Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Buku Ajar Modul 5
Uploaded by
Cynthia Sasmita DewiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Buku Ajar Modul 5
Uploaded by
Cynthia Sasmita DewiCopyright:
Available Formats
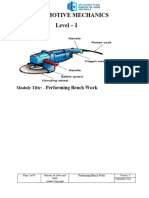
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 0
MODULE 5
BENCH WORK
OBJECTIVES
1. Students are able to understand about bench work process.
2. Students are able to understand bench work tools.
OUTLINES
5.1 Introduction of Bench Work Process
5.2 Classification of Some Bench Work Operation
5.3 Tool Used
5.4 Measuring Instruments
5.5 Safety Equipment
BASIC THEORY
Introduction of Bench Work
Bench work is any activity that the production process is done manually, without using
the engine, worked on the desk. The activities included in the bench work are chipping, filling,
scrapping, grinding, marking, drilling, reaming, tapping, dying, sawing. the process of bench
work practice required skill and precision in the execution of the workpiece, so students can
make the bench work practice as a measure to prepare for potential labor as industry
professionals.
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 1
Classification of Some Bench Work
Operation
The Bench Work Operations are classified into several process below.
1. Chipping
Chipping is working on materials by a wedge-shaped tool (the chisel) in order to
separate or chip material. The cutting effect of the chisel is achieved by hammering on
the head end of the chisel, which is an energy and time consuming operation.
Figure 5.1 Chipping
(Source: http://static.republika.co.id)
2. Hand Scraping
Hand Scraping is the process of using a scraper held in the hands to remove
small amounts of metal from a precision surface so as to provide an accurate bearing
surface to within some tolerance. The hand scraping tools usually used are made from:
a. High Speed Steel (HSS)
b. Tool Steel
c. Carbide Steel
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 2
The tools can be use to scraping a brass, casted steel, bronze, etc. The tools can’t be
used to scrap the steel, for steel we can use tools that are made from hard metal. Every
tools has a different shape on the point it depends on what it used for, example: the
tools to scrap casted steel is different with the tools to scrap brass, the tools to scrap
casted steel and to scrap brass has a different angle. So we can conclude that the shape
of the tools is depend on the material.
Figure 5.2 Hand Scraping
(Source: http://www.practicalmachinist.com)
3. Reaming
Reaming is a process of enlarging the hole with a very high accuracy dimension.
Reaming process use reaming machine. Before the reaming process, the material
should have been drilled.
Figure 5.3 Manual Reaming
(Source : www. Magneticdrillingmachines.com)
Reaming process have a few type, there are hand reamer, machine reamer,
chucking reamer, fluting reamer, expanding reamer and adjustable reamer.
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 3
4. Sawing
Sawing is a basic machining process in which chips are produced by a
succession of small cutting edges, or teeth, arranged in a narrow line on a saw “blade”.
Here are some kind of sawing.
a. Crosscut Saw
Crosscut is used to cut across the grain of the wood. Crosscut saw has a teeth
with an angle back and beveled edge.
Figure 5.4 Crosscut Saw
(Source : www.hobby-market.eu)
b. Rip Saw
Rip saw is used to cut parallel to the direction of the wood. The Rip saw cut
teeth doesn’t have an angle beveled nor beveled. Instead, the teeth bend left
and right in the alternating pattern.
Figure 5.5 Rip Saw
(Source : www.toolinfoandreviews.com)
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 4
c. Keyhole Saw
Keyhole is used to cut hole for pipe, electrical outlets or fixtures in floors,
walls, and ceilings. Keyhole saw teeth can chew through tough material like
drywall.
Figure 5.6 Keyhole Saw
(Source : www.neteberg.eu)
d. Coping Saw
Coping saw is used to cut curves and other intricate shapes, don’t forget to
bust out the coping saw.
Figure 5.7 Coping Saw
(Source : www.static.axminster.co.uk)
e. Back Saw
Back saw have a stiffening metal rib on the edge opposite the cutting edge.
This allows for better control and more precise cutting than with other
types of saws.
Figure 5.8 Back Saw
(Source : www.s3.amazonaws.com)
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 5
f. Hack Saw
The hacksaw is used to cut steel and other metals. It can also be used to cut
plastics, although it is not normally used to cut woods. Blades are supplied
in two lengths, 250 mm and 300 tmm.
Figure 5.9 Hack Saw
(Source : www.stanleytools.com)
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 6
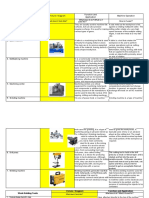
Tool Used
These are some kind of tools usually used in Bench Work Process:
Tabel 5.1 Bench Work Equipment
Tool Name Figure Description
This tool is used to cut a variety of
alloy (alloy) and steel with low
Hack Saw
carbon content.
This tool is used with a hammer to
make a point mark on a piece of steel
before using a drill. The signs point
Centre punch
to prevent the drill so as not to
deviate from the desired location of
the holes.
are names used for a type of coated
abrasive that consists of sheets of
Sandpaper paper or cloth with abrasive material
glued to one face.
Vice is a clamp tool to clamp the
workpiece to be filed, chiseled,
sawed, on tap, in sney, etc. By
Vice
rotating the shaft (handle) vice, then
vice mouth will open or removing
the workpiece that is being done.
Thread die used to make the screw
Thread die in a piece of circle iron or for fixing
screw that is damaged.
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 7
Tabel 5.2 Bench Work Equipment (cont.)
Tool Name Figure Description
Thread tap is a tool for cutting
threaded to fit the bolt or bolt
cropping partner. This tool can be
Thread tap
used to fix the nut or the same tool
that thread irregular (cross
threaded).
a tool with a characteristically
shaped cutting edge (such as wood
chisels have lent part of their name
to a particular grind) of blade on its
Chisel
end, for carving or cutting a hard
material such as wood, stone, or
metal by hand, struck with a mallet,
or mechanical power.
Policap was sandpaper shaped a cap
to ease sanding a workpiece which
Policap have the hole. Sandpaper stamp set
this used on a stamp holder and air
die grinder as backend .
Handheld power tools used for
grinding, sanding, honing,
Die Grinder polishing, or machining material
(typically metal, but also plastic or
wood).
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 8
Tabel 5. 1Bench Work Equipment (cont.)
Tool Name Figure Description
Hammer is
Ball Peen Hammer a tool or device
that delivers a
blow (a sudden
impact) to an
object. Hammers
Chisel Hammer are used to strike
Hammer a job or a tool.
They are made of
forged steel and
Straight Peen the handle is
Hammer made by wood of
various size and
shapes to suit
Soft Hammer various purposes.
Measuring Instrument
1. Steel Ruler
Steel Ruler is used for taking linear measurements of blanks and articles to an accuracy
of range from 1.0 to 0.5 mm. It consists of a strip of hardened steel having line graduations
etched or engraved at interval of fraction of a standard unit of length.
Figure 5. 10 Steel Ruler
(Source : www.hultrafos.com)
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 9
2. Divider
Divider is used to measuring, transferring, marking off the distance. These are the way
to use divider.
a. Loosen the nut.
b. Set the distance of the divider.
c. Tighten the nut.
d. Plug one of the sharp part to the surface.
e. Turn the handle until it marks.
Figure 5. 11 Divider
(Source : www.northentool.com)
3. Micrometer
Micrometer is one of the measure equipment that can be used to measure the length,
thickness, and the outer diameter of a part with the accuracy 0.001 mm.
Figure 5. 12 Micrometer
(Source : www.fowlerprecision.com)
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 10
4. Vernier Caliper
Vernier caliper is a measure equipment with the accuracy 0.01 mm. Vernier caliper
divided into 2 part : the constant part and the moving part.
Figure 5. 13 Vernier Caliper
(Source : www.chicagobrand.com)
Safety Equipment
These are some safety equipment usually used in manufacturing process laboratory.
Tabel 5. 3 Safety Equipment
Safety Equipment Figure Function
Protect eyes from dangerous
Goggles things like chips, chemical,
etc.
Safety Mask Filter the bad air quality.
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 11
Tabel 5. 2 Safety Equipment (cont.)
Safety Equipment Figure Function
Protect body from chemical,
Wearpack
cuts, or burn.
Protect foot from danger
like chemical, heavy things
Safety Shoes
sharp things, burn, etc.
Protect hands from whether
Hand gloves from chemicals, cuts or
burns.
Manufacturing Process Laboratory 12
REFERENCES
Black, J. (2008). DeGarmo's Material and Process in Manufacturing. United State of America:
Jhon Wiley and sons,inc.
Kapakjian, S. (2009). Manufacturing Engineering and Technology 6th edition. united state of
america: pearson education.
Laboratory, A. M. (2016). Modul Praktikum Proses Manufaktur. Bandung: Manufacturing
Process Laboratory.
Wagiran. (2011). Modul Praktek Kerja Bangku. Yogyakarta: Universitas Negri Yogyakarta.
13
You might also like
- Sagarmatha Engineering CollegeDocument4 pagesSagarmatha Engineering CollegePrashant Sah60% (5)
- Unit 2 Broaching: StructureDocument8 pagesUnit 2 Broaching: Structurempraga93No ratings yet
- ToolbitDocument7 pagesToolbitVon Allen DayoNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Segmented Woodturning: Projects, Techniques & Innovations for Today’s WoodturnerFrom EverandThe Fundamentals of Segmented Woodturning: Projects, Techniques & Innovations for Today’s WoodturnerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ch3 - Metal CuttingDocument30 pagesCh3 - Metal Cutting03 ABHISHEKNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 (Broaching, Lathe, Planer, Boring Machines)Document74 pagesUnit-3 (Broaching, Lathe, Planer, Boring Machines)KrupalPawarNo ratings yet
- Machining OperationsDocument5 pagesMachining Operationsaswin jithuNo ratings yet
- Me 212 Report IfiokobongDocument15 pagesMe 212 Report IfiokobongIfiokobong AkpanNo ratings yet
- 7 Cutting PDFDocument27 pages7 Cutting PDFAshwani KumarNo ratings yet
- (Group 1) Group Project Final ReportDocument17 pages(Group 1) Group Project Final ReportNurul Solehah SuhailiNo ratings yet
- CNC MachiningDocument4 pagesCNC MachiningAdrianNo ratings yet
- Dawit SolomonDocument24 pagesDawit Solomondawit solomonNo ratings yet
- What Is Fitting Workshop Practice PresenDocument35 pagesWhat Is Fitting Workshop Practice Presen22wj1a0280No ratings yet
- WorkshopDocument10 pagesWorkshopAhmed KucherNo ratings yet
- Ted 361 MaterialDocument20 pagesTed 361 MaterialNelly NelsonNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 FittingDocument33 pagesUnit - 3 Fitting20BCS4054 MADHAVAN V100% (1)
- Machining Operations: Text-Based VersionDocument5 pagesMachining Operations: Text-Based Versionvijayans_1No ratings yet
- Bench Work 1Document41 pagesBench Work 1Tadesse BalchaNo ratings yet
- HammerDocument16 pagesHammersachinkhadka009No ratings yet
- PRESSTOOL MASTER 1st SemDocument111 pagesPRESSTOOL MASTER 1st Semmathapatikumar56No ratings yet
- Compound Tool For Press Tool WasherDocument6 pagesCompound Tool For Press Tool WasherDhaneshNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis of Wood Lathe: Poonam Diwan, Amrita SinghDocument11 pagesNumerical Analysis of Wood Lathe: Poonam Diwan, Amrita SinghRitik GaudwalNo ratings yet
- Workshop ManualDocument96 pagesWorkshop ManualDatta YallapuNo ratings yet
- Fabrication ReportDocument14 pagesFabrication ReportFazliy RafiyNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Trends of 2020Document124 pagesManufacturing Trends of 2020Mr.N.S. NateshNo ratings yet
- Sheet Production TechnologyDocument23 pagesSheet Production TechnologyOmar AlyNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Tech. IIDocument13 pagesManufacturing Tech. IIanon_376852568No ratings yet
- Gamsin Manufacturing ProcessDocument6 pagesGamsin Manufacturing ProcessWiraNo ratings yet
- Descriptions of Tools in InmatproDocument6 pagesDescriptions of Tools in InmatproArabella PASAHOLNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument28 pagesReportRajesh kvNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Metal Structural RepairDocument5 pagesAircraft Metal Structural RepairKatrina VilladiegoNo ratings yet
- Me 6402-Manufacturing Technology IiDocument13 pagesMe 6402-Manufacturing Technology Iichinnarasu132No ratings yet
- A Study On Types of Lathe Machine and Operations: ReviewDocument6 pagesA Study On Types of Lathe Machine and Operations: ReviewJames UgbesNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet No5Document11 pagesInformation Sheet No5Kher Bee A. PingolNo ratings yet
- Metal Cutting Processes 2 - Milling: Home HandoutDocument13 pagesMetal Cutting Processes 2 - Milling: Home HandoutpbtambeNo ratings yet
- Buku Ajar 6Document16 pagesBuku Ajar 6Cynthia Sasmita DewiNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology Lab IDocument43 pagesManufacturing Technology Lab IMECHANICAL SMCETNo ratings yet
- Machine Picture / Diagram Function and Application Machine OperationDocument6 pagesMachine Picture / Diagram Function and Application Machine OperationArabella PASAHOLNo ratings yet
- Expose Metal Forming and PracticeDocument11 pagesExpose Metal Forming and PracticePuwa CalvinNo ratings yet
- Me8451 2 MARKS - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net 2 PDFDocument14 pagesMe8451 2 MARKS - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net 2 PDFVignesh VigneshNo ratings yet
- Key 2Document22 pagesKey 2Jury.rahulNo ratings yet
- Theory of Metal Cutting PDFDocument47 pagesTheory of Metal Cutting PDFEmmanuel KutaniNo ratings yet
- BroachingDocument20 pagesBroachingKareem AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- ME3382-MT Lab Manual Part-1Document112 pagesME3382-MT Lab Manual Part-1KIRTHIVASAN K V D 905250% (2)
- Progressive Report GRP DDocument12 pagesProgressive Report GRP Dbarkandaj0222222No ratings yet
- Design of 360 Degree Flexible Drilling Machine IJERTV8IS010084Document3 pagesDesign of 360 Degree Flexible Drilling Machine IJERTV8IS010084Yash chouhanNo ratings yet
- Krishna Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesKrishna Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringVivek BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Modelling, Analysis and Development of Progressive Die For Seat RailDocument9 pagesModelling, Analysis and Development of Progressive Die For Seat RailVineela ChNo ratings yet
- Modelling, Analysis and Development of Progressive Die For Seat RailDocument9 pagesModelling, Analysis and Development of Progressive Die For Seat RailVineela ChNo ratings yet
- The Design and Function of Surgical Drills and K-WiresDocument7 pagesThe Design and Function of Surgical Drills and K-Wirescitra ahdiNo ratings yet
- Machining and CNC: CAD/CAM Is Said As Two WordsDocument4 pagesMachining and CNC: CAD/CAM Is Said As Two WordsIvan Mario VillcaNo ratings yet
- Sawing ProcessingDocument22 pagesSawing ProcessingGilang RestuNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal OperationsDocument33 pagesSheet Metal Operationsziad almnaseerNo ratings yet
- Fitting - Fabrication Manual 2020Document14 pagesFitting - Fabrication Manual 2020Malik AbubakerNo ratings yet
- Chip Formation: Manufacturing Technology-IiDocument20 pagesChip Formation: Manufacturing Technology-IiSachin BharadwajNo ratings yet
- 6387717748PP Lab 4me4-23Document108 pages6387717748PP Lab 4me4-23suhanimalviya595No ratings yet
- Brillo John Edison V Lab3Document13 pagesBrillo John Edison V Lab3John Edison BrilloNo ratings yet
- Bab 2Document9 pagesBab 2Izat TokidokiNo ratings yet
- Classic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersFrom EverandClassic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- A Mathematical Model and Tabu Search Algorithm For Multi-Manned AlbpDocument20 pagesA Mathematical Model and Tabu Search Algorithm For Multi-Manned AlbpCynthia Sasmita DewiNo ratings yet
- A Branch-And-Bound Algorithm For Assembly Line Worker Assignment and Balancing ProblemDocument10 pagesA Branch-And-Bound Algorithm For Assembly Line Worker Assignment and Balancing ProblemCynthia Sasmita DewiNo ratings yet
- Buku Ajar Modul 4Document17 pagesBuku Ajar Modul 4Cynthia Sasmita DewiNo ratings yet
- Buku Ajar 6Document16 pagesBuku Ajar 6Cynthia Sasmita DewiNo ratings yet
- Buku Ajar 3.2Document8 pagesBuku Ajar 3.2Cynthia Sasmita DewiNo ratings yet
- Buku Ajar 3.2Document8 pagesBuku Ajar 3.2Cynthia Sasmita DewiNo ratings yet
- Juk MS-191 261 261JDocument38 pagesJuk MS-191 261 261JRHoskaNo ratings yet
- Hygrobar B WaterstopDocument2 pagesHygrobar B WaterstopMahesh SavandappaNo ratings yet
- Reducing Field Sample of Aggregate To Test Sample ASTM C 702, D75Document16 pagesReducing Field Sample of Aggregate To Test Sample ASTM C 702, D75Shekh AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Paving CodeDocument12 pagesPaving CodeSiraj KuvakkattayilNo ratings yet
- Assistant Professor Mechanical Department: Mr. G. Aravind ReddyDocument67 pagesAssistant Professor Mechanical Department: Mr. G. Aravind ReddySai RamNo ratings yet
- Formwork DesignDocument2 pagesFormwork DesignBilal Ahmed Barbhuiya67% (3)
- Determination of The Technological Parameters Process For Continuously Cast Brass IngotDocument7 pagesDetermination of The Technological Parameters Process For Continuously Cast Brass Ingotramadan slimNo ratings yet
- Pla RubricsDocument89 pagesPla Rubricsapi-313716520No ratings yet
- Sikatop 71 CuringDocument3 pagesSikatop 71 CuringVirah Sammy ChandraNo ratings yet
- Amendment No. 2 April 2017 TO Is 16098 (Part 2) : 2013 Structured-Wall Plastics Piping Systems For Non-Pressure Drainage and Sewerage - SpecificationDocument1 pageAmendment No. 2 April 2017 TO Is 16098 (Part 2) : 2013 Structured-Wall Plastics Piping Systems For Non-Pressure Drainage and Sewerage - SpecificationTesting CIPET GuwahatiNo ratings yet
- Updated SP-511Document7 pagesUpdated SP-511Feroz GullNo ratings yet
- 1920 000132 Sec 14 Rev 0Document28 pages1920 000132 Sec 14 Rev 0amber sareenNo ratings yet
- Syed Saif Ali - RA1712002010039: M.Tech - CEM - CN2050-Project Phase - IIDocument57 pagesSyed Saif Ali - RA1712002010039: M.Tech - CEM - CN2050-Project Phase - IISaif AliNo ratings yet
- Katalog ProdukDocument20 pagesKatalog ProdukWaridi RidiNo ratings yet
- IGBC - Chapter 5: Materials & ResourcesDocument1 pageIGBC - Chapter 5: Materials & Resourcesar.danielNo ratings yet
- MRTS29Document10 pagesMRTS29thecarlosgarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit Weight or Density of Different Construction MaterialsDocument2 pagesUnit Weight or Density of Different Construction MaterialsHari RNo ratings yet
- HYDAC High Pressure Ball ValvesDocument8 pagesHYDAC High Pressure Ball ValvesOscar Andrés Aponte MurciaNo ratings yet
- Strength Properties of Roller Compacted Concrete Pavement (RCCP) UnderDocument13 pagesStrength Properties of Roller Compacted Concrete Pavement (RCCP) UnderRidwanNo ratings yet
- 6063 VS 63400Document1 page6063 VS 63400siju1974No ratings yet
- Vinyl Floor InstallDocument10 pagesVinyl Floor InstallMoose112No ratings yet
- Soportes EricoDocument12 pagesSoportes EricoJulian RiverosNo ratings yet
- Fronius Cold Metal TransferDocument16 pagesFronius Cold Metal Transferbonmarche28No ratings yet
- Post Tensioned SlabsDocument25 pagesPost Tensioned SlabsTolu AdegbenjoNo ratings yet
- FabricationDocument7 pagesFabricationg-ipgp23271000No ratings yet
- Bebot 1Document9 pagesBebot 1Luna RonquilloNo ratings yet
- g+1 Bid ResponseDocument31 pagesg+1 Bid Responseabel mekonen100% (1)
- AssistantSub Engineer (असिस्टेन्ट सव इन्जिनियर)Document5 pagesAssistantSub Engineer (असिस्टेन्ट सव इन्जिनियर)asmit khadkaNo ratings yet
- Brickwork and Stonework SupportDocument20 pagesBrickwork and Stonework SupportSanel GrabovicaNo ratings yet
- Hardox 450 Data SheetDocument2 pagesHardox 450 Data SheetmatthewpincottNo ratings yet