Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basics Concepts and Formulas - Simplification PDF
Uploaded by
Payashwini KulkarniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics Concepts and Formulas - Simplification PDF
Uploaded by
Payashwini KulkarniCopyright:
Available Formats
8/19/13 Basics Concepts and Formulas - Simplification
Like 266 Send 0 Share
Java J2EE Sample Quantitative Online Tests Speed RDBMS Crash Miscellaneous
Programs Aptitude Mathematics Course
You are here : Home > Quantitative aptitude questions and answers with explanation > Simplification > Basics Concepts and
Formulas Simplification
Basics Concepts and Formulas Basics Concepts and Formulas Simplification
Simplification
Solved Examples Set 1
1. Order of Operations BODMAS Rule
Solved Examples Set 2
What is BODMAS Rule?
BODMAS rule defines the correct sequence in which operations are to be performed in a given
mathematical expression to find its value.
In BODMAS,
B = Bracket,
O = Order (Powers, Square Roots, etc.)
DM = Division and Multiplication (lefttoright)
AS = Addition and Subtraction (lefttoright)
This means, to simplify an expression, the following order must be followed.
i. Do operations in Brackets first, strictly in the order (), {} and []
ii. Evaluate exponents (Powers, Roots, etc.)
iii. Perform division and multiplication, working from left to right. (division and multiplication
rank equally and done left to right).
iv. Perform addition and subtraction, working from left to right. (addition and subtraction rank
equally and done left to right).
In India, the term BODMAS is used whereas in USA the acronym PEMDAS is used. The full form
of PEMDAS is "Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, and Subtraction". Both
are correct and only difference is that these are used in different parts of the world. Some other
Loading variations which are used across the world to represent the same concept are BIDMAS, ERDMAS,
Math PERDMAS and BPODMAS.
Symbols
Examples
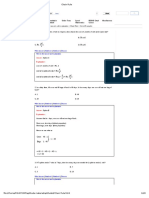
a. 12 + 22 ÷ 11 × (18 ÷ 3)2 10
= 12 + 22 ÷ 11 × 62 10 (∵ Brackets first)
= 12 + 22 ÷ 11 × 36 10 (∵ exponents)
= 12 + 2 × 36 10 = 12 + 72 10 (∵ division and multiplication, left to right)
= 84 10 = 74 (∵ Addition and Subtraction, left to right)
b. 4 + 10 3 × 6 / 3 + 4
= 4 + 10 18/3 + 4 = 4 + 10 6 + 4 (∵ division and multiplication, left to right)
= 14 6 + 4 = 8 + 4 = 12 (∵ Addition and Subtraction, left to right)
2. Modulus of a Real Number
For any real number , the absolute value or modulus of is denoted by and is defined as
Hence, the Modulus(absolute value) of is always either positive or zero, but never negative
Example
|8| = |8| = 8
/home/RGUKT/IMP/…/Basics Concepts and Formulas - Simplification.html 1/2
8/19/13 Basics Concepts and Formulas - Simplification
Comments(0)
Add a new comment ...
Sign in (optional)
Name Email
Please answer the simple math question given below
1 + 4 =
Submit
Home | careerbless@gmail.com | Copyright | Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
Copyright © 20122013 www.careerbless.com. All rights reserved.
/home/RGUKT/IMP/…/Basics Concepts and Formulas - Simplification.html 2/2
You might also like
- The Order of Operations: Week 2 Form 1 Math Day 1 TextDocument5 pagesThe Order of Operations: Week 2 Form 1 Math Day 1 TextSemone ChunilalNo ratings yet
- Parenthesis Exponent Multiplication Division Addition SubtractionDocument11 pagesParenthesis Exponent Multiplication Division Addition SubtractionQuerubin MacadangdangNo ratings yet
- Junior6 Oct8Document12 pagesJunior6 Oct8Mavis Jacquiline ManuNo ratings yet
- BODMASDocument12 pagesBODMASNisarv Urd RehhmanNo ratings yet
- What Is BIDMAS?: Bodmas Stands For Brackets, Orders, Division/Multiplication, Addition/SubtractionDocument3 pagesWhat Is BIDMAS?: Bodmas Stands For Brackets, Orders, Division/Multiplication, Addition/SubtractionrajisumaNo ratings yet
- Use BEDMAS To Remember The Order of OperationsDocument3 pagesUse BEDMAS To Remember The Order of OperationsArlene Magalang NatividadNo ratings yet
- BODMAS RuleAs Per The BODMAS Rule, We Have To Calculate The Expressions GivDocument22 pagesBODMAS RuleAs Per The BODMAS Rule, We Have To Calculate The Expressions GivHania PindatonNo ratings yet
- M1 Mathematics Cat B1 & B2 V4.3Document136 pagesM1 Mathematics Cat B1 & B2 V4.3Abhijith KaushikNo ratings yet
- 07 Mathematical OperationsDocument12 pages07 Mathematical OperationsAashishsainiNo ratings yet
- Professor Weissman's Algebra Classroom 07 Multiply Divide IntegersDocument10 pagesProfessor Weissman's Algebra Classroom 07 Multiply Divide IntegersTheMathProf100% (2)
- Lesson 2 Operations PEMDASDocument9 pagesLesson 2 Operations PEMDASAlryel Kenn AngeloNo ratings yet
- Modular Arithmetic (W - 17 Step-by-Step Examples!)Document13 pagesModular Arithmetic (W - 17 Step-by-Step Examples!)Gyebi EmmaNo ratings yet
- BODMAS ProblemsDocument4 pagesBODMAS ProblemsCharlieNo ratings yet
- SAT Math NotesDocument51 pagesSAT Math Noteschloe.2021164No ratings yet
- Sarina'sDocument6 pagesSarina'sAMARA SOPHIANo ratings yet
- What Is PEMDAS - Redoslijed RačunanjaDocument2 pagesWhat Is PEMDAS - Redoslijed RačunanjaBojan KlapčićNo ratings yet
- GMAT 6 Ed Og 2016 Fom Drill Booklet 1Document13 pagesGMAT 6 Ed Og 2016 Fom Drill Booklet 1Saumya GuptaNo ratings yet
- General Mental Ability Arithmetical ReasoningDocument7 pagesGeneral Mental Ability Arithmetical ReasoningIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - The Mathematical SystemDocument28 pagesCHAPTER 8 - The Mathematical SystemSeymour ArcegaNo ratings yet
- AtoolsofalgebraDocument10 pagesAtoolsofalgebraNavneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan of Order of OperationDocument5 pagesLesson Plan of Order of Operationabid50% (2)
- Lecture 3 Mathematics of Language and SymbolsDocument23 pagesLecture 3 Mathematics of Language and SymbolsJelaineNo ratings yet
- Draft OneDocument9 pagesDraft OnePeter MorrisNo ratings yet
- GRE Math ReviewDocument61 pagesGRE Math ReviewJosé María EgúsquizaNo ratings yet
- Factorising Into Two BracketsDocument1 pageFactorising Into Two BracketsAnotida VengereNo ratings yet
- Rules of MathDocument2 pagesRules of MathSheilaNo ratings yet
- Accentuate The Negative UNIT TEST-Study Guide: Name: - PeriodDocument3 pagesAccentuate The Negative UNIT TEST-Study Guide: Name: - PeriodjackNo ratings yet
- Data Types, Identifiers, and ExpressionsDocument24 pagesData Types, Identifiers, and ExpressionsHani HamadNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Earth ScienceDocument45 pagesMathematics For Earth ScienceAlam SyahNo ratings yet
- Maths For Healthcare Professionals: Fractions Decimals Ratio Percentages BMI Averages Unit ConversionDocument51 pagesMaths For Healthcare Professionals: Fractions Decimals Ratio Percentages BMI Averages Unit ConversionUrwa ImanNo ratings yet
- Simplification Approximation PDFDocument176 pagesSimplification Approximation PDFsaketNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1Document39 pagesAlgebra 1Sya SuhailaNo ratings yet
- Matmod 2nd Math Lang.Document10 pagesMatmod 2nd Math Lang.Renalyn PinedaNo ratings yet
- Secdocument - 288download Mathematics Fundamentals DR Des Hill Full ChapterDocument67 pagesSecdocument - 288download Mathematics Fundamentals DR Des Hill Full Chapterdavid.cockrill130100% (2)
- Mathematics in The Modern World: Instructor: Michael Angelo A. LumauigDocument25 pagesMathematics in The Modern World: Instructor: Michael Angelo A. LumauigMichael Angelo LumauigNo ratings yet
- AppraisalDocument146 pagesAppraisalKayra Theress GubatNo ratings yet
- Excel Formula FunctionDocument80 pagesExcel Formula FunctionPaing Soe ChitNo ratings yet
- Common Denominator Common DenominatorDocument3 pagesCommon Denominator Common DenominatorCadet RaparivoNo ratings yet
- MAPC5112 WorkbookDocument139 pagesMAPC5112 WorkbookSiba NqabaNo ratings yet
- BodmasDocument18 pagesBodmasYati GargNo ratings yet
- Programing in Visual Basic 2010 65Document1 pagePrograming in Visual Basic 2010 65mudassir2640No ratings yet
- Order of OperationsDocument33 pagesOrder of OperationsVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Mathematics VDocument2 pagesMathematics VKeithNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument22 pagesReportMyla BalilahonNo ratings yet
- Module 1.4: Properties of Addition: EXPLORE Your UnderstandingDocument5 pagesModule 1.4: Properties of Addition: EXPLORE Your UnderstandingRey Mamat LaguraNo ratings yet
- Programming Handout - Problem SolvingDocument5 pagesProgramming Handout - Problem SolvingTahjay KerrNo ratings yet
- Lecture slides-Stats1.13.L11 PDFDocument16 pagesLecture slides-Stats1.13.L11 PDFRicardo NascimentoNo ratings yet
- 4 Let Arithmetic - pdf9Document9 pages4 Let Arithmetic - pdf9novey_casio50% (2)
- MATH 80 Course Package (23) JanDocument172 pagesMATH 80 Course Package (23) JanDhairya ShahNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 Book 1 MathematicsDocument52 pagesMod 1 Book 1 Mathematicsranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- Quant Short Tricks For CAT 2021Document183 pagesQuant Short Tricks For CAT 2021Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Math RerrosDocument9 pagesMath RerrosjojosonioejwoixNo ratings yet
- Order of OperationsDocument9 pagesOrder of OperationsTeacher JAY-AR LAGMANNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Real Number SystemDocument25 pagesLesson 1 Real Number SystemKrystel MamarilNo ratings yet
- PEMDAS and The Order of OperationsDocument3 pagesPEMDAS and The Order of OperationsFederation NORSU AlumniNo ratings yet
- SSCE 1023 Mathematics For Surveyor I: Week 7-8 Chapter 4: AlgebraDocument39 pagesSSCE 1023 Mathematics For Surveyor I: Week 7-8 Chapter 4: AlgebraChang Xin LimNo ratings yet
- Multiply and Divide Polynomials, Distributive Property, and SubstitutionsDocument7 pagesMultiply and Divide Polynomials, Distributive Property, and SubstitutionsmujeebscribdNo ratings yet
- Math Practice Simplified: Subtraction (Book D): Developing Fluency with Basic Number Combinations for SubtractionFrom EverandMath Practice Simplified: Subtraction (Book D): Developing Fluency with Basic Number Combinations for SubtractionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hide Answer Notebook Notebook Discuss: Here Is The Answer and ExplanationDocument16 pagesHide Answer Notebook Notebook Discuss: Here Is The Answer and ExplanationPayashwini KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chain Rule PDFDocument28 pagesChain Rule PDFPayashwini KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Distributing Balls Into Boxes PDFDocument3 pagesDistributing Balls Into Boxes PDFPayashwini KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Clock PDFDocument23 pagesClock PDFPayashwini KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Basics Concepts and Formulas in Permutations and Combinations PDFDocument4 pagesBasics Concepts and Formulas in Permutations and Combinations PDFPayashwini KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Counting Integral Solutions PDFDocument3 pagesCounting Integral Solutions PDFPayashwini KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Combinations Under Restrictions PDFDocument2 pagesCombinations Under Restrictions PDFPayashwini KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Hide Answer Notebook Notebook Discuss: Here Is The Answer and ExplanationDocument14 pagesHide Answer Notebook Notebook Discuss: Here Is The Answer and ExplanationPayashwini KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) : Gate Terminal. The Other Two Contacts, The Drain and Source, Are Placed atDocument8 pagesJunction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) : Gate Terminal. The Other Two Contacts, The Drain and Source, Are Placed atkingboyNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument86 pagesLectureabhijeetramaniNo ratings yet
- Bca NotesDocument4 pagesBca NotesPayashwini KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Matemática Competitiva para o Ensino MédioDocument267 pagesMatemática Competitiva para o Ensino MédiohelioteixeiraNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument9 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogJessmiel LabisNo ratings yet
- C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis To Program Design: Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++Document81 pagesC++ Programming: From Problem Analysis To Program Design: Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++Almira SolimanNo ratings yet
- BCO 101: Business Mathematics Unit 1: Review of ArithmeticDocument8 pagesBCO 101: Business Mathematics Unit 1: Review of ArithmeticAdierson Gilvani EbelingNo ratings yet
- Python NotesDocument142 pagesPython NotesROHIT RAWATNo ratings yet
- InfixDocument23 pagesInfixSumant LuharNo ratings yet
- Python Programming (R19) - UNIT-1Document42 pagesPython Programming (R19) - UNIT-1srinivas pNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocument22 pagesChapter 8-Data Structures and AlgorithmsEdzai Nyasha TarupiwaNo ratings yet
- Variables and Data TypesDocument13 pagesVariables and Data TypesOsha Al MansooriNo ratings yet
- #5 Arithmetic InstructionDocument18 pages#5 Arithmetic InstructionTimothy King LincolnNo ratings yet
- AlgebraHandbook PDFDocument187 pagesAlgebraHandbook PDFshivam deolankarNo ratings yet
- Math 1 Unit 1 Chaoter 1 The Language of AlgebraDocument18 pagesMath 1 Unit 1 Chaoter 1 The Language of AlgebraPahilagao NelsonNo ratings yet
- Working With Integers: Using Mathematics: Real-Life ApplicationsDocument12 pagesWorking With Integers: Using Mathematics: Real-Life ApplicationsMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- April Math RampUpDocument15 pagesApril Math RampUpAbhinav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Pemdas Write Up RubricDocument1 pagePemdas Write Up Rubricapi-366582437No ratings yet
- Simplifying ExpressionsDocument27 pagesSimplifying ExpressionsSuhaila SallehNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 PPT Q2 W3 MathDocument230 pagesGrade 2 PPT Q2 W3 Mathjazmin bang-oaNo ratings yet
- Using Matlab As AlculatorDocument7 pagesUsing Matlab As AlculatorGopi ChandNo ratings yet
- 1 Math HW Q1 (Order of Operations)Document5 pages1 Math HW Q1 (Order of Operations)debNo ratings yet
- C Language Unit 1,2,3,4,5Document247 pagesC Language Unit 1,2,3,4,5Lovely VasanthNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To MATLABDocument11 pages1 - Introduction To MATLABThéu CastroNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Lesson Guide Math Book 1Document37 pagesGrade 6 Lesson Guide Math Book 1Irene LebrillaNo ratings yet
- Applications of StackDocument45 pagesApplications of StacknathanselNo ratings yet
- Python NotesDocument103 pagesPython Noteskasarla rakeshNo ratings yet
- Modul 10X Itb AqDocument179 pagesModul 10X Itb AqEmmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- Python Question With AnswersDocument7 pagesPython Question With Answersaravind ads100% (1)
- CW1 Operations and EquationsDocument16 pagesCW1 Operations and EquationspaulprovenceNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Linear Data Structure-StackDocument40 pagesUnit-2 Linear Data Structure-StackSanskruti DhananiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 6 Implemenation of A Program To Convert A Given Infix Expression To Postfix Form Using StacksDocument3 pagesLab Manual 6 Implemenation of A Program To Convert A Given Infix Expression To Postfix Form Using Stackspareshdeore.skillNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Grade 6 MathDocument14 pagesCurriculum Map Grade 6 MathAnjanette Lopez PorlucasNo ratings yet