Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CE Questions
CE Questions
Uploaded by
Sukanti Pal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
CE questions.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageCE Questions
CE Questions
Uploaded by
Sukanti PalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
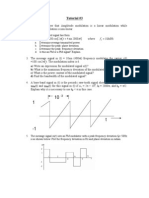
1.
a. What is line coding?
b. What are the disadvantages of PCM?
c. How many types of Pulse digital scheme are there?
d. What is the effect of inter symbol interference?
e. What is companding?
f. what are the advantages of VSB?
2. A FM modulator is used to transmit a tone message with amplitude of 4 volts and frequency of
20 Hz. The frequency deviation constant for the modulator is 25Hz/V, and the carrier wave
has amplitude 10 Volts and frequency 2000 Hz.
a. What is the power of FM modulated Signal?
b. What is the approximate band width of the FM modulated signal using Carson’s rule?
c. The output of the FM modulator is passed through a bandpass filter centered at 2000 Hz.
What should be the bandwidth of the filter such that 90% of the power in the modulated
signal passes through.
d. How would your answer to part b) change if the amplitude of the message is doubled?
e. How would your answer to part b) change if the frequency of the carrier is doubled?
3. Consider an FM wave f (t)=cos[2 π f c t + β 1 sin 2 π f 1 t + β 2 2 π f 2 t ] .What is the maximum
deviation of the instantaneous frequency from the carrier frequency f c.
4. The signal m(t) as shown I applied both to a phase modulator (with k p as the phase constant)
and a frequency modulator with (k f as the frequency constant) having the same carrier
kp
frequency .What is the ratio (in rad /Hz) for the same maximum phase deviation.
kf
5. Explain the PLL- FM demodulator.
6. Describe the spectral representation of PWM and PPM.
7. Explain PCM generator with neat diagram.
8. Explain Delta modulation.
You might also like
- Chapter 2 - Part 1-Amplitude Modulation - v2Document50 pagesChapter 2 - Part 1-Amplitude Modulation - v2Vijay Papi Reddy AllamNo ratings yet
- Frequency ModulationDocument46 pagesFrequency Modulationkrejish100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - Frequency Modulation (FM)Document25 pagesChapter 4 - Frequency Modulation (FM)David100% (1)
- Analog and Digital Communication Important Questions AnswersDocument21 pagesAnalog and Digital Communication Important Questions AnswersMehboob Khokhar75% (4)
- FM ReviewerDocument85 pagesFM ReviewerCris Vincent Rivera Sedanto100% (1)
- Angle Modulation All 0Document64 pagesAngle Modulation All 0Yanyan100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Frequency ModulationDocument46 pagesChapter 4 Frequency ModulationMompati Letsweletse100% (1)
- Tut 3Document3 pagesTut 3rohankataria26100% (1)
- FM LectureDocument33 pagesFM Lectureemg sivanNo ratings yet
- ELE 3203 - LO2 - Part2Document39 pagesELE 3203 - LO2 - Part2ashwaq alkhoori100% (1)
- FM DelieveredDocument46 pagesFM DelieveredFaizan Ashraf100% (1)
- c (t) =100 cos2 π f t .The modulation index is 6Document9 pagesc (t) =100 cos2 π f t .The modulation index is 6Nafeesa SalehNo ratings yet
- Assignment Communication Engineering: Lavish Bagga 18105128Document17 pagesAssignment Communication Engineering: Lavish Bagga 18105128Anonymous Xw1jpCpV5gNo ratings yet
- Ee 341 HWDocument2 pagesEe 341 HWOrhunNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For First Assessment. EC396 - Communication Engineering Short AnswersDocument2 pagesImportant Questions For First Assessment. EC396 - Communication Engineering Short Answersapi-78343547No ratings yet
- Class 4 FMDocument19 pagesClass 4 FMMr RobotNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document4 pagesTutorial 2Muhammad Anaz'sNo ratings yet
- Chuong 2 - 3 - Full - ENDocument2 pagesChuong 2 - 3 - Full - ENKỳ TrầnNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Amplitude Modulation and Angle ModulationDocument3 pagesAssignment of Amplitude Modulation and Angle ModulationRhelf Mae ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Analog Communications Question BankDocument10 pagesAnalog Communications Question BankSsgn Srinivasarao100% (1)
- ECE 40le1Document3 pagesECE 40le1Loryliza M DeiparineNo ratings yet
- (Ebook) US Army Electronics Course - FM Radio Transmitters MM0323Document175 pages(Ebook) US Army Electronics Course - FM Radio Transmitters MM0323João HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Principles of Communication SystemsDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Communication SystemsNithin P SNo ratings yet
- Adc QB 2020Document14 pagesAdc QB 2020priyaroopaNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation and Demodulation: EELE 3370Document28 pagesAngle Modulation and Demodulation: EELE 3370balkyderNo ratings yet
- L4Document44 pagesL4Doms100% (2)
- Tutorial Chapter 3Document4 pagesTutorial Chapter 3Ahmed Mahmoud SaeedNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (I and II)Document4 pagesQuestion Bank (I and II)Anonymous 4u5XkWGONo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Quiz AcDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Quiz AcKiranKumarNo ratings yet
- ENGG2310A/ESTR2300 (Fall 2018) Problem Set #4Document8 pagesENGG2310A/ESTR2300 (Fall 2018) Problem Set #4Tsz Wing Yip100% (1)
- FMDocument52 pagesFMZafar KhanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2barak paul munuoNo ratings yet
- Question Set - Elementary Communication EnggDocument34 pagesQuestion Set - Elementary Communication EnggKankan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Angle ModulationDocument28 pagesAngle ModulationChinmoy Ghorai100% (1)
- Comm QBDocument9 pagesComm QBMehar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationsDocument6 pagesAnalog CommunicationsSri KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Comm Lab Exp3Document2 pagesComm Lab Exp3Ahmed MashhoorNo ratings yet
- Modulation-Part 2-FMDocument67 pagesModulation-Part 2-FMAzmilWahabNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2-CE I-20 BatchDocument3 pagesAssignment 2-CE I-20 BatchKHISHORE KUMARNo ratings yet
- Dayalbagh Educational Institute, Dayalbagh, Agra Faculty of EngineertingDocument8 pagesDayalbagh Educational Institute, Dayalbagh, Agra Faculty of EngineertingTanmayKabraNo ratings yet
- Assign1 & 2 - Comm - SysDocument2 pagesAssign1 & 2 - Comm - SysBrijesh NagarNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation Unit 6Document7 pagesAngle Modulation Unit 6Cicero LuNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Test 2Document3 pagesQuestion Bank For Test 2api-194677273No ratings yet
- PCOMDocument8 pagesPCOMShreejith NairNo ratings yet
- FmodulationDocument24 pagesFmodulationNaheda ShkNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions and Answers On Amplitude ModulationDocument22 pagesMultiple Choice Questions and Answers On Amplitude ModulationDurga Bhavani AlankaNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Communication Question BankDocument4 pagesAnalog and Digital Communication Question BankPrabhakara Rao100% (1)
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentpaper.2014No ratings yet
- FMDocument76 pagesFMNicole Guzman100% (1)
- Assignment OneDocument1 pageAssignment Onetariku fkaduNo ratings yet
- Prin Com Chapter 3Document13 pagesPrin Com Chapter 3Marclouise CabahugNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication Notes EE351-Course - Presentation - CH4Document244 pagesIntroduction To Communication Notes EE351-Course - Presentation - CH4FAISAL ALOTAIBINo ratings yet
- ANLOG Communication Full Manual...Document54 pagesANLOG Communication Full Manual...ydsraju100% (1)
- B1 - CAT 2 - KeyDocument9 pagesB1 - CAT 2 - KeyVamshidhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation - NDocument34 pagesAngle Modulation - Nchristopher100% (1)
- hw06 Solutions PDFDocument5 pageshw06 Solutions PDFRana FaizanNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document3 pagesHW 3Zero ChengNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Experiment - : Aim of The Experiment: Apparatus RequiredDocument6 pagesExperiment - : Aim of The Experiment: Apparatus RequiredSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- Voltage Divider BiasDocument2 pagesVoltage Divider BiasSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- Fir Filter DesignDocument6 pagesFir Filter DesignSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- Logic GatesDocument7 pagesLogic GatesSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- Memory BankingDocument12 pagesMemory BankingSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- 8086 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument10 pages8086 Microprocessor ArchitectureSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Practice QuestionDocument21 pagesUnit Iii Practice QuestionSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- Q. 8086 Programmer's Model: Register Organization (IMP)Document6 pagesQ. 8086 Programmer's Model: Register Organization (IMP)Sukanti PalNo ratings yet
- What Is A MicroprocessorDocument10 pagesWhat Is A MicroprocessorSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- Gray-Level Image Enhancement by Particle Swarm OptimizationDocument6 pagesGray-Level Image Enhancement by Particle Swarm OptimizationSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- Practise Question From Module-1Document13 pagesPractise Question From Module-1Sukanti PalNo ratings yet
- NIST Online Class: Pel7J003 Digital Image Processing Lecture-02Document3 pagesNIST Online Class: Pel7J003 Digital Image Processing Lecture-02Sukanti PalNo ratings yet
- Radix-2 Dit FFT Algo FunctionDocument2 pagesRadix-2 Dit FFT Algo FunctionSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- NIST Online Class: Pel7J003 Digital Image Processing Lecture-02Document11 pagesNIST Online Class: Pel7J003 Digital Image Processing Lecture-02Sukanti PalNo ratings yet
- BEC007-Digital Image ProcessingDocument122 pagesBEC007-Digital Image ProcessingSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- NIST Online Class: Pel7J003 Digital Image Processing Lecture-01Document43 pagesNIST Online Class: Pel7J003 Digital Image Processing Lecture-01Sukanti PalNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Analysis - UWB - IETDocument9 pagesTime Domain Analysis - UWB - IETSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- NIST Online Class: Sample Copy of Class Material by DR - Pradyumna Ku PatraDocument11 pagesNIST Online Class: Sample Copy of Class Material by DR - Pradyumna Ku PatraSukanti PalNo ratings yet
- DIP Lecture 9Document34 pagesDIP Lecture 9Sukanti PalNo ratings yet