Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Operations at Daurala Sugar Complex
Uploaded by
Shubham0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
67 views2 pagesOriginal Title
OPERATIONS AT DAURALA SUGAR COMPLEX.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
67 views2 pagesOperations at Daurala Sugar Complex
Uploaded by
ShubhamCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
OPERATIONS AT DAURALA SUGAR COMPLEX(DCM SHRIRAM)
Introduction
Daurala Sugar Works was established in the pre independence era in the year 1932 at
Daurala , a small unknown village near Meerut on New Delhi - Haridwar National highway
no. 58.
Today it has ventured into various other activities - manufacture of pharmaceutical grade
sugar , sugarcane research farm, setting up of distillery , manufacture of IMFL, Bio-
Methanation , manufacture of aromatic chemical, co-generation of power etc.
Value Chain and Operations
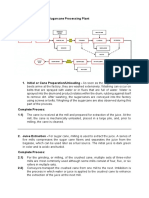
Once the sugar cane arrives at the complex, following process is followed there:-
1. Preparation:- After the cane arrives at the complex, it is mechanically
unloaded, and excessive soil and rocks are removed. The cane is cleaned by
flooding the carrier with warm water. or by spreading the cane on agitating
conveyors that pass through strong jets of water and combing drums.
Diffusion cells with a temperature of about 175 degrees F are used for the
cleaning process.
2. Juice Extraction:- crusher rollers break the cane and extract a large part of
the juice. Revolving knives cutting the stalks into chips are supplementary to
the crushers. The pressing process involves crushing the stalks between the
heavy and grooved metal rollers to separate the fiber (bagasse) from the
juice that contains the sugar.
3. The extracted juice, called vesou, contains 95 percent or more of the
sucrose present. The mass is then diffused, a process that involves finely
cutting or shredding the stalks. Next, the sugar is separated from the cut
stalks by dissolving it in hot water or hot juice.
4. The clarification (or defecation) process is designed to remove both soluble
and insoluble impurities (such as sand, soil, and ground rock) that have not
been removed by preliminary screening. The process employs lime and heat
as the clarifying agents. Milk of lime (about one pound per ton of cane)
neutralizes the natural acidity of the juice, forming insoluble lime salts.
5. The muds separate from the clear juice through sedimentation. The non-
sugar impurities are removed by continuous filtration. The final clarified juice
contains about 85 percent water and has the same composition as the raw
extracted juice except for the removed impurities.
6. To concentrate this clarified juice, about two-thirds of the water is removed
through vacuum evaporation. The vapors from one body can thus boil the
juice in the next one—the steam introduced into the first cell does what is
called multiple-effect evaporation. The vapor from the last cell goes to a
condenser. The syrup leaves the last body continuously with about 65
percent solids and 35 percent water.
7. Crystallization is the next step in the manufacture of sugar. Crystallization
takes place in a single-stage vacuum pan. The syrup is evaporated until
saturated with sugar. As soon as the saturation point has been exceeded,
small grains of sugar are added to the pan, or "strike." These small grains,
called seed, serve as nuclei for the formation of sugar crystals
8. Additional syrup is added to the strike and evaporated so that the
original crystals that were formed are allowed to grow in size.
The growth of the crystals continues until the pan is full. When
sucrose concentration reaches the desired level, the dense
mixture of syrup and sugar crystals, called massecuite, is
discharged into large containers known as crystallizers.
Crystallization continues in the crystallizers as the massecuite is
slowly stirred and cooled.
9. The high-speed centrifugal action used to separate the massecuite into
raw sugar crystals and molasses is done in revolving machines called
centrifugals. Once the sugar is centrifuged, it is "cut down" and sent to
a granulator for drying.
10. Damp sugar crystals are dried by being tumbled through heated
air in a granulator. The dry sugar crystals are then sorted by size
through vibrating screens and placed into storage bins. Sugar is then
sent to be packed.
Co- Generation and By Products
The plants generate Green Power using bagasse produced as a residue from cane sugar processing.
The green power so produced not only caters to the captive requirement of the sugar plant but is
also exported to the state-grid to replace the coal dominated power. Molasses is produced while
centrifuging which is used to produce alcohol. This is supplied to chemical and alcohol industry. The
other by product press mud is used as bio – fertilisers in the nearby areas.
You might also like
- 06 - Sugar Industry (B)Document35 pages06 - Sugar Industry (B)waleed chNo ratings yet
- Production: Santosh Kr. Paswan Roll No 138510 ME3 YearDocument21 pagesProduction: Santosh Kr. Paswan Roll No 138510 ME3 YearEricMargateNo ratings yet
- Sugar Production ProcessDocument2 pagesSugar Production ProcessedmarkNo ratings yet
- Sugar Cane to Sugar: The Refining ProcessDocument16 pagesSugar Cane to Sugar: The Refining ProcessMuhammad Irfan MalikNo ratings yet
- Production and Total Quality ManagementDocument12 pagesProduction and Total Quality ManagementPrachi PatilNo ratings yet
- OPTIMIZE CORN SYRUP PRODUCTIONDocument3 pagesOPTIMIZE CORN SYRUP PRODUCTIONJagna LannaoNo ratings yet
- Sugar Making ProcessDocument3 pagesSugar Making ProcessSameer KadamNo ratings yet
- Clarification and Defecation Process for Cane JuiceDocument10 pagesClarification and Defecation Process for Cane JuiceuglysnrNo ratings yet
- PROCESS FLOW OF MATERIALS THROUGH SUGAR REFINERYDocument12 pagesPROCESS FLOW OF MATERIALS THROUGH SUGAR REFINERYRnm ZltaNo ratings yet
- Description of Process - Nbsm-1Document10 pagesDescription of Process - Nbsm-1avisheklochunNo ratings yet
- 2005 RefineryBoilingSchemes SKILDocument12 pages2005 RefineryBoilingSchemes SKILRicardo A. PolNo ratings yet
- 02 Affination Mingling Centrifugation MeltingDocument2 pages02 Affination Mingling Centrifugation MeltingjantskieNo ratings yet
- A Summer Training Project Report in KARTHICDocument47 pagesA Summer Training Project Report in KARTHICBalu MahendraNo ratings yet
- Fresh Refined Suger-Meghna Group of IndustriesDocument16 pagesFresh Refined Suger-Meghna Group of Industriesiphone nokiaNo ratings yet
- Sugar Written ReportDocument25 pagesSugar Written Reportimo konsensyaNo ratings yet
- Engineering College Sugar Industry Waste Water ReportDocument20 pagesEngineering College Sugar Industry Waste Water ReportAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- 07-Refined Sugar Boiling, Jul. 26, 2017Document16 pages07-Refined Sugar Boiling, Jul. 26, 2017jantskie100% (1)
- Sugar IndustryDocument50 pagesSugar Industryzohaib ul hassanNo ratings yet
- 03-Carbonatation, Updated July 08Document32 pages03-Carbonatation, Updated July 08jantskie100% (2)
- Angel Rajput 2 Sem - Sugar IndustryDocument29 pagesAngel Rajput 2 Sem - Sugar IndustryMayank jain100% (1)
- Chemical Control PDFDocument85 pagesChemical Control PDFHarshit Khare100% (1)
- C04 - Automation of Sugar Boiling Process in Batch Vacuum Pans Using ABBDocument6 pagesC04 - Automation of Sugar Boiling Process in Batch Vacuum Pans Using ABBZishan TyagiNo ratings yet
- Removal of Suspended Fine Particulate Matter From Raw Juice PPT ScribdDocument45 pagesRemoval of Suspended Fine Particulate Matter From Raw Juice PPT ScribdKunchey JagadeeshNo ratings yet
- 21Document29 pages21Remington SalayaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Non-PolDocument6 pagesEffect of Non-PolKevynNo ratings yet
- 10-Refinery Control, Aug. 09, 2017Document12 pages10-Refinery Control, Aug. 09, 2017jantskieNo ratings yet
- Refining and Processing SugarDocument4 pagesRefining and Processing SugarRocío CapuñayNo ratings yet
- Sugar Plant Project ReportDocument5 pagesSugar Plant Project ReportBryan TanNo ratings yet
- Quadruple Evaporator EvaluationDocument8 pagesQuadruple Evaporator EvaluationRemington SalayaNo ratings yet
- Sugar Factory DefinitionDocument8 pagesSugar Factory Definitiontsrinivasan5083100% (1)
- Sugarcane Processing Technologies: by Md. Akram HossainDocument16 pagesSugarcane Processing Technologies: by Md. Akram HossainDeva Mk100% (1)
- Practical Action Sugar Production From SugarcaneDocument14 pagesPractical Action Sugar Production From Sugarcanesolupa2000No ratings yet
- Quality Changes During Storage of Raw Sugar.109132625Document9 pagesQuality Changes During Storage of Raw Sugar.109132625Carlos TomeyNo ratings yet
- Study of Centrifugal Sugar by Electrical MachinesDocument64 pagesStudy of Centrifugal Sugar by Electrical MachinesMohan Raj100% (1)
- Trials of A New Stirrer-Less Juice Sulphiter at Experimental Sugar FactoryDocument4 pagesTrials of A New Stirrer-Less Juice Sulphiter at Experimental Sugar FactoryInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Sugar Refinery ProcessDocument2 pagesSugar Refinery ProcessCharles Teo100% (1)
- Industrial Training Report On DSMDocument14 pagesIndustrial Training Report On DSMVipul Sharma0% (1)
- Manufacturing Amorphous Sugar in BrazilDocument9 pagesManufacturing Amorphous Sugar in BrazilnghiNo ratings yet
- RAPIDORRDocument12 pagesRAPIDORRKris FloraNo ratings yet
- CIAT Price List 2017 Cool Designs1Document60 pagesCIAT Price List 2017 Cool Designs1ikac3No ratings yet
- Automation, Control To Save FfeDocument10 pagesAutomation, Control To Save Ffenghi100% (1)
- Chemical Control (Ansi Sugar Tech. Third Year) : by Dr. Jahar Singh Apst NsikanpurDocument24 pagesChemical Control (Ansi Sugar Tech. Third Year) : by Dr. Jahar Singh Apst NsikanpurSameer Agale100% (1)
- Sugar IndustriesDocument46 pagesSugar Industriesshine king100% (1)
- Energy Audit Benefits for Sugar and Distillery UnitsDocument4 pagesEnergy Audit Benefits for Sugar and Distillery UnitsBala MuruganNo ratings yet
- Module 11: Sugar - RefiningDocument35 pagesModule 11: Sugar - RefiningsenaNo ratings yet
- Panfloor BoilingDocument45 pagesPanfloor Boilingwaziri maulidiNo ratings yet
- Final Molasses Purity ControlDocument8 pagesFinal Molasses Purity Controlzafar Bukhari100% (1)
- PROCESS in RAW SUGAR Production of FFHCDocument27 pagesPROCESS in RAW SUGAR Production of FFHCTenebroso Pevie Anne100% (1)
- Diffusion Vs MillingDocument4 pagesDiffusion Vs MillingcbqucbquNo ratings yet
- Sugar Mill ControlDocument12 pagesSugar Mill ControlZishan Tyagi100% (1)
- Performance indicators for sugar processing efficiencyDocument3 pagesPerformance indicators for sugar processing efficiencyJavier Manuel IbanezNo ratings yet
- Short Notes For InterviewDocument15 pagesShort Notes For InterviewMuhammad Arif ShafiNo ratings yet
- M.SC Sugar Tech SyllabusDocument39 pagesM.SC Sugar Tech SyllabusCandra AvengerzNo ratings yet
- Calculations Used in Cane-Sugar Factories A Practical System of 1000766688Document203 pagesCalculations Used in Cane-Sugar Factories A Practical System of 1000766688adiseif100% (3)
- Tan Quiz 2Document3 pagesTan Quiz 2Bryan TanNo ratings yet
- The Sugar IndustryDocument22 pagesThe Sugar IndustryAbraham wisdomNo ratings yet
- Sugar and Confectionery Technology: Processing and Industry DevelopmentDocument26 pagesSugar and Confectionery Technology: Processing and Industry Developmentgrace mwenjeNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations For Sugarcane PlantDocument3 pagesUnit Operations For Sugarcane PlantJohn Christian Usero100% (1)
- Sugar ProcessingDocument46 pagesSugar ProcessingChristian Jay Baliling Sablada100% (1)
- HARSHAD MEHTA: THE BIG BULL GONE WILD SCAMDocument28 pagesHARSHAD MEHTA: THE BIG BULL GONE WILD SCAMShubhamNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV Managing Currency Risk and Interest Rate RiskDocument54 pagesUNIT-IV Managing Currency Risk and Interest Rate RiskShubhamNo ratings yet
- Extension of Last Date of Examination Form 30.04.2021Document1 pageExtension of Last Date of Examination Form 30.04.2021UdbhavNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to EntrepreneurshipDocument54 pagesAn Introduction to EntrepreneurshipMd Rizwan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Equity and EfficiencyDocument4 pagesEquity and EfficiencyShubhamNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating AgencyDocument47 pagesCredit Rating AgencyShubhamNo ratings yet
- Additional Disclosure StatementsDocument40 pagesAdditional Disclosure StatementsShubhamNo ratings yet
- Operations at Daurala Sugar ComplexDocument2 pagesOperations at Daurala Sugar ComplexShubhamNo ratings yet
- Additional Disclosure StatementsDocument40 pagesAdditional Disclosure StatementsShubhamNo ratings yet
- Additional Disclosure StatementsDocument40 pagesAdditional Disclosure StatementsShubhamNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating Information Services Equity ResearchDocument6 pagesCredit Rating Information Services Equity ResearchShubhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 of LPL Textbook PDFDocument26 pagesChapter 3 of LPL Textbook PDFandreaNo ratings yet
- Performance Theory For Hot Air Balloons: The Balloon Works, Inc., Statesville, N.CDocument4 pagesPerformance Theory For Hot Air Balloons: The Balloon Works, Inc., Statesville, N.CEbubekir ErkanNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet and Presentation Skills SyllabusDocument4 pagesSpreadsheet and Presentation Skills SyllabusGbox CTCNo ratings yet
- USD - DPF Cleaning Machine - POSEYDON1000 - PolDocument8 pagesUSD - DPF Cleaning Machine - POSEYDON1000 - PolAbaidi RabieNo ratings yet
- A Powerful Graphic Liquid Crystal Display: Column #47, March 1999 by Lon GlaznerDocument16 pagesA Powerful Graphic Liquid Crystal Display: Column #47, March 1999 by Lon GlaznerVijay P PulavarthiNo ratings yet
- PassportDocument4 pagesPassportVijai Abraham100% (1)
- Types of Motivation in Language LearningDocument8 pagesTypes of Motivation in Language LearningAlya IrmasyahNo ratings yet
- 2013 KTM 350 EXC Shop-Repair ManualDocument310 pages2013 KTM 350 EXC Shop-Repair ManualTre100% (7)
- Down Syndrome Research PaperDocument11 pagesDown Syndrome Research Paperapi-299871292100% (1)
- ENGLISH 7 FIRST QUARTER EXAMDocument2 pagesENGLISH 7 FIRST QUARTER EXAMAlleli Faith Leyritana100% (1)
- Wiring Diagram Obp 1 v2Document5 pagesWiring Diagram Obp 1 v2Jorge Luis Vera AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Samsung C&T AuditDocument104 pagesSamsung C&T AuditkevalNo ratings yet
- BATCH Bat Matrix OriginalDocument5 pagesBATCH Bat Matrix OriginalBarangay NandacanNo ratings yet
- India-An Underdeveloped Economy: (Contd )Document6 pagesIndia-An Underdeveloped Economy: (Contd )Amrita Prashant IyerNo ratings yet
- School RulesDocument2 pagesSchool RulesAI HUEYNo ratings yet
- ACCT250-Auditing Course OutlineDocument7 pagesACCT250-Auditing Course OutlineammadNo ratings yet
- Kepler's ProblemDocument21 pagesKepler's ProblemGustavo MiasatoNo ratings yet
- Pathways Rw1 2e U7 TestDocument9 pagesPathways Rw1 2e U7 TestGrace Ann AbanteNo ratings yet
- Bread and Pastry Production NC II 1st Edition 2016Document454 pagesBread and Pastry Production NC II 1st Edition 2016Brian Jade CadizNo ratings yet
- MarketNexus Editor: Teri Buhl Character LetterDocument2 pagesMarketNexus Editor: Teri Buhl Character LetterTeri BuhlNo ratings yet
- Mora Solvendi (Delay of The Debtor)Document11 pagesMora Solvendi (Delay of The Debtor)John Paul100% (1)
- Sec 4 RA 6713 & Sec 3 RA 3019 OutlineDocument4 pagesSec 4 RA 6713 & Sec 3 RA 3019 OutlineAivan Charles TorresNo ratings yet
- 6 - 2010 Chapter 5 - Contrasting Cultural ValuesDocument39 pages6 - 2010 Chapter 5 - Contrasting Cultural ValuesHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Are The Risk Management Tools at Your Law Firm Working?Document17 pagesAre The Risk Management Tools at Your Law Firm Working?vantoffNo ratings yet
- Thesis Chapter 123Document15 pagesThesis Chapter 123Chesca Mae PenalosaNo ratings yet
- Policy - SIM Cards Point of Sale Registration EngDocument6 pagesPolicy - SIM Cards Point of Sale Registration EngSHALOM SHUMBANo ratings yet
- The Definition and Unit of Ionic StrengthDocument2 pagesThe Definition and Unit of Ionic StrengthDiego ZapataNo ratings yet
- Diagrama RSAG7.820.7977Document14 pagesDiagrama RSAG7.820.7977Manuel Medina100% (4)
- Teaching As Noble ProfessionDocument1 pageTeaching As Noble ProfessionJeric AcostaNo ratings yet
- Perlman Janice, The Myth of Marginality RevisitDocument36 pagesPerlman Janice, The Myth of Marginality RevisitLuisa F. RodriguezNo ratings yet