Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Longitudinal Waves: What Is Longitudinal Wave?
Longitudinal Waves: What Is Longitudinal Wave?
Uploaded by
Engr. Shahriar Kabir KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Longitudinal Waves: What Is Longitudinal Wave?
Longitudinal Waves: What Is Longitudinal Wave?
Uploaded by
Engr. Shahriar Kabir KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
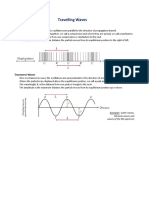
Longitudinal Waves
Mechanical waves are classified as longitudinal waves and transverse waves. Longitudinal waves
occur in the large solids and also in engineering fluids. Longitudinal waves include sound waves,
seismic P-waves, and ultrasound waves. These waves are known as compression waves as they
develop compression and refraction while traveling through any medium. When the particles are
together, the pressure is high and the region is known as compression and when the particles are
apart, the pressure is low and the region is known as rarefaction.
These other mechanical waves are known the transverse and are defined as the wave where the
displacement of the medium is at right angles to the direction of propagation and are known as t-
waves. These waves need a medium to travel through. A wave along with the length of a spring
is a good visualization where the distance between the coils increases or decreases.
What Is Longitudinal Wave?
Longitudinal waves are the waves where the displacement of the medium is in the same
direction, or in opposite direction, and direction of the travel of the wave. The distance between
the centers of two consecutive regions of compression or the rarefaction is defined by
wavelength, λ. When the compression and rarefaction regions are of two waves coincide with
each other, it is known as constructive interference and if the regions of compression and
rarefaction do not coincide, it is known as destructive interference.
You might also like
- WavesDocument27 pagesWavesBrianna MalcolmNo ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A WaveDocument28 pagesAnatomy of A WaveAnaliza ToledoNo ratings yet
- Waves As A Carrier of EnergyDocument39 pagesWaves As A Carrier of EnergyDaisy DuronNo ratings yet
- Waves 100Document6 pagesWaves 100Brook Rene JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Physics Half-Yearly Notes by Dillon Halder The World CommunicatesDocument5 pagesPhysics Half-Yearly Notes by Dillon Halder The World Communicatesuhhwot100% (1)
- BuDocument15 pagesBubreycariganNo ratings yet
- " Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueDocument12 pages" Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueMaria ClarissaNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument17 pagesWaveJevanthe Miguel ObusanNo ratings yet
- MKB PPT PhysicsDocument10 pagesMKB PPT Physicstae hyungNo ratings yet
- Two Types Waves: Transverse Waves Longitudinal Waves Transverse WaveDocument2 pagesTwo Types Waves: Transverse Waves Longitudinal Waves Transverse WaveSamuel NigatuNo ratings yet
- Physics For The Life SciencesDocument11 pagesPhysics For The Life Sciencesnawaf2016errorNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties Name: Valeria OchoaDocument2 pagesWave Properties Name: Valeria OchoaValeria OchoaNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument10 pagesWaverosalynNo ratings yet
- WAVESjsjDocument4 pagesWAVESjsjtinotaku58No ratings yet
- Transverse WavesDocument2 pagesTransverse WavesKim AciertoNo ratings yet
- E304 PhyfinalDocument15 pagesE304 PhyfinalBenj MendozaNo ratings yet
- There Are Two Types of WavesDocument5 pagesThere Are Two Types of WavesJahleel TroupeNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion PDFDocument23 pagesWave Motion PDFFRANCES VISAYA100% (1)
- Waves: Physics Departement Mathematics and Science Faculty Padang State University 2011Document13 pagesWaves: Physics Departement Mathematics and Science Faculty Padang State University 2011Yuli AriyadiNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument4 pagesArgumentative EssayFebriolla Via HashintaNo ratings yet
- Wave MotionDocument46 pagesWave Motionalingig.cleonnyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Wave Motion (Hand-Out)Document24 pagesLecture 2 - Wave Motion (Hand-Out)Richard SaputuNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument95 pagesPhysicsabdulhaadi1189No ratings yet
- Oscillation of Energy: An Oscillation That Travels Through A MediumDocument2 pagesOscillation of Energy: An Oscillation That Travels Through A MediumApril Joy Gelilang PulgaNo ratings yet
- 20 1 WavesDocument20 pages20 1 Wavesapi-276003030No ratings yet
- Longitudinal WaveDocument5 pagesLongitudinal WaveChristineNo ratings yet
- Vakev Physics Term 2 L5 Els&sodDocument21 pagesVakev Physics Term 2 L5 Els&sodvigiraneza0No ratings yet
- Waves NewDocument80 pagesWaves NewVijyata DhankharNo ratings yet
- A Level Waves PresentationsDocument7 pagesA Level Waves Presentationsgru004902No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument13 pagesLecture 1 IntroductionRocking Himanshu21No ratings yet
- Sounds of Music Study GuideDocument56 pagesSounds of Music Study GuideSherrie Wang100% (1)
- Longitudinal WavesDocument8 pagesLongitudinal WavesRonald TantiadoNo ratings yet
- MY SO Waves Notes Powerpoint - Property of WavesDocument12 pagesMY SO Waves Notes Powerpoint - Property of WavesFirdaus Kamal BahrinNo ratings yet
- Wave and Oscillatory MotionDocument9 pagesWave and Oscillatory MotionnishantNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 LESSON 1 2Document8 pagesUnit 1 LESSON 1 2kachechiekurosakiNo ratings yet
- Physics II - WavesDocument15 pagesPhysics II - WavesVicky Waran RajNo ratings yet
- PRODUCTION AND-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesPRODUCTION AND-WPS Officebilldanit4fitzNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument26 pagesWavesceline.the988No ratings yet
- Introduction and Definitions:: PH ScaleDocument11 pagesIntroduction and Definitions:: PH ScaleMay HumiwatNo ratings yet
- Waves ItroductionDocument2 pagesWaves ItroductionQuinone QuentinNo ratings yet
- Rarefactions.: Electromagnetic Waves. Although Electromagnetic Waves Do Not Need ADocument3 pagesRarefactions.: Electromagnetic Waves. Although Electromagnetic Waves Do Not Need AVerynNo ratings yet
- Presentation On WavesDocument7 pagesPresentation On Wavesmaqsood ahmadNo ratings yet
- Propagation of WaveDocument18 pagesPropagation of WaveVipul KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About Waves in The Scientific Sense. For Waves On The Surface of The Ocean or Lakes, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument1 pageThis Article Is About Waves in The Scientific Sense. For Waves On The Surface of The Ocean or Lakes, See - For Other Uses, SeeANMOLNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Travelling WavesDocument5 pages4.2 Travelling WavesEesha SajidNo ratings yet
- Wave and Optics: Form 3 Physics Bahse Miss K. BoodaiDocument26 pagesWave and Optics: Form 3 Physics Bahse Miss K. BoodaiZariah PhillipNo ratings yet
- PSC 9Document17 pagesPSC 9AryannaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Travelling Waves NotesDocument2 pages4.2 Travelling Waves NotesChrisQiNo ratings yet
- Physics ST SoldierDocument13 pagesPhysics ST SoldierAnshuli KhannaNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering and Architecture: Physics 2Document6 pagesCollege of Engineering and Architecture: Physics 2Jayson CozNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument36 pagesWavesjomelleann.pasolNo ratings yet
- Physics - Peak Science: Three Dimensions Depending On The Nature of The WaveDocument13 pagesPhysics - Peak Science: Three Dimensions Depending On The Nature of The WaveVincent TranNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 15 Waves Revision Notes - PDFDocument53 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 15 Waves Revision Notes - PDFrazi sharifNo ratings yet
- Physics 101Document3 pagesPhysics 101Munira WahidNo ratings yet
- CL 11 CH 15Document15 pagesCL 11 CH 15Mariappan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- E108 - AgustinDocument23 pagesE108 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- 6 Mechanical Waves Examples in Real LifeDocument6 pages6 Mechanical Waves Examples in Real LifeLarry MostolesNo ratings yet
- Physics 4 PDFDocument122 pagesPhysics 4 PDFBABU JOHNNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: WavesDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: WavesKyera LovesNo ratings yet
- Exponentials & Logs MediumDocument4 pagesExponentials & Logs MediumEngr. Shahriar Kabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Wave Diagrams: Name - DateDocument1 pageWave Diagrams: Name - DateEngr. Shahriar Kabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing Grade-8Document6 pagesCreative Writing Grade-8Engr. Shahriar Kabir KhanNo ratings yet
- ChemE - AMU and Percent Abundance Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesChemE - AMU and Percent Abundance Worksheet AnswersEngr. Shahriar Kabir KhanNo ratings yet
- ChemE - AMU and Percent Abundance WorksheetDocument1 pageChemE - AMU and Percent Abundance WorksheetEngr. Shahriar Kabir KhanNo ratings yet