Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Excel 2019 Intermediate: Quick Reference Guide
Uploaded by
BL Pipas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
97 views3 pagesOriginal Title
excel-2019-intermediate-quick-reference
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
97 views3 pagesExcel 2019 Intermediate: Quick Reference Guide
Uploaded by
BL PipasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
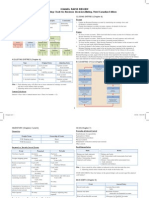
Microsoft®
Excel 2019 Intermediate
Quick Reference Guide Free Cheat Sheets
Visit ref.customguide.com
Chart Elements Chart Options
Chart Chart Types
Chart Title Elements
Column: Used to compare
different values vertically side-by-
Chart side. Each value is represented in
Styles the chart by a vertical bar.
Data Line: Used to illustrate trends
Bar Chart over time (days, months, years).
Filters Each value is plotted as a point
on the chart and values are
connected by a line.
Chart Pie: Useful for showing values as
Area a percentage of a whole when all
the values add up to 100%. The
values for each item are
represented by different colors.
Gridline
Bar: Similar to column charts,
except they display information in
horizontal bars rather than in
Axis vertical columns.
Titles
Area: Similar to line charts,
except the areas beneath the
Legend
lines are filled with color.
XY (Scatter): Used to plot
Charts Charts clusters of values using single
points. Multiple items can be
Create a Chart: Select the cell range that contains Insert a Sparkline: Select the cells you want to plotted by using different colored
the data you want to chart. Click the Insert tab on summarize. Click the Insert tab and select the points or different point symbols.
the ribbon. Click a chart type button in the Charts sparkline you want to insert. In the Location Range
group and select the chart you want to insert. field, enter the cell or cell range to place the Stock: Effective for reporting the
sparkline and click OK. fluctuation of stock prices, such
Move or Resize a Chart: Select the chart. Place as the high, low, and closing
the cursor over the chart’s border and, with the 4- Create a Dual Axis Chart: Select the cell range you points for a certain day.
headed arrow showing, click and drag to move want to chart, click the Insert tab, click the
it. Or, click and drag a sizing handle to resize it. Combo button, and select a combo chart type. Surface: Useful for finding
optimum combinations between
Change the Chart Type: Select the chart and click two sets of data. Colors and
Print and Distribute patterns indicate values that are
the Design tab. Click the Change Chart Type
button and select a different chart. Set the Page Size: Click the Page Layout tab. in the same range.
Click the Size button and select a page size.
Filter a Chart: With the chart you want to filter Additional Chart Elements
selected, click the Filter button next to it. Set the Print Area: Select the cell range you want
Deselect the items you want to hide from the chart to print. Click the Page Layout tab, click the Print Data Labels: Display values from the cells
view and click the Apply button. Area button, and select Set Print Area. of the worksheet on the plot area of the
chart.
Position a Chart’s Legend: Select the chart, click Print Titles, Gridlines, and Headings: Click the
the Chart Elements button, click the Legend Page Layout tab. Click the Print Titles button Data Table: A table added next to the
button, and select a position for the legend. and set which items you wish to print. chart that shows the worksheet data the
chart is illustrating.
Show or Hide Chart Elements: Select the chart Add a Header or Footer: Click the Insert tab and
and click the Chart Elements button. Then, click the Header & Footer button. Complete the Error Bars: Help you quickly identify
use the check boxes to show or hide each header and footer fields. standard deviations and error margins.
element.
Adjust Margins and Orientation: Click the Page Trendline: Identifies the trend of the
Insert a Trendline: Select the chart where you Layout tab. Click the Margins button to select current data, not actual values. Can also
want to add a trendline. Click the Design tab on from a list of common page margins. Click the identify forecasts for future data.
the ribbon and click the Add Chart Element Orientation button to choose Portrait or
button. Select Trendline from the menu. Landscape orientation.
2020 CustomGuide, Inc.
Click the topic links for free lessons!
Contact Us: sales@customguide.com
Intermediate Formulas Manage Data Tables
Absolute References: Absolute references Export Data: Click the File tab. At the left, Remove Duplicate Values: Click any cell in the
always refer to the same cell, even if the select Export and click Change File Type. table and click the Data tab on the ribbon.
formula is moved. In the formula bar, add dollar Select the file type you want to export the data Click the Remove Duplicates button.
signs ($) to the reference you want to remain to and click Save As. Select which columns you want to check for
absolute (for example, $A$1 makes the duplicates and click OK.
column and row remain constant). Import Data: Click the Data tab on the ribbon
and click the Get Data button. Select the Insert a Slicer: With any cell in the table
Name a Cell or Range: Select the cell(s), click category and data type, and then the file you selected, click the Design tab on the ribbon.
the Name box in the Formula bar, type a name want to import. Click Import, verify the Click the Insert Slicer button. Select the
for the cell or range, and press Enter. Names preview, and then click the Load button. columns you want to use as slicers and click
can be used in formulas instead of cell OK.
addresses, for example: =B4*Rate. Use the Quick Analysis Tools: Select the cell
range you want to summarize. Click the Quick Table Style Options: Click any cell in the table.
Reference Other Worksheets: To reference Analysis button that appears. Select the Click the Design tab on the ribbon and select
another worksheet in a formula, add an analysis tool you want to use. Choose from an option in the Table Style Options group.
exclamation point ‘!’ after the sheet name in formatting, charts, totals, tables, or sparklines.
the formula, for example: Intermediate Formatting
=FebruarySales!B4. Outline and Subtotal: Click the Data tab on the
ribbon and click the Subtotal button. Use Apply Conditional Formatting: Select the cells
Reference Other Workbooks: To reference the dialog box to define which column you want you want to format. On the Home tab, click the
another workbook in a formula, add brackets to subtotal and the calculation you want to use. Conditional Formatting button. Select a
‘[ ]’ around the file name in the formula, for Click OK. conditional formatting category and then the
example: rule you want to use. Specify the format to
=[FebruarySales.xlsx]Sheet1!$B$4. Use Flash Fill: Click in the cell to the right of the
apply and click OK.
cell(s) where you want to extract or combine
Order of Operations: When calculating a data. Start typing the data in the column. When Apply Cell Styles: Select the cell(s) you want to
formula, Excel performs operations in the a pattern is recognized, Excel predicts the format. On the Home tab, click the Cell Styles
following order: Parentheses, Exponents, remaining values for the column. Press Enter button and select a style from the menu.
Multiplication and Division, and finally Addition to accept the Flash Fill values. You can also select New Cell Style to define a
and Subtraction (as they appear left to right). custom style.
Use this mnemonic device to remember them: Create a Data Validation Rule: Select the cells
you want to validate. Click the Data tab and Apply a Workbook Theme: Click the Page
Please Parentheses click the Data Validation button. Click the Layout tab on the ribbon. Click the Themes
Allow list arrow and select the data you want button and select a theme from the menu.
Excuse Exponents
to allow. Set additional validation criteria
My Multiplication options and click OK.
Collaborate with Excel
Dear Division
Tables Add a Cell Comment: Click the cell where you
Aunt Addition want to add a comment. Click the Review tab
Format a Cell Range as a Table: Select the on the ribbon and click the New Comment
Sally Subtraction cells you want to apply table formatting to. button. Type your comment and then click
Click the Format as Table button in the outside of it to save the text.
Concatenate Text: Use the CONCAT function Styles group of the Home tab and select a table
=CONCAT(text1,text2,…) to join the text format from the gallery. Invite People to Collaborate: Click the Share
from multiple cells into a single cell. Use the
button on the ribbon. Enter the email
arguments within the function to define the text
addresses of people you want to share the
you want to combine as well as any spaces or
workbook with. Click the permissions button,
punctuation.
select a permission level, and click Apply.
Payment Function: Use the PMT function Type a short message and click Send.
=PMT(rate,nper,pv,…) to calculate a loan
Co-author Workbooks: When another user
amount. Use the arguments within the function
opens the workbook, click the user’s picture or
to define the loan rate, number of periods, and
initials on the ribbon, to see what they are
present value and Excel calculates the
editing. Cells being edited by others appear
payment amount.
Sort Data: Select a cell in the column you want with a colored border or shading.
Date Functions: Date functions are used to to sort. Click the Sort & Filter button on the
Home tab. Select a sort order or select Protect a Worksheet: Before protecting a
add a specific date to a cell. Some common
Custom Sort to define specific sort criteria. worksheet, you need to unlock any cells you
date functions in Excel include:
want to remain editable after the protection is
Date =DATE(year,month,day) Filter Data: Click the filter arrow for the applied. Then, click the Review tab on the
column you want to filter. Uncheck the boxes ribbon and click the Protect Sheet button.
Today =TODAY() for any data you want to hide. Click OK. Select what you want to remain editable after
the sheet is protected.
Now =NOW() Add Table Rows or Columns: Select a cell in
the row or column next to where you want to Add a Workbook Password: Click the File tab
Display Worksheet Formulas: Click the add blank cells. Click the Insert button list and select Save As. Click Browse to select a
Formulas tab on the ribbon and then click the arrow on the Home tab. Select either Insert save location. Click the Tools button in the
Show Formulas button. Click the Show Table Rows Above or Insert Table Columns dialog box and select General Options. Set a
Formulas button again to turn off the to the Left. password to open and/or modify the workbook.
formula view. Click OK.
2020 CustomGuide, Inc.
Click the topic links for free lessons!
Contact Us: sales@customguide.com
Get More Free Quick References!
Visit ref.customguide.com to download.
Office 365 G Suite OS Soft Skills
Access Classroom Mac OS Business Writing
Excel G Suite Windows 10 Email Etiquette
Office 365 Gmail Manage Meetings
OneNote Google Calendar Productivity Presentations
Outlook Google Docs Digital Literacy Security Basics
PowerPoint Google Drive Salesforce SMART Goals
Teams Google Sheets
Word Google Slides + more, including Spanish versions
Loved by Learners, Trusted by Trainers
Please consider our other training products!
Interactive eLearning Customizable Courseware
Get hands-on training with bite-sized tutorials that Why write training materials when we’ve done it
recreate the experience of using actual software. for you? Training manuals with unlimited printing
SCORM-compatible lessons. rights!
Over 3,000 Organizations Rely on CustomGuide
“ The toughest part [in training] is creating the material, which CustomGuide has
done for us. Employees have found the courses easy to follow and, most
importantly, they were able to use what they learned immediately.
Contact Us! sales@customguide.com 612.871.5004
You might also like
- Excel AdvancedDocument61 pagesExcel AdvancedSriram VenkatakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Teaching Excel 1627 Dikonversi 1Document30 pagesTeaching Excel 1627 Dikonversi 1elfi saharaNo ratings yet
- Data Analytics For Accounting - Chapter 3 - Data Analytics For Accouting - Performing The Test Plan andDocument10 pagesData Analytics For Accounting - Chapter 3 - Data Analytics For Accouting - Performing The Test Plan andukandi rukmanaNo ratings yet
- Excel 2019 Advanced Quick Reference PDFDocument3 pagesExcel 2019 Advanced Quick Reference PDFvksatyanNo ratings yet
- Excel Charts 2019Document159 pagesExcel Charts 2019the4rinaNo ratings yet
- Word 2019 Intermediate Quick ReferenceDocument3 pagesWord 2019 Intermediate Quick ReferencemazzagraNo ratings yet
- Dirty Data: Excel techniques to turn what you get into what you needFrom EverandDirty Data: Excel techniques to turn what you get into what you needRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Excel ShortcutsDocument26 pagesExcel ShortcutsLakshav KapoorNo ratings yet
- 78+ Best Excel Training Books To Learn Excel - ExcelDemyDocument8 pages78+ Best Excel Training Books To Learn Excel - ExcelDemyahmedNo ratings yet
- Free Excel Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesFree Excel Cheat SheetAlvian0% (1)
- Custom Number Formatting Codes PDFDocument1 pageCustom Number Formatting Codes PDFMukesh DakNo ratings yet
- Excel Shortcut Keys You SHOULD Know! - Xelplus - Leila GharaniDocument21 pagesExcel Shortcut Keys You SHOULD Know! - Xelplus - Leila GharaniMitesh VagadiyaNo ratings yet
- Top 8 Excel Data Cleaning Techniques To Know in 2023 Simplilearn 2Document1 pageTop 8 Excel Data Cleaning Techniques To Know in 2023 Simplilearn 2Mendel RaphNo ratings yet
- Excel 2019 Advanced Quick Reference EvalDocument3 pagesExcel 2019 Advanced Quick Reference Evalgopalr66No ratings yet
- Excel Data Entry TipsDocument6 pagesExcel Data Entry TipsMojca ImasNo ratings yet
- The Mega Book of Excel Keyboard Shortcuts 20190526 PDFDocument26 pagesThe Mega Book of Excel Keyboard Shortcuts 20190526 PDFAmine ChercheurNo ratings yet
- Making Charts With Excel 2003: Income & ProfitDocument9 pagesMaking Charts With Excel 2003: Income & ProfitArunNo ratings yet
- Andy S Excel Cheat Sheet 1560187358Document2 pagesAndy S Excel Cheat Sheet 1560187358Sandeep MelgiriNo ratings yet
- 101 Most Popular Excel FormulasDocument53 pages101 Most Popular Excel Formulascjust0318No ratings yet
- UH Manoa Honolulu Houseless ReportDocument51 pagesUH Manoa Honolulu Houseless ReportHawaii Public RadioNo ratings yet
- Accounts Receivable and Payable Journal EntriesDocument29 pagesAccounts Receivable and Payable Journal EntriesDinesh MirajkarNo ratings yet
- 333 Excel ShortcutsDocument10 pages333 Excel Shortcutsmanojkp33No ratings yet
- The Microsoft Excel Formulas Cheat Sheet Date and Time FormulasDocument11 pagesThe Microsoft Excel Formulas Cheat Sheet Date and Time FormulasMichael Ozora100% (2)
- Excel: Formulas, Functions, and Other Useful FeaturesDocument47 pagesExcel: Formulas, Functions, and Other Useful FeaturesRokan ZamanNo ratings yet
- Excel Formula With ExamplesDocument206 pagesExcel Formula With Examplesvickyaryan100% (1)
- Excel Custom Number Format GuideDocument40 pagesExcel Custom Number Format GuideAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Earn Certificate in Accounting AnalyticsDocument1 pageEarn Certificate in Accounting AnalyticsJason YudhaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting: Tools For Business Decision-Making, Third Canadian EditionDocument6 pagesFinancial Accounting: Tools For Business Decision-Making, Third Canadian Editionapi-19743565100% (1)
- Land Your Analytics Dream Job with Our 12-Week BootcampDocument17 pagesLand Your Analytics Dream Job with Our 12-Week BootcampRaouf MazouzNo ratings yet
- Exceljet Excel Shortcuts 150827Document22 pagesExceljet Excel Shortcuts 150827Erika HerreraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Excel Formula AuditingDocument8 pagesAdvanced Excel Formula AuditingP Singh Karki100% (1)
- Excel Charts and Graph TipsDocument6 pagesExcel Charts and Graph TipsKrystalNo ratings yet
- Excel User Forms Tips 2Document8 pagesExcel User Forms Tips 2Asad MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Suitability of analytical procedures for audit evidenceDocument7 pagesSuitability of analytical procedures for audit evidencebaabasaamNo ratings yet
- Excel Function and FormulasDocument35 pagesExcel Function and FormulasRana Sajid100% (1)
- 239 Excel Shortcuts For Windows - MyOnlineTrainingHubDocument17 pages239 Excel Shortcuts For Windows - MyOnlineTrainingHubArpan Ghosh100% (1)
- Excel Guide Handbook44Document62 pagesExcel Guide Handbook44Tata PovNo ratings yet
- Lookup Functions - PracticeDocument16 pagesLookup Functions - PracticeSweeti NankaniNo ratings yet
- Excel VBA Guide (v1.0) Last Update: 09/01/2014: Hierarchy, The Idea That Objects Can Contain OtherDocument3 pagesExcel VBA Guide (v1.0) Last Update: 09/01/2014: Hierarchy, The Idea That Objects Can Contain Otherhtmlfreak100% (1)
- Excel CheatSheet The Microsoft Excel Formulas Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesExcel CheatSheet The Microsoft Excel Formulas Cheat SheetBhushan BhikeNo ratings yet
- Excel Pivot Tables Guide: Microsoft Excel Pivot TablesDocument55 pagesExcel Pivot Tables Guide: Microsoft Excel Pivot Tablesjaithilagaraj100% (2)
- Excel 2007/2010: CTRL Shortcuts Formatting Shortcuts Navigation and Data EditingDocument2 pagesExcel 2007/2010: CTRL Shortcuts Formatting Shortcuts Navigation and Data EditingJohn Andehl AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Excel All Versions - Level 7 Course Book Revised PDFDocument116 pagesExcel All Versions - Level 7 Course Book Revised PDFuma sankarNo ratings yet
- Power Query Tutorial1Document34 pagesPower Query Tutorial1Aitr OmerNo ratings yet
- 204 Shortcuts For Microsoft Excel 2010 (Windows) : Navigate Inside WorksheetsDocument4 pages204 Shortcuts For Microsoft Excel 2010 (Windows) : Navigate Inside WorksheetsDipankar OkayNo ratings yet
- 10101010-Fast Track Your Excel Skills PDFDocument109 pages10101010-Fast Track Your Excel Skills PDFسيفل إسلامNo ratings yet
- VLookup TutorialDocument5 pagesVLookup TutorialAngel LawsonNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument30 pagesPDFShashank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Essential Spreadsheets Book-1Document40 pagesEssential Spreadsheets Book-1pawanNo ratings yet
- SQL BasicDocument33 pagesSQL BasicGokula KrishnanNo ratings yet
- ExcelBasics HandoutDocument11 pagesExcelBasics Handoutshares_leoneNo ratings yet
- Excel 2016 Intermediate Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesExcel 2016 Intermediate Cheat SheetGunay ibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Excel 2019 Intermediate Quick ReferenceDocument2 pagesExcel 2019 Intermediate Quick ReferenceStephanieD.MauroNo ratings yet
- Scientific Design Choices in Data VisualizationDocument11 pagesScientific Design Choices in Data VisualizationAdil Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- WSU - Jquery Reference CardDocument13 pagesWSU - Jquery Reference Cardcheckmeout803No ratings yet
- Jquery Visual Cheat Sheet 1.4.2Document4 pagesJquery Visual Cheat Sheet 1.4.2Antonio Lupetti100% (7)
- Jquery Visual Cheat Sheet 1.4.2Document4 pagesJquery Visual Cheat Sheet 1.4.2Antonio Lupetti100% (7)
- Manzano C#Document149 pagesManzano C#BL PipasNo ratings yet
- WSU - Jquery Reference CardDocument13 pagesWSU - Jquery Reference Cardcheckmeout803No ratings yet
- HTML5 Web Development Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesHTML5 Web Development Cheat SheetBL PipasNo ratings yet
- RGB Color Hex Cheat Sheet v1Document1 pageRGB Color Hex Cheat Sheet v1Sneetsher Crispy100% (4)
- HF HTML Cheat Sheet PDFDocument23 pagesHF HTML Cheat Sheet PDFgfdfdS100% (1)
- HTML 5 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument4 pagesHTML 5 Cheat Sheet: by ViaBL PipasNo ratings yet
- Bootstrap Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesBootstrap Cheat Sheet: by ViaTarbNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Learn Java Fundamentals with this Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesLearn Java Fundamentals with this Cheat SheetJoel Nolan de CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Java OOP-Cheat SheetDocument1 pageJava OOP-Cheat SheetzanandNo ratings yet
- Guia de Referências CSS HostingerBR PDFDocument13 pagesGuia de Referências CSS HostingerBR PDFpfind10No ratings yet
- Swift and C# Quick Reference - Language Equivalents and Code ExamplesDocument1 pageSwift and C# Quick Reference - Language Equivalents and Code ExamplesiliasNo ratings yet
- Cs Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCs Cheat SheetnandaNo ratings yet
- css3 Cheatsheet 2017 Emezeta PDFDocument6 pagescss3 Cheatsheet 2017 Emezeta PDFRosa Alicia MuroNo ratings yet
- JavaString Cheatsheet EdurekaDocument1 pageJavaString Cheatsheet EdurekaamitNo ratings yet
- Swift C Sharp PosterDocument1 pageSwift C Sharp PosterJoshua Shalom Cherkes100% (1)
- Jenkins Cheat Sheet EdurekaDocument1 pageJenkins Cheat Sheet Edurekavibhore48100% (1)
- Bootstrap Cheat Sheet: If You Plan To Pick Up Some Coding Skills, Bootstrap 4 Is A Solid Choice!Document50 pagesBootstrap Cheat Sheet: If You Plan To Pick Up Some Coding Skills, Bootstrap 4 Is A Solid Choice!BL Pipas100% (2)
- Python For Data Science Cheat Sheet: Scikit-Learn Create Your Model Evaluate Your Model's PerformanceDocument1 pagePython For Data Science Cheat Sheet: Scikit-Learn Create Your Model Evaluate Your Model's Performancesrikantkar100% (1)
- AngularJS Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesAngularJS Cheat SheetZulqarnain Hashmi100% (1)
- Java OOP-Cheat SheetDocument1 pageJava OOP-Cheat SheetzanandNo ratings yet
- PySpark CheatSheet EdurekaDocument1 pagePySpark CheatSheet EdurekaBL PipasNo ratings yet
- JavaString Cheatsheet EdurekaDocument1 pageJavaString Cheatsheet EdurekaamitNo ratings yet
- Excel 2019 Basic: Quick Reference GuideDocument3 pagesExcel 2019 Basic: Quick Reference GuideBL PipasNo ratings yet
- Java Exceptions Cheat Sheet: Error Vs ExceptionDocument1 pageJava Exceptions Cheat Sheet: Error Vs ExceptionBL PipasNo ratings yet
- The Git Workflow: Working DirectoryDocument7 pagesThe Git Workflow: Working DirectoryBL PipasNo ratings yet
- CORE JAVA CHEATSHEET: Learn essential Java concepts from experts at EdurekaDocument1 pageCORE JAVA CHEATSHEET: Learn essential Java concepts from experts at EdurekaLeogladsonNo ratings yet
- CMS3 User Manual GuideDocument84 pagesCMS3 User Manual Guideangelorum_777No ratings yet
- Smart To-Do List: Software Requirement Specification (SRS)Document18 pagesSmart To-Do List: Software Requirement Specification (SRS)Prabhu V PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Lossless EEG Compression Algorithm Based On SemiDocument84 pagesLossless EEG Compression Algorithm Based On Semivsangvai26No ratings yet
- Windows 10 NoteDocument35 pagesWindows 10 NoteAnish ShresthaNo ratings yet
- SigmaNEST Tube CuttingDocument2 pagesSigmaNEST Tube CuttingBurak Mücahit YeşiltaşNo ratings yet
- Python Data Representation Notes.Document14 pagesPython Data Representation Notes.Husain NalwalaNo ratings yet
- Edsdk Api PDFDocument149 pagesEdsdk Api PDFtempthereNo ratings yet
- Face Recognition Based Attendance System Using Machine LearningDocument7 pagesFace Recognition Based Attendance System Using Machine Learningmodena tigaNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument6 pagesContentKaren Limpo ApostolNo ratings yet
- Copy (4) of Blue Eyes TechnologyDocument23 pagesCopy (4) of Blue Eyes TechnologyyathichandraNo ratings yet
- Covesa HMC VSMDocument17 pagesCovesa HMC VSMWaseem AnsariNo ratings yet
- DOC1 Overview: An Introduction For ProgrammersDocument23 pagesDOC1 Overview: An Introduction For ProgrammersartikalraNo ratings yet
- UAVs Assess Transportation InfrastructureDocument166 pagesUAVs Assess Transportation InfrastructureEduPeñaNo ratings yet
- CS8651 Internet Programming (Downloaded From Annauniversityedu - Blogspot.com)Document539 pagesCS8651 Internet Programming (Downloaded From Annauniversityedu - Blogspot.com)SteffiNo ratings yet
- SJKT Simpang LimaDocument13 pagesSJKT Simpang LimaMUKUNDHA A/L RAVI MoeNo ratings yet
- Banker's Algorithm For Deadlock Detection: Sr. No Roll No (Sem 5) Full Name of Student Enrolment No 1 2 3 4 5Document21 pagesBanker's Algorithm For Deadlock Detection: Sr. No Roll No (Sem 5) Full Name of Student Enrolment No 1 2 3 4 5Harshal PatilNo ratings yet
- 02 Netnumen U31 Software Installation54pDocument54 pages02 Netnumen U31 Software Installation54pstefadmar adinetNo ratings yet
- Describing Functions Giving Definitions & Explanations: There Are Several Ways of Describing A Device's FunctionDocument9 pagesDescribing Functions Giving Definitions & Explanations: There Are Several Ways of Describing A Device's FunctionCường Lê XuânNo ratings yet
- Workaround For 102 Port Occupied Issue From IEDScout Upon IED SimulationDocument6 pagesWorkaround For 102 Port Occupied Issue From IEDScout Upon IED SimulationDivyesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Manual On Object Pascal Style GuideDocument161 pagesManual On Object Pascal Style GuideHendri100% (2)
- Raspberry Pi Pico Python SDKDocument46 pagesRaspberry Pi Pico Python SDKMcQ Soft100% (1)
- Excel Module 01Document35 pagesExcel Module 01jieNo ratings yet
- Reference - Manual - INTERFASES XPRDocument94 pagesReference - Manual - INTERFASES XPRLuis ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vol 44 Issue 4Document7 pagesVol 44 Issue 4Vinayak KarthikNo ratings yet
- Identification of Red Dragon Fruit Using Backpropagation Method Based On AndroidDocument6 pagesIdentification of Red Dragon Fruit Using Backpropagation Method Based On AndroidPutri AzlinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Image Processing PDFDocument88 pagesChapter 4 Image Processing PDFBrijesh B NaikNo ratings yet
- W03 CPU SimulatorDocument13 pagesW03 CPU SimulatorElsaday SimamoraNo ratings yet
- Virtual Try On DocumentationDocument60 pagesVirtual Try On Documentationthangapandi1157698No ratings yet
- System Server Log StartupDocument1,553 pagesSystem Server Log StartupAyub NiaziNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye ReportDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Eye ReportNashNo ratings yet