Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acyanotic Heart Diseases ASD-Atrial Septal Defect
Uploaded by
Princess Leganson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Ca 3
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesAcyanotic Heart Diseases ASD-Atrial Septal Defect
Uploaded by
Princess LegansonCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Congenital Heart Disease Harsh sytolic murmur
2 types
Diagnostic tests
1. Acyanotic
Cardiac catheterization
- arterial to venous
Nursing responsibilities
-left to right shunting
-consent
-oxygenated to unoxygenated
-assess v.s
Acyanotic heart - inform that fluttering feeling and
desire to cough may be experience
diseases during the procedure
-affected limb should be immobilzed
and extended
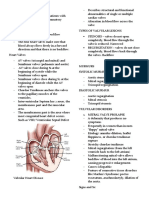
ASD- Atrial septal Echocardiography - cardiac
dysrythmias
defect Chest xray
- abnormal opening in the intra atrial
septum. ! No restrictions with client with small
-failure of foramen ovale to close ASD
3 types Sx management :small ASD-dacron
1.ostium primum-opening on the lower end patch
of ostium
VSD -Ventricular
2.ostium secundum- opening near the
center septal defect
3.sinus venosus- junction in the superior
- opening is present in the septum between
vena cava and right atrium
the 2 ventricles
- abnormal opening in the right
Manifestations
ventricle and left ventricle
Failure to thrive
-this impairs the effort of the heart because
Murmur and thrill heard best on left 2- blood that should go into the aorta and out
3rd intercostal space of the body is shunted back into
the pulmonary circulation resulting in right fetal structure that connects the
ventricle hypertrophy and increase pressure pulmonary artery to the aorta.
in the pulmonary artery. !Ductus Arteriosus -closure should
-increase pressure in left side of the heart , begin at the first breath , and the
o2 blood from left ventricle to right ventricle complete closure should be 3months
= increase blood volume in right ventricle= Functional closure - partial closure, 15
increase blood flow to the lungs = to 24 hours
pulmonary congestion Anatomic closure- complete closuee,
Signs and symptoms of left ventricle 3-4 weeks
failure One reason that the ductus remains
-loud harsh pansystolic murmur open in fetal life is because of the
-pulmonary manifestation stimulation of prostaglandins
-slow wt. Gain and poor growth particularly PGE from the placenta and
-mur mur = during ventricular systole the low o2 level of the fetal blood
Manifestations
Diagnostic tests -wide pulse pressure
Cardiac catheterization -Bounding peripheral pulses or apical
Electrocardiograph pulses
Chest x ray -Machinery murmur
! Small VSD - Dacron patch Diagnostic tests
! Large VSD - Pulmonary artery -Cardiac catheterization
banding =to prevent pulmonary -Echocardiograph
congestion -Chest x ray
Treatment
PDA- Patent ductus Ibuprofen
arteriosus Antibiotic prophylaxis
Drug of choice - INDOMETHACIN-
- opening in the pulmonary artery and
prostaglandin inhibitor , can be given
aorta
in 3 doses effective when given to
- ventricular hypertrophy and increase
clients less than 13 days old and not
pressure in pulmonary artery
effective when given after 4 - 6 weeks.
! Ductus arteriosus is an accessory
Cool lower extremities
Contraindicated with: necrotizing Epistaxis
enterocolitis, sepsis, renal failure, Headache
bleeding disorders Upper limb hypertension
COA -Coarcation of Lower limb hypertension
Intermittent claudication- decrease o2
aorta ! Nursing responsibility - monitor blood
- narrowing of the aortic arch segment pressure in all 4 extremities
- narrowing of the lumen of the aorta
due to constricting band Diagnostic tests
2 locations where it commonly occurs -ECG
1. Preductal - the constriction exists -EOG
between the subclavian artery and the -Cardiac catheterization
ductus arteriosus, or narrowing occurs -Chest x ray
before the ductus arteriosus . Treatment
2. Postductal- the constriction is distal Prostaglandin E
to the ductus arteriosus or the Dopamine - support or enhance
narrowing occurs after the ductus myocardial contraction (left ventricle)
arteriosus. Surgical Treatment
-End to end anastomosis
3 major vessels of aortic arch-they supply -Balloon angiography
blood on the upper half of the body -Stent
- brachio cephalic
- left subclavian
2. Cyanotic Heart Disease
-left common artery
- Right to Left Shunting
-Venous to Arterial
-Unoxygenated to Oxygenated
Cyanotic heart disease
Manifestations
Absent or weak femoral pulse
Complete repair: closure of the large VSD
and resection of the stenosis with pericardial
Tetralogy of fallot paetch to enlarge the right ventricular
- it consists of 4 anomalies : over outflow tract.
ridding of the aorta, large VSD,
pulmonary stenosis and right
TGA- Transposition of
ventricle hypertrophy due to the great arteries
pulmonary stenosis. - in TGA the aorta arises from the right
ventricle instead of the left and the
Manifestations pulmonary artery arises from the left
Cyanosis -tet spells or hyper cyanotic ventricle instead of the right.
spells- acute episode of cyanosis when -mixed blood flow
o2 requirement exceeds blood supply. -reverse of the major vessels
- no communication between pulmonary
Diagnostic test and systemic circulation
-Chest xray- BOOT SHAPED HEART - vital organs are supplied with
deoxygenated blood
Non pharmacologic management: Diagnostic tests
knee chest position, fetal position, -Chest xray - EGG SHAPED HEART
shrimp position, squat position Surgical management
-Balloon atrio septostomy/ rashkind
procedure- switching of the great vessels in
Pharmacologic management the ventricular level
Morphine sulfate -Jatene procedure-switching of the great
Propranolol( inderal) - DOC - vessels in atrial level
decreases pulmonary stenosis
Side effects – impotence ! Disorders with increased pulmonary
blood flow
Surgical Management Ventricular septal defect
Palliative : Blalock taussig shaunt
Atrial septal defect
Patent ductus arteriosus
You might also like
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Module No. Date: Topic:: Cues/Questions/ Keywords Notes Congenital Heart DisordersDocument28 pagesModule No. Date: Topic:: Cues/Questions/ Keywords Notes Congenital Heart Disordersanon ymousNo ratings yet
- By: Jacqueline I. Esmundo, R.N.MNDocument28 pagesBy: Jacqueline I. Esmundo, R.N.MNdomlhynNo ratings yet
- By: Jacqueline I. Esmundo, R.N.MNDocument32 pagesBy: Jacqueline I. Esmundo, R.N.MNdomlhynNo ratings yet
- Final 3 Congenital Heart DisordersDocument15 pagesFinal 3 Congenital Heart DisordersCAÑADA, JOHANNELYN M.No ratings yet
- ch28 Notes Part 2Document9 pagesch28 Notes Part 2Monica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Cardiovasucular Problems in Children: Niranjana Shalini. M.SC (N) Assistant ProfessorDocument79 pagesCardiovasucular Problems in Children: Niranjana Shalini. M.SC (N) Assistant ProfessorNIRANJANA SHALININo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Child Born With Congenital Heart DisordersDocument3 pagesNursing Care of The Child Born With Congenital Heart DisordersElijah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermDocument11 pagesChapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermJœnríčk AzueloNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspect of Maternal and Child NursingDocument21 pagesClinical Aspect of Maternal and Child NursingMarianne CoracheaNo ratings yet
- Where Problems With The Heart Mean There Isn't Enough Oxygen Present in The BloodDocument6 pagesWhere Problems With The Heart Mean There Isn't Enough Oxygen Present in The BloodRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsDocument3 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsKIANA LOUISE ROMANONo ratings yet
- NCM 118Document8 pagesNCM 118Zanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument74 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseKeith LajotNo ratings yet
- Anak 2Document107 pagesAnak 2Nency PurmayaNo ratings yet
- Mitral Valve ProlapseDocument3 pagesMitral Valve ProlapseKristine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Obstruction of Blood FlowDocument4 pagesObstruction of Blood FlowJessica Carmela CasugaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisorderDocument21 pagesCardiovascular Disorderdanica cordovaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseRitz CelsoNo ratings yet
- CME Cyanotic Heart DiseaseDocument38 pagesCME Cyanotic Heart DiseaseTan Zhi HongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document7 pagesLecture 8Grafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Peds Shelf NotesDocument73 pagesPeds Shelf NotesTanyaMusonza100% (1)
- Heart Failure: Dysfunction)Document5 pagesHeart Failure: Dysfunction)Christine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- CHD Final 1Document9 pagesCHD Final 1danica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Depend On: 1-Clinical Features: - Palpation - Auscultation 2 - CXR: - Chamber Enlargement - Plethoric LungDocument11 pagesDiagnosis Depend On: 1-Clinical Features: - Palpation - Auscultation 2 - CXR: - Chamber Enlargement - Plethoric LungYasir Al-KhateebNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiology Part 2Document3 pagesPediatric Cardiology Part 2carlosNo ratings yet
- Atrial and Ventral Septal DefectDocument3 pagesAtrial and Ventral Septal DefectJessica Carmela CasugaNo ratings yet
- Atrial Septal Defects: Presented by Dr. Maysa Abdul Haq Directed by Dr. Ali Halabi Jordan Hospital 11-9-2005Document36 pagesAtrial Septal Defects: Presented by Dr. Maysa Abdul Haq Directed by Dr. Ali Halabi Jordan Hospital 11-9-2005Joe JosephNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument43 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseSanjanaNo ratings yet
- Peds Shelf NotesDocument88 pagesPeds Shelf Notesγιαννης παπαςNo ratings yet
- VR MidtermsDocument10 pagesVR MidtermsKIANA LOUISE ROMANONo ratings yet
- Dr. Alurkur's Book On Cardiology - 2Document85 pagesDr. Alurkur's Book On Cardiology - 2Bhattarai ShrinkhalaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease-2Document57 pagesCongenital Heart Disease-2Deepika LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Kussia Ayano (MD)Document54 pagesCongenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Kussia Ayano (MD)Yemata HailuNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULAR-DISEASE Cont.Document6 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR-DISEASE Cont.Kimberly Sharah Mae FortunoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument4 pagesPediatric Cardiovascular DiseasesWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in CirculationDocument10 pagesDisturbances in CirculationSHERIE ANNE BERNABENo ratings yet
- AV - Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument10 pagesAV - Congenital Heart DiseasebakiralhamdaniNo ratings yet
- IM Cardio - PERICARDIAL DISEASESDocument4 pagesIM Cardio - PERICARDIAL DISEASESElisha BernabeNo ratings yet
- Disease Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument20 pagesDisease Rheumatic Heart DiseaseMeena KoushalNo ratings yet
- ValvularDocument2 pagesValvularJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- CORNELL NOTE Pediatric Illnesses Part 1&2Document7 pagesCORNELL NOTE Pediatric Illnesses Part 1&2Margareth DandanNo ratings yet
- Notes SC CVSDocument6 pagesNotes SC CVS202213No ratings yet
- Penyakit-Penyakit Jantung Kongenital.: M.S.GanesanDocument63 pagesPenyakit-Penyakit Jantung Kongenital.: M.S.GanesanSyukri SamsudinNo ratings yet
- מצגת קרדיולוגיה מעודכנת עם שאלות 1Document289 pagesמצגת קרדיולוגיה מעודכנת עם שאלות 1adnan shwNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease 2Document46 pagesValvular Heart Disease 2Topea BogdanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: By: S@JDocument35 pagesCardiovascular System: By: S@JD TekNo ratings yet
- Cardio Notes CH28Document6 pagesCardio Notes CH28Monica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Conginital Heart DiseaseDocument19 pagesConginital Heart DiseaseSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease: Kriti Puri, MD Hugh D. Allen, MD Athar M. Qureshi, MDDocument30 pagesCongenital Heart Disease: Kriti Puri, MD Hugh D. Allen, MD Athar M. Qureshi, MDhari ilman toniNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease - Cynotic AcynoticDocument34 pagesCongenital Heart Disease - Cynotic Acynoticvruttika parmarNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDocument15 pagesCongenital Heart DiseasessumairaNo ratings yet
- DR - Azad A Haleem AL - Brefkani: University of Duhok Faculty of Medical Science School of Medicine Pediatrics DepartmentDocument58 pagesDR - Azad A Haleem AL - Brefkani: University of Duhok Faculty of Medical Science School of Medicine Pediatrics DepartmentGomathi ShankarNo ratings yet
- NNS Tutorial NotesDocument7 pagesNNS Tutorial NotesGio AmadorNo ratings yet
- Aortic StenosisDocument8 pagesAortic Stenosisdr.moni.co.ukNo ratings yet
- MCHN P3 V.2Document4 pagesMCHN P3 V.2Ven SemillaNo ratings yet
- CV Physical ExaminationDocument29 pagesCV Physical ExaminationdanradulescuNo ratings yet
- Non-Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease-UpDate 4-22-53Document136 pagesNon-Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease-UpDate 4-22-53getnusNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Diseases: DR - Ankita Patel MPT (Cardio-Pulmonary)Document41 pagesCongenital Heart Diseases: DR - Ankita Patel MPT (Cardio-Pulmonary)heena solankiNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Lecture For C-I StudentsDocument89 pagesCongenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Lecture For C-I StudentsGomathi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Paediatric ECG Checklist 3.8Document2 pagesPaediatric ECG Checklist 3.8Muhammad Moazzam GulzarNo ratings yet
- Complication of MI (Myocardial Infarction)Document2 pagesComplication of MI (Myocardial Infarction)Zahid QamarNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Medical Students and Faculty - Edisi Keempat - Baltimore-PhiladelpiaDocument2 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Medical Students and Faculty - Edisi Keempat - Baltimore-PhiladelpiaSylvia PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure (PH 2 Bemdiji)Document1 pageCongestive Heart Failure (PH 2 Bemdiji)api-285694335No ratings yet
- Ecg HandoutDocument24 pagesEcg HandoutLeah DeeNo ratings yet
- Ecg Essentials 2 PDFDocument45 pagesEcg Essentials 2 PDFjaikishan marathe 69No ratings yet
- Case Report ASDDocument34 pagesCase Report ASDIrwansyah Ghenjy0% (1)
- Comparison Study. CARESCAPEB850Document4 pagesComparison Study. CARESCAPEB850Alberto MHNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 MidtermDocument25 pagesNCM 112 MidtermJan Charlie Sophia100% (1)
- CVS Heart MurmursDocument2 pagesCVS Heart MurmursIamTineshNo ratings yet
- ACLS Recerti Cation Exam Quiz: (/my-Account/)Document6 pagesACLS Recerti Cation Exam Quiz: (/my-Account/)andres novoaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Fahad Class 6 Cardiac AnesthesiaDocument18 pages6 - Fahad Class 6 Cardiac AnesthesiaOne ClickNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome (G4)Document6 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome (G4)Francis Josh DagohoyNo ratings yet
- ECGDocument33 pagesECGTamia PutriNo ratings yet
- Ekg Tiara Nur AliviaDocument6 pagesEkg Tiara Nur AliviatyaraNo ratings yet
- 7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraDocument57 pages7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraSurya ArhNo ratings yet
- StemiDocument11 pagesStemidoubleraNo ratings yet
- MTB Cardiology NotesDocument11 pagesMTB Cardiology Noteskabal321No ratings yet
- Sunday Academic Meet (Slides)Document34 pagesSunday Academic Meet (Slides)Narendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal DefectDocument6 pagesVentricular Septal DefectPrem AnandNo ratings yet
- Learning Ecg ModulesDocument150 pagesLearning Ecg ModulesdodiNo ratings yet
- Normal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial Node AV Node Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje FibersDocument73 pagesNormal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial Node AV Node Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje FibersIndra ToshiwayNo ratings yet
- Instruction For The Students To The Station 6 ECG DiagnosticsDocument3 pagesInstruction For The Students To The Station 6 ECG DiagnosticsCynthia GNo ratings yet
- ValvopatiasDocument97 pagesValvopatiasapi-3826574No ratings yet
- ECG Tutorial - Basic Principles of ECG AnalysisDocument16 pagesECG Tutorial - Basic Principles of ECG AnalysisneekooxNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument37 pagesTetralogy of Fallottintinlovessu100% (1)
- Kuliah MITRAL STENOSISDocument19 pagesKuliah MITRAL STENOSISekaseptiani312No ratings yet
- CMS 251 Unit 1 Cardiovascular SystemDocument114 pagesCMS 251 Unit 1 Cardiovascular SystemAmon RicoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac/Cardiogenic Shock: Clinical Practice GuidelinesDocument3 pagesCardiac/Cardiogenic Shock: Clinical Practice GuidelinesAnonymous Yo0mStNo ratings yet
- 515Document972 pages515solecitodelmarazul100% (6)