Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 01 Intro Computers
Uploaded by
DBZ sTAROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 01 Intro Computers
Uploaded by
DBZ sTARCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Computers
Notes
1
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
Computer has become indispensable in today’s life. It has become difficult to imagine the
world without computer. Everywhere computers are used whether it is office, bank,
school, college, business, hospitals etc. You must have seen Computers at your home,
school or office. Can you guess what type of a device it is?
Computer is an electronic device which accepts input, processes it and produces the
desired results. Computer is a machine which performs mathematical operations and
logical decisions at an extremely fast speed. Computer not only do calculations but also
handles different applications at a time.
In this lesson, you will learn about computers, its parts, and its uses in real life.
OBJECTIVES
After reading this lesson you will be able to:
z define Computer.
z describe generations of Computers.
z list types of Computers.
z explain the uses of Computers.
1.1 WHAT IS A COMPUTER?
You already know computer is an electronic device which accepts input, processes it and
produces the desired results. Computer is divided into two main components Hardware
and Software. Hardware consists of mechnical and electronic device, which you can see
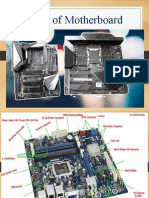
and touch. The four main hardware components of any computer are motherboard,
processor, RAM, Hard drive. Software consists of programs, operating system etc.,
Examples of software: Windows 7, Linux, MS Office, Adobe PageMaker etc. Today's
Computers have at least one CPU (Central Processing Unit) that performs most
calculations and include main memory, control unit, and an Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU).
Computer Hardware Assembly and Maintenance 1
Introduction to Computers
Computer is a general purpose device that is programmed for some task. Do you know
what are the two major characteristics of a Computer? Major charctersistics of a
Notes Computer are (i) it responds to a specific set of instructions in a well-defined manner;
(ii) it can execute a pre-recorded list of instructions (a program).
Fig. 1.1 Desktop Computer
Input → Processing → Output
Fig. 1.2 Basic operation of a Computer System
1.1.1 How does a Computer work?
z It accepts input from various input devices like keyboard, mouse, scanner, joystick
and light pen.
z Microprocessor performs arithmetic and logic operation on it and gives result.
z It communicates results through output devices like monitor and printer etc.
z It stores information in hard disk. There are other storage devices such as computer
disk, pendrive, (USB drive) etc.
1.2 WHAT ARE THE CHARACTERISTICS OF A COMPUTER?
Speed: Computers work at very high speed and are much faster than humans. Do you
know one second is very large time period for a computer? A Computer can perform
millions of calculations in a microsecond.
Storage: Computer can store large amount of data (text, video, picture etc) permanently.
You can use this data at any time.
Accuracy: Accuracy means to provide results without any error. Computers can process
large amount of data and generate error free results. A modern computer processes large
amount of information without any error.
Communication: Today's Computers have capability of communicating with other
Computers. You can connect two or more computers.
2 Computer Hardware Assembly and Maintenance
Introduction to Computers
Automatic: A computer as a machine can not start itself but it can perform some work
without human intervention. For example, you have large amount of data and you want
to perform some calculation on it. For getting the result, you have to run the appropriate Notes
software and all the calculation will be done by Computer.
Diligence: Unlike human being, computer is free from dullness and lack of concentration.
It can work for hours without any error until job is finished.
Versatility: Versatility is a most important characteristic of computer. You may use
computer to prepare salary slip and at the same time you can use the same computer for
paying electricity bill and etc. It means you can perform completely different type of work
on a single computer simultaneously.
INTEXT QUESTIONS 1.1
Fill in the blanks:
1. Computer is broadly divided into _________ and _________ categories.
2. Example of system software is _________.
3. Physical components of computer is called _____________.
4. Software consists of ___________, _____________.
1.3 COMPUTER GENERATIONS
The history of computer development is often referred in the different generations of
computer devices. A generation refers to state of improvement in the production process.
Each generation of computer is characterized by major technological development that
fundamentally changes the way computer operates.
z First Generation: The period of first generation was 1946-59. The computers of
first generation used vacuum tubes as the basic components for memory and circuitry
for CPU (Central Processing Unit). In this generation mainly batch processing
operating system were used. Punched cards, paper tape, and magnetic tape were
used as input and output devices. Example : ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator
And Computer was the first general purpose electronic digital computer ), EDVAC
(Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer), UNIVAC (Universal Automatic
Computer - world’s first commercially available computer), IBM-701 and IBM-
650.
z Second Generation: The period of second generation was 1959-65. In this generation
transistors were used. It is cheaper, consumed less power, more compact in size,
more reliable and faster than the first generation machines made of vacuum tubes.
These were also the first computers that stored instruction in their memory. The
computers used batch processing and multiprogramming operating system. Example:
IBM 1620 , IBM 7094, CDC 1604, CDC 3600, UNIVAC 1108
Computer Hardware Assembly and Maintenance 3
Introduction to Computers
z Third Generation: The period of third generation was 1965-71. The computers of
third generation used Integrated Circuits (IC’s) in place of transistors. A single IC
Notes has many transistors, resistors and capacitors along with the associated
circuitry. High-level languages (FORTRAN-II TO IV, COBOL, PASCAL PL/1,
BASIC, ALGOL-68 etc.) were used during this generation. Example: IBM-360 series,
Honeywell-6000 series, PDP(Programmed Data Processor), IBM-370/168 and TDC-
316
z Fourth Generation: The period of fourth generation was 1971-80. The computers
of fourth generation used Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits. VLSI circuits
having about 5000 transistors and other circuit elements and their associated circuits
on a single chip made it possible to have microcomputers of fourth generation. All
the high-level languages like C, C++, DBASE etc., were used in this generation.
Example: DEC 10, STAR 1000,PDP 11, CRAY-1(Super Computer) and CRAY-X-
MP(Super Computer)
z Fifth Generation: The period of fifth generation is 1980 onwards. In the fifth
generation, the VLSI technology became ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration)
technology, resulting in the production of microprocessor chips having ten million
electronic components. This generation is based on parallel processing hardware
and AI (Artificial Intelligence) software used for Robots designing.
1.4 WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF COMPUTERS?
Computer are generally classified by speed, memory size and power consumption, though
there is considerable overlap:
z Microcomputer: It is based on microprocessor chip as CPU. This is smallest category
of Digital Computer. These computers include Personal computer Desktop computers,
Notebook computers, Laptop computers, Tablet computers.
Personal computer - It is a small, relatively inexpensive computer designed for an
individaul user.
Desktop computers - A computer that is used for home application and small office
work, is Desktop computer. In this type of computer, monitor is put on the top of
computer and it is broad and low. While in tower computer, CPU cases are tall and
narrow. In our general life we interact with Desktop Computer.
Fig. 1.3 Desktop computer
4 Computer Hardware Assembly and Maintenance
Introduction to Computers
Notebook computers -It is a lightweight computer. A notebook size is also very less
in comparison to Desktop Computer and Tower Computer. The display of notebook
computer is different from Desktop Computer. Notebook computers price is very Notes
high in comparision with Desktop computer. It is easy to move from one place to
another place. Notebook computer power is same as Desktop Computer. It is made
of same configuration like 1 GB RAM, 1 TB HDD, DVD, etc...
Laptop computer -This type computer is little different from Notebook computers.
Its configuration is near about same as Notebook Computer and it can be in the
range of high configuration (4 GB RAM, 1 TB HDD, etc.) to low configuration (500
MB RAM, 500 GB HDD, etc.). Most of the times Laptop Computers are also called
Notebook Computers.
Tablets - are smaller than laptop PCs, very lightweight, and easy to carry. But they
lack the processing power of a laptop as well as a keyboard input. They rely instead
on a stylus and touch screen.
z Minicomputer: A multi-user computer capable of supporting up to hundreds of
users simultaneously. These computers are bigger in size and costlier than
Microcomputers. Minicomputers are used in universities and big organisations.
z Mainframe computer: A mainframe computer is a very large computer capable of
handling and processing very large amounts of data quickly. These are used by large
institutions, such as government agencies and large corporations.
z Supercomputers Or High Performance Computer (HPC): A supercomputer is
typically used for scientific and engineering applications that must handle very large
databases. It is an extremely fast computer that can perform hundreds of millions of
instructions per second. The speed of the supercomputer are measured by FLOPS
(Floating point operations per second).
1.5 APPLICATIONS OF COMPUTERS
You may aware that computers are very productive, efficient and can do anything
imaginable. Some of the principle applications of the computer systems are as follows:
Business: Businessmen use computer in the presentation, analysis, calculation and
making charts for their business. They also provide online service to their customers using
e-commerce, m-commerce. You or your family member must have used online shopping
website for purchasing any products. Usage of the computer has reduced the cost of man
power and its delivery in an efficient way.
Buildings: In the construction of building, Architects use computer to virtually visualize
the complete building. It is performed through different multimedia software. Computer
provides accurate structure of buildings with all measurements. It helps in reducing cost
of changes and it provides satisfcation to the customer.
Education: Now-a-days, you can see computer has become an inevitable part in spheres
of life. Students use computer for preparing or completing assignments and submit it
Computer Hardware Assembly and Maintenance 5
Introduction to Computers
through online. There are so many online contents study materials which can be viewed
by using internet.
Notes
Retailing: Most of the retailers product are based on barcode. That’s the reason they need
computers to read barcode and calculate amount on it. This system helps retailers to sum
up so many items within seconds.
Energy: In the energy sectors, companies use computers to calculate items and figure out
the place of natural resources. Computers also help in finding the correct geographical
location of company’s delivery places, vehicles information and communicating with
customers.
Transportation: Companies are using computers in the vehicles to provide more services
to the consumers. Consumers can easily determine the fuel level, AC system, temperature
with the help of this system. Some vehicles do not require driver to reach at destination on
predetermined path in some countries.
Agriculture: Farmers can check the requirements of their crops on computers. They use
it for billing, checking market value of crop, cost of fields and stock value of agricultural
firm. Computers help in prediction of weather conditions and estimation of agricultural
production also.
Weather: High Performance Computers (HPC) are also used for executing the weather
models ( Programs), analyzing weather conditions based on the data collected from
various sources like satellite/ GTS/ Internet data and forecasting weather conditions in
advance (3 days advance, weekly advance and even monthly advance) like (i) Rainfall
prediction, (ii) Temperature prediction, (iii) Wind speed prediction, (iv) Snowfall prediction
etc.
Government: Indian government is implementing E-Governance project in each
department. This project can be implemented using Computer only and all information
will be available online for citizens. Government employee use it for delivering good and
transparent services to citizens. Data entry operations, billing, calculation, presentation
are also performed through computers in organization.
INTEXT QUESTIONS 1.2
5. Vacuum tubes were used in _______ generation.
6. The first general purpose computer was _______ .
7. Fifth generation computers use _______.
8. What are the characteristics of a computer?
9. Which computer is a very large computer capable of handling and processing very
large amounts of data quickly?
10. Speed of supercomputer is measured in ______________.
6 Computer Hardware Assembly and Maintenance
Introduction to Computers
WHAT YOU HAVE LEARNT
Notes
In this lesson you learnt about functions of computer, generations of computers and types
of computers. You have also learnt about applications of computers.
Some of the keypoints to remember -
z Computer is an electronic device that can store, process and retrieve data.
z It is broadly divided into hardware and software.
z Important characteristics of computer are storage, accuracy, communication,
automatic, diligence, versatility.
z First generation computers used vacuum tubes.
z Second generation of computers used cheaper and more compact transistors.
z Third generation computers used Integrated Circuits (IC’s)
z Fourth generation computers used Very Large Scale Integrated circuits(VLSI).
z Fifth generation computers used Ultra Large Scale Integration (ULSI)
z Computers are classified on basis of speed, memory, power consumption as Personal
Computers, Microcomputers, Workstation, Minicomputers, Mainframe,
Supercomputers.
z Computers are widely used in business, education, transportation, weather, government
etc.
TERMINAL EXERCISE
1. What is a computer?
2. List down the important functions of a computer.
3. Explain any two characteristics of computer.
3. Explain the generations of computers.
4. How microcomputer is different from minicomputer?
5. What are the types of computers?
5. What are the applications of computer?
6. What is the use of computers in education?
ANSWERS TO INTEXT QUESTIONS
1.1
1. Hardware, software
2. Windows or Linux or DOS
Computer Hardware Assembly and Maintenance 7
Introduction to Computers
3. Hardware
Notes 4. Programs, operating system
1.2
5. First
6. ENIAC
7. Artificial intelligence and expert system computers
8. Speed, accuracy, diligence, versatility
9. Mainframe
10. FLOPS or Floating point operations per second.
8 Computer Hardware Assembly and Maintenance
You might also like
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Lesson 02 Computer CmponentsDocument12 pagesLesson 02 Computer CmponentsDBZ sTAR100% (1)
- Giriraj Advt 29 August 2018Document17 pagesGiriraj Advt 29 August 2018DBZ sTARNo ratings yet
- Guidelines and Instructions For Submission: Annexure B'Document9 pagesGuidelines and Instructions For Submission: Annexure B'Ajay KumarNo ratings yet
- India Physiography PDFDocument21 pagesIndia Physiography PDFSri BalajiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Toshiba M18Document56 pagesToshiba M18Barton EletronicsNo ratings yet
- Postgres 4.1Document765 pagesPostgres 4.1mónica_nava_38No ratings yet
- Question: Using Arm Assembly Language (Arm Cortex-M MicrocontrollDocument2 pagesQuestion: Using Arm Assembly Language (Arm Cortex-M MicrocontrollMustafa KhudhairNo ratings yet
- AC 800M Controller Central Unit Hardware GuideDocument2 pagesAC 800M Controller Central Unit Hardware GuideRodrigoBurgosNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputerDocument17 pagesGenerations of ComputerElrey AguadoNo ratings yet
- Pricelist Peralatan KomputerDocument2 pagesPricelist Peralatan KomputerRiska RahmaniaNo ratings yet
- Aptio V UEFI Firmware Deep Dive: Moving Beyond Legacy Bios With A Modern Uefi SolutionDocument29 pagesAptio V UEFI Firmware Deep Dive: Moving Beyond Legacy Bios With A Modern Uefi SolutionLeandro GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Engbedded Atmel AVRDocument12 pagesEngbedded Atmel AVRRobert OluchukwuNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument21 pagesSeminar Report On 8051 MicrocontrollerHapi ER50% (2)
- History of Computer (IT) Assig # 1Document3 pagesHistory of Computer (IT) Assig # 1Muhammad Talha ZaroonNo ratings yet
- Upgrade AUVIS and IPMS SystemsDocument2 pagesUpgrade AUVIS and IPMS SystemsarafsudartaNo ratings yet
- WondershareDocument2 pagesWondershareAcervo TutoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Parts GuideDocument17 pagesMotherboard Parts GuiderommelNo ratings yet
- ClickShare - Onepager - How To Share - ENDocument2 pagesClickShare - Onepager - How To Share - ENG & M Soft Technologies Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- Windows Setup (GPT Partition)Document2 pagesWindows Setup (GPT Partition)Bo SilversixNo ratings yet
- 9th Paper 3 & 4Document1 page9th Paper 3 & 4Rao HannanNo ratings yet
- TYP Commodore-Id Verwendung GerätDocument42 pagesTYP Commodore-Id Verwendung GerätAlex2801No ratings yet
- Products Description: Epad-10 Inch - ZT-180 Dual Core+512 Ram +4GB HDD+Android 7.2 OS - Support Flash 1QDocument1 pageProducts Description: Epad-10 Inch - ZT-180 Dual Core+512 Ram +4GB HDD+Android 7.2 OS - Support Flash 1QSuresh NakhuaNo ratings yet
- Wide availability of MICROSAR supported microcontrollers and compilersDocument3 pagesWide availability of MICROSAR supported microcontrollers and compilerssidduNo ratings yet
- NorthbridgeDocument2 pagesNorthbridgemanohardas31No ratings yet
- TVL Css g11 q1 m1 Computer System Servicing NC IIDocument16 pagesTVL Css g11 q1 m1 Computer System Servicing NC IICharles C. ArsolonNo ratings yet
- Essential Computer Maintenance TipsDocument2 pagesEssential Computer Maintenance TipsLEXUS CCTVNo ratings yet
- Eee PC 1225b Service Manual PDFDocument2 pagesEee PC 1225b Service Manual PDFaldi 88No ratings yet
- BIOS Password and Locked Hard Disk RecoveryDocument4 pagesBIOS Password and Locked Hard Disk Recoveryjelenjek83No ratings yet
- Axioo Diagnostic Flowcharts Guidance V.1.0Document5 pagesAxioo Diagnostic Flowcharts Guidance V.1.0St khofifahNo ratings yet
- IEI PXAGP 13S3 (R) Datasheet1 1153846873 PDFDocument1 pageIEI PXAGP 13S3 (R) Datasheet1 1153846873 PDFROYALNo ratings yet
- Reset TI-92 or Voyage 200 Calculator MemoryDocument1 pageReset TI-92 or Voyage 200 Calculator MemoryEsteban Omar Marquez CejaNo ratings yet
- How To Download CoprocessorDocument2 pagesHow To Download CoprocessorPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware: Parts & FunctionsDocument34 pagesComputer Hardware: Parts & FunctionsClarize Mae Apdohan GuceNo ratings yet
- MT-359L Microcontroller and Embedded Systems Lab ManualDocument6 pagesMT-359L Microcontroller and Embedded Systems Lab ManualMuhammad Sarmad BaigNo ratings yet