Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beaufort Scale - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDF
Uploaded by
elvi anggiovennyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Beaufort Scale - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDF
Uploaded by
elvi anggiovennyCopyright:
Available Formats
Beaufort scale - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Beaufort scale
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Beaufort scale is an empirical measure for describing wind intensity based mainly on observed sea
conditions. Its full name is the Beaufort wind force scale.
Contents
● 1 History
● 2 References
● 3 See also
● 4 External links
History
The scale was created in 1805 by Sir Francis Beaufort, a British naval officer and hydrographer. At that
time naval officers made regular weather observations, but there was no scale and so they could be very
subjective - one man's "stiff breeze" might be another's "calm conditions". The initial scale from zero to 12
did not reference wind speed numbers, but related qualitative wind conditions to effects on the sails of a
man of war, then the main ship of the Royal Navy, from "just sufficient to give steerage" to "that which no
canvas [sails] could withstand." The scale was made a standard for ship's log entries on Royal Navy
vessels in the late 1830s.
The scale was adapted to non-naval use from the 1850s, with scale numbers corresponding to cup
anemometer rotations. In 1906, with the advent of steam power, the descriptions were changed to how the
sea, not the sails, behaved and extended to land observations. Rotations to scale numbers were
standardised only in 1923. George Simpson, Director of the UK Meteorological Office, was responsible
for this and for the addition of the land based descriptors. The measure was slightly altered some decades
later to improve its utility for meteorologists. Wind speed on the Beaufort scale can be expressed by the
formula:
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Beaufort_scale&printable=yes (1 of 5)14/09/2006 20:01:33
Beaufort scale - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
v = 0.837 B3/2 m/s
where v is wind speed and B is Beaufort scale number.
Today, hurricanes are sometimes described as Beaufort scale 12 through 16, with the standard Saffir-
Simpson Hurricane Scale Category 1 equivalent to Beaufort 12, Category 2 to Beaufort 13, and so on.
Category 1 tornadoes on the Fujita and TORRO scales also begin at the end of level 12 of the Beaufort
scale.
The Beaufort scale was extended in 1944, when Forces 13 to 17 were added. However, Forces 13 to 17
were intended to apply only to special cases, such as tropical cyclones. Nowadays, the extended scale is
only used in Taiwan and mainland China, which are often affected by typhoons.
Note that wave heights in the scale are for conditions in the open ocean, not along shore.
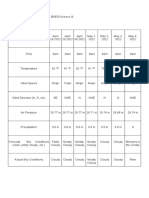
Mean
wind Wave
Wind speed speed
Beaufort height Land
(kt / Description Sea conditions
number conditions
km/
kt km/h mph m/s h/ m ft
mph)
0/0/ Calm. Smoke
0 0 0 0 0-0.2 Calm 0 0 Flat.
0 rises vertically.
Wind motion
0.3- 2 / 4 / Ripples
1 1-3 1-6 1-3 Light air 0.1 0.33 visible in
1.5 2 without crests.
smoke.
Small
wavelets.
Wind felt on
1.6- 5 / 9 / Crests of
2 4-6 7-11 4-7 Light breeze 0.2 0.66 exposed skin.
3.3 6 glassy
Leaves rustle.
appearance,
not breaking
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Beaufort_scale&printable=yes (2 of 5)14/09/2006 20:01:33
Beaufort scale - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Large
wavelets. Leaves and
3.4- 9/ Crests begin to smaller twigs
3 7-10 12-19 8-12 Gentle breeze 0.6 2
5.4 17 / 11 break; in constant
scattered motion.
whitecaps
Dust and
loose paper
11- 13- 5.5- 13 / Moderate
4 20-29 1 3.3 Small waves. raised. Small
16 18 7.9 24 / 15 breeze
branches
begin to move.
Moderate (1.2
17- 19- 8.0- 19 / m) longer Smaller trees
5 30-39 Fresh breeze 2 6.6
21 24 10.7 35 / 22 waves. Some sway.
foam and spray.
Large
branches in
motion.
Large waves Whistling
22- 25- 10.8- 24 / with foam heard in
6 40-50 Strong breeze 3 9.9
27 31 13.8 44 / 27 crests and overhead
some spray. wires.
Umbrella use
becomes
difficult.
Whole trees in
Sea heaps up
motion. Effort
28- 32- 13.9- 30 / and foam
7 51-62 Near gale 4 13.1 needed to
33 38 17.1 56 / 35 begins to
walk against
streak.
the wind.
Moderately
high waves
Twigs broken
with breaking
34- 39- 17.2- 37 / from trees.
8 63-75 Gale 5.5 18 crests forming
40 46 20.7 68 / 42 Cars veer on
spindrift.
road.
Streaks of
foam.
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Beaufort_scale&printable=yes (3 of 5)14/09/2006 20:01:33
Beaufort scale - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
High waves
(2.75 m) with
dense foam.
Light
41- 47- 20.8- 44 / Wave crests
9 76-87 Strong gale 7 23 structure
47 54 24.4 81 / 50 start to roll
damage.
over.
Considerable
spray.
Very high
waves. The sea
Trees
surface is
uprooted.
48- 88- 55- 24.5- 52 / white and there
10 Storm 9 29.5 Considerable
55 102 63 28.4 96 / 60 is considerable
structural
tumbling.
damage.
Visibility is
reduced.
60 / Widespread
56- 103- 64- 28.5- Exceptionally
11 111 / Violent storm 11.5 37.7 structural
63 117 72 32.6 high waves.
69 damage.
Huge waves.
Air filled with
foam and
Massive and
spray. Sea
widespread
12 >63 >117 >72 >32.7 N/A Hurricane 14+ 46+ completely
damage to
white with
structures.
driving spray.
Visibility very
greatly reduced.
The scale is used in, and may be most recognizable to some from, the Shipping Forecasts broadcast on
BBC Radio 4 in the United Kingdom.
This scale is also widely used in China. Taiwan uses the Beaufort scale extended in 1944 with Forces 13-
17 to better represent the wind caused by typhoons. On the morning of May 15, 2006, mainland China
suddenly introduced the extended scale to Force 17 without any prior notice. [1] This extended scale was
immediately put into use for Typhoon Chanchu. Hong Kong and Macau keep using Force 12 as the
maximum and adopted a set of simpler descriptions for public. The descriptions used in Hong Kong are
shown here. Macau used similar descriptions except the term gentle is retained for Force 3.
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Beaufort_scale&printable=yes (4 of 5)14/09/2006 20:01:33
Beaufort scale - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In the United States, winds of Beaufort 6 or 7 result in the issuance of a small craft advisory, with force 8
or 9 winds bringing about a gale warning, 10 or 11 a storm warning (or "tropical storm warning" for 8 to
11 if related to a tropical cyclone), and anything stronger a hurricane warning.
References
● Scott Huler, Defining the Wind : The Beaufort Scale, and How a 19th-Century Admiral Turned
Science into Poetry, Crown, 2004, ISBN 1-4000-4884-2
See also
● Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale
● Fujita scale
● TORRO scale
● Cliwoc
External links
● UK Meteorological Office: The Beaufort Scale
● Investigating Clouds : A lesson plan from the National Science Digital Library that uses the
Beaufort Scale.
● National Public Radio : The Beaufort Scale on NPR - interview with Scott Huler.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beaufort_scale"
Categories: Articles with unsourced statements | Scales | Winds
● This page was last modified 14:29, 13 September 2006.
● All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License. (See Copyrights
for details.)
Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.
● Privacy policy
● About Wikipedia
● Disclaimers
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Beaufort_scale&printable=yes (5 of 5)14/09/2006 20:01:33
You might also like
- Wind Speed and Wind RoseDocument10 pagesWind Speed and Wind RoseHoney Nhassie Marie GonzagaNo ratings yet
- The Beaufort ScaleDocument7 pagesThe Beaufort ScaleViqy Muhammad RafiNo ratings yet
- Tabel Beaufort ScaleDocument2 pagesTabel Beaufort ScalewisnukerNo ratings yet
- Beaufort Scale - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesBeaufort Scale - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMohammad SwalehNo ratings yet
- Beaufort ScaleDocument7 pagesBeaufort ScalebogdanNo ratings yet
- Beaufort ScaleDocument6 pagesBeaufort Scaleavi_cha5215No ratings yet
- Beaufort Scale1Document3 pagesBeaufort Scale1ciprian predaNo ratings yet
- Beaufort ScaleDocument32 pagesBeaufort ScalefsdfsNo ratings yet
- Wind Speed: SafetyDocument3 pagesWind Speed: Safetyal bauerNo ratings yet
- 6 WindsDocument68 pages6 WindsAmitoj SinghNo ratings yet
- WK 5 WIND Beaufort ScaleDocument11 pagesWK 5 WIND Beaufort Scalekimcristobal52No ratings yet
- Beaufort ScaleDocument9 pagesBeaufort ScaleBorislav PetrovNo ratings yet
- BeaufortDocument5 pagesBeaufortJay Lord TumambingNo ratings yet
- BeaufortDocument12 pagesBeaufortshenNo ratings yet
- Beaufort Wind Scale ChartDocument1 pageBeaufort Wind Scale Chartrjv.premi74No ratings yet
- Sea StateDocument10 pagesSea StateviahulNo ratings yet
- Beaufort Wind Force Scale - Met OfficeDocument1 pageBeaufort Wind Force Scale - Met OfficeWee WeeNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Modul 2A Pengantar - Penghawaan AlamiDocument57 pages2018 - Modul 2A Pengantar - Penghawaan AlamiGilbert SalampessyNo ratings yet
- Beaufort Scale: Navigation SearchDocument6 pagesBeaufort Scale: Navigation SearchTom AlexNo ratings yet
- Beaufort ScaleDocument3 pagesBeaufort ScalemounirbenchammaNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Modul - 1 - Penghawaan - Alami - (A4) - ARSITEKTUR UKDWDocument69 pages2020 - Modul - 1 - Penghawaan - Alami - (A4) - ARSITEKTUR UKDWNELFIN GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Beaufort ScaleDocument6 pagesBeaufort ScaleWisnu KertaningnagoroNo ratings yet
- New 2016 Boat Design CategoriesDocument3 pagesNew 2016 Boat Design CategoriesYankov StoianovNo ratings yet
- Wind Speed TableDocument3 pagesWind Speed Tablesujith s pNo ratings yet
- FOrmat of BAltic QuestionnaireDocument7 pagesFOrmat of BAltic QuestionnaireNingkhanngam RUivahNo ratings yet
- BeaufortDocument1 pageBeaufortscotty.dubdubNo ratings yet
- Beaufort PDFDocument5 pagesBeaufort PDFAnonymous lVbhvJfNo ratings yet
- Beaufort eDocument1 pageBeaufort eHendrick SipahutarNo ratings yet
- PAGASA Weather TerminologyDocument4 pagesPAGASA Weather TerminologyRone Da-anoy100% (1)
- Nav III, s2 - Unit 4Document14 pagesNav III, s2 - Unit 4Alex BarbanNo ratings yet
- WDCS Shorewatch Seastate 3Document2 pagesWDCS Shorewatch Seastate 3sarana pengawasanNo ratings yet
- Quiz 11Document3 pagesQuiz 11Kris Myka J. Eg-oganNo ratings yet
- Weather Maps Overview and InterpretationDocument10 pagesWeather Maps Overview and InterpretationDwight TejanoNo ratings yet
- Present WeatherDocument30 pagesPresent WeatherHelloWorldNo ratings yet
- Beaufort ScalesDocument1 pageBeaufort ScalesBradley SmithNo ratings yet
- AE 6009 - Industrial Aerodynamics 2 MARKS & 16 MARKSDocument166 pagesAE 6009 - Industrial Aerodynamics 2 MARKS & 16 MARKSSrinivasan MuthuvelNo ratings yet
- Beaufort Wind ScaleDocument1 pageBeaufort Wind Scalekohinoor 1No ratings yet
- Beaufort Wind Scale: Developed in 1805 by Sir Francis Beaufort, U.K. Royal NavyDocument2 pagesBeaufort Wind Scale: Developed in 1805 by Sir Francis Beaufort, U.K. Royal NavyMIRCEANo ratings yet
- Mareviles - NatSci - Module 3Document3 pagesMareviles - NatSci - Module 3jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Wind Speed 1Document5 pagesWind Speed 1azim kaziNo ratings yet
- Sea StateDocument2 pagesSea StatepothirajkalyanNo ratings yet
- Local Winds: Circulation (Under Primary Circulation Planetary Wind Comes I.E. Trade Winds, Westerlies andDocument7 pagesLocal Winds: Circulation (Under Primary Circulation Planetary Wind Comes I.E. Trade Winds, Westerlies andMukesh Kumar100% (1)
- Best Practices - Design - Wind LoadsDocument10 pagesBest Practices - Design - Wind Loadsdheeraj SureshNo ratings yet
- Beaufort Scale Matching CardsDocument19 pagesBeaufort Scale Matching CardsqwertyNo ratings yet
- Coastal FieldworkDocument4 pagesCoastal FieldworkebidNo ratings yet
- NORTH - FIELD - Weather Forecast 1 PDFDocument3 pagesNORTH - FIELD - Weather Forecast 1 PDFMayank DixitNo ratings yet
- Beaufort ScaleDocument2 pagesBeaufort Scalezizu81No ratings yet
- StormGeo PT Pertamina - PHE-5 2017030408Document3 pagesStormGeo PT Pertamina - PHE-5 2017030408linkencielNo ratings yet
- Beaufort ScaleDocument1 pageBeaufort ScalejsstreetNo ratings yet
- Variable DescriptionDocument1 pageVariable DescriptionapurvaNo ratings yet
- Variable DescriptionDocument1 pageVariable DescriptionapurvaNo ratings yet
- Guide To Estimating Wind SpeedsDocument1 pageGuide To Estimating Wind SpeedsfcaskiiNo ratings yet
- Wind Speed Table For Conversion of Knots, Beaufort, M/s and KM/HDocument4 pagesWind Speed Table For Conversion of Knots, Beaufort, M/s and KM/HaauppalNo ratings yet
- Delhi ForecastDocument2 pagesDelhi ForecastAum PathakNo ratings yet
- 5 13+Beaufort+ScaleDocument4 pages5 13+Beaufort+ScaleJiramet NoompremNo ratings yet
- Beaufort ScaleDocument1 pageBeaufort ScaleEddie SenekalNo ratings yet
- A Level Stats 1 The Large Data SetDocument1 pageA Level Stats 1 The Large Data SetAlice BrancaNo ratings yet
- Sea State Description CodesDocument1 pageSea State Description CodesСимеон АйковNo ratings yet
- CicloviasDocument53 pagesCicloviasMari EstradaNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram Template 09Document1 pageFishbone Diagram Template 09elvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram Template 03Document1 pageFishbone Diagram Template 03elvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram Template 11Document1 pageFishbone Diagram Template 11elvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram Template 41Document1 pageFishbone Diagram Template 41elvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram Template 01Document1 pageFishbone Diagram Template 01Mixrajul MahfudziNo ratings yet
- Climate - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument6 pagesClimate - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Anemometer - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesAnemometer - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Barometer - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument5 pagesBarometer - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Barograph - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument3 pagesBarograph - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer Winds - More of Friction's Impact On Low Level Winds PDFDocument2 pagesBoundary Layer Winds - More of Friction's Impact On Low Level Winds PDFelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure - Force Exerted by The Weight of The AirDocument2 pagesAtmospheric Pressure - Force Exerted by The Weight of The Airelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesAtmospheric Pressure - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Circulation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesAtmospheric Circulation - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Anticyclone - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesAnticyclone - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Anemometer - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesAnemometer - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Throughflow - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument1 pageIndonesian Throughflow - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Itajaí Previsão Do TempoDocument1 pageItajaí Previsão Do TempoRobson SchneiderNo ratings yet
- 1517479331darwin F PDFDocument9 pages1517479331darwin F PDFJo K ERNo ratings yet
- Mind Map On Human Activities On RiverDocument1 pageMind Map On Human Activities On RiverMalia DamitNo ratings yet
- Reticulate Ice Veins in Ermafrost Northern Canada: Reply: MackayDocument3 pagesReticulate Ice Veins in Ermafrost Northern Canada: Reply: MackayFelipe PereiraNo ratings yet
- ClimateGlobalSystemsDocument96 pagesClimateGlobalSystemsMacsie Trish AndayaNo ratings yet
- Climate Study: Kota, RajasthanDocument11 pagesClimate Study: Kota, RajasthanMiriam ThomasNo ratings yet
- QuickGuide CIRA Geocolor 20171019Document2 pagesQuickGuide CIRA Geocolor 20171019Dardo Melgar RocaNo ratings yet
- SMS SRH-2D SedimentTransportDocument19 pagesSMS SRH-2D SedimentTransportthendyNo ratings yet
- Bsed Iii - Social Studies The Elements of GeographyDocument2 pagesBsed Iii - Social Studies The Elements of GeographyLulu BritanniaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Geology Plate Tectonics, Structural Geology Drifting Continents and Spreading SeasDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Geology Plate Tectonics, Structural Geology Drifting Continents and Spreading SeasshanecarlNo ratings yet
- Mizoram Civil Service ExaminationDocument2 pagesMizoram Civil Service ExaminationMapuii FanaiNo ratings yet
- Cec 207 Theory - HydrogeologyDocument76 pagesCec 207 Theory - HydrogeologyVietHungCao78% (18)
- Name - Period - : The Nike Shoe InvestigationDocument4 pagesName - Period - : The Nike Shoe InvestigationAnthony Bonafide Dakush0% (1)
- L9b Introduction To Flood HydrologyDocument9 pagesL9b Introduction To Flood HydrologyRachit GandhiNo ratings yet
- On India HomelandDocument31 pagesOn India HomelandNeel KamalNo ratings yet
- Leyte Is A Province That Located in The East of VDocument6 pagesLeyte Is A Province That Located in The East of Vedgar godinezNo ratings yet
- 11.metar and TafDocument51 pages11.metar and TafgebNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Earth Science FinalDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Test Earth Science FinalAngela Elaine UrquiaNo ratings yet
- Pre Board 12 22-23.pdf OneDocument17 pagesPre Board 12 22-23.pdf OneAraman AnsariNo ratings yet
- USA Comparison6Document30 pagesUSA Comparison6api-27259648No ratings yet
- Environmental Development: Edward Cornwell, Victor Sposito, Robert FaggianDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Development: Edward Cornwell, Victor Sposito, Robert FaggianAlexander VassilevNo ratings yet
- Danger Message Solas ch.5 Reg 31 and 32Document2 pagesDanger Message Solas ch.5 Reg 31 and 32PL BALASUBRAMANIANNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Delhi Ridge ForestDocument2 pagesA Case Study of Delhi Ridge ForestAksa RajanNo ratings yet
- 02 METARsDocument24 pages02 METARssaudia686No ratings yet
- Reservoirs & DamsDocument101 pagesReservoirs & DamsFarhan KaziNo ratings yet
- S7 Q4 Summative-Test-2Document7 pagesS7 Q4 Summative-Test-2joan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- Flood Risk Assessment Tuguegarao DILGDocument21 pagesFlood Risk Assessment Tuguegarao DILGMark Jerbert Gelacio100% (2)
- Anakisley - Vostok Ice Core ProjectDocument7 pagesAnakisley - Vostok Ice Core Projectapi-534698816100% (1)
- Hydraulics Engineering Lecture 1Document23 pagesHydraulics Engineering Lecture 1HashamSanchiNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Cause and Effects LA WorksheetDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming Cause and Effects LA WorksheetsasarckrcNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersFrom EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationFrom EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (37)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (64)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesFrom EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)