Professional Documents
Culture Documents
India Bihar: Chota Nagpur, Plateau in Eastern
Uploaded by
Siddharth AgarwalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
India Bihar: Chota Nagpur, Plateau in Eastern
Uploaded by
Siddharth AgarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
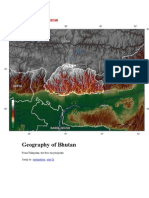
Loc-The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as
adjacent parts of Orissa, West Bengal, Bihar and Chhattisgarh. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the
plateau, and the basin of the Mahanadi River lies to the south. The total area of the Chota Plateau is approximately
65,000 square kilometres (25,000 sq mi).[1]
Form-The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a continental plateau - an extensive area of land thrust above the general land. The
plateau has been formed by continental uplift from forces acting deep inside the earth.[3] The Gondwana substrates
attest to the plateau's ancient origin. It is part of the Deccan Plate, which broke free from the southern continent during
the Cretaceous to embark on a 50-million-year journey that was violently interrupted by the northern Eurasian continent.
The northeastern part of the Deccan Plateau, where this ecoregion sits, was the first area of contact with Eurasia.[4]-The
Clim-Chota Nagpur Plateau has an attractive climate. For five or six months of the year, from October onwards the days
are sunny and bracing. The mean temperature in December is 73 °F(23 °C). The nights are cool and temperatures in
winter may drop below freezing point in many places. In April and May the day temperature may cross 100
°F (38 °C) but it is very dry and not sultry as in the adjacent plains. The rainy season (June to September) is pleasant.
[18]
The Chota Nagpur Plateau receives an annual average rainfall of around 1400 mm, which is less than the
rainforested areas of much of India and almost all of it in the monsoon months between June and August.[19]
Alt-The Chota Nagpur Plateau consists of three steps. The highest step is in the western part of the plateau,
where pats, as a plateau is locally called, are 3,000 feet (910 m) - 3,500 feet (1,100 m) above sea level. The highest
point is 3,819 feet (1,164 m). The next part contains larger portions of the old Ranchi and Hazaribagh districts and some
parts of old Palamu district, before these were broken up into smaller administrative units. The general height is 2,000
feet (610 m). The topography in undulating with prominent gneissic hills, often dome-like in outline.
Chota Nagpur, plateau in eastern India, in Bihar state. The plateau is composed of Precambrian rocks (i.e., rocks
more than about 540 million years old)
Chota Nagpur dry deciduous forests are wide spread in the Chota Nagpur Plateau of Eastern India
covering Jharkhand, Orissa, Bihar and Chhattisgarh. The region comprises of dry to wet deciduous forests. The area is
fully surrounded by the plateaus, rocky hills and verdant valleys. The forests of the Chota Nagpur cover some of the
rare and endemic species. The plateau receives the less rainfall that makes the vegetation drier in this region.
The Tibetan also known as the Qinghai-Tibetan (Qingzang) Plateau is a vast, elevated plateau in Central Asia[1][2][3]
[4]
or East Asia[5][6][7][8] covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region and Qinghai Province in western China, as well as
part of Ladakh in Jammu and Kashmir. It stretches approximately 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) north to south and 2,500
kilometres (1,600 mi) east to west. With an average elevation exceeding 4,500 metres (14,800 ft), the Tibetan Plateau is
sometimes called "the Roof of the World" and is the world's highest and largest plateau, with an area of 2.5 million
km2 (0.97 million sq. mi., or about four times the size ofFrance).[9]
The average elevation is over 4500 metres (14800 ft)
the plateau dates back 13.5 million years and has reached a maximum average height of five kilometers.
You might also like
- Deccan PlateauDocument1 pageDeccan PlateaumoneybackNo ratings yet
- Tripura: India Bangladesh Mizoram Assam AgartalaDocument4 pagesTripura: India Bangladesh Mizoram Assam AgartalaMadhuNo ratings yet
- Asia: Physical Geography: Biology, Earth Science, Geology, Geography, Human Geography, Physical GeographyDocument10 pagesAsia: Physical Geography: Biology, Earth Science, Geology, Geography, Human Geography, Physical GeographyAilene Nace GapoyNo ratings yet
- About MaharashtraDocument9 pagesAbout MaharashtraMadhuNo ratings yet
- Geography of IndiaDocument15 pagesGeography of IndiaKhushal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Geology: Topic-Peninsular PlateauDocument48 pagesPresentation of Geology: Topic-Peninsular PlateaupoornaanandNo ratings yet
- About Arunachal PradeshDocument6 pagesAbout Arunachal PradeshMadhuNo ratings yet
- Uttarakhand: Written byDocument7 pagesUttarakhand: Written byMadhuNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument189 pagesGeographyNijam Nagoor100% (1)
- Geography and Major Biomes: WetlandsDocument11 pagesGeography and Major Biomes: WetlandsrahulunknownNo ratings yet
- Geography of OdishaDocument22 pagesGeography of OdishaHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physical Features of NepalDocument3 pagesPhysical Features of NepalSunny ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Geography of IndiaDocument12 pagesGeography of IndiaPrateek GahlanNo ratings yet
- Fact About India GeograpyDocument13 pagesFact About India GeograpyVeera Shekar GNo ratings yet
- Meghalaya, State ofDocument4 pagesMeghalaya, State ofMadhuNo ratings yet
- Mount Everest: Continent Populous Supercontinent BorderDocument2 pagesMount Everest: Continent Populous Supercontinent Borderangela roxas 16No ratings yet
- Geography of India - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument16 pagesGeography of India - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFSaurabh KalkarNo ratings yet
- Assignment in APDocument9 pagesAssignment in APRey MarkNo ratings yet
- Hill Architecture Along Beas RiverDocument19 pagesHill Architecture Along Beas RiverAnkush BhartiNo ratings yet
- RAJASTHANDocument2 pagesRAJASTHANHarshit VishnoiNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography UPSC NotesDocument15 pagesIndian Geography UPSC NotesKeShav JasrotiaNo ratings yet
- Central Development RegionDocument7 pagesCentral Development RegionRabindra Raj BistaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Deccan PlateauDocument1 pageWhat Is The Deccan PlateauPiweNo ratings yet
- Nepalese Society and Culture Himalayan Society and CultureDocument7 pagesNepalese Society and Culture Himalayan Society and CultureRajendra MagarNo ratings yet
- Nepal p7-9Document3 pagesNepal p7-9Ayushonline442No ratings yet
- Asian StudiesDocument42 pagesAsian StudiesBhea Dhenesse M ManaloNo ratings yet
- Ecology: Ālaya (Dwelling)Document5 pagesEcology: Ālaya (Dwelling)Tennety MrutyumjayaNo ratings yet
- Physical Features of IndiaDocument13 pagesPhysical Features of IndiaSwara KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Bihar.: The LandDocument9 pagesBihar.: The Landchemy_87No ratings yet
- Geography of IndiaDocument75 pagesGeography of Indianeeraj royalNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Conservation in IndiaDocument28 pagesWildlife Conservation in IndiaPavan Kumar P N82% (17)
- Geo-Ecological Zones of IndiaDocument49 pagesGeo-Ecological Zones of IndianabiNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan: National Disaster Risk Reduction PortalDocument13 pagesRajasthan: National Disaster Risk Reduction PortalHansel GoyalNo ratings yet
- Geo of IndiaDocument9 pagesGeo of IndiaParul BatraNo ratings yet
- Sapnanil ReportDocument31 pagesSapnanil ReportDipayan RoyNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography Complete 9 HRDocument248 pagesIndian Geography Complete 9 HRMurtaza Yousuf100% (1)
- World History GeographicDocument8 pagesWorld History GeographicMikaelaNo ratings yet
- Physiographic Division of IndiaDocument30 pagesPhysiographic Division of IndiaGurdarshan Singh Singh100% (1)
- Physiographic RegionsDocument4 pagesPhysiographic RegionsAppoorv DuaNo ratings yet
- Project Work: Abhishek TripathiDocument10 pagesProject Work: Abhishek TripathiPushpa TripathiNo ratings yet
- 10Th STD Geography Unit - 1Document9 pages10Th STD Geography Unit - 1Sathish K. SamyNo ratings yet
- Desertification: Conservation, Ecology, and EconomyDocument5 pagesDesertification: Conservation, Ecology, and EconomyrNo ratings yet
- About West BengalDocument9 pagesAbout West BengalMadhuNo ratings yet
- Geographical FeaturesDocument35 pagesGeographical FeaturesJielyn DulaNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument90 pagesGeographydevendradubey100% (1)
- A Case Study On Melting of IceDocument7 pagesA Case Study On Melting of IceRishav Dev PaudelNo ratings yet
- Physical Features of India: Tectonic Plate TheoryDocument5 pagesPhysical Features of India: Tectonic Plate TheoryPooja ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Division of IndiaDocument11 pagesTectonic Division of IndiaPatel axaliNo ratings yet
- Geography of PakistanDocument52 pagesGeography of Pakistankhushbakhttariq794No ratings yet
- Biogeographical LassificationDocument31 pagesBiogeographical LassificationErfana Yasmin100% (1)
- Asia - Physical GeographyDocument9 pagesAsia - Physical GeographyArchie Gabuyo Jr.No ratings yet
- HimalayDocument6 pagesHimalaybaburaogtrwNo ratings yet
- The Northern Mountain WallDocument23 pagesThe Northern Mountain WallRita RanikhetwallaNo ratings yet
- SSTDocument11 pagesSSTOJASNo ratings yet
- Geogrphy of Pakistan A1, Q1Document4 pagesGeogrphy of Pakistan A1, Q1fahadNo ratings yet
- Geography of IndiaDocument9 pagesGeography of IndiaSARTHAK MAJUMDARNo ratings yet
- Important Things About Uttar Pradesh TourismDocument61 pagesImportant Things About Uttar Pradesh TourismAbhimanyu SinghNo ratings yet
- 3 Early EarlyDocument144 pages3 Early EarlySatheesh VagiNo ratings yet
- Geography of India: Indo-Gangetic PlainDocument5 pagesGeography of India: Indo-Gangetic PlainchunnumunnuNo ratings yet
- Full Form FMDocument1 pageFull Form FMSiddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- GMAT VulnerabilitesDocument1 pageGMAT VulnerabilitesSiddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Baptised Poet Playwright National Poet Collaborations Plays Sonnets Narrative PoemsDocument1 pageBaptised Poet Playwright National Poet Collaborations Plays Sonnets Narrative PoemsSiddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- AWADocument1 pageAWASiddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Awa 2Document1 pageAwa 2Siddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Awa 2Document1 pageAwa 2Siddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Awa Gmat Example 3Document1 pageAwa Gmat Example 3Siddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Awa Gmat 4Document1 pageAwa Gmat 4Siddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- AwaDocument2 pagesAwaSiddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Awa Gmat Example2Document2 pagesAwa Gmat Example2Siddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Awa Gmat ExampleDocument1 pageAwa Gmat ExampleSiddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Set TheoryDocument0 pagesSet Theorykrreation7086No ratings yet
- Cracking The GMAT, 2019 Edition: PremiumDocument4 pagesCracking The GMAT, 2019 Edition: PremiumSiddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Permutations and Combinations SimplifiedDocument15 pagesPermutations and Combinations SimplifiedTina UniyalNo ratings yet
- 5 Bowlers Virat Kohli Won'T Want To Face in The World CupDocument3 pages5 Bowlers Virat Kohli Won'T Want To Face in The World CupSiddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 3 5 Final Essay Earth 1Document6 pages3 5 Final Essay Earth 1api-546975577No ratings yet
- Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument20 pagesHydrometeorological HazardsRonn Jacob Medina TamsiNo ratings yet
- LyricsDocument3 pagesLyricsFrederick FajardoNo ratings yet
- Seo2021 Book ClimateChangeAndEconomicsDocument278 pagesSeo2021 Book ClimateChangeAndEconomicsDanu OlgaNo ratings yet
- Spring Easy ReadingDocument1 pageSpring Easy ReadingАміна БондарNo ratings yet
- Imperdan FP 50 GP (10X1) : Bituminous WaterproofingDocument3 pagesImperdan FP 50 GP (10X1) : Bituminous WaterproofingAANo ratings yet
- Eo 2023-9Document2 pagesEo 2023-9WXMINo ratings yet
- Lesson - 68 - 4th - Quarter - Science - 4. Role of Sun in The Water CycleDocument3 pagesLesson - 68 - 4th - Quarter - Science - 4. Role of Sun in The Water CycleVenus Cureg100% (2)
- IGCSE English As A Second Language 0510 - 21 Paper 2 Oct - Nov 2020Document2 pagesIGCSE English As A Second Language 0510 - 21 Paper 2 Oct - Nov 2020rajeanniarajNo ratings yet
- Seasonal Incidence of Spotted Pod Borer, Maruca: Vitrata (Geyer) On PigeonpeaDocument5 pagesSeasonal Incidence of Spotted Pod Borer, Maruca: Vitrata (Geyer) On PigeonpeaRAC HawkeyeNo ratings yet
- Fab Avt 2115 Prelim Module No.2 PDFDocument32 pagesFab Avt 2115 Prelim Module No.2 PDFHanz AlecNo ratings yet
- Gst-Passages EnglishDocument5 pagesGst-Passages EnglishJeh ArwitaNo ratings yet
- Yashoda Cancer Hospital Ghaziabad, IndiaDocument65 pagesYashoda Cancer Hospital Ghaziabad, IndiaSuren Adithyaa (RA1911201010043)No ratings yet
- RYA Navigation Courses - Chapter 7 Tide Prediction From Charts and Tables.Document21 pagesRYA Navigation Courses - Chapter 7 Tide Prediction From Charts and Tables.Thwin Yar Zar PhyoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3e The Ice Age ComethDocument4 pagesUnit 3e The Ice Age ComethSoumya SinghNo ratings yet
- Geography NotesDocument4 pagesGeography NotesPassw0rdNo ratings yet
- 6ºY7º TALLER FINAL-Seasons Weather ClothesDocument7 pages6ºY7º TALLER FINAL-Seasons Weather ClothesNelson FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Hydro HazardsDocument156 pagesHydro HazardsJane ErlanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: An Excursion: MatchingDocument12 pagesUnit 6: An Excursion: MatchingMoon Gaming VnNo ratings yet
- 7B Q3 L7 PHIẾU TRÊN LỚP + HWDocument7 pages7B Q3 L7 PHIẾU TRÊN LỚP + HWMinh Nguyen QuangNo ratings yet
- The Climate of India PDFDocument3 pagesThe Climate of India PDFSanjeevan Aravindan (JEEV)No ratings yet
- Types of Succulents ID Cards Alphabetical Order 2 1Document460 pagesTypes of Succulents ID Cards Alphabetical Order 2 1FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Permission LetterDocument3 pagesPermission LetterJeddedeah M. CapilaNo ratings yet
- Ramanan: (Can't Be Baroness Coz She Is Not Married)Document4 pagesRamanan: (Can't Be Baroness Coz She Is Not Married)Online BNRNo ratings yet
- Resumen Hechizos D&D 5Document39 pagesResumen Hechizos D&D 5TarusentNo ratings yet
- A Level Geography Notes - Dune - Desert - 1617339267564Document24 pagesA Level Geography Notes - Dune - Desert - 1617339267564Aleck ChitandaNo ratings yet
- First ConditionalDocument2 pagesFirst ConditionalOzan DemirciNo ratings yet
- Shadowdark Druid - Adapted From OSE AdvancedDocument8 pagesShadowdark Druid - Adapted From OSE Advancedkefit29187No ratings yet
- Chemtrails, Geoengineering, Weather Modification & Weather Warfare PDFDocument129 pagesChemtrails, Geoengineering, Weather Modification & Weather Warfare PDFkitty katNo ratings yet
- IJRANSS - Study On "The Delayed in Intervention of Science' in Climate Change Solution(s), Clutching The Sustainability of Species Life" On Earth by Averting Weather Like Mars".Document6 pagesIJRANSS - Study On "The Delayed in Intervention of Science' in Climate Change Solution(s), Clutching The Sustainability of Species Life" On Earth by Averting Weather Like Mars".Impact JournalsNo ratings yet