Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Manufacturing Processes For Sheetmeatl Parts
Uploaded by
rohan zagadeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Manufacturing Processes For Sheetmeatl Parts
Uploaded by
rohan zagadeCopyright:
Available Formats
Manufacturing Processes
Sheet Metal Cutting & Forming Processes
The raw material for sheet metal manufacturing processes is the output of the rolling process. Typically,
sheets of metal are sold as flat, rectangular sheets of standard size. Therefore the first step in any sheet
metal process is to cut the correct shape and sized ‘blank’ from larger sheet.
Sheet metal processing is an important process for many industries, producing home appliances (fridge,
washer, dryer, vacuum cleaners etc.), electronics (DVD- and CD-players, stereos, radios, amplifiers etc.),
toys and PC’s. Most of these products have metal casings that are made by cutting and bending sheet
metal. We look at some of the basic sheet metal cutting and forming processes.
The operations are performed on relatively thin sheets of metal:
Thickness of sheet metal = 0.4 mm to 6 mm
Thickness of plate stock > 6 mm
Operations usually performed as cold working
Advantages of Sheet Metal Parts
High strength
Good dimensional accuracy
Good surface finish
Relatively low cost
Economical mass production for large quantities
Classification
1. Cutting Operations
2. Bending Operations
3. Drawing
Basic Types of Sheet Metal Processes
1. Cutting
– Shearing to separate large sheets
– Blanking to cut part perimeters out of sheet metal
– Punching to make holes in sheet metal
2. Bending
– Straining sheet around a straight axis
3. Drawing
– Forming of sheet into convex or concave shapes
Three principal operations in pressworking
that cut sheet metal:
Shearing
Blanking
Punching
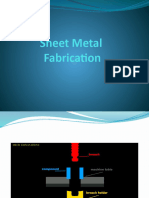
1.1 Shearing Sheet metal cutting operation along a straight line between two cutting edges. Typically
used to cut large sheets
You might also like
- Sheet MetalDocument8 pagesSheet MetalPrabir Kumar Pati100% (1)
- Cutting of Soft Gummy MetalsDocument26 pagesCutting of Soft Gummy MetalsManoj Dhage100% (1)
- U-2 Sheet Metal OperationsDocument72 pagesU-2 Sheet Metal Operationsapi-271354682No ratings yet
- Sheet Metal DesignDocument13 pagesSheet Metal Designsivakumar subramanianNo ratings yet
- IC Learning Series 2013 - Sheet Metal FabricationDocument19 pagesIC Learning Series 2013 - Sheet Metal FabricationnskumarmNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process - PresentationDocument15 pagesManufacturing Process - PresentationAnwesha PandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Manufacturing Processes - Metal and Sheet Forming, Bulk Deformation Processes - DR Bilal Ahmad PDFDocument62 pagesLecture 7 - Manufacturing Processes - Metal and Sheet Forming, Bulk Deformation Processes - DR Bilal Ahmad PDFjawad khalidNo ratings yet
- SID1Document18 pagesSID1Siddharth Srinivasan100% (1)
- Sheet Metalworking: ©2002 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. M. P. Groover, "Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing 2/e"Document34 pagesSheet Metalworking: ©2002 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. M. P. Groover, "Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing 2/e"Himanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- U1e Sheet Metal 1Document23 pagesU1e Sheet Metal 1vatsalya 185No ratings yet
- Plastc ProcessingDocument23 pagesPlastc Processinghodmech scenashikNo ratings yet
- 43-Sheet Metal Punching MachineDocument25 pages43-Sheet Metal Punching MachinesathishNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal WorkingDocument23 pagesSheet Metal WorkingSujit MishraNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal WorkingDocument23 pagesSheet Metal WorkingAlrino Dwi PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- 2 Reading Matl CH - 6 Sheet Metal Parts MFG ProcessDocument62 pages2 Reading Matl CH - 6 Sheet Metal Parts MFG ProcessCaldwellNo ratings yet
- Conformado de Planchas 2Document44 pagesConformado de Planchas 2smartcad60No ratings yet
- Core ThingsDocument11 pagesCore ThingsVigneshNo ratings yet
- Sheet MetalDocument16 pagesSheet MetalYusha Patel100% (1)
- Sheetmetal Design Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesSheetmetal Design Interview Questionsgopoji100% (1)
- Chapter 4 (Sheet Metal Fabrication) With VideoDocument71 pagesChapter 4 (Sheet Metal Fabrication) With VideoSamrat BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1-Introduction To Manufacturing Processes 1Document28 pagesTopic 1-Introduction To Manufacturing Processes 1lihinNo ratings yet
- Sheet MetalDocument75 pagesSheet MetalVenkata ChakradharNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical Engineering: Manufacturing ProcessesDocument49 pagesBasic Mechanical Engineering: Manufacturing Processespritam goleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Metal Forming ProcessesDocument103 pagesChapter 3 Metal Forming Processesdagimawgchew777No ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Design1Document57 pagesSheet Metal Design1Mohamed ZeinNo ratings yet
- Module 5 PDFDocument93 pagesModule 5 PDFVishal Shanmuga SundramNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal OperationDocument17 pagesSheet Metal Operationsekar_scribd60% (5)
- Machining by CuttingDocument4 pagesMachining by CuttingSiddhi JainNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Forming - PpsDocument26 pagesSheet Metal Forming - PpsNhan LeNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 6 Shearing Process in Sheet MetalDocument5 pagesAssignment No 6 Shearing Process in Sheet MetalSameer Ahmed 20 - MCE - 60No ratings yet
- UnitC-Manufacturing Processes 1Document26 pagesUnitC-Manufacturing Processes 1Gino LacandulaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering I Chapter 1Document29 pagesManufacturing Engineering I Chapter 1Abiyot egataNo ratings yet
- Metal CuttingDocument39 pagesMetal Cuttingavinashn12No ratings yet
- Sheet MATALDocument9 pagesSheet MATALSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of Chips in Metal CuttingDocument5 pagesTypes of Chips in Metal CuttingMUKIIBI GERALDNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Forming Process Chapter 7Document155 pagesSheet Metal Forming Process Chapter 7Arun Pravin APNo ratings yet
- MEng-I Chapter 1 06979Document29 pagesMEng-I Chapter 1 06979Abi DemNo ratings yet
- Assignment No - IDocument3 pagesAssignment No - Ivikas.thoratNo ratings yet
- Quiz 7Document40 pagesQuiz 7Vysakh VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Forming ProcessDocument5 pagesSheet Metal Forming ProcessAbdulbar kelilNo ratings yet
- T John Institute of Technology: Mahanthesh S 1TJ15ME025 B.E (Mechanical Engineering)Document21 pagesT John Institute of Technology: Mahanthesh S 1TJ15ME025 B.E (Mechanical Engineering)Chandu SunagNo ratings yet
- Metal Buttons Making ProcessDocument2 pagesMetal Buttons Making ProcessZain Ali Kidwai100% (1)
- UnitC-Manufacturing Processes 1Document26 pagesUnitC-Manufacturing Processes 1Sankalp KumarNo ratings yet
- Quiz 7: 1. Write Down The 5 Important Steps Involved in Powder MetallurgyDocument40 pagesQuiz 7: 1. Write Down The 5 Important Steps Involved in Powder MetallurgyFelipe SaavedraNo ratings yet
- L19 Sheet MetalDocument36 pagesL19 Sheet Metalharrywilson.harish77No ratings yet
- Design Study of Progressive Tool DesignDocument34 pagesDesign Study of Progressive Tool Designsudheer9289% (9)
- Sheet MetalDocument14 pagesSheet Metal019SAURABH GUPTANo ratings yet
- Lecture05-Sheet Metalmorking ProcessDocument54 pagesLecture05-Sheet Metalmorking ProcessberhaneNo ratings yet
- Processing: Hot Forming Heat Treatments MachiningDocument32 pagesProcessing: Hot Forming Heat Treatments MachiningThân KhaNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Lab ReportDocument10 pagesAhmed Lab ReportM. AhmedNo ratings yet
- Casting Forming Sheet Metal Processing Powder-And Ceramics Processing Plastics ProcessingDocument44 pagesCasting Forming Sheet Metal Processing Powder-And Ceramics Processing Plastics ProcessingRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Working of MetalsDocument76 pagesMechanical Working of MetalsPradip GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Design Guidelines - Design For ManufacturingDocument13 pagesSheet Metal Design Guidelines - Design For ManufacturingShashank Maheshwari100% (1)
- Feedstock Technology for Reactive Metal Injection Molding: Process, Design, and ApplicationFrom EverandFeedstock Technology for Reactive Metal Injection Molding: Process, Design, and ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Jewelry Making for Beginners: 32 Projects with MetalsFrom EverandJewelry Making for Beginners: 32 Projects with MetalsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Thixoforming: Semi-solid Metal ProcessingFrom EverandThixoforming: Semi-solid Metal ProcessingGerhard HirtNo ratings yet