommunicationsDocument5 pagesTransmission Characteristics of SMS Fiber Optic Sensor Structures 2003 Optics CommunicationsRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Kinamatic FundamentalsDocument49 pagesKinamatic FundamentalsFaisal IrfanNo ratings yet
- 2009 ICNDENuclear Dupond SCCCiva-Athena ENDocument8 pages2009 ICNDENuclear Dupond SCCCiva-Athena ENHyujeii MceNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Simple Link Compound LinkDocument9 pagesChapter One: Simple Link Compound Linkusman yimerNo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of Control SystemDocument36 pagesBasic Elements of Control Systemeugeni madaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Theory of Machines, Mechanics of Machines, Mechanics of MaterialsDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Theory of Machines, Mechanics of Machines, Mechanics of MaterialsArif ZainNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Introduction - Part CDocument13 pagesLecture 3 - Introduction - Part CMuhammad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Degree of FreedomDocument26 pagesDegree of Freedomumair rasheedNo ratings yet
- Extended Composite Right/Left-Handed (E-CRLH) Metamaterial and Its Application As Quadband Quarter-Wavelength Transmission LineDocument4 pagesExtended Composite Right/Left-Handed (E-CRLH) Metamaterial and Its Application As Quadband Quarter-Wavelength Transmission LineNgoc Lan NguyenNo ratings yet
- "Beamanal" - Single-Span and Continuous-Span Beam AnalysisDocument4 pages"Beamanal" - Single-Span and Continuous-Span Beam AnalysisRonald Rusbell Madera ArnaoNo ratings yet
- 3x3 Multimode Interference Optical Switches Using Electro-Optic Effects As Phase ShiftersDocument6 pages3x3 Multimode Interference Optical Switches Using Electro-Optic Effects As Phase ShiftersTran Tuan AnhNo ratings yet
- INCOSE Certification of Systems Engineers: Certification Program Briefing For ChaptersDocument35 pagesINCOSE Certification of Systems Engineers: Certification Program Briefing For ChaptersIndran KunusilinNo ratings yet
- UNIMAP INFO BI Jan Dec 2017 PDFDocument109 pagesUNIMAP INFO BI Jan Dec 2017 PDFIndran KunusilinNo ratings yet
- Commissioning of Mechanical Systems For Command, Control, Communications, Computer, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (C4Isr) FacilitiesDocument102 pagesCommissioning of Mechanical Systems For Command, Control, Communications, Computer, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (C4Isr) FacilitiesIndran KunusilinNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Bearing Loading Conditions in Rotating EquipmentDocument1 pageEvaluation of Bearing Loading Conditions in Rotating EquipmentIndran KunusilinNo ratings yet
- Sample Test 1 For RevisionDocument4 pagesSample Test 1 For RevisionIndran KunusilinNo ratings yet
- MDP PosterDocument1 pageMDP PosterIndran KunusilinNo ratings yet
- Managing and Performing: Chapter OneDocument40 pagesManaging and Performing: Chapter OneIndran KunusilinNo ratings yet
- Memb453 NDT LP IntroDocument13 pagesMemb453 NDT LP IntroIndran KunusilinNo ratings yet
- Network Name (SSID) :: dlink-CBE8Document1 pageNetwork Name (SSID) :: dlink-CBE8Indran KunusilinNo ratings yet